
Bernoulli HMMs for Off-line Handwriting Recognition
⋆
Adri`a Gim´enez-Pastor and Alfons Juan-C´ıscar
DSIC/ITI, Univ. Polit`ecnica de Val`encia, E-46022 Val`encia, Spain
Abstract. Hidden Markov models (HMMs) are widely used in off-line hand-
writing recognition to model the probability (density) of an observation sequence,
given its corresponding text transcription. Observation sequences typically con-
sist of fixed-dimension feature vectors which are computed locally, using a slid-
ing window along the handwritten text image. However, there is no standard set
of local features being used by most of the systems proposed. In this paper we
explore the possibility of raw, binary pixels instead of “complicated” features. To
this purpose, we propose the use of Bernoulli HMMs, that is, HMMs in which
the state-conditional probability (density) function is not a conventional Gaus-
sian (mixture) density, but a multivariate Bernoulli (mixture) probability func-
tion. Promising empirical results are reported on two tasks of handwriting word
recognition.
1 Introduction
Hidden Markov models (HMMs) have received significant attention in off-line hand-
writing recognition during the last years [1–4]. As in speech recognition [5], HMMs
are used to model the probability (density) of an observation sequence, given its corre-
sponding text transcription or simply its class label.
Observation sequences typically consist of fixed-dimension feature vectors which
are computed locally, using a sliding window along the handwritten text image. How-
ever, there is no standard set of local features being used by most of the systems pro-
posed; on the contrary, it seems that each system proposed is tuned using a significantly
different set of features. For instance, in [2], the preprocessed text image is transformed
into a sequence of 60-dimensional feature vectors, each comprising 20 normalised gray
levels plus 40 gray-level derivatives (20 horizontal and 20 vertical). In [3], however,
only 9 local features are computed: 3 characterising the sliding window globally, and
6 capturing additional information about the writing. Another example can be found
in [4], where both discrete and continuous features are combined.
In this paper, we explore the possibility of not using “complicated” local features
and using raw, binary pixels instead. This is done with two ideas in mind. On the one
hand, this guarantees that no discriminative information is filtered out during feature
extraction, which now has to be somehow integrated into recognition. On the other
hand, this allows us to introduce probabilistic models that deal more directly with the
⋆
Work supported by the EC (FEDER) and the Spanish MEC under the MIPRCV ”Con-
solider Ingenio 2010” research programme (CSD2007-00018), the iTransDoc research project
(TIN2006-15694-CO2-01), and the FPU grant AP2005-1840.
Giménez-Pastor A. and Juan-Císcar A. (2008).
Bernoulli HMMs for Off-line Handwriting Recognition.
In Proceedings of the 8th International Workshop on Pattern Recognition in Information Systems, pages 86-92
Copyright
c
SciTePress

object to be recognised. To this purpose, we propose the use of Bernoulli HMMs, that
is, HMMs in which the state-conditional probability (density) function is not a con-
ventional Gaussian (mixture) density, but a multivariate Bernoulli (mixture) probability
function.
The paper is organised as follows. The definition of Bernoulli HMM and its EM-
based maximum likelihood estimation are given in Section 2. In Section 3, some em-
pirical results are reported on two tasks of handwriting word recognition. Finally, some
concluding remarks and future work are discussed in Section 4.
2 Bernoulli Hidden Markov Model
The definition of Bernoulli HMM and its Baum-Welch re-estimation formulae do not
differ significantly from those of the conventional HMMs, based on either discrete
(multinomial) probability functions or continuous (Gaussian) densities. In this Section
we only describe the basic differences. Please see [5, 6] for more details.
Let O = (o
1
, . . . , o
T
) be a sequence of D-dimensional binary observation vectors
and let Q be a set of states. A Bernoulli HMM is an HMM in which the probability of
observing o
t
, given that the HMM is in state q at time t, is
b(o
t
| s
t
= q) =
D
Y
d=1
p
x
d
qd
(1 − p
qd
)
1−x
d
, (1)
where p
qd
is the probability for bit d to be 1 when the observation vector is generated
in state q. Note that (1) is just the product of conditionally independent unidimensional
Bernoulli variables given s
t
. Therefore it can not capture any kind of dependencies
or correlations between individual bits. The parameter vector associated with state q,
p
q
= (p
q1
, . . . , p
qD
)
t
, will be referred to as the prototype of the Bernoulli distribution
in state q.
Maximum likelihood estimation of the parameters governing an HMM can be car-
ried out using the EM algorithm for HMMs; i.e. using Baum-Welch (forward-backward)
re-estimation formulae. Assume that the likelihood is calculated with respect to N se-
quences O
1
, . . . , O
N
; with O
n
= (o
n1
, . . . , o
nT
n
) for all n = 1, . . . , N . At the end of
iteration k, the Bernoulli prototype corresponding to state q has to be updated as:
p
(k+1)
q
=
P
N
n=1
1
p(O
n
)
(k)
P
T
n
t=1
α
(k)
ntq
β
(k)
ntq
o
nt
P
N
n=1
1
p(O
n
)
(k)
P
T
n
t=1
α
(k)
ntq
β
(k)
ntq
, (2)
where α
(k)
ntq
, β
(k)
ntq
and p(O
n
)
(k)
are derived in the E step, as usual, from the parameters
obtained in the previous iteration.
In order to avoid zero probabilities in Bernoulli prototypes, these are smoothed by
a linear interpolation with a flat (uniform) prototype, 0.5,
˜
p = (1 − λ) p + λ 0.5 , (3)
where typically λ = 10
−6
.

3 Experiments
In order to test the proposed model, experiments were carried out using two corpus
based on real tasks: recognition of handwritten Arabic cheques and recognition of hand-
written English text. The corpora, experiments and results obtained results are described
in what follows.
3.1 Corpora
The first corpus that we used is a handwrittenArabic cheque database from CENPARMI
(Centre for Pattern Recognition and Machine Intelligence) [7]. Arabic script presents
several differences from Latin script. Arabic is written from right to left in cursive
script. Out of the 28 basic Arabic letters, 22 are cursive while 6 are non-cursive. Within
a word, cursive letters can be connected to succeeding letters, while non-cursive letters
can not. Therefore, an Arabic word can be separated into several subwords. The shape
of an Arabic letter may depend significantly on its position within a subword. Because
of this, it is usual to use subwords instead of letters as basic recognition units.
The corpus was acquired from 3000 real cheques from a banking corporation in
Saudi Arabia. Images were preprocessed by binarisation and noise reduction. As a re-
sult, several databases were obtained and, for each database, a division into training and
testing sets was proposed. In this work we have used the non-touchingArabic subwords
database.
The non-touching Arabic subwords database has 96 different subwords and around
28000 samples. The amount of samples per subword is very variable, for example the
five most frequent subwords are above the 1000 for training, and the five less frequent
subwords haveonly one sample for training, furthermore,some subwords have not sam-
ples for testing. The width and height of samples between subwords are very variable
too, with aspect ratios between 0.3 and 4.8. Furthermore the aspect ratio of samples of
a subword could be very variable. In Figure 1 there are some examples.
The second corpus e used is the IAM-database [8],[9]. This corpus contains forms
of unconstrained handwritten English text. All texts were extracted from the LOB cor-
pus [10]. A total of 657 writers contributed. Several datasets were obtained by using
segmentations techniques, in particular we have used the handwritten words dataset. In
Figure 2 there are some examples.
This dataset contains approximately 115000 samples and approximately 13500 dif-
ferent words, but we only have considered those that are correctly segmented. There-
fore, the number of samples is approximately 96000 and the number of words approxi-
mately 12000. The amount of samples per word is very variable. For example, the most
frequent word has 4986 samples, and there are 6620 words with one sample and 11199
words with less than 10 samples. There is a great aspect ratio variability in corpus, with
values between 0.3 and 14.
In Table 1 some basic statistics are shown for both datasets.
3.2 Experiments
In order to test the Bernoulli HMMs without preprocess influence, a minimum (neces-
sary) preprocessing has to been done over the images. All images have been scaled in
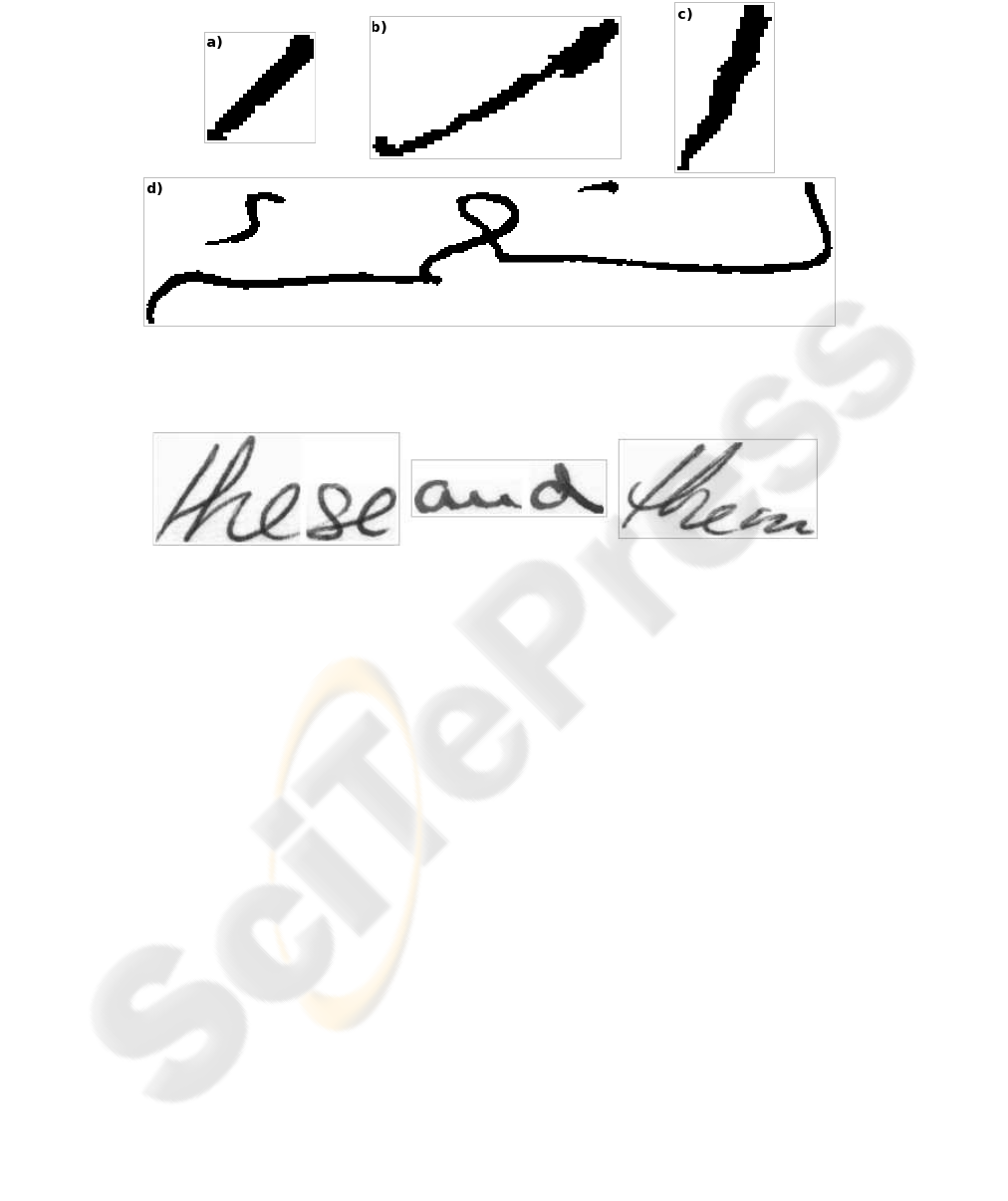

Fig.1. Four samples from Arabic subwords dataset. Three samples (a,b,c) from subword 1-08
with different aspect ratio and scaled ×4. The sample (d) of subword 6-01 scaled ×2.
Fig.2. Three samples from IAM words dataset. From left to right the words: these, and and them.
height to the same size while maintaining their original aspect ratio. Different heights
(D) have been considered: 10 and 20. In addition to this, an Otsu binarisation has been
carried out on the IAM words dataset.
Since both datasets have a great variability of the number of samples per class, we
have carried out the experiments with subsets from the original datasets. In the case of
Arabic subwords dataset, the ten most frequent subwords have been selected, and the
samples have been divided into training and testing sets respecting the original propor-
tion. For the IAM words dataset, the classes with at least 50 samples have been selected
(this includes samples from the 657 writers), and for each class, the 80% of samples are
intended for training and the others for testing. In Table 2 some characteristics of the
subsets are shown.
Experiments have been carried out for varying number of states, Q ∈ {10, 20,
40, 80, 160, 320}. The Bernoulli HMMs were initialised using a left-to-right topology
with skips as follows: first we set up an order in hidden states, 1 being the first and Q the
last, and for each parameter a counter is set to zero. Second, for each training sample
we distribute the binary vectors, at same distance each from other, over the states, and
the associated transition counters are increased. Bernoulli counters are increased in the
same way. Finally, initial parameter estimations are obtained by normalising counters.
After each Baum-Welch iteration, each Bernoulli prototype p is smoothed as explained

Table 1. Number of samples, average width, average height and average aspect ratio, for the three
most frequent classes from each dataset.
Arabic subwords
Class N.Samples Width Height A.Ratio
1-08 2920 37 25 1.58 ± 0.69
1-14 2677 42 28 1.52 ± 0.49
2-09 2450 72 59 1.25 ± 0.48
IAM words
Class N.Samples Width Height A.Ratio
the 4986 110 69 1.67 ± 0.54
, 4376 16 30 0.54 ± 0.24
. 4094 8 9 1.05 ± 0.35
Table 2. Number of classes, number of training samples, number of testing samples and average
ratio in both testing and training samples, for the Arabic subword dataset with the ten most
frequent subwords, and for the IAM words dataset with words that at least have 50 samples.
N.Classes N.S.training N.S.testing A.Ratio
Arabic subwords 10 13106 5456 1.26 ± 0.66
IAM words 180 44492 11122 1.63 ± 1.00
in (3). For each class-conditional Bernoulli HMM, 10 Baum-Welch iterations were ex-
ecuted.
For each experiment, several repetitions have been performed, by means of ran-
domly selected testing and training sets, respecting the original proportions for each
class. With the Arabic subwords dataset about 10 repetitions for Q = {320} and 30
repetitions for Q = {10, 20, 40, 80, 160} were carried out. With the IAM words dataset
about 2 repetitions for Q = {160, 320} were carried out, for Q = {10 , 20, 40, 80} 10
and 5 repetitions were carried out for D = 10 and D = 20, respectively.
3.3 Results
In Figure 3 the results for the Arabic subwords dataset are shown. The best result
(10.9%) is obtained with D = 20 and Q = 320. For D = 20 the results could
be improved by increasing the Q, however for D = 10 the best result is achieved
with Q = 160. The lowest classification error (14.3%) is obtained with D = 20 and
Q = 160.
In Figure 4 the results for the IAM words dataset are shown. As in Arabic subwords,
the best results are obtained with D = 20, despite that better results are obtained with
D = 10 for low values of Q. The best result obtained, 31 .0%, is similar to the best
result in [3] using a single Gaussian density in each HMM state. It is worth noting,
however, that we use an independent Bernoulli HMM for each class while, in [3], each
class-conditional continuous HMM is built from more elementary HMMs at character
level.
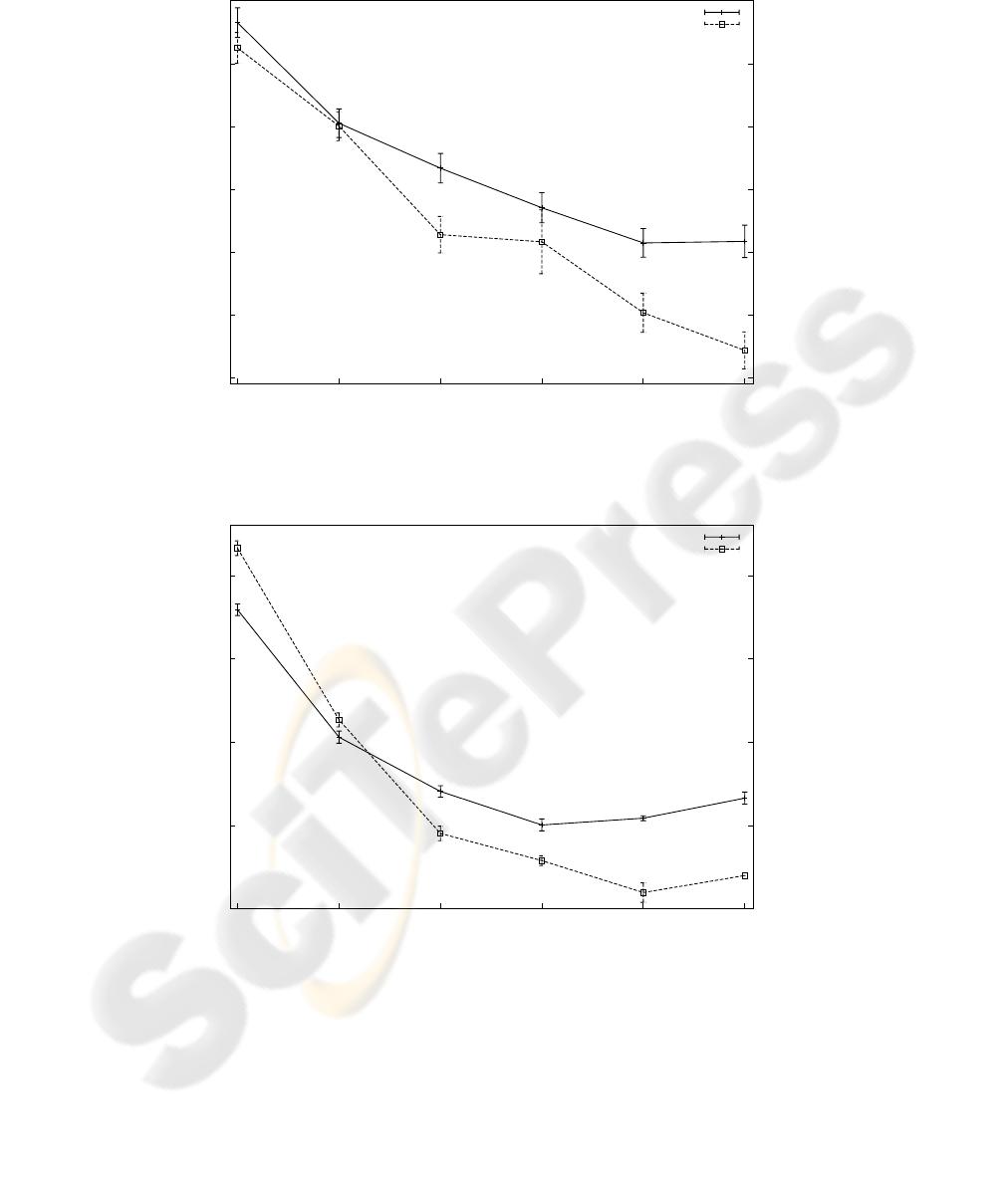
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
320 160 80 40 20 10
10
12
14
16
18
20
22
D=10
D=20
Error %
Number of States (Q)
Fig.3. Error classification with different number of states and heights (D) for the Arabic sub-
words dataset, with the ten most frequent subwords and several repetitions for each point.
30
35
40
45
50
320 160 80 40 20 10
30
35
40
45
50
D=10
D=20
Error %
Number of States (Q)
Fig.4. Error classification with different number of states and heights (D) for the IAM words
dataset, with the words that have at least 50 samples and several repetitions for each point.

4 Concluding Remarks and Future Work
Bernoulli HMMs have been proposed for off-line handwriting recognition in order to
directly model text image data in binary form. Empirical results have reported on two
tasks of off-line handwritten word recognition: Arabic subwords from CENPARMI cor-
pus, and English words from IAM database. In both cases each word (subword) has
been modelled with one HMM, and only the required preprocess to obtain binary im-
ages of same height, has been done. Feature vectors of different sizes, as well as HMMs
with different number of states have been tested. The results on the Arabic subwords
task are promising. In the case of the IAM words, the results were very similar to those
obtained using HMMs with one Gaussian per state.
Ongoing work is focused on the use of Bernoulli HMMs at subword (character)
level and extend them by using Bernoulli mixtures instead of single Bernoulli probabil-
ity functions in each state. A first step is to study the optimal number of states, training
iterations and Bernoulli components, as was done in [3] for the case of Gaussian com-
ponents. Then, we also plan to include explicit modelling of invariances in Bernoulli
components. In addition we plan to compare the results with other recognisers, mainly
with Gaussian HMMs recognisers.
References
1. Plamondon, R., Srihari, S.N.: On-Line and Off-Line Handwriting Recognition: A Compre-
hensive Survey. IEEE Trans. on PAMI 22 (2000) 63–84
2. Toselli, A.H., Juan, A., Keysers, D., Gonz´alez, J., Salvador, I., H. Ney, Vidal, E., Casacu-
berta, F.: Integrated Handwriting Recognition and Interpretation using Finite-State Models.
International Journal of Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence 18 (2004) 519–539
3. G¨unter, S., Bunke, H.: HMM-based handwritten word recognition: on the optimization of
the number of states, training iterations and Gaussian components. Pattern Recognition 37
(2004) 2069–2079
4. Xue, H., Govindaraju, V.: Hidden Markov Models Combining Discrete Symbols and Con-
tinuous Attributes in Handwriting Recognition. IEEE Trans. on PAMI 28 (2006) 458–462
5. Rabiner, L., Juang, B.H.: Fundamentals of speech recognition. Prentice-Hall (1993)
6. Young, S., et al.: The HTK Book. Cambridge University Engineering Department (1995)
7. Al-Ohali, Y., Cheriet, M., Suen, C.: Databases for recognition of handwritten Arabic
cheques. Pattern Recognition 36 (2004) 111–121
8. Marti, U., Bunke, H.: The IAM-database: an English sentence database for off-line hand-
writing recognition. Int. J. Doc. Anal. Recogn. (2002) 39–46
9. Zimmermann, M., Bunke, H.: Automatic segmentation of the IAM off-line database for
handwritten English text. In: Proc. of the ICPR 2002. Volume 4., Quebec (Canada) (2002)
35–39
10. Johansson, S., Leech, G., Goodluck, H.: Manual of information to accompany the Lancaster-
Oslo/Bergen Corpus of British English, for use with digital Computers. Department of En-
glish, University of Oslo, Norway. (1978)
11. Romero, V., Gim´enez, A., Juan, A.: Explicit Modelling of Invariances in Bernoulli Mixtures
for Binary Images. In: Proc. of the 3rd Iberian Conference on Pattern Recognition and Im-
age Analysis (IbPRIA 2007). Volume 4477 of Lecture Notes in Computer Science., Girona
(Spain), Springer-Verlag (2007) 539–546
