
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER
EDUCATION FINANCING
Ljerka Luić
b4b, Vukovarska 271, Zagreb, Croatia
Damir Kalpić
Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Computing, Unska 3, Zagreb, Croatia
Keywords: Higher education financing, ERP, Integration, Management.
Abstract: Despite all the talk about new economy, higher education institutions still live by the old rules. Budgets are
lean, yet agile enough to reflect changing requirements. With these realities, higher education institutions
need proven solutions, the kind that only an ERP solution that integrates all financial processes: funds,
financial accounting and managerial accounting can offer. The Ministry of Science, Education and Sports of
the Republic of Croatia was implementing an integrated financial information system of 6 universities based
on lump-sum principles and supported by SAP ERP solution. Some experiences regarding this project are
presented in the paper.
1 INTRODUCTION
The time we live in, the 21
st
century that we have
just entered, is marked by permanent arrival of new
information technologies and trends that assume
global knowledge. Information society that we are
all witnessing is imbued with new relationships
between higher education and society as a whole.
Analysts of these relationships increasingly
emphasize the need for development of a theory of
'academic capitalism' (Slaughter, Rhoades, 2004) by
which they explain the process of integration of
university system/colleges and the new economy.
The theory that originated within the American
university system believes that universities and other
institutions of higher education should not be turned
into corporations or reorganized by external factors
but it envisages groups of internal factors such as
faculties, students, administration and academics as
resources an individual country has, and these
resources need to create a new framework of
knowledge that would integrate higher education
institutions with the new economy.
The role of internal factors is directed towards
using resources given by the state to create
prerequisites that would draw corporations to
university sector and higher education institutions,
thus building a new network which would enable
interaction of private and public sectors. This
network would also enable expansion of managerial
capacities to the sphere of monitoring the flow of
external resources and to the sphere of investments
drawn for development of infrastructure with one
purpose – to support the trends of the new economy,
invest into marketing of higher education, in its
products and different services needed by students.
This approach has a large impact on all universities,
its faculties and all its other component parts
because it envisages a reconstruction of universities’
operation by lowering the costs of classes.
The 'academic capitalism' theory goes even
further from treating a student as a customer to
treating him or her as promoter, i.e. subject of
university marketing. More and more we witness
students rationalizing their choice of university and
studies, thinking about investments they have to
make, and the return on the invested time and
money. On the other hand, they rationalize the
economic elements: business opportunities after
degree, communication and media. Studying at a
university does not only stand for getting a classical
education any more but it also increasingly starts to
resemble becoming a part of an image the university
339
Lui
´
c L. and Kalpi
´
c D. (2008).
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCING.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 339-347
DOI: 10.5220/0001881603390347
Copyright
c
SciTePress

of choice generally has in the market, together with
its name and brand. Students thus gain the name and
the brand of their university upon gaining a degree
from it.
When they finish their studies, universities
present their students as their products, their
contribution to the new economy and at the same
time they start treating them as alumni, i.e. potential
donors.
It is necessary to point out that academic identity as
market value of a student is not a constant,
unchangeable value. It is a value that changes with
the change of market status of university of choice
or other higher education institution (Newman,
Couturier, Scurry, 2004).
2 NEW THEORIES ON
MANAGING HIGHER
EDUCATION INSTITUTIONS
Universities, their component parts, higher education
as a whole, have a special obligation to rational and
efficient spending of their resources no matter if the
resources come from state budget or their own
incomes. To enable management of universities and
colleges to lower costs and increase efficiency of
budget spending, it is necessary to create the system
in which cost bearers (carriers) will be identified, the
system of profit centres, and enable permanent
tracking and analysis of costs, i.e.: of all
expenditures on one side and all types of income on
the other. (Brumec, et al, 2000)
2.1 Market Dimension of Higher
Education Institutions
To enable universities and other higher education
institutions to be successful in market competition,
they need to be aware of bringing information and
their management up front as their management
strategic commitment. That commitment brings the
prestige and thus draws more and more of the
quality students, as well as sponsors, and thus
directly draws more financial resources.
Having in mind the global economy and its features,
we can expect a further expansion of market
influence on higher education, its work and
development. This also indicates a need for
managing the risks such flows bring. To enable
managing structures of universities and higher
education institutions to efficiently manage risks,
they need to institute a business-information system
for risk management. (Bok, 2005)
The relationship between higher education
system and the market is visible from: competition
between universities in the first place, focus on
generating prestige for themselves, and putting their
campuses in the function of achievement of this
goal. As prices of studying are rising higher and
higher, the universities and colleges are starting to
differ more and more in their offer of packages for
different financial supports. In this way individual
institutions of higher education become more or less
attractive, that is, reachable to potential students.
Except financial support, universities/colleges differ
in other elements of student care – duration of study,
help with employment of students, help with
continuing education, caring for and following
students after their degree. It is necessary that the
market accepts better this diversification of offer
when it comes to institutions and their programs, i.e.
higher degree of specialization of a university.
2.2 Autonomous vs. Nonautonomous
Higher Education Institutions
The relationship between higher education
institutions and market becomes a relationship of
greater concern to society and, thus, to the line
ministry as the representative body of the state. This
care is, in the first place, visible in consolidation of
higher education and it can be continued in two
directions: intensifying the diversity of offer, or
intensifying the homogenization. To ensure market
survival of certain universities/colleges, especially
those specialized in less attractive curricula, the line
ministries in some countries intensify mergers with
the universities/colleges which are in a better market
position, all with a single goal – for the less
attractive ones to survive. Here we need to stress
that merging of universities/colleges and their large-
scale consolidation can influence a reduced choice in
studies which is the reason why countries are very
careful when approaching this issue.
Within the academic community around the
world there are different opinions on strategic
development and the concept of operation, as well as
management of higher education in conditions of
contemporary economic flows. Researches that have
been conducted prove the university/college
management resistance to privatization of these
institutions or some of their parts, their redesign, a
resistance to outsourcing, branding and establishing
a system of tracking and risk management.
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
340

In countries that are only entering the sphere of
'academic capitalism', a rising trend of striving for
independence from state and government is visible
by large. In this process new challenges are poised
in front of university management, or college
management, especially public, i.e. state-owned
universities. Autonomy of university becomes the
basic question in talks and negotiations between
academic society and state (Marcella, Knox, 2004).
Two models are distinguishable in this field – one is
the American model where autonomy is very high
and the state invests in higher education by giving
financial aids to students and giving help in many
other ways. The other is the European model, in
which the tradition is that universities are financed
from state budget. The degree of university
autonomy from the state can be measured from the
method of their financing and is influencing the
work and operations of university (Galliers, Leidner,
2003).
3 HIGHER EDUCATION
INSTITUTIONS AND THEIR
INFORMATION SYSTEMS
Information systems have become the backbone of
each complex organization in economic as well as
public sector. Thus, they have become also the
backbone of higher education. Implementation of a
new information system, especially a new integrated
business-information system (IBIS) is a complex
undertaking that oftentimes does not bring the
expected results. Mistakes, if made in the beginning
phase of implementation, are the most costly and
most difficult to correct. Therefore, the development
of a new IBIS must be connected to a mission, a
vision and a strategic plan of business development,
business processes need to be reengineered,
potentials of using the modern ICT technologies
anticipated, and method of their application
optimized for use in higher education institutions.
The Bologna process initiated the problem
sphere of optimizing utilization of resources
available: budget, own income, personnel, space,
equipment, and division of funds using 'lump-sum'
principles of financing. Based on the above
mentioned, it is important to anticipate the fact that
development and management of a complex system
such as a unified information system of all
universities of a country presupposes an integral
information strategy as the point connecting
academic strategy, information system strategy, and
business strategy.
3.1 Integrated Business-Information
Systems
Besides the traditional method of solving academic
questions, in order to be as competitive as possible,
the management of higher education institutions
needs to be increasingly oriented to management of
financial and human resources. Application of new
business strategies demands high quality and timely
information on competition, potential markets,
potential financing sources, technology, economic
and political flows.
A business-information system of higher education
has certain special characteristics not present in
other business systems. They do not only provide
information needed to run a university but
information are provided here which help managing
other members/institutions of academic society. Due
to a high degree of autonomy of individual
components, they need to be flexible enough and
due to a big scope of users they need to be usable,
reliable, efficient, sustainable and secure, together
with being user-friendly. Unfortunately, most
existing university business-information systems do
not satisfy these pre-conditions well enough. The
most common deficiencies are insufficient coverage
of information needs of a university and lack of
connection between certain business components, or
parts (Luić, Schwarz, Uzelac, 2007).
Business-information system of universities is a
very complex and specific system. Thus, larger
demands for information are to be expected when
compared to other organizations, arriving from its
management, administrative personnel, professors
and students. Of great impact and importance here is
the high level of independence certain departments
and persons within university have when compared
to regular companies. Regular and often changes in
Rector’s office (elections of new Rector, Deputy
Rector, and dean) also imply different approaches to
IS.
3.2 Technical Aspect of
Implementation of Integrated
Information System
Setting up an adequate ICT architecture needs to be
observed as a cyclical process, main initiator of
which is the business architecture, characterized by
organizational plans, visions, targets and tasks,
problems and information for their support. User
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCING
341
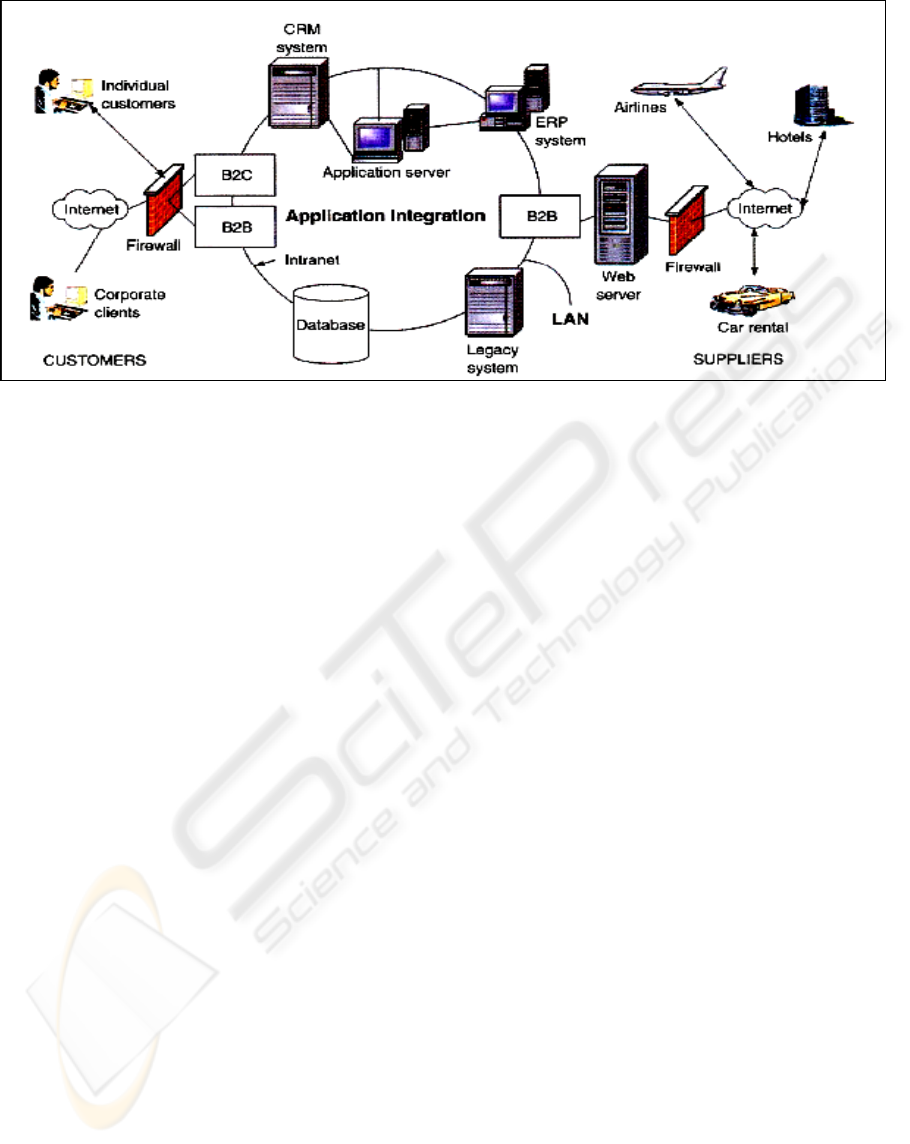
Figure 1: Example of ICT architecture
must have a role in business architecture as well,
because only after setting up the ICT and business
architecture, a higher education institution can fulfil
its long-term targets and needs. Technical
complexity of ICT architecture is visible in its
simplified version in Figure 1. (Turban, McLean,
Wetherbe, 2004).
Before setting up ICT architecture, it is necessary to
define the following architectures:
• Business architecture: plans, visions, targets,
tasks;
• Information architecture: information needs and
ways of satisfying the needs;
• Data architecture: needs, sources, quality, security,
scalability, storage, updating, data maintenance;
• Application architecture: integration, security,
scalability, possible vendors;
• Technical architecture: hardware, software,
networks, vendors, protocol standards;
• Organizational architecture: needs for human
resources and outsourcing.
After designing the ICT architecture, the next
step in construction of an integrated business-
information system is consideration of needs of
individual business, functional areas and their need
for an ICT. Priorities oftentimes need to be adjusted
to priorities of individual business functions which is
of crucial influence to dynamics and duration of the
project.
4 ERP-ENTERPRISE RESOURCE
PLANNING
ERP is one of the most successful tools for resource
management of a certain organization. It is also an
integral software solution with ‘client-server’
architecture and software architecture enabling
business process management in real time. The main
goal and task of ERP is integration of all
departments and functions inside an organization
with the help of integrated computer system that
covers all needs of that organization. ERP systems
represent integral support to business processes of
organization thus creating prerequisites for
integration of all business processes of an
organization into an information system.
Conceptually designed and constructed by the
end of the 1950s and the beginning of the 1960s,
their orientation is to production and planning of
material movement through productive cycles.
Nowadays, it can be firmly stated that an ERP
represents the backbone of a company. No matter
what possible difficulties arise when implementing
and ERP, the implementation itself becomes a
necessity in contemporary organizations. Upon
implementing an ERP system, transactional
information systems rise from business and
bureaucratic operations to networks of service
delivery. Parallel to this, integration of different
applications later saves time and minimises
possibility of errors.
When we first start implementing an ERP
system, we are dealing with many disconnected
systems. We have a set of isolated applications to
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
342

which business events are written and these
applications are not technologically connected.
Gradually, individual modules of an ERP system are
implemented and the system becomes partially
functional.
Still, the consolidation on the level of
organization is still not achieved. Further
development brings us to the phase of complete
functioning in individual business units which is
well manifested in large and spatially dispersed
organizations. Finally, in the last phase an ERP
system becomes completely connected and fully
functional (Ward, Peppard, 2002).
The largest and most frequently used ERP
systems worldwide are SAP, Baan, PeopleSoft,
Oracle, SCALA – software solutions for resource
planning of an organization. These are integrated
sets of solutions which cover implementation into
almost all business segments and hyphenate
structural functionality (based on best business
practices) and reliability of the system.
Experiences from using and ERP system give
proofs of positive effects on efficiency, positive
influence on relationships as well as customer
satisfaction – external customer satisfaction when
dealing with this company. The implementation of
ERP solution to institutions of higher education
needs to be observed in the same context.
4.1 Specific Demands of Academic
Community
Has it ever been more challenging for universities,
colleges, and research institutions to succeed in their
core missions? Reduced funding from traditional
sources has trimmed revenues, and competition for
private funding – including grants, endowments, and
alumni donations – is growing. Burgeoning student
populations are creating physical space and service
challenges. Government regulations pressure
institutions to operate with a high degree of
transparency, which intensifies the need to report,
document, and track financial, demographic, and
educational information. Demographic and
regulatory reporting requirements are prompting
additional spending on human resources
management systems. Demand for corporate
outreach and continuing education programs is
increasing.
Competition has intensified for the best students,
faculty, and academic and research professionals. To
address these myriad challenges, higher education
and research institutions need to leverage IT that
aligns with business requirements and supports
change. Organizations need to operate more
efficiently and integrate processes, from business
services to academic affairs and student care, while
collaborating externally with government agencies,
service providers, and other constituents. Yet many
organizations still use fragmented, non-integrated
business systems. Inefficient, outdated, and
expensive to maintain, these systems foster decision
making that is tactical and reactive at best.
ERP solutions for Higher Education is a portfolio
of highly scalable solutions specifically designed to
meet the unique needs of public and private
universities, multicampus institutions, research
agencies and medical colleges. It supports all
organizational processes, including campus
management for student and academic services,
grants management, Student Lifecycle Management,
financials, operations, human capital management,
procurement, analytics, research, and asset
management. With these solutions, it is possible to
sustain the continuing cycle of innovation and
standardization in a single technology environment.
One of the possible ERP solutions is powered by the
SAP NetWeaver® platform, which allows creation
of applications on top of existing infrastructure and
fully leveraging current IT investments – for long-
term adaptability, reduced costs, and flexible
response to changing strategies.
4.2 Functionalities for Financial
Management of Higher Education
For the purposes of this research it is necessary to
mention some ERP solutions used in Higher
Education institutions:
Grants and Funds Management – Solution which
helps organizations compete for and manage a
variety of department and sponsored grant programs,
endowments, and research awards across their life
cycles – including proposal development and
submission, budgeting, award, spending and payroll,
reporting, renewal, closeout, evaluation, and
analysis. It provides principal investigators, fund
administrators with timely and accurate information
on financial activities, accountants, and research and
transactions, ensuring that sponsored programs are
conducted according to a sponsor’s requirements. In
this way, improved effectiveness of grant
administration from pre-award to post-award, across
multiple fiscal years, with enhanced accuracy of
spending tracking is reached. Unified sponsored-
program life cycle regulations and guidelines are
made, such as the ones for enhanced funding streams
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCING
343

Figure 2: Key Business Processes for Higher Education and Research Mapped to SAP® Solutions. (www.sap.com, 2008.)
while supporting academic research missions.
Competitiveness in pursuing grant funds is
enhanced.
Manual processes and workload in planning,
managing, and reporting grants are reduced.
Financial Management, Budgeting, and Planning
– With this solution higher education institutions in
Croatia create proactive financial planning, real-time
budget visibility, and consolidated financial
reporting. It streamlines cash flow activities and
optimizes financial transactions through enhanced
visibility of financial processes, including treasury
management, billing, dispute resolution, collections,
receivables, and payables – in a single, consistent,
reconcilable, and auditable solution. Efficiency of
budgeting is improved, as well as of planning
processes, via cross-organizational financial control
and visibility. Centralized financial and management
reporting is achieved. Increased visibility of working
capital, streamlined cash flow activities, reduced
billing and payment costs, optimized financial
transactions, and simplified financial consolidations
across the organization. (Schwarz, Tipurić, Luić,
2007.)
Business Process Integration – is very important,
because without it, it would be impossible to achieve
efficiency of workflow processes through integrated
systems. Final results are improved information and
process integration of third-party applications and
systems, increased collaboration through data shared
across departments, organizations, suppliers,
partners, and other stakeholders, reduced need for
custom integration. Increased savings through
reduced integration and maintenance, enhanced
employee efficiency via single entry point and single
sign-on functions are features this solution provides.
Human Capital Management (HCM) – For
processes such as recruitment, administration,
payroll, time management, and legal reporting, final
score are reduced costs. It is also important to
mention: maximized impact of training with reduced
training costs, accelerated time for productive
employees, reduced employee turnover, enhanced
support for unique payroll requirements such as
deferred pay and unions.
Public and
Private
Stakeholders
Students and
Alumni
Strategic Planning Academic Portfolio Operational Planning Teaching and Study
Student Billing and
Financial Aid
Enter
p
rise Mana
g
ement & Su
pp
ort
Institutional Develo
p
ment
Market Research and Anal
y
sis
Institutional Advancement
Donor and Alumni Mana
g
ement
Partnershi
p
s
Institutional Communications
Academic Profile
Strate
g
ic Plannin
g
and Execution
Student Life C
y
cle Mana
g
ement
Student Records
Student Financials
Recruitment & Admission
Academic Advisin
g
Financial Aid
A
cademic Services
Academic Structure and Class Schedulin
g
Content Develo
p
ment and Mana
g
ement
Learnin
g
Academic Services
Student Services
On Cam
p
us Services
Student Communications and Service Market
p
lace
Librar
y
and Media Mana
g
ement
Student Housin
g
IT Services
Enter
p
rise Mana
g
ement & Su
pp
ort
A
nal
y
tics
Financials
Human Ca
p
ital Mana
g
ement
Cor
p
orate Services
O
p
erations Su
pp
ort
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
344

5 EXPERIENCES FROM
CROATIA
With a joint effort of the Ministry of Science,
Education and Sports (MSES), representatives of all
universities in Croatia (Zagreb, Split, Osijek, Rijeka,
Zadar, Dubrovnik) and b4b company, the main goal
of the project of implementation of an I
ntegrated
F
inancial Information System of 6 Universities
(IFIS-U6) based on lump-sum principles and
supported by SAP application solution, has been
achieved.
The project has been financed with MSES
resources but for the benefit of universities, and this
is the reason why the project had to meet the needs
and interests of both parties. The main motive of
MSES has been to integrate the financial system
which would ensure transparency of budget
spending of the assigned financial resources. On the
other hand, universities’ motive has been directed
toward independence regarding the purpose of
spending the budget resources and toward a
stronger, more efficient management of the
universities. In line with the motives and interests,
project business goals have been defined and they
had to ensure the following: independent spending
of assigned budget resources by universities,
development and integration of financial processes
of university and their integration with financial
processes of MSES, unification of the processes,
creating an IT basis for high-quality decision-
making and high-quality university management
with the help of scalable application solution which
shall meet highest standards of reporting.
IFIS-U6 project started in January 2006 and was
completed in October of that same year, and since
then, users and management of all six Croatian
universities have been using SAP transactions and
reporting and analytical system in their work.
5.1 Project Goals
Single project goals were directed towards:
• Permanent tracking of budget funds by individual
university
• University’s independent management of assigned
budget funds
• University business process improvement and
integration
• Uniform approach to necessary data and
information
• Integration of university business processes with
the business processes of MSES
• Solution scalability (ability for growth and further
development)
• Achievement of highest business standards (data
transparency and credibility).
Project being finished, it has helped in achieving
transparency of management of assigned funds in
terms of giving information on its purpose and
spending, at the same time university retained its
autonomy. Universities Rector’s office became
responsible for its regular operations while the
Ministry of Science, Education and Sports took over
the function of monitoring university’s operations.
(MSES, 2006)
5.2 Project Results and its Effect on the
Institutions
IFIS-U6 system has achieved vertical integration
upon which IFIS system of each university is
integrated with the Ministry of Science, Education
and Sports information system, and via this system,
with State Treasury information system. The vertical
integration includes business processes of budget
execution, as well as financial accounting. The result
of the above mentioned integration enables
processes to be carried out in real time, by principle
of event occurrence (on transaction level it implies
posting of documents at one place only and their
automatic transfer to connected systems) which
contributes to data authenticity. This also creates a
prerequisite for a stronger internal control. The
process consists of budget fund provision which
enables procurement of financial funds to
universities on time, which also implies more
orderly obligation fulfilment. The universities can
also decide on obligation fulfilment method on their
own: from a unique state treasury account (with the
Ministry of Science, Education and Sports as a
mediator) or directly, by university order.
As the most important project results, the
following ones should be singled out:
y Setting up a vertical integration of university
financial system with MSES information system,
and via MSES with the central state treasury
system, y setting up an independent financial
information system at university level as a
prerequisite for future establishment of university's
autonomy,
y enabling document entering at one place and their
automatic transfer to all connected systems,
.
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCING
345
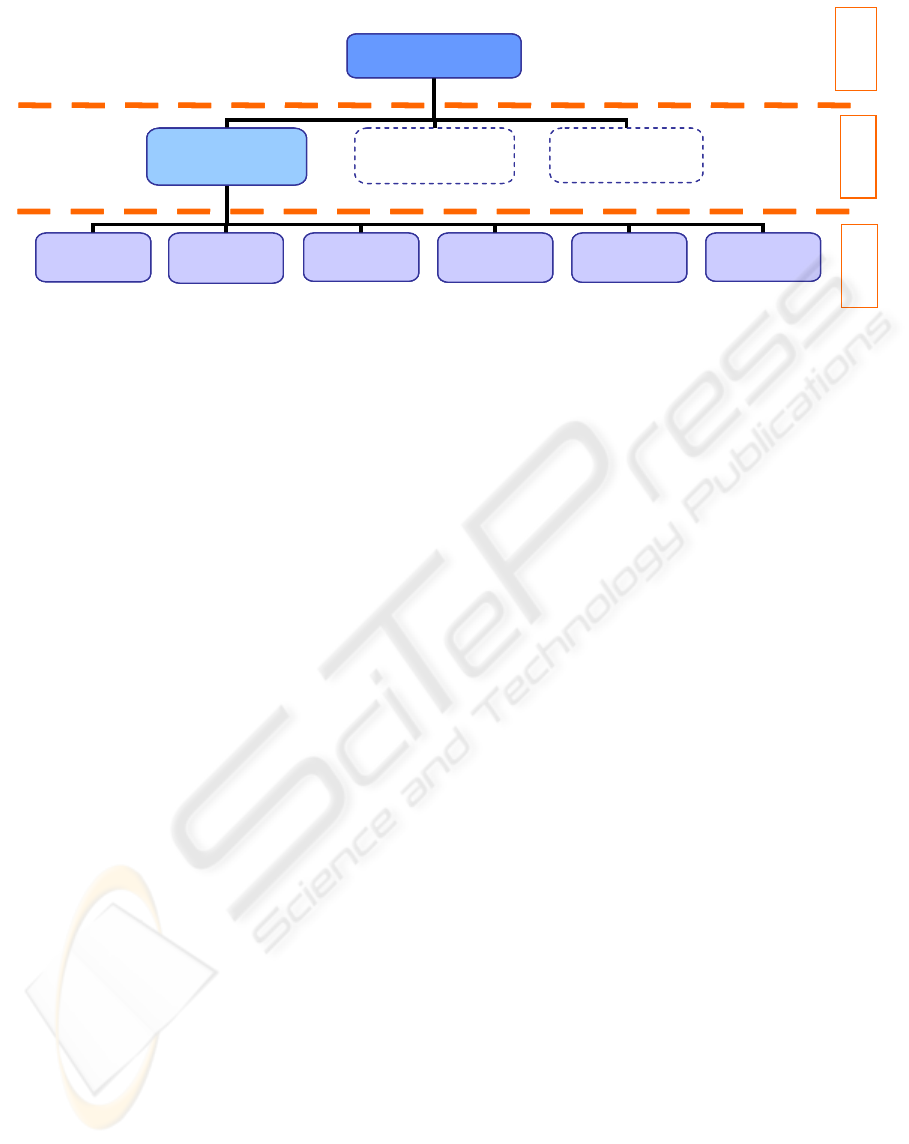
Figure 3: Integrated system of budget money management (IFIS-U6, 2006).
y running of processes in real time by event
occurrence principle which results in availability of
relevant information to all system users.
5.3 Project Application to Other
Institutions
Based on experience and knowledge acquired in the
project of concern, it can be said that IFIS system is
also applicable to faculties, new universities and
institutions, not only at administrative level but it
could be used by students through Campus
Management module after it has been upgraded.
Thus, the whole project could be expanded to the
sphere of a higher quality of education and to
stimulus for scientific and research work
5.4 Open Problems and Long Term
Goals
An integrated information system of higher
education is a prerequisite for a serious reform of the
financing scheme in this sector in Croatia. Currently
the university staff salaries are regulated on the state
level and depend only upon the formal status of a
person. There is practically no correlation neither
with the quality nor quantity of the work performed.
The formal status is achieved mostly due to the
count of published papers, for some fields especially
if referenced in Current Contents. In applied fields,
a valuable scientific article can be best produced as a
side effect of some real-world project. Such papers
should probably be more appreciated than the purely
speculative ones? There is no difference in
educators’ salary between professions in high
market demand and those that are maintained only
due to preserve some tradition. The alleged
university autonomy is seriously challenged as long
as the Ministry decides regarding new employments.
There are no serious criteria in the newly established
lump sum financing how to distribute the funds
among single faculties. Faculties in most of Croatia
are rather independent, spatially dispersed
institutions varying heavily in their quality,
relevance, size and local regulations. Nowadays, an
incremental budgeting is performed, based on
historical rights and it is hardly correlating with any
rational indicator. As long as the full information is
not available, the majority in university decision
boards preserves the current status as more
favourable for them, while the most advanced
constituents have to pay the price. Here may lay the
most serious risk for further advancement of
computerisation in higher education financing.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Reduced funding from traditional sources has
trimmed revenues, and competition for private
funding – including grants, endowments, and alumni
donations – is growing. Burgeoning student
populations are creating physical space and service
challenges. Government regulations pressure
institutions to operate with a high degree of
transparency, which intensifies the need to report,
document, and track financial, demographic, and
educational information. Demographic and
regulatory reporting requirements are prompting
additional spending on human resources
management systems. Demand for corporate
outreach and continuing education programs is
increasing. Competition has intensified for the best
students, faculty, and academic and research
professionals.
MZOŠ
fakultet
State Treasury
MSES
Ministry ...
Ministry ...
University of
Zagreb
University of
Rijeka
University of
Osijek
University of
Split
University of
Zadar
University of
Dubrovnik
Level 1
Level 3
Level 2
MZOŠ
fakultet
State Treasury
MSES
Ministry ...
Ministry ...
University of
Zagreb
University of
Rijeka
University of
Osijek
University of
Split
University of
Zadar
University of
Dubrovnik
State Treasury
MSES
Ministry ...
Ministry ...
University of
Zagreb
University of
Rijeka
University of
Osijek
University of
Split
University of
Zadar
University of
Dubrovnik
Level 1
Level 3
Level 2
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
346

To address these myriad challenges, higher
education and research institutions need to leverage
IT that aligns with business requirements and
supports change. Organizations need to operate more
efficiently and integrate processes, from business
services to academic affairs and student care, while
collaborating externally with government agencies,
service providers, and other constituents. Yet many
organizations still use fragmented, non-integrated
business systems. Inefficient, outdated, and
expensive to maintain, these systems foster decision
making that is tactical and reactive at best.
Development, design and application of an
integrated business information system are very
complex processes. That is why planning and project
management of implementation of an integrated
information system should be carried out on the
level of state and business system. Strategic
planning of IBIS is a starting point in this process,
and putting information in the middle of a
corporative success, be it in private or public sectors,
is the way in which information is used in the
organization as a crucial factor of their
competitiveness, efficiency and finally, their
profitability. The importance of this research is first
of all concerned with acquiring new knowledge that
can indirectly influence qualitative changes in
strategic planning processes, and its social
significance lies in improving the knowledge and
spreading its application into business practice.
From all the mentioned, scientific and social
justification of this research can be derived from the
fact that this research is an initial and starting
research for a more detailed dealing with
interdisciplinary issues of strategic planning of an
integrated business information system.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Publication of this paper was supported by grant
#036-0361983-3137 by the Croatian Ministry of
Science, Education and Sports, to which the authors
of this article are grateful for the support.
REFERENCES
Bok, D., 2005. Universities in the Marketplace, The
commercialization of Higher Education, Published by
Princeton University Press, New Jersey.
Brumec, J., et al, 2000. Strategic Planning of Information
Systems - From Theory to Practice. Proceedings of 7
th
European Concurrent Engineering Conference,
Leicester, United Kingdom.
Galliers, R.D., Leidner, D.E., 2003. Strategic Information
Management: Challenges and Strategies in Managing
Information Systems, Third Edition Butterworth-
Heinemann, Oxford, Great Britain
IFIS-U6 project documentation, 2006. Blueprint,
Integration Test and Production, Ministry of Science,
Education and Sports, Zagreb, Croatia.
Luić, Lj., Schwarz, D., Uzelac, S., 2007. Strategic
planning of integrated business information system of
universities. Lisabon.
Marcella, R., Knox, K., 2004. Systems for the management
of information in a university context: an investigation
of user need, Information Research, Vol. 9 No. 2
paper 172 [Available at http://InformationR.net/ir/9-
2/paper172.html
Newman, F., Couturier, L., Scurry, J., 2004. The Future
of Higher Education, Rhetoric, Reality, and the Risks,
of the Market, Published by Jossey-Bass-AWiley
Imprint, San Francisko, USA – 1st ed.
Schwarz, D., Tipurić, D., Luić, Lj., 2007. Integrated
financial information system of the universities in the
Republic of Croatia based on lump-sum principles and
supported by SAP application solution, EUNIS,
Grenoble.
Slaughter, S., Rhoades, G., 2004, Academic
Capitalism and the New Economy: Markets,
State, and Higher Education, The Johns Hopkins
University Press – Baltimore and London.
Turban, E., McLean, E., Wetherbe, J., 2004, Information
Technology for Management, Transforming
Organizations in the Digital Economy, John Wiley &
Sons, Inc, USA.
Ward, J., Peppard, J., 2002. Strategic Planning for
Information Systems, Third Edition John Wiley, New
York, USA.
Science & Technology Strategy of the Republic of Croatia
2006–2010, 2006. Ministry of Science, Education and
Sports, Zagreb, Croatia, [online] http://public.mzos.hr
www.sap.com, 2008.
ROLE OF ERP IN MANAGEMENT OF HIGHER EDUCATION FINANCING
347
