
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE
ENVIRONMENT CHANGES
A Pattern Driven Approach
Nicola Boffoli, Daniela Castelluccia, Fabrizio Maria Maggi and Roberto Rutilo
Department of Computer Science, University of Bari, Via E. Orabona 4, Bari, 70126, Italy
Keywords: Flexible process modeling, process patterns, decision tables.
Abstract: Nowadays enterprises perform in an extremely competitive business environment, therefore business
processes, although complex must be highly flexible to react to new demands. This purpose implies that
these processes should be continuously maintained through a flexible modeling. This paper addresses this
problem and provides a process modeling approach able to govern the high variability of the environment
parameters affecting the processes in use, through the well-known pattern paradigm and the decision tables
formalism. Furthermore, the authors discuss the experience of the proposed approach in a real case. Results
are encouraging and drive further investigations in such a way.
1 INTRODUCTION
In order to improve competitiveness, enterprises
have to make business processes flexible, adapting
them to the business environment. New objectives,
new technologies, industrial standards, quality
programs, budget, workers, tools, cultural factors or
changes rising from acquired experience impact
directly on the adequacy of the business processes
and on the enterprise responsiveness (Morisio, 2000)
(Singh, 2004). Therefore, when we model a process,
we have to take into account the complexity of its
relationship with business environment. Moreover,
process formalization has to be very flexible so that
processes models can change so quickly as business
environment (Bhat, 2005). In the last years, these
needs have deeply urged enterprises to Business
Process Management (BPM) (Van der Aalst 1,
2003) (Elzinga, 2005), that provides methodologies
for business process modeling, deploy, monitoring
and continuous improvement, in order to govern the
process complexity and the environment dynamism
in a more and more effective and efficient manner.
This paper provides an approach to support BPM
through flexible process modeling according to the
operative environment. We start from the concept
that modeling a process means also modeling the
environment factors influencing it. For this purpose
our approach uses the well-established concept of
pattern: a pattern identifies a recurring problem and
a solution and aims to capture and explicitly state
abstract problem–solving knowledge that is usually
implicit and gained only through experience (Winn,
2002). Any pattern refers to a tern <Problem,
Context, Solution>: given a problem, a pattern not
only suggests a general solution, but also it identifies
a more specific one according to the actual context.
For this reason, patterns support flexible process
modeling from a methodological point of view as
they allow to represent the relationships between
contexts and solutions.
In particular, the study presented here suggests
the use of decision tables as implementative support
to the pattern theory: they assure compact overview
of a large number of information, modular
knowledge organization, effective evaluation of
consistency, completeness and redundancy. These
peculiarities guarantee a representation of the
relationships among problems, contexts and
solutions in a complete manner, without
inconsistencies and fast reusable. That’s why
decision tables allow to represent all the possible
contexts for each problem and to reject the
inconsistent ones, so that they identify the
corresponding specialized solution for each possible
context. Moreover, decision tables are easily
maintainable. This fact increases flexibility of
dynamic reengineering of the relationships among
problems, contexts and solutions: when the
147
Boffoli N., Castelluccia D., Maria Maggi F. and Rutilo R. (2008).
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE ENVIRONMENT CHANGES - A Pattern Driven Approach.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering, pages 147-156
DOI: 10.5220/0001766401470156
Copyright
c
SciTePress
environment changes, we can identify the new
specialized solution just changing some elements of
the decision tables and we can easily change the
process replacing the existing solution with a
specialized one according to the new context.
Briefly, the approach here proposed investigates
the following Research Questions (RQ):
- RQ1: How to organize and relate environment
factors, general processes and specialized
processes.
- RQ2: How to represent and use the relationships
among environment factors, general processes
and specialized processes.
In order to face this research questions the following
instruments are respectively proposed:
- a pattern-driven model
- an appropriate decision tables set
Logical LevelTheoretical Level
Pattern-Driven Model
Decision Tables Set
Question1:
How to organize and relate
environment factors, general
processes and specialized
processes
Question2:
How to represent and use the
relationships among environment
factors, general processes and
specialized processes
- GOAL -
Environment Aware
Process Modeling
Figure 1: GQM Schema of the proposal.
The paper is structured as following: in section 2
related works are explained and compared; section 3
presents our proposal, including theoretical and
logical model; section 4 discusses the application of
the methodology in a real case; finally, the last
section explains the conclusion and the future
development of this work.
2 RELATED WORKS
The flexible process modeling is a question long
debated by the scientific community in the last years
and there are many literary contributions
investigating in such a way.
A formal approach to defining patterns for
business processes is presented in (Van der Aalst 2,
2003), (Van der Aalst, 1996). These works are based
on the workflow view of business processes. The
patterns define many ways of ordering activities in
workflow for example task sequencing, split
parallelism, join synchronization, and iteration. This
approach can be quite useful for tasks as analysis
and design patterns definition or workflow
management systems building and evaluation. It
differs from approach proposed in this paper because
even if it applies the process components reuse,
however it focuses only on organizing a sequence of
activities without identifying a relationship between
process and context.
A methodology to define and exploit business
process patterns is presented in (Malone, 2003),
(Brynjolfsson, 1989). Here a general process pattern
is defined as a number of generalized activities that
will be specialized at design time. A large collection
of general and specialized patterns has been built
based on this approach, and it is in use for process
improvement. The main aspect we learn from this
approach is the idea of pattern specialization.
However process patterns specialization is at design
level, not at analysis and modeling level, so the
process reengineering becomes complex and not
flexible to adapt to a new context.
In (Hongli, 2006) an approach taking in account
context variability is shown. Here a flexible
modeling method has been proposed based on the
capability of extensible organization description, but
this approach considers only the changes in the
organizational context without taking into account
the ones in other contexts (for example legislative
context or market context).
Finally, in (Yao, 2006) the authors represent the
relationship between the context and the solutions
specialized for that specific context through the
Cased-based Reasoning technique. This technique
consists in solving a new problem remembering a
previous similar situation and reusing information
and knowledge of that situation.
The approach introduced in this paper is born
from the demands highlighted by the state of the art
about process modeling. It aims to elaborate a new
methodology for process modeling as a set of tasks
and process components, which can be specialized
according to the operational context through an
unique and schematic representation of environment
conditions and previous acquired experiences.
ENASE 2008 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
148

3 PROPOSED APPROACH
The proposed approach adapts the pattern concept to
the business processes modeling: a pattern allows to
find a solution (a process component) able to model
a given problem (a part of a process to be modeled)
according to the specific context where the solution
has to work. In particular:
- for “problem” we mean a part of a process to be
modeled to which a general process component
(general solution) to specialize has to be
associated;
- for “context” we mean the set of factors
characterizing the context where the process
works (i.e. technologies, industrial standards,
budget, tools, cultural factors), whose values
determine the suitable actions to specialize the
general solution;
- for “solution” we mean the process component
suitably specialized solving the problem in that
specific context.
A typical scenario consists of modeling a
problem in a specific context starting from a general
solution and identifying a set of actions to specialize
the solution itself according to the given context.
The specializing actions can have influence on the
activities, on the artifacts or on the control flow of
the general solution. In fact they can:
- add new activities
- specialize existent activities
- modify artifacts
- modify control flow
The pattern-driven approach is then implemented
through decision tables. That’s why the approach
consists of two different levels:
- Theoretical Level, representing concepts and
functions supporting the pattern-driven
approach;
- Logical Level, implementing the theoretical
level through the decision table formalism.
3.1 Theoretical Level
At this level the proposed approach is formalized
through specific functions.
The theoretical level consists of two steps:
- Problem Step: beginning from a specific
problem, we identify a general solution
modeling it.
- Context Step: beginning from a general solution
and a specific context, we identify the
specialized solution solving the problem in that
context.
3.1.1 Problem Step
Given a problem, we have to find a general solution
modeling it. If we call P the set of the problems, to
which a general solution is associated, and if we call
GS the set of the general solutions themselves, we
define:
φ: P→GS, ∀p∈P: ϕ(p)=gs
where φ is the function able to select the general
solution gs solving the problem p.
Moreover, given a problem, it can be useful to
specify it through the identification of a sub-
problem. This requires in some cases the
investigation of a hierarchy of more and more
specific problems before the identification of a
general solution. So the function φ becomes:
gs if lp=1
∀p∈P: ϕ(p)=
ϕ*(p*) if lp>1
where ϕ* is a ϕ-type function able to investigate a
set of sub-problems of p (i.e. problems more specific
than p), p* is a sub-problem of p and lp is the depth
level in the problems hierarchy.
3.1.2 Context Step
Many factors (here called diversity factors)
characterize a context: business environment,
technology, industrial standard, quality program,
vision, budget, size, structure and culture of
enterprise. These factors have an influence on
processes and must be taken into account when we
model them. So, after having identified the suitable
combination of diversity factors able to characterize
the context, we can define a specific context (here
called context profile) assigning a value to each
diversity factor.
To each gs∈GS is associated a set CP of context
profiles as to which the general solution can be
specialized. A context profile characterizes a
specific context and can be represented as a vector
of instantiated diversity factors DF
i
i=1, …, n. Each
DF
i
is a factor characterizing a particular aspect of
the environment and has a definition domain
[DF
i
]={df
i1
, df
i2
, …, df
iq
} where each df
ij
j=1,...q is
an instance of DF
i
. So we can say that the set CP is:
CP= [DF
1] × [DF2] × ...... × [DFn]
∀gs∈GS given a context profile, we have to
identify the set of the actions able to specialize gs
according to that specific context profile. If we call
SA the set of the actions we can apply to specialize
gs, and SAS the set of the SA subsets, i.e. the set of
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE ENVIRONMENT CHANGES - A Pattern Driven Approach
149

all the possible combinations of specializing actions,
we define:
χ’
: CP→ SAS
∀cp∈CP: χ
’(cp)=sas, with
sas= {sa
1
, …, sa
r
}
where χ
’
is the function that, given a context profile,
determines sas the set of specializing actions
corresponding to the specific context profile.
Moreover, fixed a specific context in some cases
it can be useful to specify it much more through a
more in-depth survey considering a more specific
context profile. This requires in some cases the
investigation of a hierarchy of more and more
specific context profiles before the identification of
the set of specializing actions. In these cases the
function χ
’ becomes the function:
∀cp∈CP: χ
’(cp)= {sa
1
, sa
2
,…, sa
h
} ∪ χ’
1
(cp
1
) ∪
∪ χ’
2
(cp
2
) ∪...∪ χ’
k
(cp
k
)
where sa
i
are specializing actions, cp
j
are context
profiles specifying cp and ∀j χ’
j
is a χ’-type
function able to investigate more specific profiles.
When the specializing actions are identified, it’s
necessary to find the specialized solution applying
these actions to the general solution gs. So for each
function χ
’ we can define the function:
χ’’: SAS→ SS,
where χ’’ is the function able to identify the
specialized solution ss
corresponding to a set of
specializing actions. So, for each general solution gs
it is possible to define the function χ = χ’’⋅χ’:
∀cp∈CP: χ(cp)= ss
where ss is the specialized solution obtained
applying on the general solution gs the set of actions
specializing it according to the context cp.
In conclusion, for each general solution gs it is
possible to define a function χ to suitably specialize
this component according to the context where it
works.
3.2 Logical Level
This level aims to implement the theoretical level
functions through the decision tables formalism.
A decision table is a tabular representation of a
decision-making task, where the state of a set of
conditions determines the execution of a set of
actions (Vanthienen, 1998), (Maes, 1988), (Ho,
2005), (Bar-Or, 2005). In general, a decision table
has four quadrants: conditions (Cond), conditional
states (S), actions (Act) and rules (x) as shown in
figure 2. The table is defined so that each
combination of conditions and conditional states
corresponds to a set of actions to carry out. The
conditional-oriented approach of a decision table
allows to express knowledge related to the examined
problem.
At this level, we implement the functions defined
in the Theoretical Level (ϕ, χ’, χ’’) through suitable
decision tables:
- Problem Decision Table (DTp)
- Context-Action Decision Table (DTca)
- Context-Solution Decision Table (DTcs)
Figure 2: An example of decision-table.
3.2.1 Problem Decision Table
For each function ϕ a DTp is implemented and
structured as following:
- the CONDITION quadrant contains the
problems domain
- the CONDITIONAL STATE quadrant contains
the possible problem in the specific domain
- the ACTION quadrant contains
- the general solutions available
- a set of links to more specific DTp in order
to investigate more specific problems
- the RULE quadrant identifies the relationship
between each faced problem and the
corresponding general solution or link to a more
specific DTp.
Figure 3: An example of DTp schema.
ENASE 2008 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
150
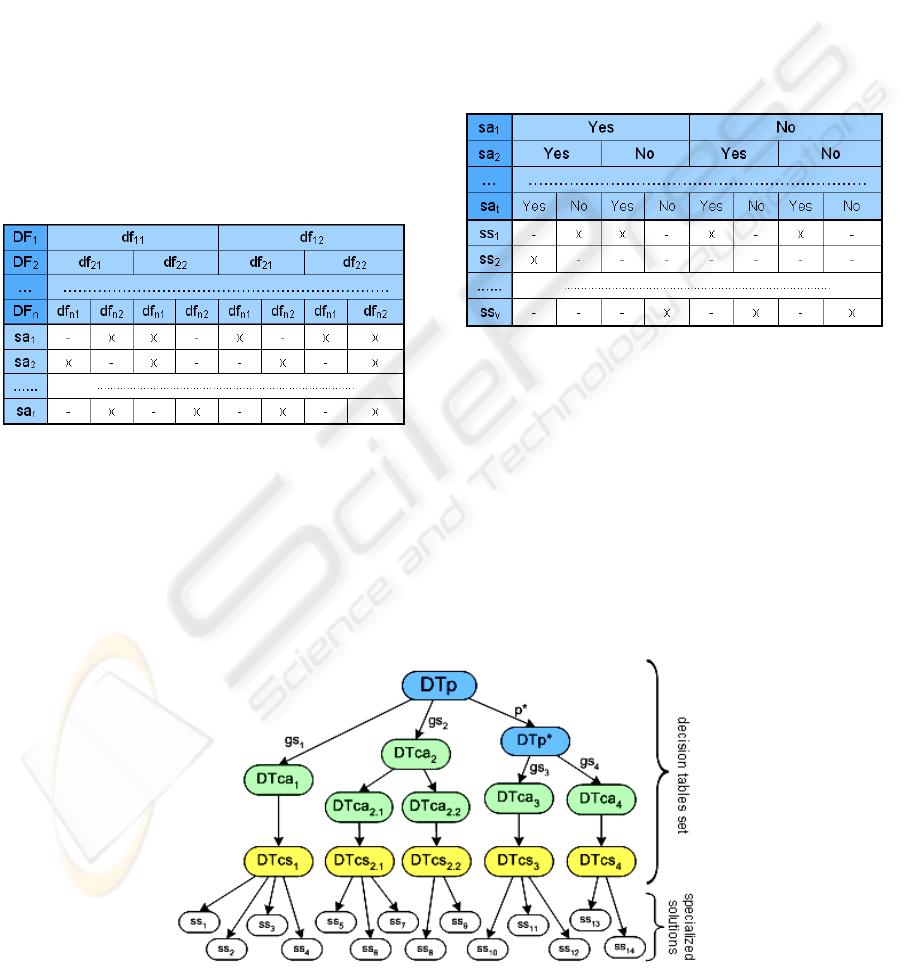
3.2.2 Context-Action Decision Table
For each function χ’ a DTca is implemented and
structured as following:
- the CONDITION quadrant contains the
diversity factors DF
i
i=1,...n specializing the
related general solution gs
- the CONDITIONAL STATE quadrant contains
the possible value of each diversity factor:
[DFi]={df
i1
, df
i2
, …, df
iq
}
- the ACTION quadrant contains
- all the possible actions specializing the
general solution gs
- a set of links to more specific DTca in order
to investigate more specific contexts
- the RULE quadrant identifies the relationship
between each context profile and corresponding
specializing actions and links to more specific
DTca.
Figure 4: An example of DTca schema.
3.2.3 Context-Solution Decision Table
For each function χ’’ a DTcs is implemented and
structured as following:
- the CONDITION quadrant contains all the
possible actions specializing the general
solution gs
- the CONDITIONAL STATE quadrant contains
the possible values for the specializing actions
(“Yes” or “Not”) indicating if the corresponding
specializing action must be executed or not.
- the ACTION quadrant contains the specialized
solutions facing the given problem
- the RULE quadrant identifies the relationship
between each set of specializing actions and the
corresponding specialized solution
It is clear that the previously described structure
allows to verify the completeness and effectiveness
of the executed actions and consequently to extend
and update the experience acquired during process
execution.
Figure 5: An example of DTcs schema.
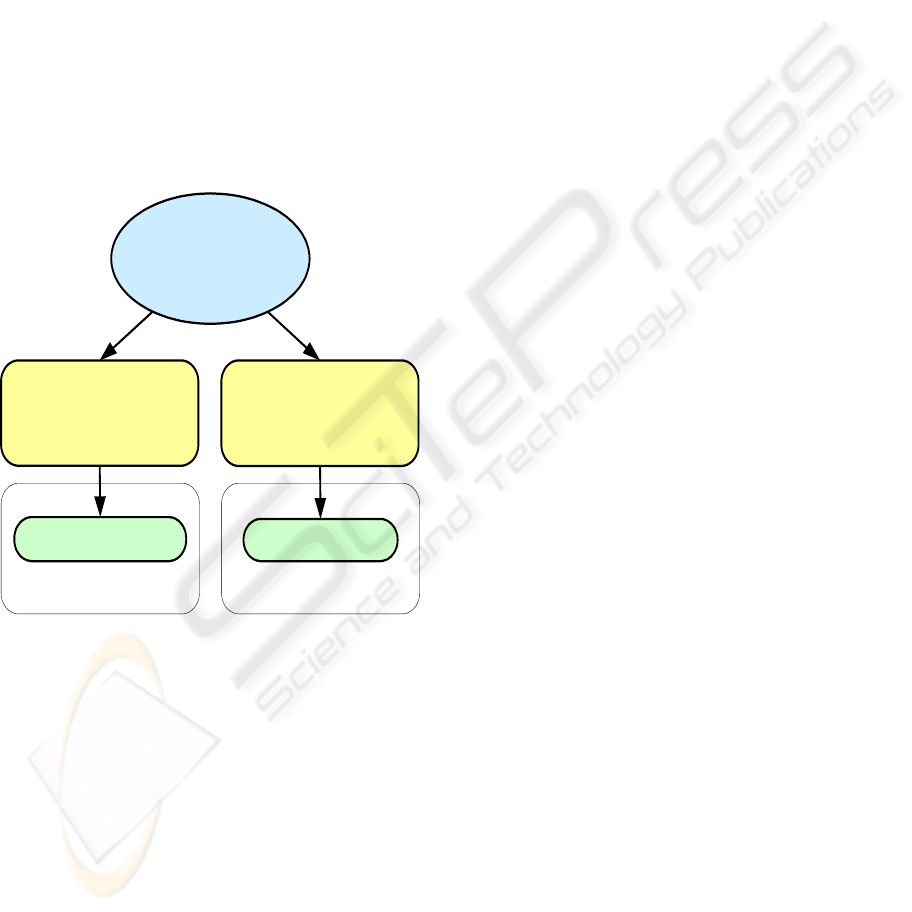
The figure 6 shows a typical example of the
structure of a Decision Tables Set build according
the proposed approach.
4 EXPLORATIVE
INVESTIGATION
At the moment, the proposed approach is being
investigated in an industrial case during a research
Figure 6: A typical net of the decision tables set and related specialized solutions.
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE ENVIRONMENT CHANGES - A Pattern Driven Approach
151
project. This project investigates the management of
business processes about the “Data Archiving
Management and Acquisition”.
The enterprise collaborating to the realization of
this experimentation is a stable ICT company, whose
core business is about document management
solutions for public and private financial institutions.
Every day the company receives packets of
documents from its clients. Such documents are
primarily banking files containing pure text, images,
diagrams, charts and so on. Because of the high
number of documents to be stored, the enterprise
needs the implementation of automated processes
able to scan every document in the packets,
recognize errors in words, distinguish images from
pure text and store everything according to proper
category. To model such business processes, we
have implemented two automated tools supporting
the execution of the proposed methodology:
- a process developer tool, provided with a
knowledge base of process patterns, for a visual
business process modeling;
- a decision tables management system.
These tools support the automation of our
methodology and are very useful to manage a large
number of process components and decision tables.
Following it is explained in detail how the
investigation has been conducted.
4.1 Start-Up Analysis
A start-up analysis has been conducted on the 8
processes in use within the enterprise in order to:
- identify the general processes and the related
general solutions (GS)
- organize and formalize, for each general
process, the appropriate diversity factors (DF)
affecting it
- elicit the specializing actions (SA) for each
process specialization
- define the specializing processes representing
the set of the specialized solutions (SS)
- relate problems, diversity factors, actions and
solutions
The table 1 summarizes the extracted items
ordered by the general solutions:
Table 1: A summary of extracted items.
General Solution (GS) #DF #SA #SS
Consulting 6 7 12
Documents organizing 7 9 14
Documents reception 6 7 15
Documents recognizing 3 4 8
Indexing and verifying 6 8 10
Optical archiving 7 8 9
Physical archiving 5 7 8
Scanning 5 8 12
Total 47 60 88
According to the approach presented in section 3,
all the collected items have been used to build a
Decision Tables Set. Such set is made of:
- 1 DTp: managing all the general solutions
- 8 DTca: one DTca for each general solution
- 8 DTcs: one DTcs for each DTca
Using 17 decision tables the approach was able to
handle 8 different general solutions, to characterize
them through 47 diversity factors, to modify them
using 60 specializing actions and to obtain 88
specialized solutions.
4.2 Case Study
Later, a case study investigation is started in order to
evaluate, on field, the effectiveness of the approach
to quickly adapt the processes in use according to
the environment changes.
In this section, for space reasons, a specific part
of the case study is presented. In particular a part of
the business process Document Recognizing is
discussed. Such part is representative of two
different kinds of events that may affect a business
process in use:
- expected change: faced through “pattern”
peculiarities
- unexpected change: managed through “decision
tables” properties
4.2.1 Starting Scenario
In the Document Recognizing field a general process
component is provided. It represents the general
solution gs of this kind of problems (figure 7).
Figure 7: Process model for general solution in use.
ENASE 2008 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
152
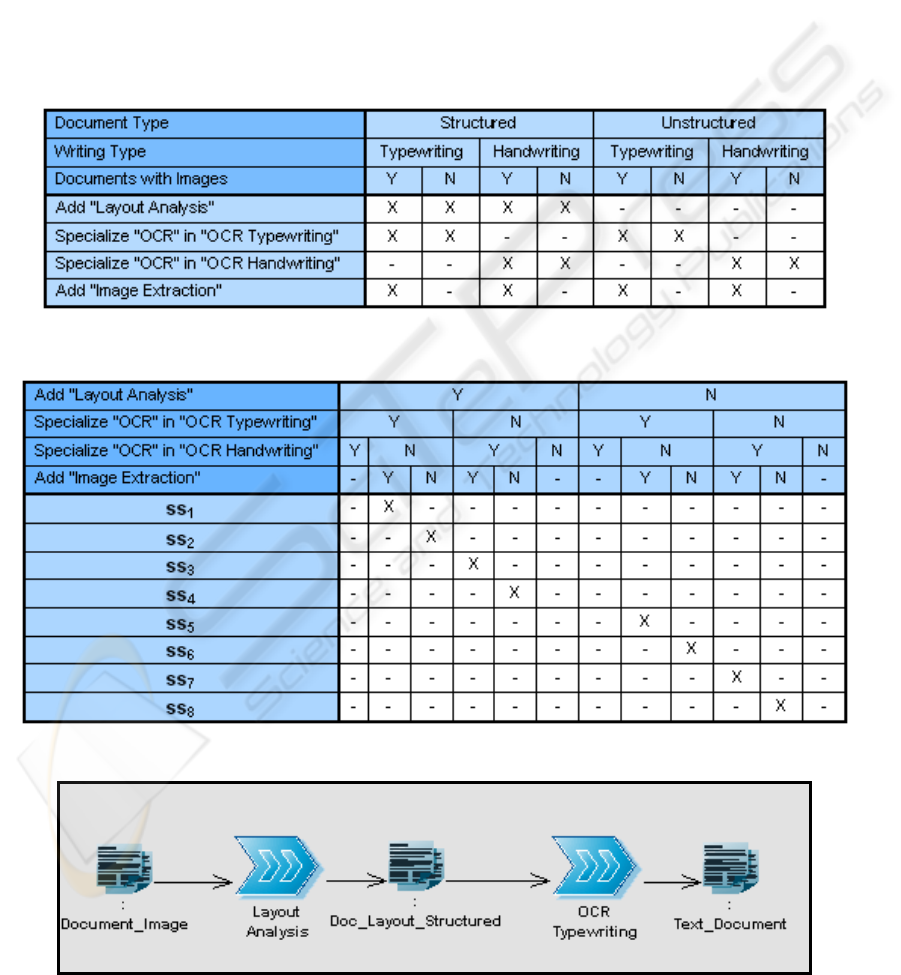
According to gs an appropriate DTca is build and
adopted (figure 8). This table aims to support all the
possible specialization. The table illustrates the
possible causes of context variability represented by
a diversity factor (DF) as: “document type”, “writing
type” and “document with images”.
Therefore according to their possible values we
can identify the actions needed to properly specialize
the general process gs.
Moreover, the DTca is related to a DTcs
specifying the actions specializing the general
solution gs to obtain the final specialized solutions
(figure 9).
At first, the type of banking documents to be
elaborated and stored was like “structured” and
“typewriting” documents “without images”. Such
values represent the context profile “cp
1
” and
generate, by the means of the DTca consultation, the
extraction of the following actions:
- Add "Layout Analysis"
- Specialize "OCR" in "OCR Typewriting"
These actions compose “sas
1
”, the final set of
specializing actions. According to DTcs contents the
specialized solution “ss
2
” is extracted and used
(figure 10).
Figure 8: DTca supporting the “Document Recognizing” gs.
Figure 9: DTcs specializing the “Document Recognizing” gs(compact version table).
Figure 10: Specialized solution “ss
2
”.
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE ENVIRONMENT CHANGES - A Pattern Driven Approach
153

Figure 11: Specialized solution “ss
1
”.
Figure 12: Updated DTca (adding “Formal Control” diversity factor).
4.2.2 Expected Change
After just six months, a business intelligence
strategy suggested to manage also images inside the
documents. Such change was expected and planned,
according to the Pattern-Driven Model, in the
Decision Tables Set. Therefore this change is mainly
faced through pattern model and then it implies just
a new browsing of the tables set. In fact a new
context profile (cp
2
) is considered (now we consider
diversity factor “Document with Images”=“Y”). The
result of the DTca consultation is represented by the
following actions:
- Add "Layout Analysis"
- Specialize "OCR" in "OCR Typewriting"
- Add "Image Extraction"
These actions compose “sas
2
”, the new set of
specializing actions. According to DTcs contents the
specialized solution “ss
1
” is extracted and used
(figure 11).
4.2.3 Unexpected Change
Eight months later, a new type of banking order
required a formal control activity in order to verify
the text content after the recognizing phase. Such
unexpected diversity factor requests a reorganization
in the Decision Tables Set of the relationship
between the general solution “gs” and all of the
possible specializations, also adding the variants
referred to the introduced diversity factor. The
decision table formalism supports the impact of such
changes through the updating of DTca and DTcs
(figure12 and 13):
- the DTca is updated adding one row for the
diversity factor “Formal Control” and one row
for the specializing action “Add Formal
Control”.
- the DTcs is updated adding the specializing
action “Add Formal Control” and eight rows
referring to the new specialized solutions that
the table is able to provide.
ENASE 2008 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
154
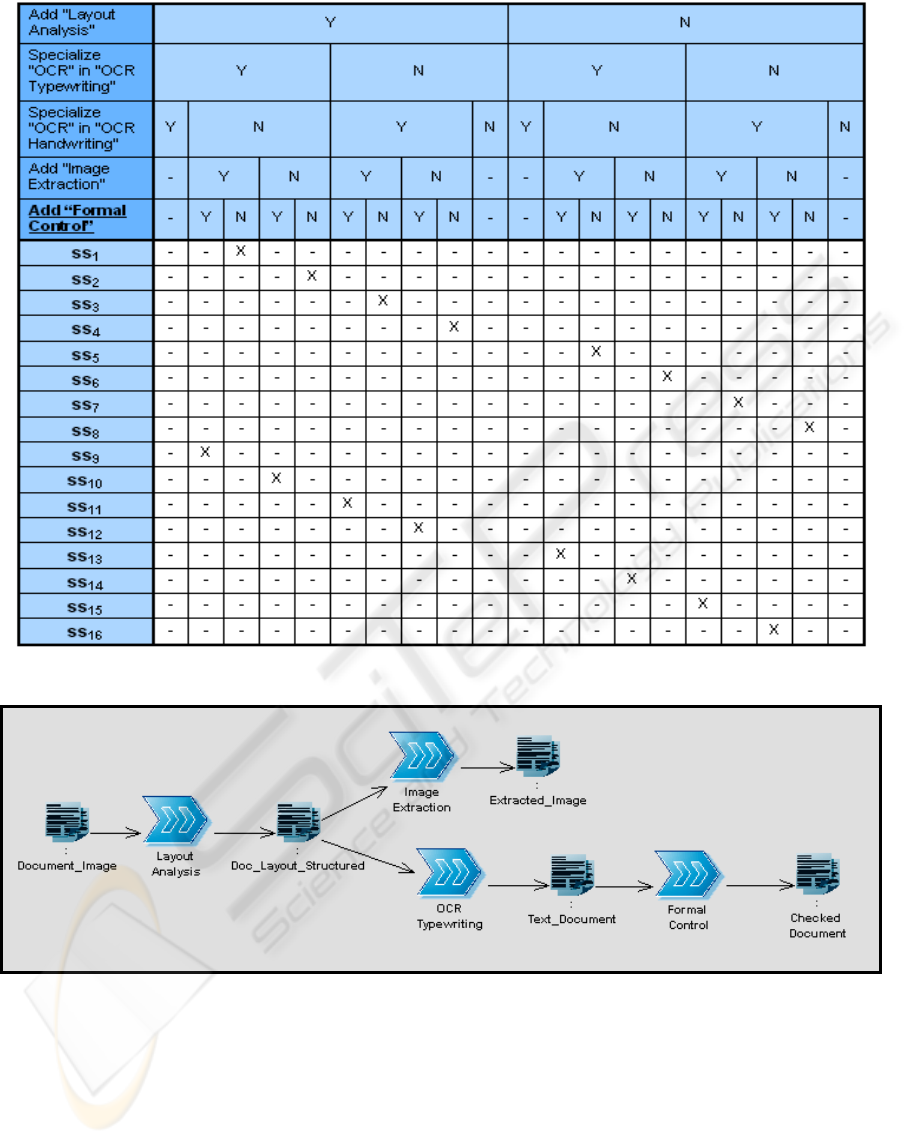
Figure 13: Updated DTca (adding “Formal Control” specializing action).
Figure 14: Specialized solution “ss
9
”.
After the tables updating, the DTca is consulted
and the result of the consulting is represented by the
following actions:
- Add "Layout Analysis"
- Specialize "OCR" in "OCR Typewriting"
- Add "Image Extraction"
- Add “Formal Control”
These actions compose “sas
3
”, the new set of
specializing actions. According to the new DTcs
contents the specialized solution “ss
9
” is extracted
and used (figure 14).
In synthesis, within one year and a half, the
enterprise has been able to opportunely reengineer
business processed and quickly adapt them
according to two context changes. Using the
proposed methodology, the enterprise has been able
to increase business flexibility and constantly
guarantee reliability, correctness and completeness.
BUSINESS PROCESS MODELING AWARE TO THE ENVIRONMENT CHANGES - A Pattern Driven Approach
155

5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper represents a contribution in the process
modeling issues. In particular it concerns with the
relationships between processes and operative
environment that drives to a context-based process
model specialization.
We propose a pattern-driven approach to capture
and explicitly represent abstract problem–solving
knowledge. This approach uses a decision tables set
to formalize the relationships between all the
possible environment factor configurations and the
specialized solutions.
This approach has been experimented in a real
context with encouraging results. The combined use
of the pattern-driven model and the decision table
notation has been able to promptly react to each
environment change. In particular, it is adequate
mainly for expecting changes because the pattern-
driven approach permits to show the path for the
new specialized solution: a new context factor value
implies a table consultation and the extraction of
new specialized actions in order to re-modeling the
business process on use. The proposed approach is
useful also for unexpected changes because it
implies the reorganization of relationships between
processes and the operative context through a quick
decision table update.
In order to validate the proposed approach, we
have conducted an on-field investigation in several
industrial environments using two automated tools.
Our future studies will be aimed to the optimization
of these tools.
REFERENCES
Bar-Or, A., Keren, D., Schuster, A., Wolff, R., 2005,
Hierarchical Decision Tree Induction in Distributed
Genomic Databases, IEEE Transactions on
Knowledge and Data Engineering, Vol.17.
Bhat, J. M., Deshmukh, N., 2005, Methods for Modeling
Flexibility in Business Processes. In 6
th
Workshop on
Business Process Modeling, Development and
Support. Business Processes and Support Systems:
Design for Flexibility.
Brynjolfsson, E., Malone, T., Gurbaxani, J. and Kambil,
A., 1989, Does Information Technology Lead to
Smaller Firms?, Technical report 106. Center for
Coordination Science, MIT.
Elzinga, D.J., Horak, T., Lee, C.Y., Bruner, C., 2005,
Business process management: survey and
methodology Engineering Management, IEEE
Transactions Vol. 42/2, pp.119 – 128, IEEE Computer
Society.
Ho, T.B., Cheung, D., and Liu, H., 2005, Advances in
Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining, 9
th
Pacific-
Asia Conference, Vietnam.
Hongli, W., Baolin, Y., Xia, Z., Gang, X., 2006 A
Workflow Model Supporting Flexible Process Based
on Extensible Organization, School of Computer
Science & Engineering, Beihang University.
Maes, R., Van Dijk, J. E. M., 1988, On the Role of
Ambiguity and Incompleteness in the Design of
Decision Tables and Rule-Based Systems, The
Computer Journal, 31(6).
Malone, T.W., Crowston, K., Lee, J., Pentland, B., 2003,
Tools for Inventing Organizations: Toward a
Handbook of Organizational Processes, In 2
nd
IEEE
Workshop on Enabling Tech. Infrastructure for
Collaborative Enterprises.
Morisio, M., Tully, C., Ezran, M., 2000, Diversity in
Reuse Processes, IEEE Software Vol.17 N°.4, pp. 56-
63, IEEE Computer Society.
Singh, M.P., Chopra, A.K., Desai, N.V., Mallya, A.U.,
2004, Protocols for processes: programming in the
large for open systems, In 19
th
annual ACM SIGPLAN
Conference on Object-oriented programming systems,
languages, and application.
Van der Aalst, W.M.P., Van Hee, K.M., 1996, Business
Process Redesign: A Petri-net-based approach, Vol
29(1-2) 1996. pp:15-26, Computers in Industry.
Van der Aalst, W.M.P., Ter Hofstede, A.H.M., Weske,
M., 2003, Business Process Management: A Survey,
In International Conference on Business Process
Management.
Van der Aalst, W.M.P., Ter Hofstede, A.H.M.,
Kiepuszewski, B., Barros, A.P., 2003, Workflow
Patterns, 14(1) 2003. pp:5-51, Distributed and
Parallel Databases.
Vanthienen, J., Mues, C., Wets, G., Delaere, K., 1998, A
tool-supported approach to inter-tabular verification,
Expert Systems with Applications, 15, pp. 277-285.
Winn, T., Calder, P., 2002, “Is this a pattern?”, IEEE
Software Vol.19, N°1 pp. 59-66, IEEE Computer
Society.
Yao, Q., Chen, Z., Wang, H., 2006, Improving Flexibility
and Reusage of Business Process Management: the
Role of Cased-based Reasoning Technique, ICEBE’06
IEEE International Conference on e-Business
Engineering.
ENASE 2008 - International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering
156
