
HOW TO SUPPORT SCENARIOS-BASED
INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN
A Domain-Specific-Modeling Approach
Pierre Laforcade, Boubekeur Zendagui and Vincent Barré
LIUM / IUT de Laval, 52 rue des Docteurs Calmette et Guérin,53020 Laval Cedex 9, France
Keywords: Instructional Design, Learning Scenario, Educational Modeling Language, Model Driven Engineering,
Domain Specific Modeling, Visual Instructional Design Language.
Abstract: Over recent years, Model-Driven-Engineering has attracted growing interest as much as a research domain
as an industrial process that can be applied to various educational domains. This article aims to discuss and
propose such an application for learning-scenario-centered instructional design processes. Our proposition is
based on a 3-domain categorization for learning scenarios. We also discuss and explain why we think
Domain-Specific Modeling techniques are the future new trend in order to support the emergence of
communities of practices for scenario-based instructional design. The originality resides in the support we
propose to help communities of practitioners in building specific Visual Instructional Design Languages
with dedicated editors instead of providing them with yet another language or editor.
1 INTRODUCTION
Over recent years, the Model-Driven Engineering
(MDE) principles
(Schmidt, 06) have been frequently
applied and acclaimed as of great interest within
various educational disciplinary fields. In this paper,
we are particularly concerned with the application of
MDE principles for instructional design processes,
mainly the ones dealing with learning scenarios.
Current context analysis about languages, tools
and techniques for learning scenarios
(Kinshuk et al.,
06)
highlights the need for user-friendly languages or
tools to help designers in setting up Learning
Management Systems (LMS). We are interested in
providing end-users, acting as both teachers and
designers (sometimes mentioned as 'practitioners'),
with dedicated Educational Modeling Languages
(EML) or Visual Instructional Design Languages
(VIDL)
(Botturi et al., 07), and tools to help them
specify learning scenarios with their own
terminology, graphical formalism, and editing
preferences, without leaving aside computerizing
trends concerning the produced scenarios (reuse,
interoperability, etc.).
Our experiences about graphical representations
of learning scenario and transformations between
EMLs
(Laforcade et al., 07), lead us to deal with MDE
techniques and to a new promising orientation we
are currently exploring: Domain-Specific Modeling
(DSM) as a new way for modeling and formally
specifying learning scenarios. We discuss interest of
DSM techniques and tools applied to our context
(instructional design). The conceptual framework
underlying our approach is a categorization based on
a domain-oriented separation of concerns.
We first present the MDE and discuss its
application to the context of learning-scenario
centered instructional processes. We also discuss our
3-domain categorization for learning scenarios and
our orientation towards DSM. We illustrate and
discuss our first results about the use of DSM tools
to specify VIDL and to build dedicated editors.
2 MDE BACKGROUND
The Model Driven Architecture (MDA) is a
framework for software development adopted by the
Object Management Group in 2001
(OMG, 01). It
aims to provide a solution to the problem of software
technologies continual emergence that forces
companies to adapt their software systems every
time a new ‘hot’ technology appears. The solution
327
Laforcade P., Zendagui B. and Barré V. (2008).
HOW TO SUPPORT SCENARIOS-BASED INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN - A Domain-Specific-Modeling Approach.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - PL/DPS/KE, pages 327-332
DOI: 10.5220/0001889203270332
Copyright
c
SciTePress

proposed consists of separating the enterprise
functionalities of an information system from the
implementation of those functionalities on specific
technological platforms, and also by using an
intensive model-based design and development.
MDA approach sorts models into three classes:
the Computation Independent Model (CIM) view of
a system where the used vocabulary is the business
one. A CIM helps to specify exactly what the system
is expected to do. The Platform Independent Model
(PIM) view leads to independence from specific
platforms but should be expressed in a
computational way, so as to be suitable for use with
a number of different platforms of similar type.
Finally, the Platform Specific Model (PSM) view
links the specifications in the PIM with details that
specify how this system will be implemented on a
specific platform. Mappings between PIM and PSM
can be done by means of model transformations.
Finally, code can be generated from the PSM.
The Model Driven Engineering (MDE) is a more
general and global approach than the MDA aiming
to apply and generalize its principles for every
technological space (object-oriented space, XML
documents, etc.). The MDE is founded on: i/
capitalization: models are to be reusable, ii/
abstraction: domain models have to be independent
from technologies used to implement them, iii/
modeling: models are no longer contemplative (used
to document, communicate, etc.) but used in a
productive way (they are machine-interpretable), iv/
separation of concerns: usually between domain and
technology but other separations are possible.
In order to dispose of productive models, they
must be well-defined, i.e. linked to a specific meta-
model. Productive models can be handled,
interpreted with MDE tools
(Bézivin et al., 03): meta-
model/language definition tools, transformation
tools, code generation tools, weaving tools,
generation of domain-specific model editors, etc.
3 MDE APPLIED TO
INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN
3.1 Past and In-progress Research
Many research works focus on the definition of
EML and also discuss the IMS-LD language (IMS,
03)
considered as the current standard for specifying
scenarios. Some of the following works explicitly
claim their MDE positioning.
The CPM Language
(Laforcade, 05) is a UML-
based (UML profile) visual language dedicated to
the definition of Problem Based Learning situations
by specific designers. CPM models act as a support
for thinking and communicating within a
multidisciplinary design team. Model transformation
from CPM activity diagrams to IMS-LD-compliant
scenarios have also been studied.
Research works from the Bricole project
(Caron,
07) propose a transformation model application to set
up an LMS from any IMS-LD-compliant scenario.
They transform the IMS-LD source scenario
(graphically modeled with the ModX tool) into
another graphical LMS specific scenario (Gendep
tool) that is interpreted to automatically configure
the LMS via a specific service web based API.
The LDL Language
is a CSCW domain-specific
language aiming to specify such dedicated scenarios.
This language is concretely proposed as a specific
XML binding but recent works aim to provide it
with a visual formalism
(Martel et al., 07).
(Paquette et al., 06) propose an extension of their
MOT notation and dedicated edition tool to conform
to the IMS-LD standard for defining learning
scenarios: the MOT+LD formalism.
Other works aim to automatically provide
teacher-designers with a graphical representation of
IMS-LD scenario (XML document). The concrete
technique uses imperative transformations from
XML to a UML4LD representation (UML profile
dedicated to IMS-LD)
(Laforcade, 06).
Recent works
(Dodero et al., 07) also proposed a
graphical environment, called MDLD (Model-driven
Learning Design Environment), in order to help
learning designers to generate units of learning
(XML) conformed to IMS-LD by graphically
specifying BPEL-oriented modeling (an abstract
language for modeling business process execution).
3.2 Discussions
Models produced/transformed into MDE processes
correspond to the learning scenarios in instructional
design processes. These scenarios are generally
defined/specified with an EML. Whatever the
formalism used (graphic, textual, etc.) we can
consider that every EML can describe its underlying
terminology as a meta-model. The final system, in
a MDE process, corresponds to the learning situation
aimed in an instructional design process. The
difference is that this learning situation relies on
both human and system artifacts, not only code.
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
328

Indeed, instructional design processes aim to
produce units of learning that can be deployed or
configured into LMS that pre-exist them. All EML
or VIDL languages can be compared from many
point of views or separations of concerns.
We also want to highlight the omnipresence of
the business learning domain: whatever the
EML/VIDL used to express a learning scenario
(from very specific domain scenarios to standards
based or LMS specific ones) they all are expressed
with a more or less abstract/specific learning syntax
and semantics. All these business domains reflect
some specific particularities (pedagogical theories,
didactical domains, etc.) shared by pluridisciplinary
design teams. Another key point concerns the visual
representation of learning scenarios. It appears to be
as equally important for domain-specific learning
scenarios, as for understanding shared scenarios
which comply to standards, or for helping the
manual configuration of LMS.
Finally, all those points led us to the idea that a
simple CIM/PIM/PSM application is not relevant
because of business omnipresence and overall visual
interest for representing scenarios. This is why we
propose the following domain-specific approach.
4 A DOMAIN-SPECIFIC
APPROACH
4.1 The 3-leaf Domain-clover
Proposition
We propose three categories for learning scenarios
and languages from a separation of concerns
reflecting different communities of practices sharing
a comparable business learning domain towards
specific objectives.
Practitioners-centered Scenario (PS). The
vocabulary is the one shared by a pluridisciplinary
design team; it expresses their common vocabulary
(for example in relation to some pedagogical
theories, didactical fields as well as specific
references to the LMS they use). The objectives of
such scenarios are to ease the definition of the
learning scenario, to act as a design guide, and a
support to thinking/communicating.
Abstract Scenario (AS). The vocabulary aims to be
independent from any LMS in order to support the
interoperability of scenarios. This abstraction also
usually reflects a high-level abstraction of the
vocabulary used from pedagogical theories and
didactical fields. The objectives aim at supporting
pedagogical diversity and innovation, while
promoting the exchange and interoperability of e-
learning scenarios.
LMS-centered Scenarios (LS). The vocabulary is
specific to a dedicated LMS or other e-learning
platforms. The objectives are to act as a guide for the
manual or semi-automatic configuration of the
technical dispositive by humans as well as for
automatic configuration by machines when possible.
We also propose to split each categorization into
two parts corresponding to the targeted public: one
part for human-directed interpretation, and
dedicated visual formalism (human-readable
textual/graphical notation); and the other one for
machine-directed interpretation (machine-
interpretable formal notation, i.e. no ambiguous
semantics).
Although these two parts can be used as a new
feature to compare VIDLs/EMLs, we think that they
are both useful and have to be both provided by any
instructional design language. This approach is
conformed to the MDE paradigm where models
have now to be productive. For us, learning
scenarios have to be both contemplative (for human
interpretation objectives) and productive (for
machine execution in order to realize simulations,
predictions, transformations, exchanges, etc.).
In our thinking the three categorizations
(PS/AS/LS) share fuzzy frontiers between each
other. Also, we do not think instructional design
processes handling learning scenarios must
systematically follow all these categorizations. We
do not propose a systematic way to transform
scenarios from one to another. On the contrary we
think that designers must be free to decide which
EML/VIDL is useful according to their objectives
and target public (human or machine interpretation).
One key point concerns the transformation from
one type of scenario to another. When source and
target scenarios are from different EMLs, the
transformation is extra-domain; it necessary happens
from one category to another but also between
different EMLs from the same category. Interest of
such transformations is to gain the objectives of the
targeted categorization, when changed, or to
exchange and reuse scenarios with other
communities of practices that do not share the same
business learning domain. On the contrary, when
source and target scenarios share the same abstract
syntax (metamodel) but differ from the used
concrete syntax (notation), the transformation is
intra-domain. This kind of transformation is useful
to adapt to a different target public and objectives by
only changing the format of the learning scenarios.
HOW TO SUPPORT SCENARIOS-BASED INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN - A Domain-Specific-Modeling Approach
329

4.2 Illustration
We illustrate our proposition into the figure 1.
Figure 1: The three-leaf domain-clover annotated with a
projection of current research works.
CPM and LDL are practitioners-centered langua-
ges; CPM being more a VIDL because of its human-
directed notation than LDL which only offers a
machine-interpretable formalism for now
(Martel et
al., 07). Also, the CPM tooling proposes a service
transforming CPM diagrams into IMS-LD scenarios.
The abstract category with a machine-oriented
formalism suits the IMS-LD standard well. We
position the MOT+LD proposition in the same
category but with a human-directed notation (the
MOT+ formalism has been extended to include the
IMS-LD vocabulary). UML4LD is both a visual
formalism for IMS-LD (abstract category with
human notation) and a transformation mechanism
from IMS-LD scenarios to UML4LD ones. MDLD
is also position in this category since it offers an
abstract language (but not dedicated to learning
scenarios) to model chunks of learning processes
that are then transformed into IMS-LD code.
Finally, the Bricole Project propose ModX tool
to model scenarios in both abstract and LMS-
centered visual notations, and GenDep tool to ensure
transformations between these two formalisms. Note
that CPM and ModX tools can save the produced
scenarios in a machine-interpretable formalism
(XMI serialization).
4.3 How to Support our Proposition?
The 3-leaf domain clover we propose can be
considered as, and used as, a theoretical tool for
classifying given VIDL/EML or tools. It also
materialize our vision of current communities of
practices about learning scenarios. The 3-leaf
domain clover is then a model of this vision.
Our works aim at supporting the emergence of
communities of practices from this model. In order
to do that, we need concrete tools and techniques to
support and ease emergence of such communities:
1. tools for defining domain-oriented VIDL /
EML (concepts/relations specification plus
techniques to define both machine-interpre-
table and human-readable formalisms).
2. tools/techniques for defining learning
scenarios corresponding to existing domain-
oriented VIDL/EML (eg. graphic editors).
3. tools/techniques for intra & extra
transformations of learning scenarios
(bridges between these emergent
communities are very important).
Although current instructional design research
proposes some VIDL and various kind of user-
friendly editors
(Botturi et al., 07), there is no work
that proposes the tooling we have highlighted,
technically addressing support of emergent VIDL-
based communities of practices. We think that the
Domain-Specific Modeling (DSM) provides tools
and techniques supporting most of these needs.
5 DOMAIN-SPECIFIC
MODELING AND
INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN
5.1 DSM Domain and Tools
DSM (Kelly et al., 08) is a software engineering
methodology for designing and developing systems,
mostly IT systems such as computer software. It
involves the systematic use of a graphic Domain-
Specific Programming Language (DSL) to represent
the various facets of a system
. We are particularly
interested by these graphical DSL, also called
Domain-Specific Modeling Languages (DSML).
Several technical approaches coexist to support
DSML specification: commercial products
(MetaCase/MetaEdit+), the Microsoft DSL tools,
academic or open-source projects (VMTS, TIGER,
EMF, GMF, etc.). All these DSM tools propose
metamodeling techniques capable of expressing
domain-specific vocabularies (abstract syntaxes),
and propose facilities to construct various notations
(concrete syntaxes). These editing frameworks are
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
330
supporting the techniques and many more
customizations with minimal programming effort.
As a result, these tools can generate powerful and
user-friendly dedicated editors for DSM languages.
They are kind of meta-CASE editors capable of
generating CASE tools. The final editors give
domain-designers the ability to graphically specify
models from their domain, and propose some
persistence facilities to load and store these models
in a machine-interpreted format.
5.2 Using DSM Tools
These DSM tools meet most of the needs we need in
order to support our domain-oriented proposition for
the EML and learning scenarios. Concretely, needs
previously numbered 1/, 2/ and 3/a (intra-
transformations) are supported (cf. §4.3). DSM
principles are also convenient with our 3-leaf
domain-clover and more generally seem able to
support the emergence of VIDL/EML communities
of practices as well as providing practitioners with
user-friendly visual editors for specifying scenarios.
Although DSM tools support most of the needs
we mentioned, we also need tools for supporting
some bridges between the future communities.
These tools would have to transform learning
scenarios produced by a DSM-based instructional
design editor (conforming to a dedicated VIDL) to
another format compatible with another DSM-based
editor (dedicated to another VIDL). Such
transformations tools exist from the MDE domain.
(Abdallah et al., 2008) have already experimented
some of these tools: the ATL tooling has been used
to transform learning scenarios conformed to a
Project-based and collaborative pedagogy, towards
Moodle-specific scenarios. We plan to experiment
more with these transformation tools.
5.3 Illustration and First Results
We are currently experimenting an Eclipse project,
the Graphical Modeling Framework (GMF) (Eclipse,
08), to support the DSM approach for learning
scenarios. Its goal is to form a generative bridge
between EMF and GEF, two other Eclipse meta-
modeling projects, whereby a diagram definition is
linked to a domain model as an input to the
generation of a visual editor.
Among the various case studies we have
experimented with GMF, we sketch the following
one. Some practitioners have expressed these
pedagogical expressiveness and notation needs: a
UML' UseCase-like diagram that permits to express
performing relations between roles and learning
activities at a high-level of abstraction. Also, the
practitioners would like to express precedence /
following relationships between the learning
activities. Because the UML UseCase diagram is not
able to express time-related relationships between
usecases, our work consisted in providing these
practitioners with a dedicated visual editor, built
using GMF, able to express such scenario
representation. Also, we decided to provide them
with a specific VIDL guarantying that the produced
models will be both human-readable for them but
also machine-interpretable for further usages.
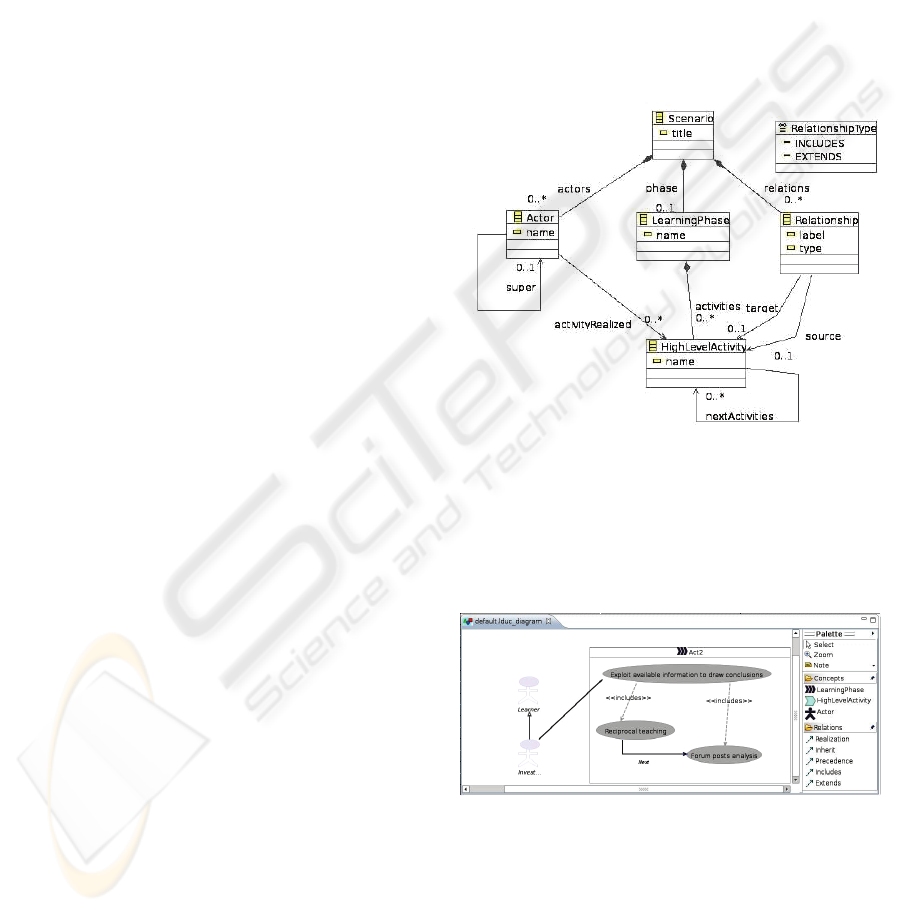
Figure 2: The 'Learning-UseCase' meta-model (or domain
model) experimentation.
A basic domain model for the « Learning Design
Use Case » view has been defined. It is illustrated
into figure 2 (a diagrammatic view of the concrete
domain model whose native format is XML).
Figure 3: Example of model designed with a specific
editor generated with the GMF DSM meta-tool.
According to the GMF engineering process, we
have successively designed a graphical definition
model, a tooling definition model, and a mapping
definition model. Finally, after a code generation
step, a specific editor (embedding the VIDL
dedicated to the practitioners' requirements) is
HOW TO SUPPORT SCENARIOS-BASED INSTRUCTIONAL DESIGN - A Domain-Specific-Modeling Approach
331

generated. Figure 3 shows a scenario graphically
realized with this editor (the human-readable
« view » ; because the scenario is concretely
serialized in a machine-interpretable format (XMI)).
6 CONCLUSIONS
We have presented and discussed a specific MDE
application for scenario-based instructional design.
The originality of our proposition resides in the three
categories for learning scenarios and languages: they
reflect different communities of practices sharing a
same business learning domain towards specific
objectives. We also propose a two-part division for
each category to distinguish the targeted public:
human or machines.
We have then argued our current orientation
about DSM techniques and tools. DSM is a model-
based approach giving domain experts the freedom
to use structures and logic that are specific to their
learning domain. Another originality of our position
is that we do not aim to provide practitioners with
yet another VIDL with its dedicated editor but we
aim to provide them with techniques and tools that
help and support them in specifying and building the
VIDL and editors they need.
We have also illustrated our first results about
the use of the GMF from the Eclipse project. These
first results have proved the ability of such DSM
tools to build specific VIDL and to generate user-
friendly dedicated editors. We are currently
improving our experiments of the DSM tools. We
are also experimenting model transformations tools
in order to support the design of 'bridges' between
different learning scenario communities of practices.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
These works are funded by the French MILES project and
the ANR LEA project.
REFERENCES
Abdallah, F., Toffolon, C., Warin, B., 2008. Models
transformation to implement a Project-Based
Collaborative Learning (PBCL) scenario: Moodle case
study. In Proceedings of ICALT'08. Santender, Spain,
IEEE. To appear.
Bézivin, J., Gérard, S., Muller, P-A, Rioux, L., 2003.
MDA components: Challenges and Opportunities. In:
Metamodelling for MDA.
Botturi, L., Todd Stubbs, S., 2007. Handbook of Visual
Languages for Instructional Design: Theories and
Practices. Information Science Reference. ISBN-13:
978-1599047317.
Caron, P.-A., 2007. Web services plug-in to implement
"Dispositives" on Web 2.0 applications. In
Proceedings of EC-TEL'07. Crete, Greece. Springer
LNCS.
Dodero, J. M., Díez, D., 2006. Model-Driven Instructional
Engineering to Generate Adaptable Learning
Materials. In Proceedings of ICALT'06, Kerkrade, The
Netherlands: IEEE.
Dodero, J.-M., Tattersall, C., Burgos, D., Koper, R., 2007.
Non-representational authoring of learning designs:
from idioms to model-driven development. In
Proceedings of ICWL'07.
Eclipse, The Eclipse Graphical Modeling Framework,
http://www.eclipse.org/gmf/, retrieved from 2008.
IMS, 2003. Learning Design Version 1.0 Final
Specification. Technical report.
Kelly, S, Tolvanen, J.-P. 08. Domain-Specific Modeling.
ISBN: 978-0-470-03666-2. Paperback. 427 pages.
March 2008. Wiley-IEEE Computer Society Press.
Kinshuk, Sampson D.G., Patel A., Oppermann R. (Eds),
2006. Special issue: Current Research in Learning
Design. Journal of ET&S. V(9)-1.
Laforcade, P., 2005. Towards a UML-based Educational
Modeling Language. In Proceedings of ICALT'05.
Kaohsiung (Taiwan), p. 855-859.
Laforcade, P., 2007. Graphical representation of abstract
learning scenarios: the UML4LD experimentation. In
Proceedings of ICALT'07. Niigata (Japan). pp. 477-
479.
Laforcade, P., Nodenot, T., Choquet, C., Caron, P.-A.,
2007. MDE and MDA applied to the Modelling and
Deployment of Technology Enhanced Learning
Systems: promises, challenges and issues. Architecture
Solutions for E-Learning Systems. Claus Pahl (ed.).
Martel, C., Vignollet, L., Ferraris, C., 2007. LDL for
Collaborative Activities. In Handbook of Visual
Languages for Instructional Design: Theories and
Practices, Information Science Reference, ISBN-13:
978-1599047317.
OMG, 2001. MDA specification guide version 1.0.1.
Report – omg/03-06-01.
Paquette, G., Léonard, M., Lundgren-Cayrol, K., Mihaila,
S., Gareau, D., 2006. Learning Design based on
Graphical Knowledge-Modeling. Educational
Technology & Society, 9 (1), 97-112.
Schmidt, D.C., 2006. Model-Driven Engineering, IEEE
Computer, 39 (2).
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
332
