
AN ONTOLOGY IN ORTHOPEDIC MEDICAL FIELD
Harold Vasquez, Ana Aguilera
Departamento de Computación, FACYT, Universidad de Carabobo, Valencia, Venezuela
Leonid Tineo
Departamento de Computación, Universidad Simón Bolívar, Caracas, Venezuela
Keywords: Ontology, Medical Data Base, Orthopedic, SQLf.
Abstract: At present time, Ontology is a powerful Knowledge Representation tool for Web Information Retrieval and
Mining. In particular, lots of medical applications in the field of diagnosis and tele-health would take
advantage of information sharing and publication on the Web with the use of Ontology. We are especially
interested in the field of orthopedic pathologies of human march. There are several laboratories in the world
working in this topic but they are not exploiting potential of the Web in theirs works, they are almost isolate
in information management. We have already carried out mining in database from the Venezuelan Hospital
Ortopédico Infantil, nevertheless, it is necessary to build an ontology in order to query and mine
information from different laboratories in the world. We would like in the near future to apply fuzzy logic
techniques and fuzzy querying over such information. In this paper, we present the building of an
orthopedic medical ontology, to the best of our knowledge, has not been reported other in this specific field
that we are interested on.
1 INTRODUCTION
Several investigations aiming at optimizing the
handling of medical information so that it becomes
both useful and agreeing with the user requirements,
in the sense of extracting significant knowledge to
be used in the detection and cure of diseases, have
been reported.
In the sense of allowing both manipulation and
access to medical information with the purpose of
satisfying exigent user requirements, it is important
to have computational tools to perform this.
Currently, the relational database querying has
answered to some extent these needs.
Queries could be improved using ontologies,
since they are very useful to represent knowledge
within a specific domain. This representation tool
has desirable features, such us: re-usability,
interoperability and formality. Therefore, there are
many current researches in the area of knowledge
representation and manipulation based on
ontologies.
Ontologies have demonstrated to be very
advantageous tools to formalize, maintain, reuse,
share, generalize and communicate knowledge in a
specific dominion. The ontologies provide a
common vocabulary, in relation with an area of
knowledge and define, at different formal levels, the
meaning of the terms and relations among them
(Valencia, 2005).
We are interested in querying medical
information, in particular for orthopedics, employing
SQLf, a fuzzy querying language (Goncalves &
Tineo, 2006), (Bosc & Pivert, 1995). It obeys to the
fact that fuzzy sets are powerful manners to
represent user preferences, imperfect data and weak
relationships. We would like our project to be not
limited to a single database but capable of accessing
information from diverse health centers.
We would like to build a fuzzy Ontology, based
on knowledge, in the medical database of the March
Laboratory at Hospital Ortopédico Infantil (HOI) in
Caracas, Venezuela.
Nevertheless, before to obtaining this Fuzzy
Ontology, it is necessary to build a classic ontology
and subsequently convert it with fuzziness. There
are a lot of mechanism to get this done but not all
them it are useful to our proposal, so we need to
372
Vasquez H., Aguilera A. and Tineo L. (2008).
AN ONTOLOGY IN ORTHOPEDIC MEDICAL FIELD.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - PL/DPS/KE, pages 372-375
DOI: 10.5220/0001888503720375
Copyright
c
SciTePress
study and apply some of these strategies that accord
fit to our necessity.
This paper shows the process of making this (up
to our knowledge very first) Ontology of knowledge
about medical studies over patients with Orthopedic
diseases in pathological walking.
2 SOURCE DATA BASE
Venezuelan March Laboratory at Hospital
Ortopédico Infantil (HOI) is one of the biggest and
most advanced laboratory for diagnostics, research
and treatment of march pathologies in Latin
America. HOI uses an advanced mediation system
for both diagnostic and treatment of the illness
related with the locomotive and neuromuscular
system. This system allows to collect simultaneously
both data and images in three dimensions, and after
an adequate treatment. HOI also has a database that
keeps tracks of all its patients’ cases since 1997. For
the purpose of this research work, HOI has provided
a copy of this database with registers until December
2006 (Vasamon & León, 2007).
HOI database was developed in Ms.Access™.
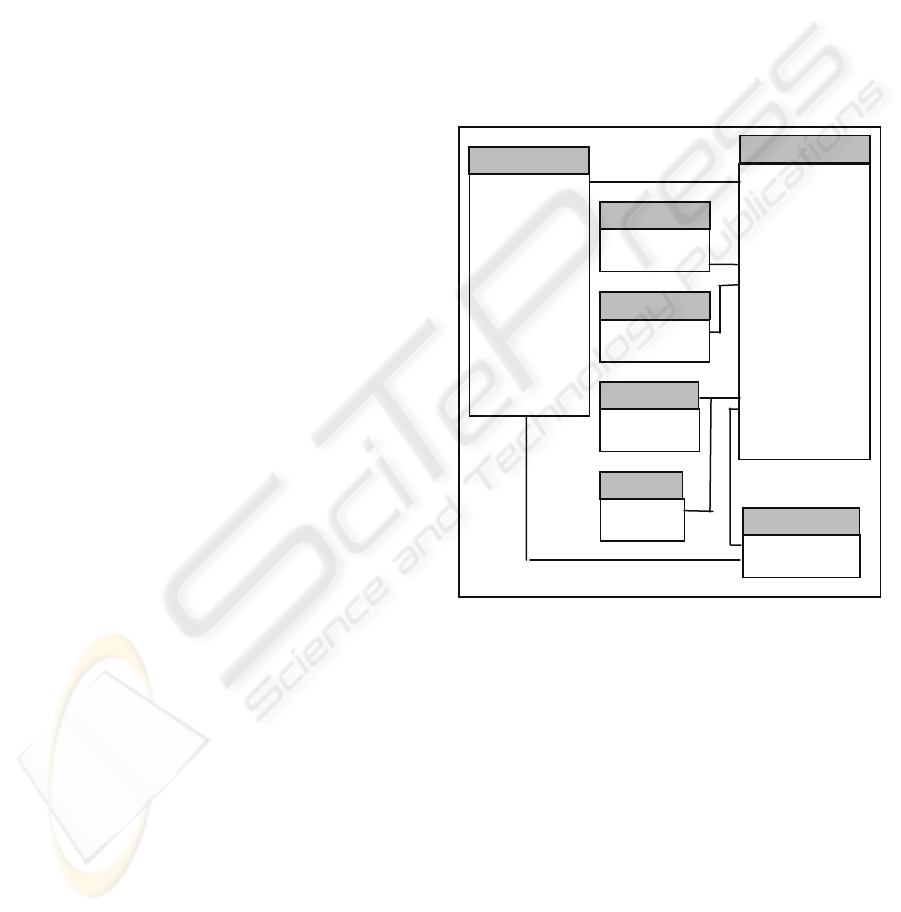
This database has the logic scheme show in Figure
1. Names in he scheme are in Spanish, because this
is the Venezuelan current language. Semantics of
tables is as follows:
Paciente. This table has basic information of
patients. – ID_paciente, primary key code. –
Nombre, given name. – Apellido, family name. –
Sexo, gender. – Fecha_Nac, date of birth, –
Historia_HOI_I, medical history identification
number. – ID-DIAGNOSTICO, foreign key to the
main diagnostics disease for the patient. –
Fundational/Privado, indicates whereas the patients
comes from a beneficial foundation or a private
consultation. – Lado, Tono, Lado 1, Tono 1,
indicators for the side leg (left/right) and a measure
of muscular tone of this side. – Nivel, regarding to
the level of the main disease in the patient.
Estudio. this contains information about studies
performed to patients, some of the main columns are
the following. – Estudio_ID, primary key code. –
Paciente_ID, foreign key to the patient. – Pre_Post,
indicates whereas the study is made as a requisite
previous or posterior to a surgical intervention. –
Fecha_estudio, date of the study, – Master_Video,
number of the video register for the exam. –
Tipo_Estudio_ID, foreign key to the study kind
register. – ID-DIAGNOSTICO, foreign key to
study’s analysis resulting diagnostics disease.
Tipo_estudio. This part of the database gives
identification and name of different kinds of studies.
Interpretador. This table gives identification and
name of physicians that interpret studies.
Referente. Here give identification and name of
physicians that reference patients and ordain studies
for patients.
Referente 1. As the previous one, it gives
identification and name of physicians that reference
patients and ordain studies.
Diagnostico. This table gives identification and
name of different diseases or pathologies
diagnostics.
Figure 1: Logical schema of HOI Data Base.
3 BULDING THE ONTOLOGY
There are many definitions of ontologies, but the
most accepted is the one given (Gruber, 1993) that
states: “an ontology is an explicit, formal
specification of a shared conceptualization of a
domain of interest”. However, since we are going to
use the method described in (Men et al, 2005), we
adopt the following definition:
An Ontological Structure O is a 5-tuple
O = {C, R, H
c
, rel, A
o
}
where C is a finite set of concepts; R is a finite
set of relations; H
c
is called concept hierarchy or
taxonomy, which is a directed relation H
c
⊆ C×C,
Paciente
Id_Paciente
Nombre
Apellido
Sexo
Fecha_Nac
Historia_HOI_ID
ID_Diagnostico
Fundacional/Privado
Lado
Lado1
Tono1
Tono
Nivel
Estudio
Estudio_ID
Paciente_ID
Pre_Post
Fecha_estudio
Master_Video
Interpetrador_ID
Tipo_Estudio_ID
Notas
Combo
EDAD
TALLA
PESO
Referente_ID
ID-Diagnostico
Diagnostico_referencia
EXAMINADO POR
Diagnostico
ID-DIAGNOSTICO
DIAGNOSTICO
Referentes
Referente_ID
Referente
Referentes_1
Referente_ID
Referente
Interpretador
Interpretador_ID
Interpretador
Tipo_Estudio
Tipo_Estudio_ID
Tipo_De_Estudio
1 ∝
AN ONTOLOGY IN ORTHOPEDIC MEDICAL FIELD
373
for example, H
c
(C
1
, C
2
) specifies that C
1
is a
subconcept of C
2
; rel relates concepts non-
taxonomically, for example, rel (R) = (C
1
, C
2
)
specifies that C
1
and C
2
have relation R.; A
o
is a set
of axioms, which is expressed in an appropriate
logical language, e.g. First Order Logic (FOL).
3.1 Language of Representation
Typically, an ontology can be generated from
various data types such as textual data, dictionaries,
knowledge-based semi structured schemata and
relational schemata (Quan et al, 2006). However, in
all those cases, the ontology can be represented with
different languages, but the most commonly used
today are XML, OWL and RDF. Because OWL is
one of the most used languages in the field of
ontologies and it is standardized by the W3C, it is
going to be used to model the medical ontology that
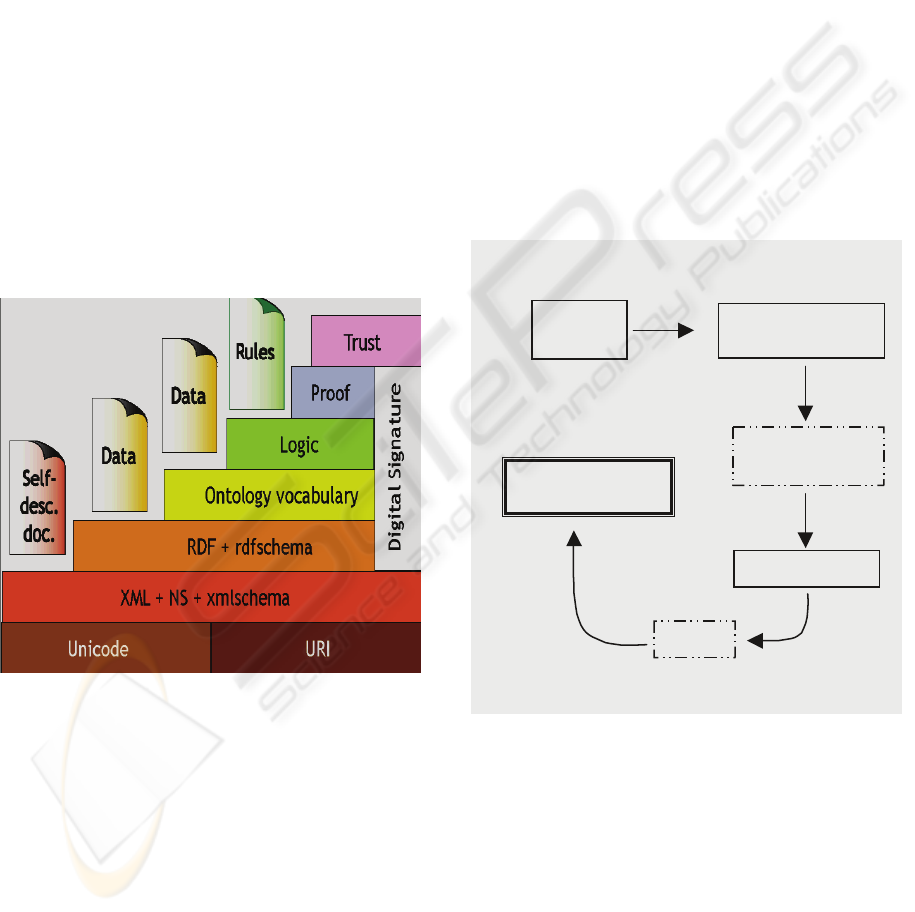
will use in this investigation. The following figure
presents the evolution of the different languages
employed to represent Ontologies.
Figure 2: The architecture of Levels of T. Berners Lee.
3.2 Methodologies Building
In (Men et al, 2005), they propose an approach of
learning an OWL ontology from data in a relational
database. Compared with existing methods, the
approach can acquire ontologies from relational
databases automatically by using a group of learning
rules instead of using a middle model. However, this
proposal has the inconvenient that an ontology is
created in OWL directly without an intermediate
model, so if the database is poor in knowledge, then
Ontology is poor too. Furthermore, it’s important
this intermediate model, that makes rich the learning
produced, is important.
There are so many methodologies for learning
ontologies (Garcia, 2005), but only few are helpful
for our purpose. Among them, it is the so-called
Methontology (Fernández et al, 1997 and Gómez-
Pérez, 1998). This methodology guides the ontology
building by specifying a set of intermediate
representations (IRs) at the knowledge level. These
IRs bridge the gap between how people think about
a domain and the languages in which ontologies are
formalized, that it allows us both to extend and
enrich our ontology, previously generated with the
HOI database. We sketch this methodology,
followed by our study case, in Figure 3.
At the end, we will evaluate our ontology,
generated by using quality assuring metrics,
according to pervious work what is proposed in
(Lozano, 2002).
Schema
DB-HOI
Middle Building
Ontology
Methontology
IRs
Orthopedic Medical
Ontology in OWL
Method described
in Men et al, 2005
Figure 3: Model to building the Orthopedic Medical
Ontology.
3.3 Editing and Browsing Tool
Instead of using the Methontology tool which
supports the ontology maker during the entire life
cycle of the ontology development process, called
ODE (Ontology Design Environment); we prefered
to use another environment to carried out this. The
reason to do that was the fact that ODE has the
inconvenient that it does not work with the OWL.
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
374

Because these reason of that, we are
experimenting using Protege or OntoWeb with those
two mechanisms to build our ontology instead.
These tools are well known, free and with a profuse
support.
4 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORKS
In this work we combine several methodologies in
order to build an Ontology of knowledge regarding
medical studies that have been performed over
patients with Orthopedic diseases in pathological
walking or march. The work has been undertaken on
the basis of the Venezuelan Hospital Ortopédico
Infantil (HOI) March Laboratory database. The
result of this work would be an original contribution
to the research for this kind of laboratories, because
there is no precedent ontology in this field. Several
institutions could take advantage of this as a support
tool for the diagnosis and treatment of these
diseases. This work would allow the publication and
sharing of this kind of information for querying and
mining purposes. In future works we will apply
fuzzy logic tools for mining and querying medical
information from march laboratories. In order to do
so, we will extend such techniques with the use of
Ontology. We hope to reach a benefit for humanity.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We acknowledge that the inspiration and all that we
need for working an living come from Heaven, from
our Lord and Eternal Father. For this work, we have
the financial aid of Venezuelan National Foundation
for Science, Technology and Innovation FONACIT
by means of the project G-200500278. We also give
thanks to the Hospital Ortopédico Infantil
Foundation and especially to the staff of the March
Laboratory who have cooperate in this research
proposing valuable data and knowledge. Finally, we
want to express acknowledgement to Dr. Miriam
Rodríguez, physician, specialist in rehabilitation and
physiatrists, medical advisor of our project.
REFERENCES
Goncalves, M., Tineo, L.: SQLf vs. Skyline - Expressivity
and Performance. Proceedings of FUZZY-IEEE 2006.
Vancouver, Canada (2006).
Bosc, P., Pivert, O.: SQLf: A Relational Database
Language for Fuzzy Querying. IEEE Transactions on
Fuzzy Systems. 3(1). (1995)
Valencia R.: Un Entorno para la Extracción Incremental
de Conocimiento desde Texto en Lenguaje Natural.
Departamento de Ingeniería de la Información y las
Comunicaciones. Universidad de Murcia. Murcia,
España (2005)
Gruber T. A translation approach to portable ontology
specifications. Technical Report KSL 92-71.
Knowledge System Laboratory. (1993)
Man Li, Xiao-Yong Du and Shan Wang: Learning
Ontology from Relational Database. Proceedings of
the Fourth International Conference on Machine
Learning and Cybernetics, Guangzhou. pp. 18-21.
(2005)
Vasamon, D. y León, Y. Aplicación de Minería de Datos
en Bases de Datos Médicas. Departamento de
Computación. Universidad de Carabobo. Carabobo,
Venezuela (2007)
Quan Thanh Tho, Siu Cheung Hui, Fong and Tru Hoang
Ca: Automatic Fuzzy Ontology Generation for
Semantic Web. In: IEEE transactions on knowledge
and data engineering, 18(6). pp. 842--856. (2006)
García V., Rafael. Un Entorno para la Extracción
Incremental de Conocimiento desde Texto en
Lenguaje Natural. Tesis Doctoral. Universidad de
Murcia. Departamento de Ingeniería de la Información
y las Comunicaciones. (2005).
Fernández, M.; Gómez-Pérez, A.; Juristo, N.
METHONTOLOGY: From Ontological Art Towards
Ontological Engineering. Spring Symposium Series.
Stanford. PP: 33-40. (1997).
Gómez-Pérez. A. Knowledge Sharing and Reuse. The
Handbook of Applied Expert Systems. Edited by
Liebowitz. CRC. (1998).
Lozano T., Adolfo. Metrica de Idoneidad de Ontologias.
Tesis Doctoral. University of Extremadura.
Departamento de Informatica. (2002)
AN ONTOLOGY IN ORTHOPEDIC MEDICAL FIELD
375
