
Implementing EPCIS with DEPCAS RFID Middleware
Carlos Cerrada, Ismael Abad, José Antonio Cerrada and Ruben Heradio
Departamento de Ingeniería de Software y Sistemas Informáticos
Escuela Técnica Superior de Ingeniería Informática, UNED
C/ Juan del rosal 16, 28040 Madrid, Spain
Abstract. RFID middleware is a new breed of software acquisition system that
allows transfer data between device readers and business applications. RFID
middleware has been structured in facto with several layers: infrastructure
layer, event processor, tag data translator, rules and composite process, and ap-
plication integration or EPCIS. EPCIS term is a generalization to refer the up-
per layer that link RFID middleware with external systems like SCMs, ERPs,
WMSs or any user application that use auto identification data. In this paper we
want to present the EPCIS DEPCAS layer. DEPCAS (Data EPC Acquisition
System) is a RFID middleware proposal based on an extension of control and
data acquisition systems (SCADAs). We examine the elements that compound
EPCIS in DEPCAS based on SOA (Service-Oriented Architecture) and pub-
lish/subscribe message technologies implemented with JMS (Java Message
Service). EPCIS in DEPCAS solves the two-way communication: it receives
the configuration back-end information to increase the RFID semantic process
defined with scenarios and offers the services to exploit the RFID acquisition
results.
1 Introduction
As part of the optimization effort, companies of diverse application areas are
exploring the use of RFID technology [1]. The noncontact identification applied
to control, to supervise or to acquire any kind of information holds the promise to
provide real time visibility for the most heterogeneous activities [2]. These activi-
ties which are so different as supply chain management, inventory control, asset
management, medical survey, access restriction, individual or animal identifica-
tion, codification and food traceability, etc., manage the same source information
but with very different purposes and objectives.
In traditional RFID applications there was a reduced middleware needed be-
cause the RFID infrastructure was much compact (even there was not networked
RFID readers) and the RFID information was used directly in the business proc-
ess [3]. But nowadays we can start to use a huge variety of RFID infrastructure
and a very complex ubiquitous information network with redundancy, backup
acquisition system or hierarchical organizations [4]. Now, the objective is how to
encompass current and future technology at the same time, and how this informa-
tion could be combined with current capabilities.
Cerrada C., Abad I., Antonio Cerrada J. and Heradio R. (2008).
Implementing EPCIS with DEPCAS RFID Middleware.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on RFID Technology - Concepts, Applications, Challenges, pages 167-174
DOI: 10.5220/0001740001670174
Copyright
c
SciTePress

Of course, we cannot forget the real migration environment that we are going
to solve. There are thousands of applications that are using identification through
codes, bar codes, plates, badges, 2D codes, etc. [5] that in a mid-time will change
to RFID auto identification. From the little applications that we can find in any
little market wherever you look in the world, to the large and more complex in-
formation system of a big and global company, the change from identification to
auto identification will arrive.
This state of the art in the integration of RFID in the existing and real systems
provide a research prospect to propose a general middleware architecture that
process and consolidate RFID information solving the pending questions and
helping efficiently to migrate from identification to auto identification systems.
To leverage the RFID data sharing between RFID acquisition software and
disparate business applications the EPCGlobal [6], an organization that develops
world-wide standards for RFID technology proposed the EPC Information Ser-
vice [7] a data repository that covers most issues related to RFID data manage-
ment and uniform programming interfaces for data acquisition and sharing. In a
general meaning, EPCIS is the upper middleware layer of any RFID middleware
that interconnect business process to RFID data.
This paper is organized as follows. Section 2 introduces the EPCIS standard
proposal and compares some existing EPCIS implementations. Section 3 de-
scribes the general DEPCAS architecture and the main ideas introduced in these
middleware architecture. Section 4 describes the EPCIS DEPCAS implementa-
tion using JMS technology. And section 5 concludes our paper.
2 EPCIS Review
Despite the variety of existing RFID applications, the EPCIS main functionalities
are almost similar. Therefore, the EPCGlobal propose an EPCIS specification
framework designed to be “layered, extensible, and modular”. This framework is
a definition about a minimal set of use cases that the EPCGlobal working group
has identify like basic functionality. Other use cases are projected to be included
in future specification releases. From this initial spec the existing middleware
projects has develop their own EPCIS layer to solve the link between RFID data
models and business applications demands.
2.1 EPCIS Network Specification. From PML to the Abstract Data Model
The EPC Information Service provides a specification framework to solve the
external RFID middleware applications to capture, secure and access RFID data.
The original EPC network architecture was defined from EPCIS White Paper in
October 2003 [8] like an “omniscient entity” to provide relevant information re-
quired from business application to RFID middleware. The main four functions
included in EPCS in this started proposal were: to provide a long term repository
of EPC event data, to supply an access point to higher-level information obtained
168

from EPC process acquisition, to solve the storage and access to detailed business
information associated to EPC process acquisition, and to provide transparent on-
demand access to data attribute held in others systems.
These general functions were so broad that introduces a general confusion
about how to solve and implement it. These pending questions are got pass in the
definite EPCIS specification definition [7][10] including an standard interface to
allow EPC data interchange. This standard interface is characterized by: manag-
ing only historical data (real-time EPC data is decoupled from EPCIS), operating
with cooked EPC related information (raw EPC data is processed in low EPC
Network layers), and dealing only with enterprise systems environment. All this
specific functions are solved using a three layer interface: the abstract data model
layer, the data definition layer and the service layer. The abstract data model is a
closed and defined interface that proposes a specification of general requirements
for creating data definitions in the data definition layer. This data definition is
called core event type. This structural organization in the interface allow to use
standard vocabulary elements used by inter organizations and user specific vo-
cabulary elements defined and meaning inside intra organizations.
2.2 EPCIS Implementations
There are several implementations of generic functions of EPCIS. We want to
include in this comparative point the Sun Java RFID System v3.0 [11], the Web-
Sphere RFID Premises Server [12], the WinRFID middleware [2] and the Accada
EPC Network open source RFID prototyping platform [13]. There exists other
EPCIS implementations from other companies, like RFID Anywhere EPCIS layer
or the BEA WebLogic RFID Enterprise Server.
The EPCIS layer is solved in Sun Java RFID System by the RFID Information
Server a J2EE application that covers the business connection with the Sun Java
infrastructure components. The RFID Information Server uses a permanent re-
pository (in version 3.0, ORACLE 9i, ORACLE 10g or PostgreSQL 8) that allows
defining metadata to be interchanged. The transport mechanism is implemented
using HTTP or JMS of XML messages according to their specific schema. The
WebSphere RFID Premises Server includes the WebSphere RFID Information
Server to support EPCIS functionality. This information server includes a DB2 or
and Oracle as backend database. The WinRFID platform dedicates the two upper
layers: XML framework and the data presentation layer to solve the basic EPCIS
operations and a generic rule engine to manage interface interchange. The Accada
EPC Network prototype includes an EPCIS layer composed itself the same three
standard layers: EPCIS capture application, the EPCIS repository and the EPCIS
query application.
Despite the objective of all these implementations is the same: to connect
business with RFID middleware, there are a set of characteristics that differ be-
tween specific solutions. This analysis introduces the following features:
- Standard compliance, what is the compliance degree in the existing implementa-
tion according to EPC Network standard.
169

- EPCIS permanent data model implementation, what is the existing repository
implementation supported by EPCIS solutions.
- Security EPCIS control. There is a large range of security control levels in EPCIS
data, from general user access to low granular data access.
- Metadata management. The business process defines process data and specific
attributes that are introduced in the EPCIS repository.
- Supply chain support. The EPCIS implementation has specific elements to solve
supply chain questions.
- Reports. The EPCIS includes report facility to data access using XML exporters.
The comparative values for existing implementations are shown in the following
table:
Table 1. EPCIS attributes versus existing implementation.
Sun RFID WebSphere
RFID
WinRFID Accada
Standard com-
pliance
Partial Complete Partial Partial
Datamodel Oracle
PostgreSQL
Oracle
DB2
Oracle
SQLServer
MySQL
Web Server Jini WebSphere Unknown Apache
Security WebServer
security
Proprietary
security in-
fraestructure
Remote
objects
Authentica-
tion and au-
thorization for
query opera-
tions
Metadata Using data in
repository
Specific meta
data model
XML
framework
No support
for new vo-
cabulary type
Supply chain
support
Yes Yes Specific
adaptor
Yes
Reports Not included BIRT: Busi-
ness Intelli-
gence Report-
ing Tool
Not included Not included
EPCIS events Yes, abnor-
mal process
Events and
alerts EPCIS
manager in-
cluded
Rule man-
ager excep-
tions
Yes, abnormal
process
3 DEPCAS Architecture
DEPCAS (Data EPC Acquisition Systems) is a software architecture solution to
solve the RFID acquisition in heterogeneous and real systems. The scheme pro-
170
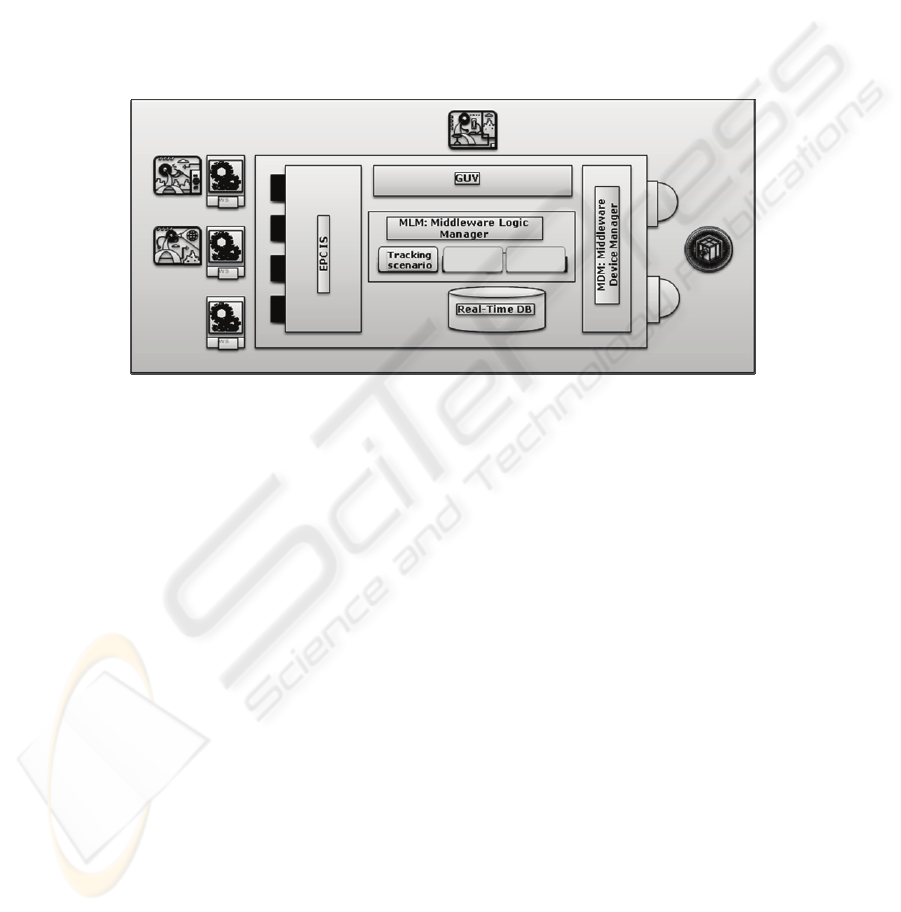

posed here takes origin in the architecture of modern SCADA systems. This archi-
tecture is applied to solve the RFID middleware requirements previously de-
scribed. In the system that we propose the remote equipment of systems SCADA
are replaced by the systems RFID antenna-readers who receive the auto identifi-
cation information. The communication network can be anyone of supported by
the hardware equipment that is commercialized now: communications via series,
Ethernet... And finally the central software system that in this case is the funda-
mental nucleus. The basic structure of the acquisition system that we propose is
organized in four great subsystems: Middleware Device Manager (MDM), Mid-
dleware Logic Manager (MLM), the graphical user viewer (GUV) and the subsys-
tems of exchange information (EPCIS: EPC Information Services).
Fig. 1. Functional architecture of DEPCAS.
The Middleware Device Manager (MDM) main functions are three. The main
purpose is to establish the communication management of one or several devices
hiding their particularities. Another function is to solve the communication proto-
col with the readers and the event processing implementation. The last MDM
main function is to support the topological acquisition network configurations
formed by the antennas and the reading equipment.
The Middleware Logic Manager (MLM) objective is to implement the logical
processes for the auto identification in different scenarios. The “scenario” concept
is the key idea in DEPCAS objective. In the same way that analog and status
processing are the basic process in SCADA systems, one particular scenario in
DEPCAS is associated to an specific purpose and abstract scenario, The logical
processing to solve will depend on each particular scenario. This process will
generate the permanent and non permanent information that results in each situa-
tion. The basic scenarios on which we are working are: operations of tracking,
aggregation of items information to generate new information, operations of items
classification, conversion of information formats and execution of states ma-
chines. Each one of these scenarios generates a set of processed information that
could be used by other systems though the EPCSIS systems or exploited with the
user interface of DEPCAS.
171
The Graphical User Viewer (GUV) will allow having a graphical interface to
the configuration components of DEPCAS, for example, the management of de-
vices, the scenarios configuration, etc. Also it will include the possibility to access
to the information that has being processed in some scenarios or the information
already consolidated. Also it must present/display the corresponding result of
alarms and events that middleware generates.
Finally, services EPCIS will solve the bridge of information between the data
consolidated by the MDM and the MLMs, and the external applications of busi-
ness to DEPCAS. These services will allow to receive as to send information
from system DEPCAS to other systems.
The scenario concept is equivalent to the logical process that with general ap-
plication it is possible to be used in a set of situations where the information takes
advantage of auto identification. In each scenario there are information that is
received, processed, summarized and accumulated, according to their own logic.
4 EPCIS DEPCAS Implementation
The main functionalities of EPCIS in DEPCAS are: to solve publish/subscription
manager, to manage permanent historical data information, to transfer in/out data
between DEPCAS and business applications, to establish a security distribution of
DEPCAS information, a XML data mapping, and to define specific application con-
nector with DEPCAS.
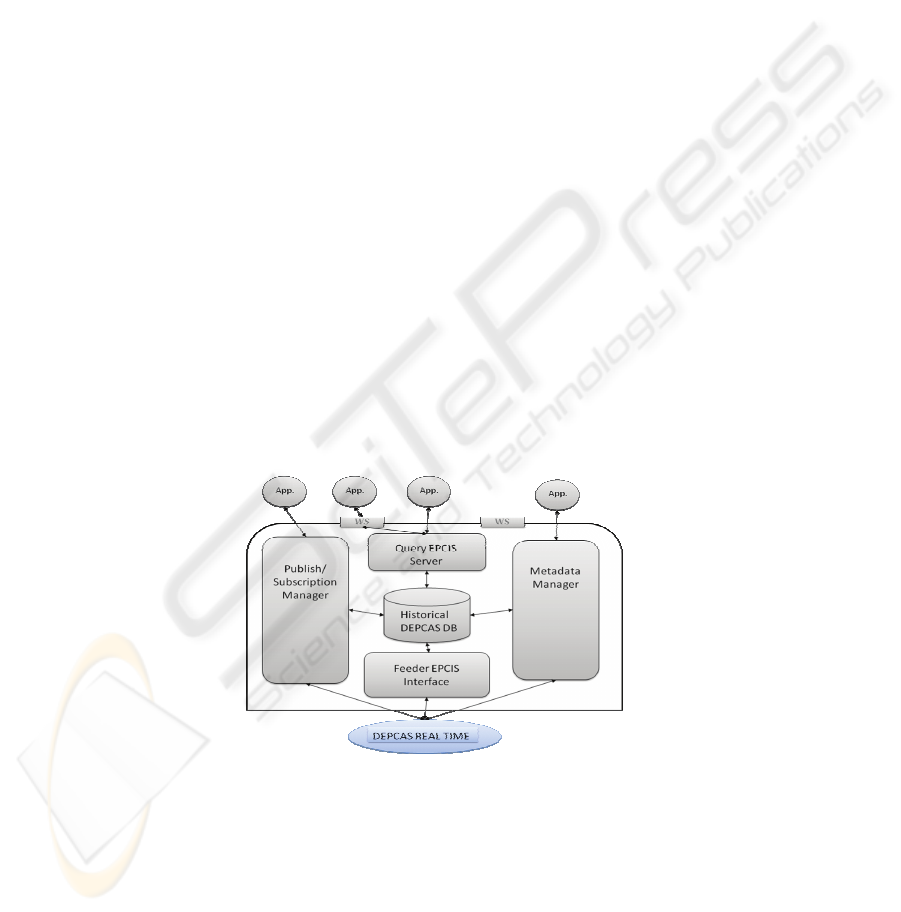
This general functions are implemented using a four subsystem development (fig. 4):
the publish and subscription manager, the data converter manager or metadata man-
ager, the EPCIS feeder and the EPCIS server.
Fig. 2. EPCIS DEPCAS subsystems.
The Publish/Subscription Manager supports two kinds of relationships: relation-
ships that are simple data representations of some actual relationship that exists be-
tween business atomic data and DEPCAS data, and relationships between tables that
have their own properties. Data representations of relationships can contain a Web
172

service reference to access the relationship Web service. The EPCIS implementation
defines interfaces to query a manageable resource about the relationships it partici-
pates in directly, such as a containment relationship. The Publish/Subscription man-
ager also defines an interface for a service that offers relationship information for
many manageable resources enabling a relationship registry. Manageable resources
do not have to be aware that they are participating in relationships.
The metadata or converter manager implements a global repository that captures
the relationships between the RFID product-process data, that we call scenario in
DEPCAS terminology, and existing business data. The converter manager layer offers
the possibility to control the level of aggregation by customized combination of sev-
eral built-in filters as well as those developed by specific environments. Hence a wide
range of variation is at hand. Attaching meta-data from backend-systems to DEPCAS
scenarios is requires connecting specific existing external data to DEPCAS scenarios
tables.
Feeder EPCIS interface works using a JMS structure to exchange data from
DEPCAS real time processing scenarios to EPCIS process. This capturing interface
distribute the information to the consolidate database and to synchronous ECPIS
connectors. The message structure is defined using an XML schema. This schema
structures the general data field of any message according to specific scenario. For
example, the JMSType for a tracking scenario includes: general position, specific
place, building, area, reader used, department, auto id read.
The Query EPCIS server supports the DEPCAS servers/clients connections. It
solves the different data interchange (HTTP, web services or XML ) between
DEPCAS and external business applications. In the same way, EPCIS server is de-
signed as a platform with a uniform query and update interface to applications, while
the actual implementation solves the details and data binding to existing databases
and information systems. EPCIS server supports simultaneous binding to multiple
databases and information systems from multiple vendors, as well as EPCIS as a
managed application service. In order to accommodate various types of data relation-
ships such as routes, predictions, reader points, associations with particular transac-
tions, EPCIS server is being is implemented as a modular framework, with a very
lightweight core functionality, which merely described which ‘profiles’ or relation-
ship types are implemented on any particular instantiation providing an EPCIS inter-
face.
5 Conclusions
The RFID middleware research is oriented to find new alternatives to solve the better
way to include auto identification in productive processes. The new topological read-
ers network and the heterogeneous business application must be connected though
RFID middleware solving all the established requirements.
This paper shows how EPCIS is included in DEPCAS architecture and the main im-
plemented possibilities. The prototype system of the introduced middleware software
suite is ready to be applied to the field test in order to apply to many business do-
mains.
173

The existing DEPCAS implementation represents a prototype limited by the read-
er protocols, the scenarios solved, and the EPCIS functions. Future versions of EPCIS
DEPCAS will include specific connector to external applications and EPCIS exten-
sions to connect with thin clients and wireless external demands.
Acknowledgements
This research has been carried out under contract with the Spanish CICYT through
the DPI2005-03769 and DPI2007-61287 projects.
References
1. Frontline-Sep, 2004, RFID benefits will come in phases. Frontline Solutions 5, 9, Septem-
ber.
2. Prabhu, B.S., Su, X., Ramamurthy, H., Chu, G., Gadh, R..: WinRFID: A midddleware for
the enablement of Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) based Applications. (2005).
3. Russell, R.: Manufacturing Execution Systems: Moving to the Next Level, Pharmaceutical
Technology, January 2004, pp 38-5.
4. Ramamurthy, H., Lal, D., Prabhu, B.S., Gadh, R.: ReWINS: A Distributed Multi-RF Sen-
sor Control Network for Industrial Automation, IEEE Wireless Telecommunications Sym-
posium (WTS 2005), pp 24-33, April 28-30, 2005, Pomona, California.
5. Brewer, A., Sloan, N., Landers T.L.: Intelligent Tracking in Manufacturing, Journal of
Intelligent Manufacturing, Vol. 10, 1999, pp245-250.
6. EPCGlobal Inc., http://www.epcglobal.com/
7. EPCglobal, EPC Information Service (EPCIS) Version 1.0 Specification, Mar. 2006.
8. Harrison, M.: EPC Information Service – Data Model and Queries. WhitePaper. Auto-ID
MIT. October 2003.
9. EPCglobal, PML Core Specification 1.0, September 2003.
10. EPCglobal, EPC Information Service (EPCIS) Version 1.0.1 Specification, Sept. 2007.
11. “Sun RFID and Sensor Community”, http://sun.java.net/rfid-sensors/
12. “Web Sphere RFID Premises Server”, http://www-306.ibm.com/software/integration
/ws_rfid_premises_server/
13. Floerkemeier, C., Lampe, M.: RFID middleware design – addressing application require-
ments and RFID constraints. In Proceedings of SOC’2005 (Smart Objects Conference),
pages 219–224, Grenoble, France, October 2005.
174
