
AN
EXTENSION OF PUBLISH/SUBSCRIBE
FOR MOBILE SENSOR NETWORKS
Hiroki Saito
Dept. of Infomation Systems and Media Design, Tokyo Denki Univ., 2-2 Kanda-nishiki-cho, Chiyoda-ku, Tokyo, Japan
Keywords:
Sensor networks, mobile computing, and publish/subscribe model.
Abstract:
The miniaturization of computing, sensing and wireless communication devices enable the development of
wireless sensor networks (WSNs). One of interesting research in sensor networks is utilizing moving nodes.
The benefit of the moving sensor nodes is to measure wide-ranging area by small number of nodes. De-
spite of the rapid development of the network protocols in mobile sensor nodes, the application platforms for
moving sensor nodes have not been much discussed. In this context, Publish/subscribe model is one of reason-
able solution with sensor networks. Publish/subscribe model has become a prevalent paradigm for delivering
data/events from publishers (data/event producers) to subscribers (data/event consumers) across large-scale
distributed network. In sensor networks, a user who is interested in the specific location and attributes can
send subscription to the system to receive all desired events. This paper proposes a novel schema that allows
us to control sensor nodes for location-based publish/subscribe system. In our schema, sensor nodes can be
deployed to the most effective location for event delivery.
1 INTRODUCTION
The miniaturization of computing, sensing and wire-
less communication devices enable the development
of wireless sensor networks (WSNs) (Estin et al.,
2001; Akyildiz et al., 2002), an new form of dis-
tributed computing where sensors deployed to gather
and report information about real world phenomena.
One of interesting research in sensor networks is uti-
lizing moving sensor nodes. For example, it allows
us to cover wide sensing area by mobility, to ob-
serve surroundings of 360 degrees with swiveled cam-
eras, and to receive reflections by on-demand sig-
nal transmitters. The benefit of the moving sensor
nodes is to measure wide-ranging area by small num-
ber of nodes. Since the moving sensor nodes gen-
erally consume much energy by positive movement,
the most important challenge is to develop the con-
trol schema regarding with wide-ranging area sensing
and energy efficiency. Several works have been de-
veloped in moving sensor nodes such as (Zhao and
Ammar, 2003; Zhao et al., 2004). These works are
mainly dedicated in data dissemination and simple
round-trip-like movement. Despite of the rapid de-
velopment of the network protocols in moving sensor
nodes, the application platforms for sensor nodes have
not been much discussed.
In this context, Publish/subscribe model is
one of reasonable solution with sensor networks.
Publish/subscribe model has become a prevalent
paradigm for delivering data/events from publishers
(data/event producers) to subscribers (data/event con-
sumers) across large-scale distributed network. In
typical Publish/subscribe system, subscribers register
their interests to the system using a set of subscrip-
tions, and publishers can simply submit information
to the system using a set of publications. Once re-
ceiving a publication, the system matches it to the
subscriptions and then delivers it to the interested sub-
scribers. In sensor networks, a user who is interested
in the specific location and attributes can send sub-
scription to the system to receive all desired events.
Conventional researches of sensor networks which
publish/subscribe architecture is applied have been
focued on routing algorithm (Costa et al., 2005) or
data manegement (Yang and Hu, 2007).
This paper proposes a novel schema that allows
us to control moving sensor nodes for location-based
publish/subscribe system. In our schema, sensor
nodes can be deployed to the most effective location
for event delivery. For example, the mobile sensor
node can move to where the subscriptions are con-
190
Saito H. (2008).
AN EXTENSION OF PUBLISH/SUBSCRIBE FOR MOBILE SENSOR NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - PL/DPS/KE, pages 190-193
DOI: 10.5220/0001889701900193
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Publish/
Subscribe
System
(Message
Broker)
Mobile Sensor
Nodes
Users
(Application
etc.)
Subscriptions
Data/EventsData/Events
Analysis of Subscription /
Sensor Deployment
Information
Figure 1: Extention of Publish/Subscribe Model.
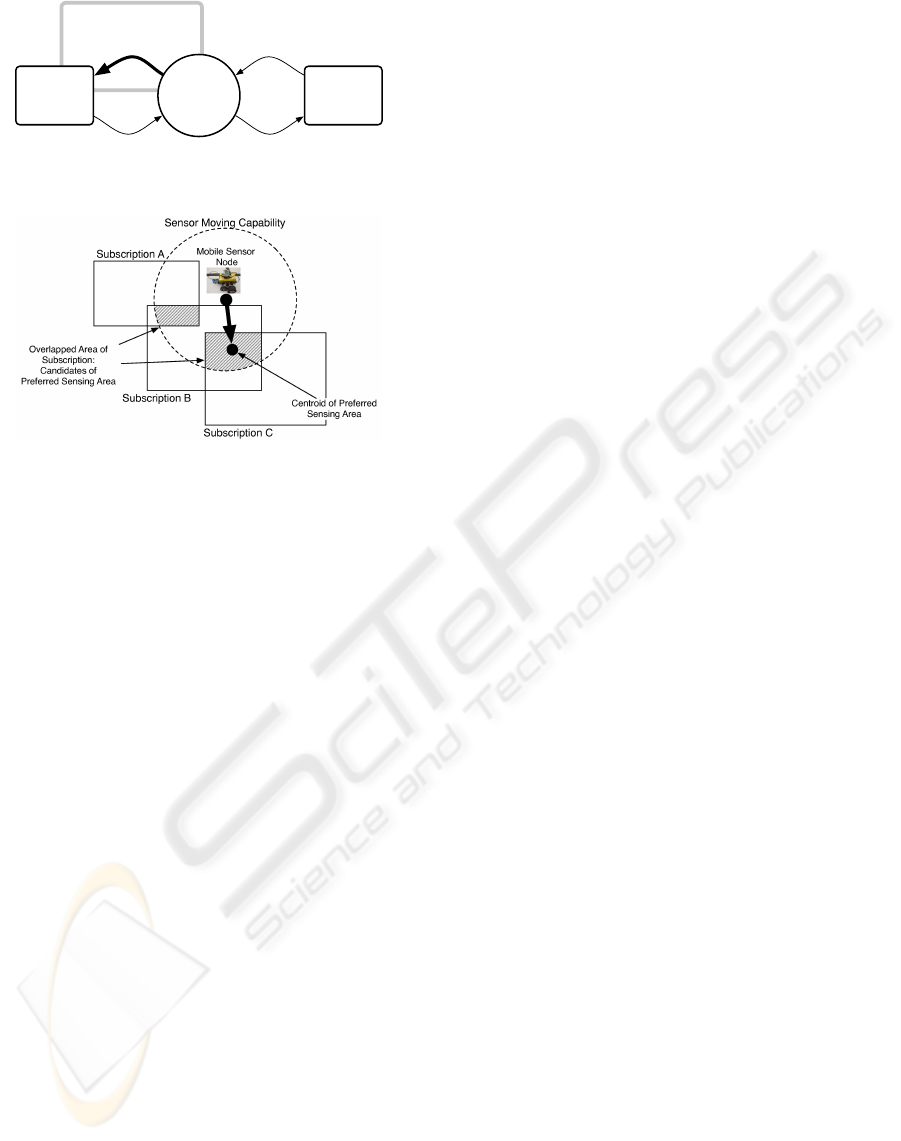
Figure 2: Candidate of preferred sensing area.
verged on. Also the swiveled 360 degrees camera sen-
sor can always focus to the center of the subscriptions.
2 PROBLEM STATEMENT
2.1 Moving Sensor Nodes
We assume that moving sensor nodes are deployed
to sensing space and are available to move to where
users desire to know (Dahlberg et al., 2005; Sibley
et al., 2002), and assume that all sensor nodes can
communicate to a base station. For example, sensor
nodes have the following features: (1) Mobile sensor
nodes enable to move directly to sensing point. (2)
Moving camera sensor nodes are fixed sensor nodes
which the observation camera is equipped. The cam-
era can focus to target object by swiveled it and zoom-
ing. (3) Active signal detection nodes are fixed sen-
sor nodes that receive reflections by on-demand signal
transmitters.
2.2 Publish/Subscribe Model
As described in (Fabret et al., 2001), a pub-
lish/subscribe schema can be defined as: PS =
{A
1
, A
2
, ..., A
n
}, where each A
i
represents an attribute.
Each attribute is defined by a name, a type and a do-
main. An event is a set of equalities on all attributes in
schema PS. A subscription is a conjunction of predi-
cates on one or more attributes, where each predicate
specifies a range for an attribute. An event e is sent
from a publisher, if a predicate of subscription s is
satisfied by value corresponding attribute contained
in event e, it matches a subscription s. In the pub-
lish/subscribe model mentioned above, the content
space of a publish/subscribe schema can be modeled
as a multi-dimensional space, where each dimension
represents an attribute.
3 EFFICIENT SENSOR
DEPLOYMENT SCHEMA
Figure 1 shows our concept of the extention of
publish/subscribe model. In conventional pub-
lish/subscribe model, publishers generally are not
aware of subscribers and data/events transfer, and
publishes simply send data/events. Compared with
that, in our schema, publishers are positively con-
trolled with subscribers.
It allows us to control moving sensor nodes which
can be deployed to the most effective location for
event delivery. In our schema, sensor nodes positively
measure the area where subscribers is interested in.
3.1 Location-based Map
It is necessary to consider a suitable data structure
for publish/subscribe system in location-based sensor
networks. In our schema, a multi-dimensional sub-
scription space is divided into location-based sensor
maps.
Consider a n-dimensional content space Ω =
{L, A
1
, A
2
, A
3
, ..., A
n
}, where L is range of location,
and A
i
is type of data and range of sensed data which
subscriber is interested in. Ω is divided into the maps
of each attribute and uniform location, that is, the
location-based map Λ
n
is defined as Λ
A
i
= {L, A
i
},
for each A
i
∈ Ω (1 ≤ i ≤ n).
3.2 Analysis for Preferred Sensing
Location
Since sensor nodes have the sensing range where it
can move, the method for estimating a preferred sens-
ing area is required. The following conditions should
be satisfy to determine preferred location where sen-
sors are deployed:
• The location where many subscribers are inter-
ested in.
• The largest area where subscribers are interested
in.
AN EXTENSION OF PUBLISH/SUBSCRIBE FOR MOBILE SENSOR NETWORKS
191

To determine the preferred sensing area which sat-
isfies the conditions, the following procedure is per-
formed:
1. For each sensor, let S to set of subscription which
is exist within range of sensing capability R.
2. For each subscription S, calculate the intersection
of S, let I to set of the most overlapped area.
3. Consider I = {I
1
, I
2
, I
3
, ..., I
n
}, for each I
i
, calcu-
late the intersection of I
i
and the sensing capabil-
ity R. The largest area of the intersection is pre-
ferred sensing area.
For example, figure 2 shows the overlap of sub-
scriptions and sensing capability. Each rectangle rep-
resents the subscriptions, and the circle represents the
sensing capability of the sensor node. There are two
overlapped areas of the subscriptions within the sens-
ing capability. These become candidates of the pre-
ferred sensing area. Since the intersection of Sub-
scription B and C is wider than another intersection,
the preferred sensing area is the intersection of sub-
scription B, C and the area of the sensing capability.
Then, the centroid of the preferred sensing area is cal-
culated, the sensor node move to the sensing point.
3.3 Algorithms
To install a subscription, the first of all, a multi-
dimensional subscription is divided location-based
subscription by its location and data types. The fol-
lowing algorithm is to produce location-based sub-
scriptions SL
Ai
= {L, A
i
} (L and A
i
represent location
and attribute respectively) from spliting a subscription
S = {L, A
1
, A
2
, ..., A
n
}.
Algorithm 1. Divide n-d Subscription to Location-
based Subscriptions.
Require: {L: location, A
1
, A
2
, ..., A
n
: attributes}
1: for each a ∈ A
1
...A
n
do
2: SL
a
← {L, a}
3: end for
4: return SL
a
And then, SL
Ai
is installed into the location-based
map Λ
Ai
. Since the location-based map should be
maintained overlapped subscription for calculating
the prefer sensing point, it consists of the multi-
layered map. The following algorithm is to install the
location-based subscription SL
a
to the location-based
map Λ
a
.
Algorithm 2. Subscription Installation.
Require: { SL
a
: location-based subscription regard-
ing with attribute a, Λ
n
: n-degree location-based
map}
Table 1: Simulation setup.
Size of sensed area 10,000 m × 10,000 m
Radius of moving capability
50 m
in mobile sensors
Radius of visibility
50 m
in swivel camera sensors
Energy for movement 1 J/m
Energy for rotation 1 J
Simulation time 10,000 sec.
0
200000
400000
600000
800000
1000000
1200000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Total events received by subscribers
Number of subscriptions
N=600 / Efficient
N=400 / Efficient
N=200 / Efficient
N=600 / Random
N=400 / Random
N=200 / Random
N=600 / No-move
N=400 / No-move
N=200 / No-move
Figure 3: Received events and subscriptions.
1: deg ← 0
2: S ← deg-degree subscriptions in Λ
a
overlapping
with SL
a
3: while S 6= φ do
4: for each s ∈ S do
5: t ← new subscription for intersection of SL
a
and s
6: for each b ∈ subscriptions linked from s do
7: link t and b
8: end for
9: link SL
a
and t
10: Λ
deg
.add(t)
11: end for
12: deg + +
13: S ← deg-degree subscriptions in Λ
a
overlap-
ping
with SL
a
14: end while
4 EVALUATION
We implemented the location-based pub-
lish/subscribe architecture in our simulator. We
use synthetic datasets in our simulation. Subscrip-
tions and sensor locations are generated based Zipfian
distribution.
The conditions of our simulation are listed in table
1. We scheduled 100,000 sensor events and 1000 sub-
scribers’ joining/leaving generated on randomly cho-
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
192
40000
60000
80000
100000
120000
140000
160000
180000
100 200 300 400 500 600 700 800 900 1000
Total energy consumed by sensors [J]
Number of subscriptions
N=600 / Efficient
N=400 / Efficient
N=200 / Efficient
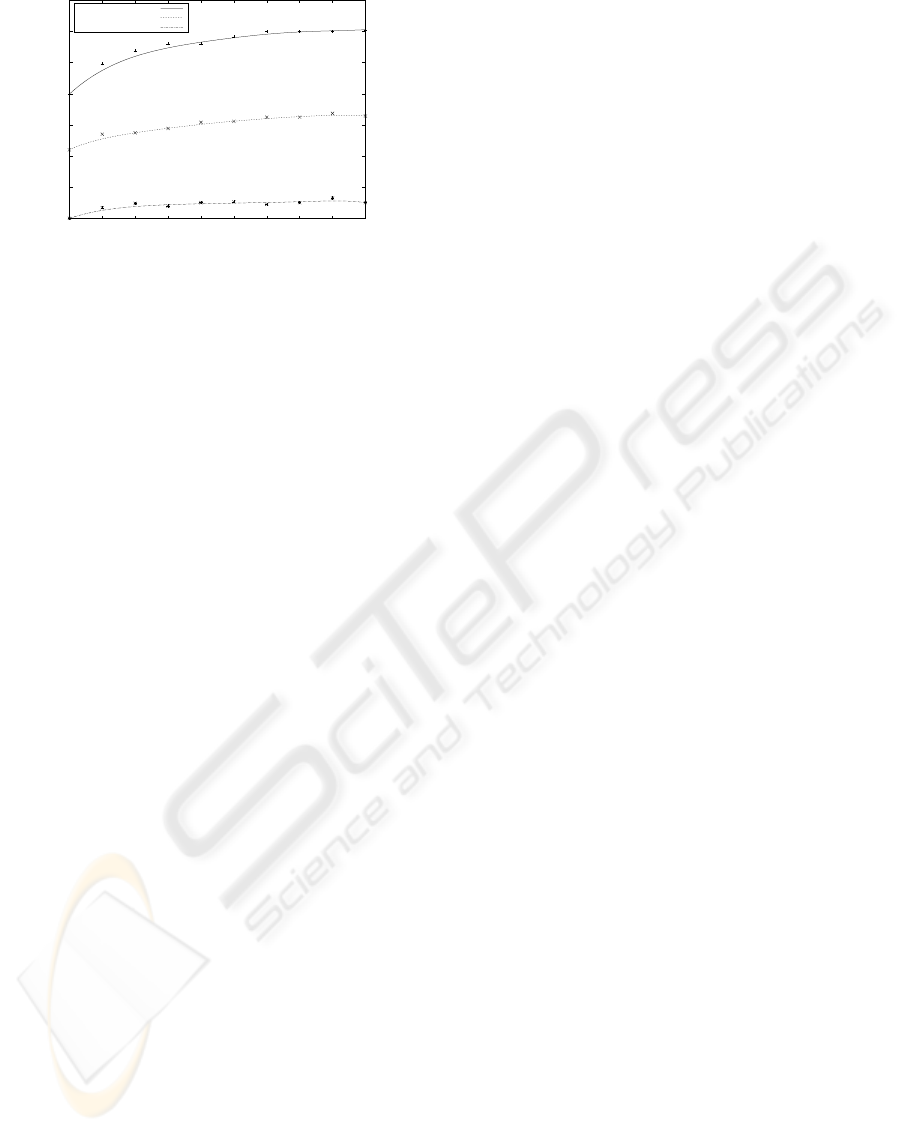
Figure 4: Consumed energy and subscriptions.
sen node/subscription.
The interval of events/joining/leaving is the pois-
son distribution. The cost model of energy consump-
tion is based on (Heinzelman et al., 2000; Goldenberg
et al., 2004).
We examine the following moving schema: (1)
Efficient (our proposed method), (2) Random, (3)
Static (No-movement) Figure 3 shows number of
events received by all subscribers. N represents the
number of sensor nodes. As compared with our model
and others, our model significantly increases the sens-
ing efficiency. Moreover, no siginifacant difference
is shown between the random model and the static
model. Therefore, the result shows that moving sen-
sor nodes without user consideration is not suitable.
Figure 4 shows the energy consumption in all sen-
sor nodes concerning the number of subscription. Al-
though rising the number of events by increasing sub-
scriptions, the energy consumption is almost constant.
Therefore, the result shows that our model is energy
efficient in increasing the number of subscriptions per
a sensor.
5 SUMMARY
This paper proposed a novel schema that allows us to
control mobile sensor nodes for location-based pub-
lish/subscribe system. In our schema, sensor nodes
can be deployed to the most effective location for
event delivery. Also, to confirm its effectiveness, the
simulation result are presented and discussed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by Research Institute for Sci-
ence and Technology, Tokyo Denki University, Grant
No. Q07J-02.
REFERENCES
Akyildiz, I. F., Shu, W., Sankarasubramaniam, Y., and
Cayirci, E. (2002). Wireless sensor networks: a sur-
vey. In Computer Networks Journal (Elsevier), Vol.
38, No. 4, pp. 393–422.
Costa, P., Picco, G. P., and Rossetto, S. (2005). Publish-
subscribe on sensor networks: A semi-probabilistic
approach. In Proceedings of IEEE International Con-
ference on Mobile Ad-hoc and Sensor Systems 2005
(MASS05).
Dahlberg, T. A., Nasipuri, A., and Tayler, C. (2005). Ex-
plorebots: A mobile network experimentation testbed.
In Proceedings of ACM SIGCOMM 2005 Workshop
on Experimental Approaches to Wireless Network De-
sign and Analysis (E-WIND 2005), pp. 76–81.
Estin, D., Girod, L., Pottie, G., and Srivastava, M. (2001).
Instrumenting the world with wireless sensor net-
works. In Proceedings of International Conference
on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP
2001).
Fabret, F., Jacobsen, H. A., Llirbat, F., Pereira, J., Ross,
K. A., and Shasha, D. (2001). Filtering algorithms and
implementation for very fast publish/subscribe sys-
tem. In Proceedings of ACM SIGMOD 2001, pp. 115–
126.
Goldenberg, D. K., Lin, J., Morse, A. S., Rosen, B. E., and
Yang, Y. R. (2004). Towards mobility as a network
control primirive. In Proceedings of ACM Interna-
tional Symposium on Mobile Ad-hoc Networking and
Computing 2004 (Mobihoc 2004).
Heinzelman, W. R., Chandrakasan, A., and Balakrishnan,
H. (2000). Energy-efficient communication protocol
for wireless microsensor networks. In Proceedings of
Hawaii International Conference on System Science
2000 (HICSS 2000), pp.1–10.
Sibley, G. T., Rahimi, M. H., and Sukhatme, G. S. (2002).
Robomote: A tiny mobile robot platfomr for large-
scale ad-hoc sensor networks. In Proceedings of IEEE
International Conference on Robotics and Automation
2002 (ICRA 2002), pp. 1143–1148.
Yang, X. and Hu, Y. (2007). A dht-based infrastructure for
content-based publish/subscribe services. In Proceed-
ings of IEEE International Conference of Peer to Peer
Computing 2007 (P2P 2007), pp. 185–192.
Zhao, W. and Ammar, M. (2003). Message ferrying: Proac-
tive routing in highpartitioned wireless ad hoc netroks.
In Proceedings of IEEE Workshop on Future Trends of
Distributed Computing System 2003 (FTDCS 2003).
Zhao, W., Ammar, M., and Zegura, E. (2004). A message
ferrying approach for data delivery in sparse mobile
ad hoc networks. In Proceedings of ACM MobiHoc
2004.
AN EXTENSION OF PUBLISH/SUBSCRIBE FOR MOBILE SENSOR NETWORKS
193
