
Context-based Configuration of Process Variants
Alena Hallerbach
1
, Thomas Bauer
1
and Manfred Reichert
2
1
Group Research and Advanced Engineering, Daimler AG, Ulm, Germany
2
Institute of Databases and Information Systems, Ulm University, Germany
Abstract. When designing process-aware information systems, usually, variants
of the same process type have to be defined and maintained. Each of these process
variants constitutes an adjustment of the same process to specific requirements
building the variant context. Current business process management tools do not
support the context-based definition and configuration of such variants in an ade-
quate manner. Instead, each process variant has to be defined from scratch and be
kept in a separate model. This results in considerable redundancies when model-
ing and adapting process variants, and is also a time consuming and error-prone
procedure. This paper presents a more flexible and context-based approach for
configuring and managing process variants. In particular, we allow for the con-
figuration of process variants by applying a context-dependent set of well-defined
change operations to a base process.
1 Introduction
The flow of activities which have to be performed to achieve specific goals is often
captured in a process model. Usually, each model implements a particular process type
(e.g., handling a credit request or travel cost refund) by describing process activities,
execution constraints, required resources (e.g., humans or IT systems), and informa-
tion processed. There exists a variety of tools like ARIS Business Architect [1], ADO-
NIS [2], or WebSphere Business Modeler [3] for creating and managing such process
models. Typically, respective process modeling tools are used to improve process trans-
parency, to optimize a process, or to implement a process-aware information system,
e.g., based on a Workflow Management System (WfMS) [4,5].
Process support is required in almost all business domains (e.g., healthcare [6],
engineering [7], or public administration). Characteristic process examples from the
automotive domain, for example, include product creation, product change manage-
ment, and release management [7]. In practice, different variants of a particular process
type are usually required. Figure 1 a, for example, depicts a simplified product change
process that starts with initiating a change request (Activity 1). Afterwards comments
(cmts.) are requested from those departments that might be affected by the change (Ac-
tivities 2a, 2b, and 2c). After all comments have been received an integrated change
document is created (Activity 3). This document is then passed to the decision board
which either approves the requested change or rejects it (Activity 4). In case of approval,
the development department implements the change (Activity 5). Otherwise this step is
skipped.
Hallerbach A., Bauer T. and Reichert M. (2008).
Context-based Configuration of Process Variants.
In Joint Proceedings of the 5th International Workshop on Ubiquitous Computing (IWUC 2008) 4th International Workshop on Model-Driven Enterprise
Information Systems (MDEIS 2008) 3rd International Workshop on Technologies for Context-Aware Business Process Management (TCoB 2008),
pages 31-40
DOI: 10.5220/0001729600310040
Copyright
c
SciTePress
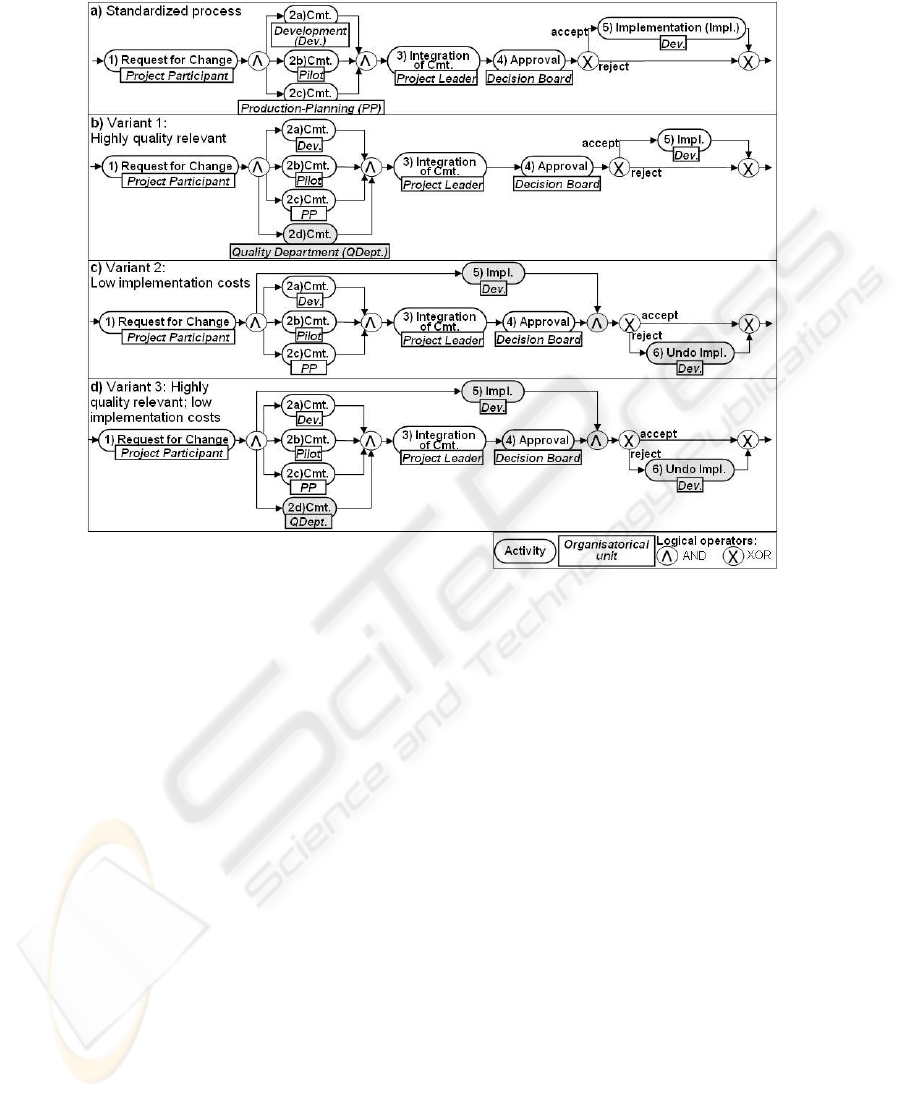
Fig.1. Variants of a Standardized Product Change Process.
Different variants of this process exist in practice: Variant 1 (cf. Figure 1 b) treats
quality critical changes in a special way; i.e., the quality department is involved in the
commenting process. At the model level this behavior can be realized by inserting an
additional activity (Activity 2d) into the original process. Figure 1 c shows Variant 2
for which the change request is shortened. Particularly for changes with low implemen-
tation costs the development department often starts implementing the change without
waiting for its approval. If the decision board rejects the request, change implementa-
tion will be undone later. This variant can be realized by moving Activity 5 to a position
parallel to the commenting activities and by conditionally inserting the Undo activity
(Activity 6). Finally, Variant 3 (cf. Figure 1 d) will be required if the change affects
quality critical issues and can be shortened as well. This variant constitutes the com-
bination of Variant 1 and 2. Thus, the process inherits all adjustments from these two
variants; i.e., an additional comment is requested from the quality department and early
implementation of the change becomes possible.
In practice, additional variants are required, e.g., satisfying specific constraints of
the respective vehicle project or development phase. In existing approaches such pro-
cess variants have to be defined and maintained in separate process models similar to
those of Figure 1. This results in a large amount of redundant model data as the vari-
ant models are identical or similar for the most part. Considering the large number of
32

variants required in practice, this drawback increases modeling and maintenance ef-
forts significantly. This is both time-consuming and error-prone. Unfortunately, current
business process management tools do not allow for the context-based definition and
configuration of a process variant that captures a given situation best.
This paper introduces the Provop (PROcess Variants by OPtions) approach. In par-
ticular, it provides an advanced solution for modeling process variants starting with a
common process model and using an operational modeling approach. Provop allows
for the context-based configuration of process variants, as discussed in detail in this
paper, and enables full life cycle support [8]. The remainder of this paper is structured
as follows: In Section 2 we introduce basic concepts of the Provop approach. Section
3 presents the configuration of process variants using context rules. Section 4 discusses
related work. The paper concludes with a summary and an outlook in Section 5.
2 Basic Concepts of Provop
Our Provop approach has been motivated by the fact that a process variant can be typi-
cally created by “cloning” a given process model and by adjusting it to a given context.
In Provop we adapt this method to base the different variants of a particular process
type on a single
base process
. This base process can be a standard process or espe-
cially created for variant definition [9]. The variant-specific adjustments of the base
process are expressed in terms of high-level
change operations
. Provop itself allows to
INSERT
,
DELETE
, and
MOVE
process fragments
3
. Furthermore, a
MODIFY
operation for
changing attributes (e.g., actor assignment, activity durations) is provided. To allow for
more complex process adjustments, change operations can be grouped into reusable
sets, which we denote as
options
. Thus a particular process variant is configured by ap-
plying one or more options to the respective base process, i.e., by performing all change
operations set out by these options [9].
Figure 2 illustrates the basic concepts of our approach taking the example of a pro-
duct change process from Figure 1 (for the sake of readability we have reduced activity
names to logically corresponding numbers): The process model depicted in Figure 1 a
is considered as the base process from which all variants shall be derived (cf. Fig-
ure 2 a). The difference between Variant 1 (cf. Figure 1 b) and the base process can
be described by an option (i.e., Option 1). This option comprises an
INSERT
opera-
tion that adds Activity 2d to the base process. The
INSERT
operation requires the exact
position for inserting Activity 2d. Therefore we define
adjustment points
which are
used to connect the incoming and outgoing edges of the new fragment with the base
process
4
. By applying Option 1, i.e., by inserting Activity 2d between the adjustment
points “start-comments” and “end-comments”, the process model named Variant 1 can
be created (cf. Figure 2 c). To configure the model of Variant 2 (cf. Figure 1 c) we
define Option 2 which consists of the following change operations: The first operation
constitutes an insertion of the undo activity (Activity 6) between the adjustment points
3
A process fragment is a sub-graph with at least one process element (e.g., node or edge).
4
Note that adjustment points are placed at the entry or exit of a node in the base process and are
used by a change operation as reference.
33
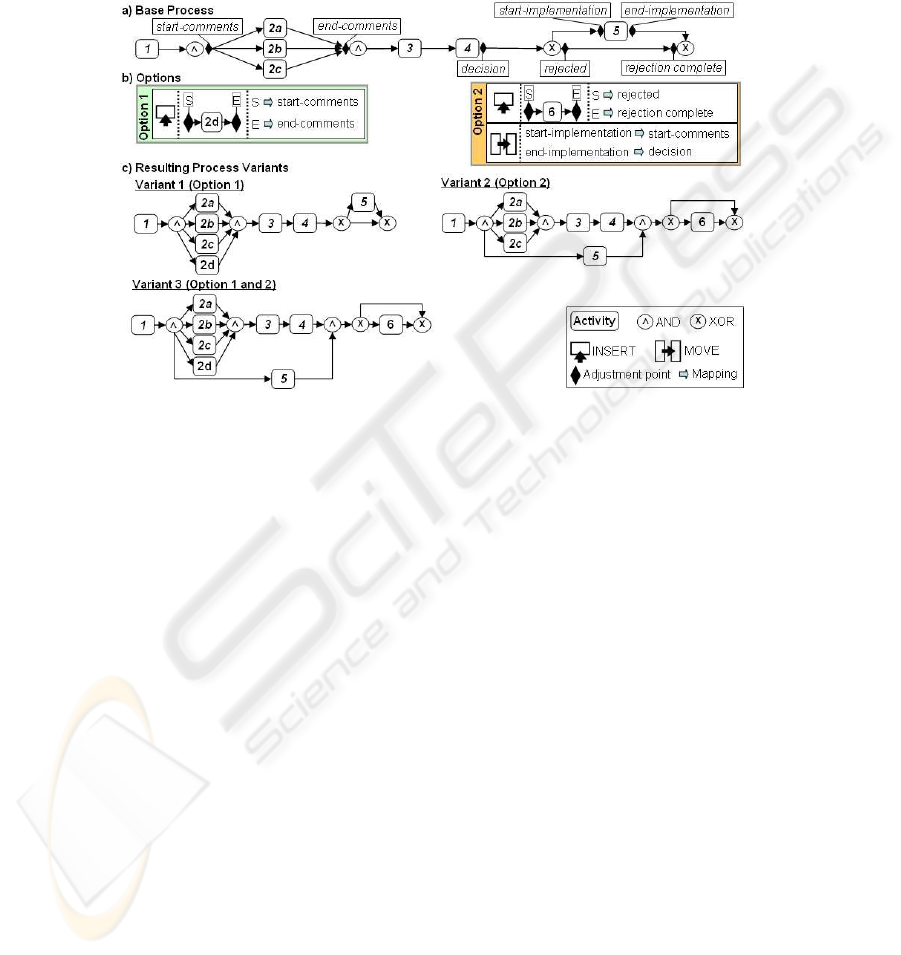
“rejected” and “rejection complete” from the base process. The second operation per-
forms a
MOVE
of Activity 5 from its original position (given by the adjustment points
“start-implementation” and “end-implementation” in the base process) to its new posi-
tion between “start-comments” and “decision”. The resulting process model is depicted
in Figure 2 c.
Fig.2. Options and Process Variants in Provop.
A main advantage of this operational modeling approach is the ability to configure
new process variants without additional modeling efforts. More precisely, when apply-
ing both options conjointly and therefore performing all change operations defined by
them the process model of Variant 3 (cf. Figure 1 d) results.
3 Configuring Process Variants based on Context Rules
Basic to variant configuration in Provop is the controlled usage of change operations
grouped as reusable sets (i.e., options). By selecting respective options and by applying
them to a given base process the desired variant can be defined. Typically, particular
process variants are required in a specific context. Therefore, Provop considers context-
based variant configuration as a crucial concept. In Section 3.1 we motivate the need
for context-awareness and describe the resulting requirements for our approach. Sec-
tions 3.2 - 3.4 explain how these requirements are met.
3.1 Use Cases and Requirements
The product change management process as depicted in Figure 1 a can be considered as
“standard” process that is used to derive different variants (cf. Figures 1 b - 1 d). Each
variant then corresponds to a use case that occurs in a given context. This context is
34
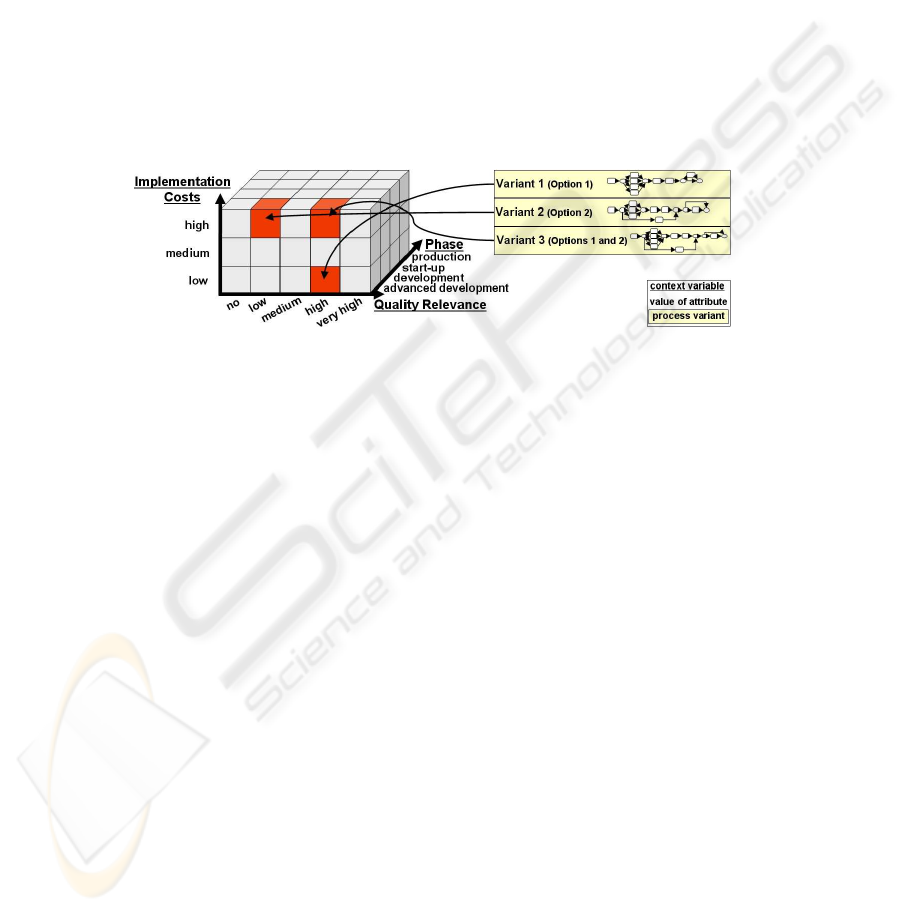
provided by the attributes of the change request, which indicate, for example, whether
the change is relevant for product quality, what the expected implementation costs are,
and which product components are affected by the change. This can be expressed in
terms of context variables, each with a given value range; e.g., the context variable
Implementation Costs
has one of the values “low”, “medium”, or “high”. Gener-
ally, each context variable defines one dimension of the process context which might be
relevant for variant configuration. Consequently, multiple context variables correspond
to a multidimensional cube. For example, the context of the product change process is
given by the
context cube
depicted in Figure 3 (simplified view): The axes are corre-
sponding to the context variables
Quality Relevance
,
Implementation Costs
, and
Phase
. When specifying the values for all context variables or a subset of them we
obtain a particular process context, which logically corresponds to a
sub-cube
within
the context cube. Simply speaking, each process variant is linked to a sub-cube which
describes its valid context (cf. Figure 3).
Fig.3. Context Cube of Possible Context Descriptions.
To allow for context-based variant configuration several requirements have to be met
[10]:
Req. 1 (User-friendly Definition of Context). A key prerequisite concerns the defini-
tion and maintenance of a process context model. To obtain optimal support, an intuitive
method is required to support these tasks.
Req. 2 (Definition of Valid and Invalid Value Combinations). A particular sub-cube
of the context cube might not be valid. This will be the case, for example, if the combi-
nation of certain context values for a given set of variables does not make sense. Con-
sequently, no consistent process variant is required in this context. All valid sub-cubes,
in turn, require a consistent and correct variant assignment. In some way all “valid”
sub-cubes must be identified and captured within the context model.
Req. 3 (Context-based Selection of Options). To allow for the context-based config-
uration of variants, options (i.e., collections of change operations) and context descrip-
tions have to be linked. Thereby, it must be defined, which option(s) shall be used in a
particular context (i.e., sub-cube). As Provop aims at modularity and reuse, single op-
tions should be applicable in different context; i.e., it must be possible to assign them to
several sub-cubes. A process designer must further be able to design a particular variant
by setting the respective context.
Req. 4 (Context Changes During Runtime). The values of context variables may
change during process execution. Thus the currently selected process variant might be-
come obsolete and might have to be replaced by another one; i.e., other options have to
be chosen and applied to configure the desired process. If such a context change occurs
35
during runtime (i.e., while process instances of the variant to be replaced are executed in
a WfMS), reconfiguration of the running process instances has to be supported. Such a
reconfiguration may apply additional options to the base process and undo adjustments
of obsolete options as well.
In the following we describe in detail how Provop deals with these requirements.
3.2 Process Context Definition
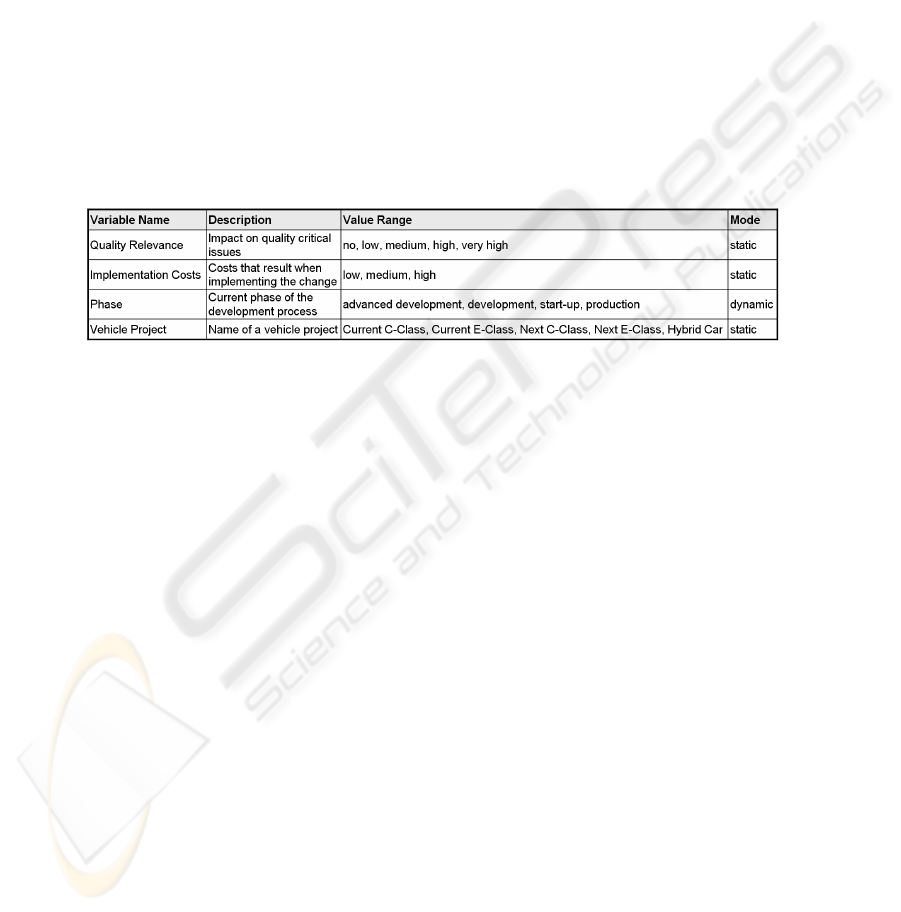
To allow for the context-based configuration of a process variant, first of all, a model for
capturing the process context is needed (cf. Req. 1). In Provop, such a model comprises
a set of
context variables
. Each context variable represents one specific dimension of
the process context, and is defined by a name, a variable description, and a value range.
In Provop we capture this context information in a table (cf. Figure 4). This allows
the context modeler to create new entries and to manage existing ones in a simple and
intuitive way.
Fig.4. Example of a Context Definition in Provop.
The context variables shown in Figure 4 do not only differ in their names and val-
ues, but also in another important aspect. While some context variables are static (e.g.,
Vehicle Project
) others are dynamic. For example, the context variable
Phase
has
dynamic nature since it is updated after a development phase is completed (e.g., switch-
ing from “start-up” to “production”). This information is relevant, for example, to de-
cide whether an option that is chosen based on a certain value of a context variable is
ultimately defined or whether it may become obsolete during process execution. There-
fore Provop captures the
mode
of a context variable as well (cf. Table 4).
Based on our experience there exist valid and invalid combinations regarding the
values of the different context variables (cf. Req. 2). One simplified example that is
highly relevant in practice is as follows: Due to its “very high”
Quality Relevance
a requested product change necessitates extended validation and verification actions,
which leads to additional expenses. Consequently, setting the value of the context vari-
able
Implementation Costs
to “low” at the same time is not a valid combination in
practice. For each valid value combination, in turn, it must be ensured that a consistent
and correct process model exists for the required variant. Therefore the consideration of
such value interdependencies is crucial. Referring to the context cube depicted in Fig-
ure 3 a, a classification of valid and invalid combinations (i.e., sub-cubes) would lead
to high efforts when considering the number of possible context variables in practice
(typically about 10 to 20 variables) and their respective value ranges. In such scenarios
a context cube is no longer sufficient. Simple constraints, for example, the value of one
36
context variable directly implies the value of another one (e.g., a
Vehicle Project
is always in exactly one
Phase
), can be modeled as a dependency graph like the one
depicted in Figure 5 b. To be able to handle more complex dependencies, e.g., between
multiple variables, Provop offers a rule-based logic (cf. Figure 5 c) in addition. All de-
pendencies (i.e., simple and complex ones) are graphically illustrated in an overview on
context variable level as depicted in Figure 5 a. By doing so, a user-friendly definition
of complex context constraints with sufficient graphical support is realized.
Fig.5. a) Dependencies between Context Variables (Overview), b) Dependency Graph, and c)
Dependency Rules.
3.3 Context Rules
Provop follows an operational approach for variant modeling. Therefore, a direct map-
ping of already configured variants to a context description is not feasible. Instead,
for configuring a process variant in a particular context, the relevant options must be
selected based on the contextual knowledge (cf. Req. 3). In Provop this relationship
between options and context values is realized by so called
context rules
. Regarding the
current context all options whose context rules evaluate to “true” are applied to the base
process and therefore determine the required variant. As a special case, the base process
itself may be used as one particular process variant (i.e., no option is applied).
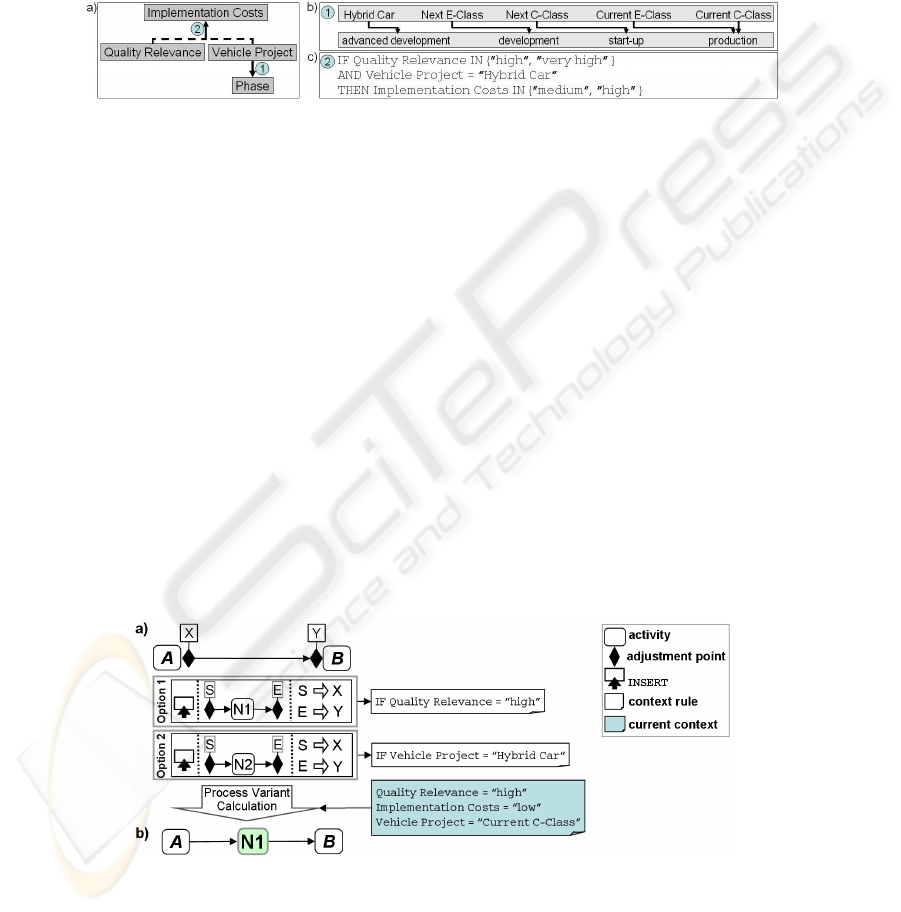
Figure 6 shows an example: Option 1 will be applied if a product change is of
“high”
Quality Relevance
. Option 2, in turn, will be applied if the product change is
requested for the
Vehicle Project
“Hybrid car”. For example, when evaluating the
current context as specified by “high”
Quality Relevance
, “low”
Implementation
Costs
, and the
Vehicle Project
“Current C-Class”, only the context rule assigned to
Option 1 evaluates to “true”. As a consequence, Option 1 is applied to the base process
creating the process model of the variant depicted in Figure 6 b.
Fig.6. a) Context Rules assigned to Options and b) the Resulting Process Variant.
37
3.4 Context-based Reconfiguration of a Process Variant at Runtime
To capture context changes during process instance execution, Provop allows for the
usage of dynamic context variables, whose values may change during process execu-
tion.
5
If dynamic context variables are used for defining a context rule of an option,
the decision whether to apply the corresponding change operations or not has to be
made at runtime (cf. Req.4). As a consequence, the respective process variant either
cannot be completely configured when creating the process instance or has to be re-
configured during runtime. To allow for the configuration of a complete (and therefore
executable) process instance of a variant, Provop uses
variant branches
in its process
models. The basic idea is to encapsulate the adjustments of single options within these
variant branches. The split condition at the variant branch corresponds to the context
rule of the option. Whenever process execution reaches a variant branch, the current
context is evaluated. If the split condition evaluates to “true” the variant branch is exe-
cuted, i.e., the change operations are applied to the base process. Otherwise, the variant
branch is skipped and therefore all adjustments of the option are ignored.
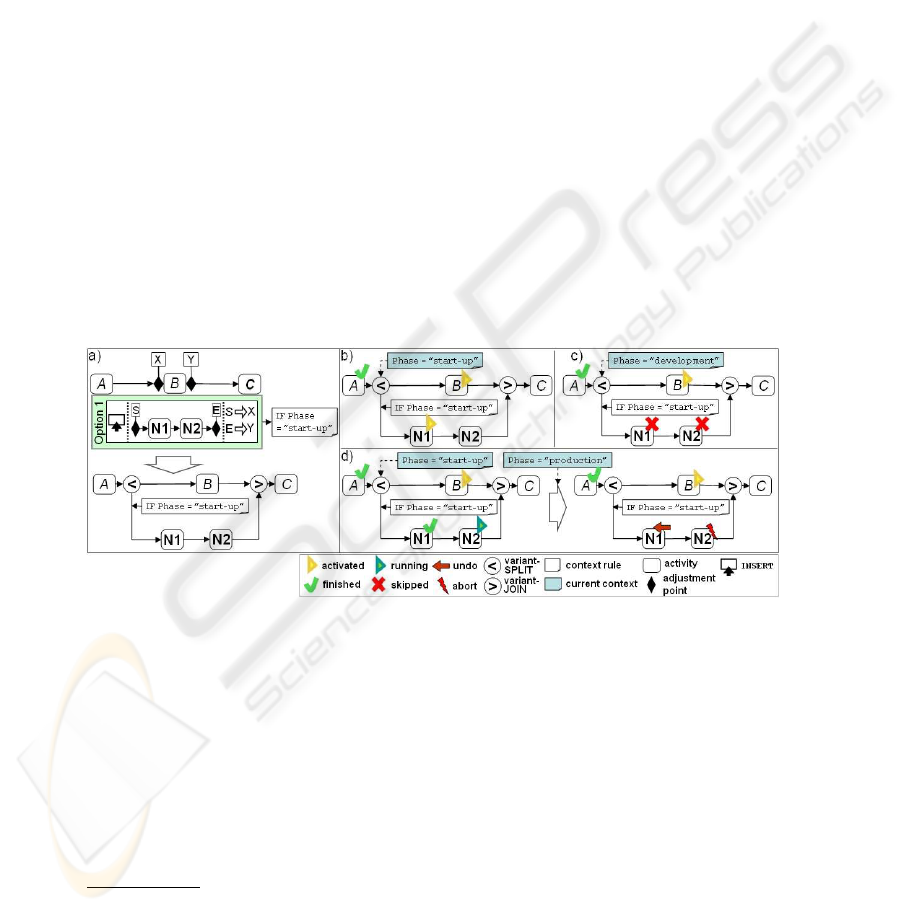
Figure 7 a shows an example of a variant branch definition: As the application of
Option 1 depends on the dynamic context variable
Phase
the corresponding process
fragment is encapsulated in a variant branch (indicated by the encircled “less than” and
“greater than” symbols). Furthermore, the context rule of Option 1 is used as a split
condition during process execution. If it evaluates to “true” (cf. Figure 7 b) the variant
branch will be executed, otherwise it will be skipped (cf. Figure 7 c).
Fig.7. Context Change during Runtime.
A change update of a dynamic context variable at runtime may affect variant bran-
ches that are (partially) finished. Thus, if an evaluation result of a split condition be-
comes invalid a reconfiguration of the process will be required. In Figure 7 d, the prod-
uct change process was started during the
Phase
“start-up”. Consequently the variant
branch of Option 1 was activated. During the execution of this variant branch a context
change occurs for the dynamic context variable
Phase
, which is set to “production”.
Therefore, the context rule assigned to Option 1 evaluates to “false”. As a consequence
the execution of the corresponding variant branch must be rolled back by an abort re-
spective undo of the Activities N2 respective N1.
5
Static variables are defined at process instance creation and cannot change during runtime.
38

Since a rollback of completed activities is accompanied by the loss of work it is
not always feasible. Therefore the behavior is controlled by a steering parameter. It
indicates that rollbacks i) are always enabled, or ii) are always disabled, or iii) always
require a decision of the process administrator whether or not they are performed.
4 Related Work
The context of an actor or a software system can be utilized to realize context-aware
applications in different domains (e.g., healthcare [11] or learning solutions [12]). Such
applications gather contextual information about a user or system and adapt their behav-
ior accordingly. For example, in mobile computing context-aware applications might
use information about the location of a user as well as the output device to provide
context-specific services and to visualize information in an adequate way [13, 14].
Process management is concerned with context related aspects as well. For exam-
ple, the context of a specific process task can be used to display data, information and
knowledge relevant to perform this task.
In [15] a bottom-up approach for the (semi-)automatic configuration of project-
specific process models is presented. Respective processes are created by combining
generic process building blocks, taking into consideration project-specific context (e.g.,
expressed in terms of requirements that influence the process configuration). This ap-
proach requires a complete and therefore also extensive rule set to build consistent and
executable processes out of process building blocks.
A top-down approach for process model configuration is described in [16]. Refer-
ence process models are represented using configurable Event-Process-Chains (c-EPC)
[17]. Generally, such a reference process model is of recommending character and can
be customized in different ways to meet specific needs. Therefore, a reference process
model represents all possible control flow alternatives. Using a questionnaire that com-
prises questions expressed in natural language, configuration facts are gathered. These
facts are evaluated at variation points within the reference process model to configure a
specific model by either executing, skipping or optionally skipping a process element.
As one drawback this approach only allows for the configuration of single elements at
given points in the process model (i.e., it is not possible to mark a complete branch
as mandatory or optional). It is also not possible to move or add model elements or to
adept element attributes like we do in Provop. As compared to reference process mod-
els, the basic process in Provop can be modeled without any restriction; i.e., it needs
not to be defined with a specific use case in mind nor it constitutes a recommendation
for all processes of a given type.
5 Conclusions
We have described the Provop approach for configuring context-based process variants:
Context variables, context values and context constraints (e.g., valid value combina-
tions) are defined in a user-friendly manner. The options used for a process variant are
selected when evaluating context rules. This enables a process variant configuration
based on the current context. In addition, Provop allows reacting to context changes
39

during runtime by late evaluation of split conditions of variant branches or the recon-
figuration of running process variants. The need of the presented concepts and related
requirements have been elicited in a number of case studies we conducted in the auto-
motive domain; i.e., practical relevance of Provop is high.
In future work we will detail the Provop approach: We will address the configura-
tion of consistent process variants, when multiple options are required in the specified
context. Sophisticated techniques are required to prevent errors and consistency prob-
lems (e.g., deadlocks, data flow inconsistency) due to conflicting change operations.
Finally, a detailed validation study of our concept based on a prototype that implements
the Provop concept will be conducted.
References
1. IDS Scheer: ARIS Platform Method 7.0. (2006)
2. BOC: The Business Process Management Tool ADONIS. (2007) (in German).
3. IBM: IBM WebSphere Business Modeller, Version 6.1. (2007)
4. Dumas, M., van der Aalst, W., ter Hofstede, A.: Process-aware Information Systems. Wiley,
Los Angeles, CA (2005)
5. Weske, M.: Business Process Management - Concepts, Languages, Architectures. Springer
(2007)
6. Lenz, R., Reichert, M.: IT Support for Healthcare Processes - Premises, Challenges, Per-
spectives. Data and Knowledge Engineering 61 (2007) 39–58
7. M¨uller, D., Herbst, J., Hammori, M., Reichert, M.: IT Support for Release Management
Processes in the Automotive Industry. In: Proc. of the 4th Int. Conf. on Business Process
Management. (2006) 368–377
8. Hallerbach, A., Bauer, T., Reichert, M.: Managing Process Variants in the Process Life
Cycle. In: Proc. of the 10th Int. Conf. on Enterprise Information Systems. (2008)
9. Hallerbach, A., Bauer, T., Reichert, M.: Modelation and Visualization of Process Variants
in Provop. In: Proc. of Modellierung, Berlin (2008) (in German).
10. Hallerbach, A., Bauer, T., Reichert, M.: Requirements for Modelation and Visualization of
Process Variants. In: Datenbank Spektrum. (2008) (in German).
11. Bricon-Souf, N., Newman, C.: Context-awareness in Healthcare: A Review. In: International
Journal of Medical Informatics. Number 76. Elsevier (2007) 2–12
12. Schmidt, A.: Potentials and Challenges of Context-awarness for Learning Solutions. In:
Proc. 13th Annual Workshop of the SIG Adaptivity and User Modeling in Interactive Sys-
tems. (2005)
13. Schilit, B., Theimer, M., Welch, B.: Customizing Mobile Applications. In: Proc. of the
Symp. on Mobile and Location-independent Computing, Cambridge, MA (1993) 129–138
14. Schilit, B., Adams, N., Want, R.: Context-aware Computing Applications. In: Proc. Work-
shop on Mobile Computing Systems and Applications. (1994) 85–90
15. Rupprecht, C., Rose, T., van Halm, E., Zwegers, A.: Project-specific Process Configuration in
Virtual Enterprises. In: Proc. of the 4th Int. Conf. on the Design of Information Infrastructure
Systems for Manufacturing, Deventer, The Netherlands (2000) 46–53
16. Rosa, M.L., Lux, J., Seidel, S., Dumas, M., ter Hofstede, A.: Questionnaire-driven Configu-
ration of Reference Process Models. In: Proc. of the 19th Int. Conf. on Advanced Information
Systems Engineering. (2007)
17. Rosemann, M., van der Aalst, W.: A Configurable Reference Modelling Lanugage. Infor-
mation Systems 32 (2007) 1–23
40
