
ADJUSTING ANALOGY SOFTWARE EFFORT ESTIMATION
BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC
Mohammad Azzeh, Daniel Neagu
Department of Computing, University of Bradford, Bradford, BD7 1DP, U.K.
Peter Cowling
Department of Computing, University of Bradford, Bradfrod, BD7 1DP, U.K.
Keywords: Analogy Software Effort Estimation, Fuzzy Logic, Software Project Similarity Measurement.
Abstract: Analogy estimation is a well known approach for software effort estimation. The underlying assumption of
this approach is the more similar the software project description attributes are, the more similar the
software project effort is. One of the difficult activities in analogy estimation is how to derive a new
estimate from retrieved solutions. Using retrieved solutions without adjustment to considered problem
environment is not often sufficient. Thus, they need some adjustment to minimize variation between current
case and retrieved cases. The main objective of the present paper is to investigate the applicability of fuzzy
logic based software projects similarity measure to adjust analogy estimation and derive a new estimate. We
proposed adaptation techniques which take into account the similarity between two software projects in
terms of each feature. In earlier work, a similarity measure between software projects based on fuzzy C-
means has been proposed and validated theoretically against some well known axioms such as: Normality,
Symmetry, transitivity, etc. This similarity measure will be guided towards deriving a new estimate.
1 INTRODUCTION
Although much research has been carried out in the
context of software cost estimation (Kirsopp and
Shepperd, 2002), none of the existent models has
consistently proved to produce credible estimate
than others (Menzies, Chen, Hihn and Lum, 2006).
Amongst them, estimation by analogy (EA) has been
achieved a considerable interest of many researchers
(Mendes and Mosley, 2002). In one sense, it is
formal estimation with expert judgement which can
be viewed as a systematic development of the expert
opinion through experience learning and exposure to
analogue case studies (Shepperd and Schofield,
1997) (Mendes and Mosley, 2002). It is based on
underlying assumption: the more similar the
software project description attributes are, the more
similar the software project cost is (Mendes, Mosley
and Counsell, 2003). Therefore, the similarity
measurement between two software projects is the
key accuracy of software prediction because it
attempts to retrieve the most similar historical
project to a new project. But, in many circumstances
the use of retrieved projects without adapting them
to considered environment leads to potential
overestimation or underestimation problems. The
most difficult activity in analogy estimation is how
to derive a new estimate from retrieved cases. Thus,
it fits the case in hand and minimizes the variation
between current case and retrieved case.
In this paper, we proposed two adaptation rules
to derive new estimate from retrieved cases using
our fuzzy logic based software projects similarity
measurement (Azzeh, Neagu, Cowling, 2008). The
first Adaptation Rule (AR1) attempts to adapt the
retrieved analogies according to their similarity
measurement with estimated project in each feature
dimension, then the new estimate is aggregated
based on one of these operators (minimum,
maximum, and mean). The second Adaptation Rule
(AR2) is to adapt each analogy individually
according to its similarity with estimated one in
terms of each feature dimension.
The reminder of the paper is organised as
follows: Section 2 discusses related works about EA
and adaptation rules. Section 3 introduces Fuzzy
Logic. Section 4 presents in more details our
127
Azzeh M., Neagu D. and Cowling P. (2008).
ADJUSTING ANALOGY SOFTWARE EFFORT ESTIMATION BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - SE/GSDCA/MUSE, pages 127-132
DOI: 10.5220/0001876601270132
Copyright
c
SciTePress

proposed analogy estimation with adaptation rules
and fuzzy logic based software projects similarity
measurement. Section 5 introduces evaluation
criteria. Section 6 compares the efficiency of
adaptation rules in analogy effort estimation.
Finally, section 7 summarizes our work and outlines
the future studies.
2 RELATED WORKS
The accuracy EA has been confirmed and evaluated
in previous researches such as those were
undertaken by (Shepperd and Schofield, 1997),
(Mendes and Mosley, 2002), (Kirsopp and
Shepperd, 2002) and (Briand, Langleyand
Wieczorek, 2000), (Myrtveit and Stendsrud, 1999)
and (Mendes, Mosley and Counsell, 2003).
Chiu et. al. (Chiu and Huang, 2007) reported that
EA always needs more sensed similarity methods.
They investigated the use of Genetic Algorithms
(GA) based project distance to adjust retrieved
effort. The results showed that using adjusted
similarity mechanism gave better accuracy than
using traditional similarity distance. Jorgensen et. al.
(Jorgensen, Indahl and Sjoberg, 2003) investigated
the use of regression towards the mean (RTM)
method to adjust the analogy estimation. They
indicated that the adjusted estimation using RTM
method was significantly more accurate than EA
without adjustment.
Idri et al. (Idri, Abran and Khoshgoftaar, 2001)
proposed alternative approach for Analogy software
cost estimation based on fuzzy logic and linguistic
quantifiers. They tried to adjust analogy estimation
based on fuzzy similarity between two software
projects that are described as linguistic quantifiers.
In some sense, this approach does not have learning
ability (Auer, 2004) and the results are not
promising.
3 FUZZY LOGIC
Fuzzy logic as introduced by Zadeh (Zadeh, 1997)
provides a representation scheme and mathematical
operations for dealing with uncertain, imprecise and
vague concepts. Fuzzy logic is a combination of set
of logical expressions with fuzzy sets. Each fuzzy
set is described by membership function such as
Triangle, Trapezoidal, Gaussian, etc., which assigns
a membership value between 0 and 1 for each real
point on universe of discourse. This membership
value represents how much a particular point does
belong to that fuzzy set. Software estimation is
generally complex and vague with some
uncertainties in attribute measurement. The most
common problem in software estimation arises from
using categorical data (nominal or ordinal scale).
Fuzzy logic provides a way to map between input
and output space with clear natural expressions of
fuzzy rules (Bezdek, J.C, 1981) (Zadeh, 1997) (Xu
and Khoshgoftaar, 2004).
Property 1. Fuzzy set A is called normal fuzzy set if
it has at least one element x in the universe of
discourse whose membership value is unity or height
of A=1. A fuzzy subset that is not normal is called
subnormal (Ross, 2004).
4 ESTIMATION BY ANALOGY
EA requires identification of a list of main software
project attributes the effort estimation will be based
upon. Then similar but completed projects are found,
for which the cost is known. The estimation is later
based on these effort values. In this paper we will
use fuzzy logic based software projects similarity to
adjust analogy estimation and derive new estimate.
In next subsection we will give more details about
proposed similarity measure and adaptation rules.
4.1 Similarity Measurement
In earlier work, we have proposed similarity
measurement approach based on fuzzy C-means and
theoretically validated against some well known
axioms such as: Normality, Symmetry, transitivity,
etc. (Azzeh, Neagu, Cowling, 2008). The similarity
measure is described as follows:
Let p
x
, p
y
be two software projects described by
M features F
j
(j=1…M), for each feature (linguistic
variable) there are several normal fuzzy sets
j
k
A
obtained by FCM and fuzzy identification, where k
represents number of clusters. Particularly, we
impose our approach to use Gaussian membership
function. The similarity measure is explained in the
following steps:
1. For each linguistic variable, find fuzzy set
j
x
A that
represents maximum membership value of F
j
(p
x
)
and fuzzy set
j
y
A that contains maximum
membership value of
F
j
(p
y
) by using maximum
operators.
)}(),...,(),(max{)(
21
pppp
CcCCC
i
μμμμ
=
(1)
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
128

2. For each linguistic variable, find SM
j
(
j
x
A
,
j
y
A )
using
approaching degree (Azzeh, Neagu,
Cowling, 2008). In terms of one feature,
SM
j
(F
j
(p
x
), F
j
(p
y
)) is intuitively identical to SM
j
(
j
x
A ,
j
y
A ).
SM
j
(F
j
(p
x
), F
j
(p
y
))=min(
2
)+(
2
)-(-
y
σ
x
σ
yx
e,1)
(2)
where
x, y are the mean values and
yx
σσ , are the
standard deviation for Gaussian membership
functions
j
x
A and
j
y
A respectively.
3. Find overall similarity between two software
projects as shown in equation 3. Consequentially,
the closest analogue to a particular project is the
project with maximum similarity.
(3)
4.2 Adaptation Strategy
Adaptation is mechanism used to derive a new
estimate; thus, to minimize the differences between
retrieved case and current case (Sankar, Simon and
Shiu, 2004). It is important step in estimation by
analogy because it reflects structure of problem case
on retrieved case. In this step we have to decide
how many analogies should be employed to derive
new estimate by adaptation. As yet, there are two
main approaches used in EA model (Shepperd and
Schofield, 1997). First approach is concerned with
taking all software projects that fall in a particular
distance of new project. This approach could lose
some valuable project when distance between
selected and unselected projects is notably very
small (i.e. few fractions). Second, is to use fix
number of analogies. This approach has been
followed by many researchers such as (Briand,
Langleyand Wieczorek, 2000) and (Mendes, Mosley
and Counsell, 2003). The second approach has been
followed in this research where number of analogies
is limited to 3, which we believe is sufficient to
drive new estimate. Several analogy adaptation
rules have been used in software engineering
literature. Mendes et. al. (Mendes, Mosley and
Counsell, 2003) used Linear Size Adjustment to
adapt individual project. This approach takes the
effect of each feature value on the final estimate.
(Idri, Abran and Khoshgoftaar, 2001) used linear
distance adjustment where the distance between two
software project in each features is used to adapt
new estimate.
In this work we proposed a set of candidate
adaptation rules. The first adaptation rule (AR1)
calculates the aggregated effort estimate based on
the similarity between estimated project and other
closest analogies in each feature dimension. The
underlying mechanism of AR1 is to adapt the
retrieved efforts according to the similarity in each
feature, then the final estimated effort is aggregated
based on one of these operators (minimum,
maximum, or mean).
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
=
=
=
)p,p(SIM
E*)p,p(SIM
ARE
si
N
i
j
N
i
isij
M
j
s
∑
∑
1
1
1
1
(4)
Where:
M: number of features, N: number of analogies.
AR1: is an effort aggregation operator which might
be (max, min or average).
The second adaptation rule (AR2) is to adapt
each analogy individually according to its feature
similarity with estimated one as shown in equation
5. Then adaption cases such as: (mean of closes
analogies and inverse ranked weight mean) are used
to derive the final estimate. The inverse ranked
weight mean takes the influence of each case into
account where the higher closes cases takes the high
weight than lower cases. For example, in our case
we have three analogies so the estimation by inverse
ranked would be calculated as (3*closes case +
2*second closest + third closes/6)
∑
∑
=
=
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎥
⎦
⎤
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎢
⎣
⎡
=
M
j
M
j
sij
isij
s
)p,p(SM
E*)p,p(SM
E
i
1
1
(5)
The comparison between two adaptation rules is
that the AR1 adapts all retrieved efforts together in
each feature then aggregates all adapted efforts to
derive a new estimate. While in AR2, each retrieved
effort is adapted individually in terms of feature
similarity.
()
))p(F),p(F(SMavg)pp(SM
yjxjj
m
j
y,x
1=
=
ADJUSTING ANALOGY SOFTWARE EFFORT ESTIMATION BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC
129
5 EVALUATION CRITERIA
Many prediction evaluation criteria have been
proposed in literature, among them Magnitude
Relative Error MRE and mean of magnitude relative
error MMRE have achieved a considerable interest
from researchers. Previous research has criticised
that MMRE does not identify the best estimation
model and is unbalanced in many validation
circumstances which leads to overestimation more
than underestimation (Shepperd and Schofield,
1997) (Tron, Stensrud, Kitchenham and Myrtveit,
2003). Rather, we used MMER and Pred(0.25).
MER Computes the degree of estimating error in an
individual estimate and should be less than 25% to
be acceptable. Pred(0.25) is proportion of prediction
within 25% of actual value for all predictions. It
should be larger than 75% to be acceptable.
∑
1
-
1
n
i
i
ii
estimated
|estimatedactual|
n
MMER
=
=
(6)
projects#
eMERwithprojects#
=Pred(e)
≤
(7)
6 EVALUATION OF FUZZY
LOGIC ADJUSTMENT
In this section we evaluate the efficacy of fuzzy
logic based software projects similarity
measurement and proposed adaptation rules to
derive more credible estimate. We used Jack Knifing
validation (also known as Leave one-out cross
validation) approach because it mimics the real
world estimation. The data used in this paper come
from (ISBSG, 2007), (
Sentas and Angelis, 2006). and
Desharnais datasets (Boetticher, Menzies and
Ostrand, 2007) as shown in Table 1.
Table 1: Data set Characteristics.
Characteristics ISBSG Desharnais
No. of features 15.73% 82.0%
No. of projects 15.724% 82.0%
Table 2: Legend for empirical validation.
CC1NA One analogy without adaptation rule
CC2NA Mean of 2 analogies without adaptation
rule
CC3NA Mean of 3 analogies without adaptation
rule
INV2NA Inverse ranked for 2 analogies without
adaptation rule
Table 2: Legend for empirical validation (cont.).
INV3NA Inverse ranked for 3 analogies without
adaptation rule
MD3NA Median of 3 analogies without
adaptation rule
MAX_AR1 AR1 with MAX operator (3 analogies)
MIN_AR1 AR1 with MIN operator (3 analogies)
MEAN_AR1 AR1 with MIN operator (3 analogies)
CC1WAR2 One analogy with AR2
CC2WAR2 Mean of 2 analogies with AR2
CC3WAR2 Mean of 3 analogies with AR2
INV2WAR2 Inverse ranked for 2 analogies with
AR2
INV3WAR2 Inverse ranked for 3 analogies with
AR2
MD3WAR2 Median of 3 analogies with AR2
6.1 ISBSG Dataset
Table 3 shows the estimation results of ISBSG
dataset. These results have been obtained by
considering two new adaptation techniques based on
fuzzy logic based software projects similarity. By
comparing these different adaptation rules based on
lower MMER, and higher Pred(0.25), we can
observe that models without adaptation (i.e. only
case adaptations) and those using adaptation rule 1
(AR1) produced significantly better results than
AR2. Only closest case with AR2 obtained
reasonable accuracy while other case adaptations
with AR2 did not contribute to credible estimate.
This was arose a question about what are the reasons
behind this variation between two adaptation rules
AR1 and AR2. This may be related to variation in
similarity between estimated project and other
closest projects, and to the range of data. The results
obtained by AR2 corroborated the results obtained
by (Mendes, Mosley and Counsell, 2003) that
showed using adaptation rules does not often
improve estimation accuracy.
Table 4 shows that there is no significant
difference between aggregation operators for AR1.
Minimum, maximum and average aggregation
operators have approximately the same influence on
the adjustment because the closest projects are often
fall in the same fuzzy set in most features. This
make similarity between new project and closest
projects is slightly different. We also observed that
when using AR1 did not have as many best
predictions as it did with CC3NA and INV3NA.
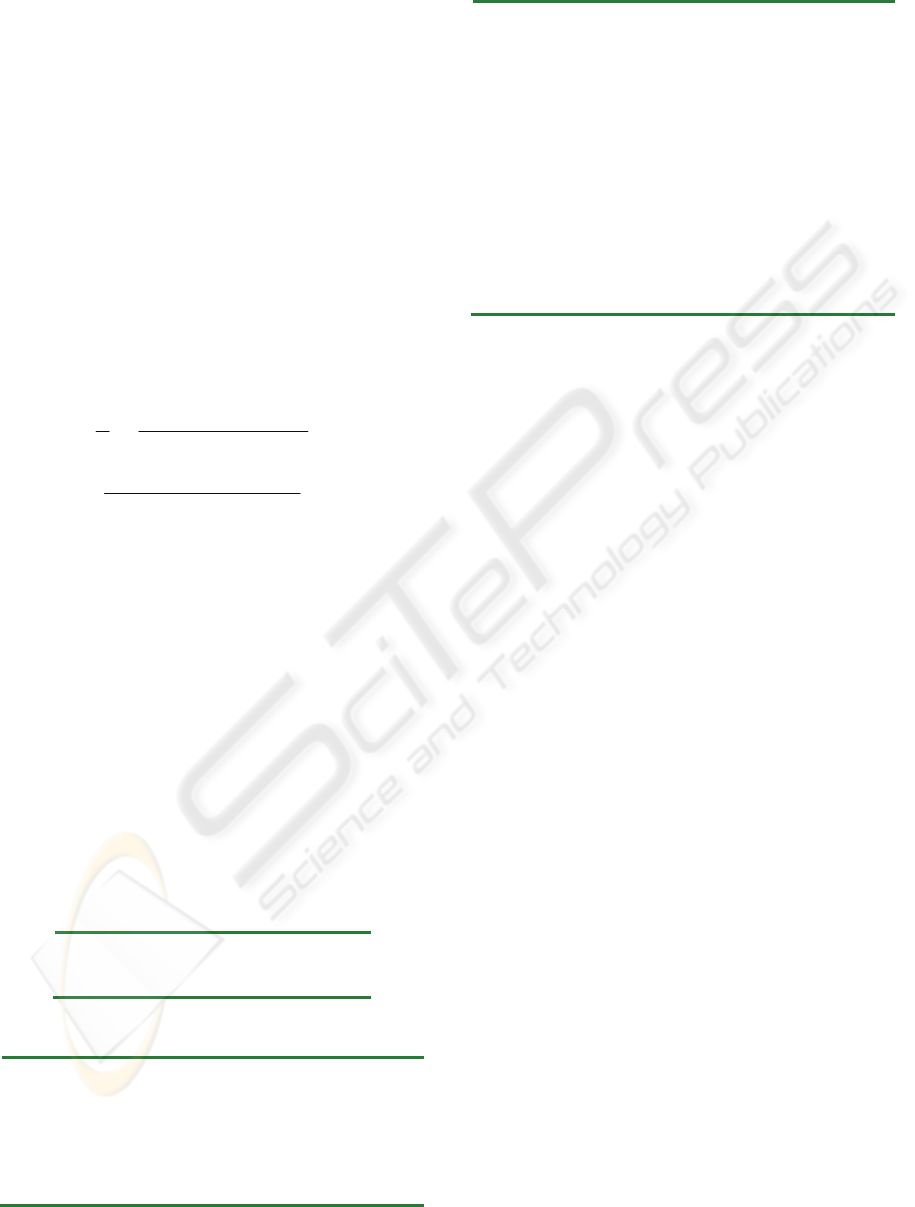
Figure 1 shows Boxplots of estimation results in
MER. The Boxplots illustrates inter-quartile rage
that contains 50% of projects, median and outlier
projects in terms of estimation results as measured
by the MER. The upper and lower tails indicate the
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
130
distribution of the observations. The Boxplots shows
that CC3NA, IN3NA, MINAR1, MAXAR1 are
statistically significant than others because they
present a low dispersion of the MER values and
small median than others. This revealed that AR1 is
significantly better than AR2 for ISBSG.
Furthermore, the smaller range of upper and lower
tails suggests the MAX_AR1 is statistically the most
significant adjustment among the others.
Table 3: Results for ISBSG with case adaptations and
AR2.
Case
adaptation
Without
adaptation rules
With AR2
MMER Pred MMER Pred
CC1 17.2% 76% 15.9% 80.0%
CC2 15.4% 80% 33.0% 44.0%
INV2 15.3% 78% 25.4% 50.0%
CC3 14.3% 86% 49.8% 30.0%
MD3 15.0% 76% 49.4% 27.0%
INV3 14.6% 84% 39.9% 42.0%
Table 4: Results for ISBSG with AR1.
AR1 MMER Pred)
MIN-adaptation 15.73% 82.0%
MAX-adaptation 15.724% 82.0%
MEAN-adaptation 15.6% 82.0%
Figure 1: MER Boxplots for ISBSG dataset.
6.2 Desharnais Dataset
Tables 5 and 6 present the estimation results and
corresponding accuracy for Desharnais dataset. The
first observation is that the accuracy obtained by
different adaptation did not reach target of
acceptable accuracy which is less or equal 25% for
MMER and more than 75% for Pred (0.25). This
may be related to dataset size and range of values. It
seems there is strong linear relationship between
effort and other features caused this problem.
Adjusted analogy estimation with Adaptation rule
AR1 and AR2 contribute to better estimation results
than others without adaptation. From table 4 we can
notice that the value of MMER was decreased for all
case adaptations except CC3.
Table 6 suggests that using MIN operator for
AR1 has significantly given a slight better result
than MAX and MEAN operators. On the other hand,
adjusted analogy models with AR2 gave better
accuracy than analogy models with AR1. The best
result obtained with AR2 was by CC2.
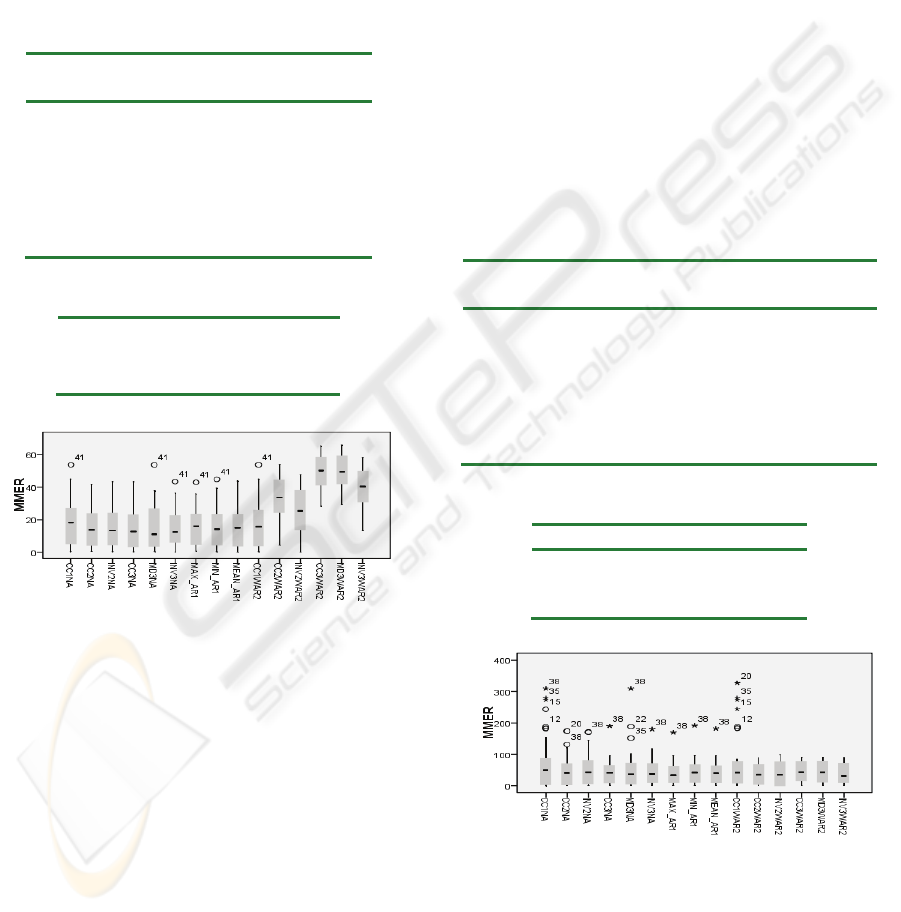
Figure 2 suggests that using fuzzy adjustment
exhibits a smaller range of upper and lower tails of
the MER values than other without adaptation.
Furthermore, the adjusted models with AR1 showed
small standard deviation than others. It also showed
that adjusted analogy models with AR1 and AR2 are
marginally more accurate than others without
adjustment. The overall results show the adequacy
of AR1 for both datasets, whilst AR2 performed
better in Desharnais dataset.
Table 5: Results for Desharnais with case adaptations and
AR2.
Case
Adaptation
Without
adaptation rules
With AR2
MMER Pred MMER Pred
CC1 50.4% 26.0% 43.7% 32.0%
CC2 44.5% 38.0% 38.5% 38.0%
INV2 48.4% 32.0% 39.4% 36.0%
CC3 42.7% 32.0% 45.7% 22.0%
MD3 48.1% 40.0% 45.0% 30.0%
INV3 43.8% 30.0% 39.7% 36.0%
Table 6: Results for ISBSG with AR1.
AR1 MMER Pred
MIN-adaptation 40.44% 36.0%
MAX-adaptation 45.6% 30.0%
MEAN-adaptation 42.5% 32.0%
Figure 2: MER Boxplots for Desharnais dataset.
7 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we have proposed two adaptation rules
using fuzzy logic based on software project
ADJUSTING ANALOGY SOFTWARE EFFORT ESTIMATION BASED ON FUZZY LOGIC
131

similarity measurement. We have compared the use
of Adaptation rules AR1 and AR2 with non
adjustment analogy models. The results showed that
adjusted analogy model with AR1 has significantly
improved the analogy estimation in both datasets,
while AR2 performed better only for Desharnais
dataset. The reasons behind that arose from number
of features, relevancy of features, range of data
values, and number of cases. Future extension of the
proposed model is planned to consider the effect of
feature subset selection.
REFERENCES
Auer S. B. M. 2004. Increasing the Accuracy and
Reliability of Analogy-Based Effort Estimation with
Extensive Project Feature Dimension Weighting,
Proceedings of the International Symposium on
Empirical Software Engineering (ISESE’04), 147-155.
Azzeh M., Neagu D., Cowling P., 2008, Software Project
Similarity measurement based on Fuzzy C-means,
International Conference on Software Process.
Springer.
Bezdek, J.C.: Pattern Recognition with Fuzzy Objective
Function Algorithms, Kluwer Academic Publishers,
Norwell, MA, New York (1981)
Boetticher G., Menzies T. Ostrand T. 2007. PROMISE
Repository of empirical software engineering data
http://promisedata.org/ repository, West Virginia
University, Department of Computer Science.
Briadn L., Langley T., Wieczorek I. 2000, Using the
European Space agency data set: a replicated
assessment and comparison of common software cost
modeling techniques, 22
nd
IEEE international
conference on software engineering.
Chiu N.-H., Huang S.-J. 2007. The adjusted analogy-based
software effort estimation based on similarity
distances. Journal of Systems and Software 80, 628-
640.
Huang, S.J., Chiu, N.H.: optimization of analogy weights
by genetic algorithm for software effort estimation. J.
Information and software technology (Elsevier) 48 ,
1034-1045 (2006)
Idri, A., Abran, A: A fuzzy logic based set of measures for
software project similarity: validation and possible
improvements. In: Seventh International Software
Metrics Symposium, pp. 85-96, London (2001)
Idri, A., Abran, A., Khoshgoftaar, T. 2001. Fuzzy
Analogy: a New Approach for Software Effort
Estimation, 11th International Workshop in Software
Measurements. 93-101.
ISBSG. 2007. International Software Benchmarking
standards Group, Data repository release 10, Site:
http://www.isbsg.org.
Jorgensen M., Indahl U., and Sjoberg D., Software effort
estimation by analogy and "regression toward the
mean". Journal of Systems and Software 68 (2003)
253-262.
Kadoda, G., Michelle C., Chen, L., Shepperd, M. 2000.
Experience using Case Based reasoning to predict
Software project effort, Proceeding of Fourth
international conference on empirical Assessment and
evaluation in software engineering. 1-17.
Kirsopp, C., Shepperd, M. 2002. Case and Feature Subset
Selection in Case-Based Software Project Effort
Prediction, Proc. 22nd SGAI Int’l Conf. Knowledge-
Based Systems and Applied Artificial Intelligence.
Kirsopp C. , Shepperd M. J. , Hart J. 2002. Search
Heuristics, Case-based Reasoning and Software
Project Effort Prediction, Proceedings of the Genetic
and Evolutionary Computation Conference, 1367-
1374.
Mendes E., Mosley N. 2002. Further investigation into the
use of CBR and stepwise regression to predict
development effort for Web hypermedia applications,
79-90.
Mendes, E., Mosley, N., Counsell, S. 2003. Do adaptation
rules improve web effort estimation?, In Proceedings
of the fourteenth ACM conference on Hypertext and
hypermedia (Nottingham, UK). 173-183.
Menzies, T. , Chen Z., Hihn, J. Lum, K. 2006.
Selecting Best Practices for Effort Estimation. IEEE
Transaction on Software Engineering. 32, 883-895
Mittas N., Athanasiades M., Angelis L., 2007, improving
analogy-based software cost estimation by a
resampling Method. J. of Information and software
technology
Myrtveit I., Stendsrud E., 1999, A controlled experiment
to assess the benefits of estimating with analogy and
regression models, IEEE transactions on software
engineering 25 4, 510-525
Ross, T.J. 2004. Fuzzy Logic with engineering
applications, John Wiley& Sons
Sankar K. Pal and Simon C. K. Shiu , 2004, Foundations
of Soft Case-Based Reasoning. John Wiley & Sons.
Sentas, P., Angelis, L.: Categorical missing data
imputation for software cost estimation by
multinomial logistic regression. J. Systems and
Software 79, 4040-414 (2006)
Shepperd, M. J., Schofield, C. 1997. Estimating Software
Project Effort Using Analogies, IEEE Trans. Software
Eng. 23, 736-743.
Stamelos, I., Angelis, L., Morisio, M.: Estimating the
development cost of custom software. J. Information
and management (Elsevier) 40. 729-741 (2003)
Tron, F., Stensrud, E., Kitchenham, B., Myrtveit, I. 2003.
A Simulation Study of the Model Evaluation Criterion
MMRE, IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering,
29, 985-995.
Xu, Z., Khoshgoftaar, T., 2004. Identification of fuzzy
models of software effort estimation. Fuzzy Sets and
Systems 145, 141-163
Zadeh, L. 1997. Toward a theory of fuzzy information
granulation and its centrality in human reasoning and
fuzzy logic. Journal of fuzzy sets and systems 90,
111-127.
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
132
