
TOWARDS A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR
WEB APPLICATIONS
Tiago Garcia and Luís Morgado
ISEL - Instituto Superior de Engenharia de Lisboa, R. Conselheiro Emídio Navarro, Lisboa, Portugal
Keywords: Software Engineering, Multi-Agent Systems, Service Oriented Architectures, Web 2.0, Model-Driven
Architecture.
Abstract: In this paper we propose an approach that integrates multi-agent system architectures and service oriented
architectures to address web application modelling and implementation. An adaptation of the common three
tier architecture is used, with the intervening entities being agents and multi-agent societies. To address the
specificity of web applications subsystems, three distinct agent types are proposed, each with specific
concerns. A model driven approach is proposed to concretize the mapping between agent based and service
based layers.
1 INTRODUCTION
Since the beginning of information technologies
there has been an effort to overcome the complexity
of software production. The study, design,
implementation, support and management of
information systems has oriented IT evolution
through a path of complexity reduction by way of
numerous approaches.
However, nowadays, besides the growing
complexity other factors have emerged that need to
be addressed, such as the increasing system
dynamism. Despite the need for systems to be
lasting, integrated and updated, most software
continues to be written ignoring the constantly
changing infrastructure, constantly changing
requirements and the possibility of new
technological advancements.
At the forefront of liberating software
engineering from technological constraints, are
Service Oriented Architectures (SOAs). SOA
represents a new and evolving model for building
distributed applications. Services are distributed
components that provide well-defined interfaces that
process and deliver XML messages (Hasan, 2006).
They allow the development of information systems
that are based on services or business processes
which encapsulate application components or parts
in a loosely coupled way.
As mentioned earlier, one of the problems with
software development is the growing dynamism, and
in that sense SOAs are an advantage. SOAs are all
about reuse, and doing so in a simple, clearer,
structured and secure way. Moreover, if any changes
need to be done it will be simple, fast and
straightforward, without compromising the system’s
operation.
Despite these advantages in using a service
oriented architecture, services have complex
standards and tend to be static in their internal
processes and in the point-to-point communication.
Another concept that has the characteristics
needed to reduce software complexity and deal with
its increasing dynamism is the Multi-Agent System
(MAS) concept. Multi-Agent systems are
agglomerates of agents that communicate amongst
each other and are able to proactively coordinate
their activities in order to achieve local or system
level goals.
Analyzing the history and evolution of software
development, other paradigms played an important
role in order to address the increasing complexity of
software systems, namely: object orientation,
distributed object orientation and component
technologies, dynamic distributed computing
(service oriented architectures) and finally
autonomic computing (Kephart & Chess, 2003). The
last is not yet a trend but it has the characteristics
needed to face nowadays challenges and, as others
before it, adding another abstraction layer.
194
Garcia T. and Morgado L. (2008).
TOWARDS A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR WEB APPLICATIONS.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - PL/DPS/KE, pages 194-199
DOI: 10.5220/0001892301940199
Copyright
c
SciTePress
One area of application that could particularly
benefit from autonomic and multi-agent system
approaches is web application architecture.
In this paper we propose an approach that
integrates multi-agent system architectures and
service oriented architectures to address web
application modelling and implementation.
The paper is organized as follows: in section 2,
we present an overview of the proposed approach; in
section 3, we describe the mapping between the
abstraction layers defined; in section 4, we establish
comparisons with related work; and in section 5, we
draw some conclusions and directions for future
work
2 A MULTI-AGENT
ARCHITECTURE FOR WEB
APPLICATIONS
The web was initially created with the intent to share
documents in hypertext. With the growing interest
and consequent boom in users, many other uses have
come forth, and as a consequence many adaptations
and technologies or practices were added to the
initial standard. Moreover, the web has emerged
from a medium where few people centrally
determined what others had to use, and evolved to
one where very many people participate and jointly
create, publish and manage content (Vossen &
Hagemann, 2007). This attests the dynamic nature of
the current web, which has transformed itself from a
document repository that could only be consulted
and navigated (read), to a dynamic repository of
applications that can be accessed and managed in
real time (read/write). Examples of such applications
are blogs, wikis, forums or communities, just to
name a few.
This evolution and current direction of the web is
called web 2.0. O’Reilly (2005) defines the web as a
platform with a set of principles and practices.
Therefore, web 2.0 refers to the technologies and
methodologies that are now being used to allow the
web to be more participatory, more semantic, and
more real-time (Tenenbaum, J., 2005).
2.1 MAS Architectural Overview
The use of agents and Multi-Agent Systems is
motivated by their autonomous, adaptive nature.
Agents have the ability to perceive their
environment, process the collected information (with
more or less reasoning involved) and based on that
take action in their environment. This is in fact an
agent’s definition.
But what distinguishes agents from other
software entities, such as objects? The following list
shows the standout features of agents (Wooldridge,
M., 2002 and Jennings, N., Wooldridge, M., 1998).
• Autonomy – ability to, given a vague and
imprecise specification, determine how the problem
is best solved and then solve it, without constant
guidance from the user;
• Reactivity – ability to perceive the environment,
and respond in a timely fashion to changes that
occur in it in order to satisfy design objectives;
• Proactiveness – ability to exhibit goal-directed
behaviour by taking the initiative in order to satisfy
design objectives;
• Adaptability – ability to come to know user’s
preferences and tailor interactions to reflect these;
• Social Ability – ability of interacting with other
agents (and possibly humans) in order to satisfy their
design objectives.
2.1.1 Proposed Agent Model
To have the desired characteristics an agent model
needs to be defined. A proposal for such a model is
shown in Figure 1.
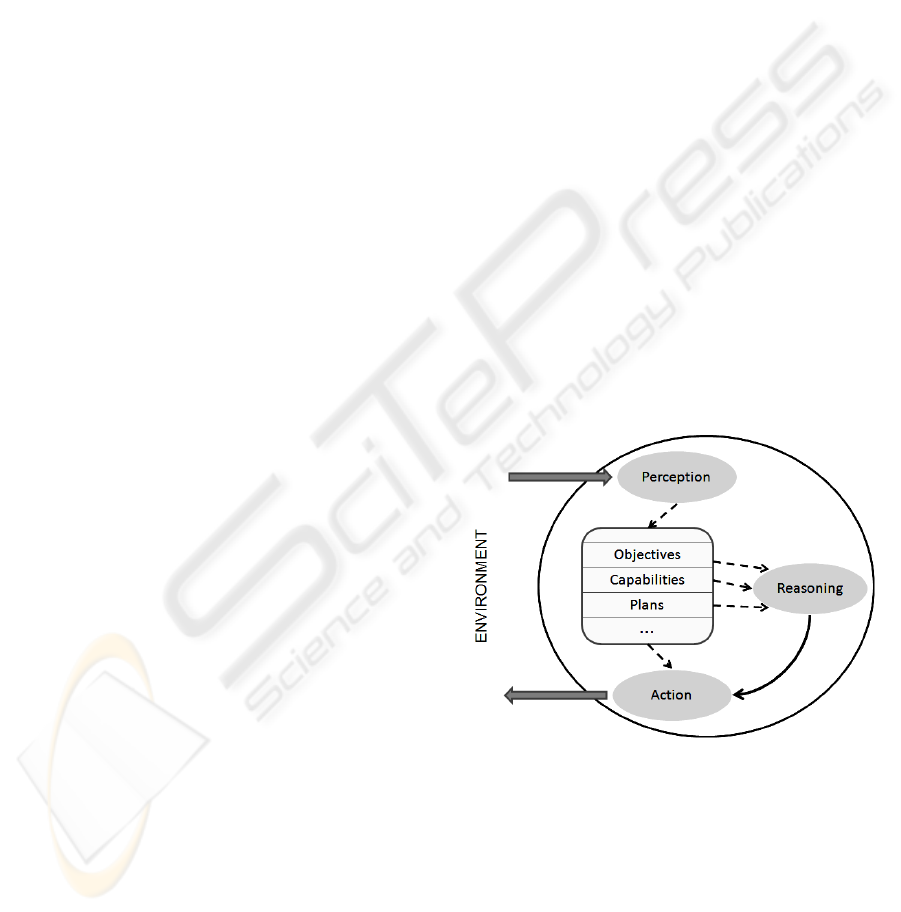
Figure 1: Inner Agent Model.
As shown in Figure 1, an agent is characterized
by three basic elements (Morgado & Gaspar, 2000):
(i) objectives – what the agent wants to achieve and
what is used to guide the agent’s reasoning and
acting operations in order to achieve them; (ii) plans
– defines the way in which the agent will attempt to
achieve its objectives; (iii) capabilities – are the
activities, primitive or non-primitive, that the agent
can achieve. Activities are the constituting elements
of a plan and can be themselves plans, which allows
TOWARDS A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR WEB APPLICATIONS
195
for the creation of hierarchies. There are 2 kinds of
activities, primitive and non-primitive. The first kind
is directly matched to an agent’s action, while the
last kind has no direct mapping to any action and
requires the agent to have a plan, which is composed
of other activities that the agent might not have in
his capabilities.
With MASs it is possible to take advantage not
only of the reasoning and autonomy of a single agent
but of a community of agents, which work together
communicating, and cooperating to achieve mutual
goals or even negotiating. Communication is the
prime feature of MASs, as it allows for dynamic
systems that might have a behaviour that goes from
being reactive to having reasoning and learning
skills. These characteristics of a MAS allied with the
proposed agent model make for a consistent social
interaction basis for the system.
As previously referred, a relevant issue with
MASs is communication, and finding a suitable
communication language that allows for a
knowledge level (Newell, 1981) interaction is of the
utmost importance.
Unlike services or other remote code invocation
techniques, which work on an information level,
agents and agent communication are not procedural.
This means that an agent doesn’t interact with others
by calling a procedure, instead, upon recognizing
that another agent has a desired capability, an agent
will establish contact and request for a service to be
granted, and in case of denial it will attempt to
negotiate. The explained scenario leads to the use of
speech acts theory, and an agent communication
language that is based on it. Speech act theory treats
communication as action. It is predicated on the
assumption that speech actions are performed by
agents just like other actions, in the furtherance of
their intentions (Wooldridge, 2002).
2.2 Proposed Architecture
The proposed overall architecture is based on the
common three tier architecture, with the intervening
entities being agents and multi-agent societies. To
address the specificity of web applications
subsystems, three distinct agent types are proposed,
each with specific concerns.
As shown in Figure 2, a three tier architecture is
used where one can find different types of agents
and a different notion of web applications, no longer
based on web servers or the constant loading of
pages.
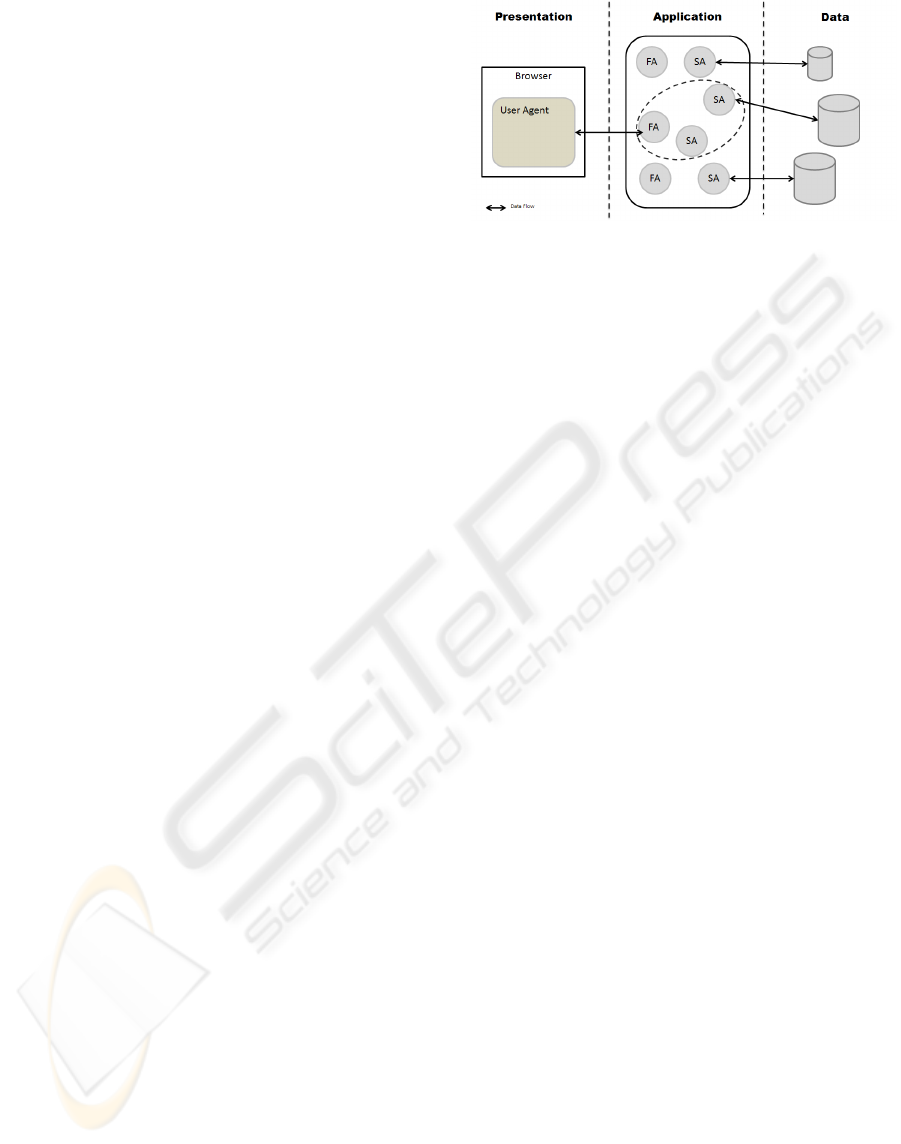
Figure 2: Overall architecture diagram.
We clearly identify three types of agents: (i) the
user agent or personal agent – the agent that is sent
to the user when a web application (site) is accessed,
making the bridge between the user interaction and
the web application located in a server or cluster of
servers; (ii) the facilitator agent (FA) or interface
agent – type of agent that receives the user agent’s
messages and processes them, elaborating a plan of
action to produce responses; (iii) finally, the service
agent (SA) or worker agent – agent that is
specialized in any particular type of service, from
accessing a data source, to interpreting or analyzing
data, to validating user ids, the possibilities are
numerous.
Also, as shown in Figure 2, the user agent (that
might be a MAS itself) communicates with a
facilitator agent (across the web), which translates
the request from the HTTP request (SOAP, AJAX,
etc.) to the speech acts-based agent communication
language, that may be defined by the engineer. Upon
receiving the message, the FA produces a plan of
action and makes the necessary arrangements,
communicating and establishing coalitions with the
service agents, to respond to the user agent’s
request. This is much in line with the proposed agent
model, in which an agent was described as having
plans that were made from hierarchies of activities.
For example, in Figure 2, the plan established by the
FA has some activities that are not in its capabilities,
so a coalition with two SA agents is made, and the
results of those coalitions managed by the FA.
2.2.1 User Agent
There is one particular situation in this architecture
that deserves a further explanation, and that is the
User Agent and its interaction with humans.
The first issue that needs to be dealt with is how
to send an agent across the web to the user’s
browser. There are several technologies that are
suitable for having a rich client-side web
application, and that may allow for agents to work
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
196
within a browser’s boundaries. JavaScript (AJAX),
Flash and Java Applets are examples of such
technologies.
Applets are probably the most complete of these
technologies because they can make use of the java
API, but their also the less integrated with the
browser and need the java virtual machine to run in
order for them to work.
Flash is known for allowing the construction of
animations and is typically used with a design
purpose. Also, similarly to Applets, it needs a Flash
Player to run in order for it to work, which, despite
being lighter than the JVM, is an upset.
AJAX on the other hand, is fully integrated to a
web browser, not requiring any plug-ins like Java or
Flash. But AJAX isn’t really a technology itself but
a technique that is a combination of standards-based
presentation using XHTML and CSS, dynamic
display and interaction using the Document Object
Model (DOM), data interchange and manipulation
using XML and XSLT, asynchronous data retrieval
using XMLHttpRequest, and JavaScript binding
everything together (Garrett, J., 2005). Compared
with Java Applets and Flash, AJAX is more in line
with the objective of this paper’s approach, which is
to facilitate the work of developers and improve user
experience.
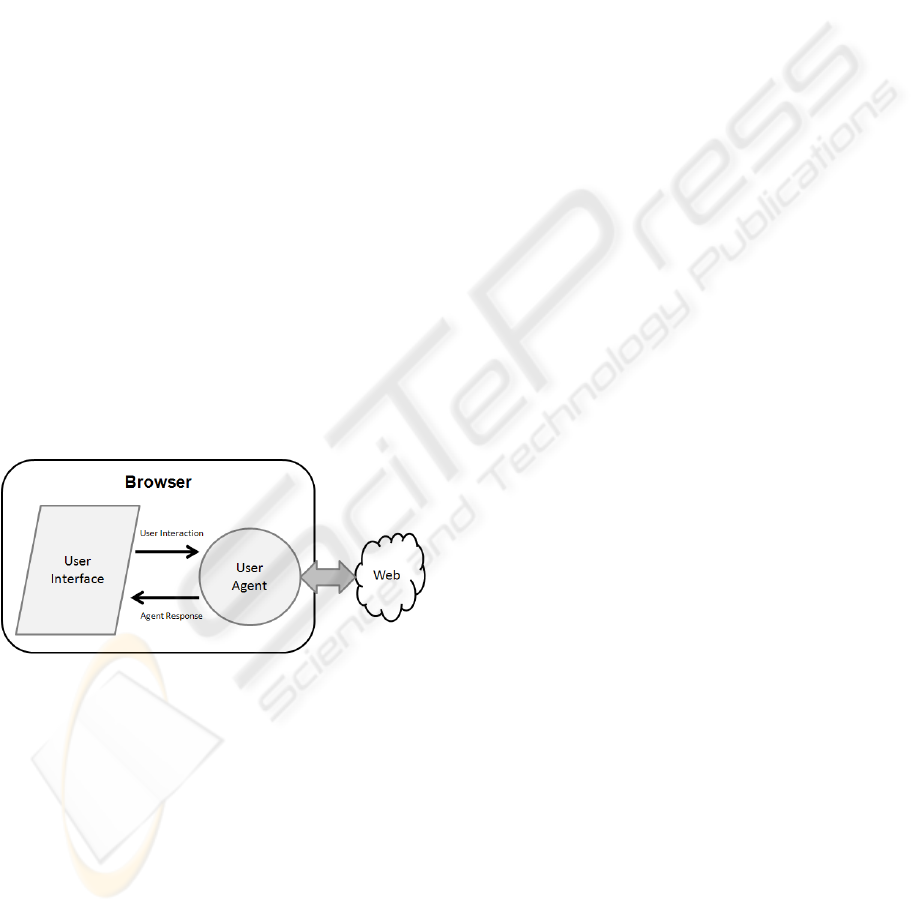
Figure 3 recreates the scenario of the user
agent’s environment.
Figure 3: User Agent’s environment interactions.
Once an AJAX user agent is at the browser it
will have to communicate both with the user
interface (web page) and with the multi-agent
server-side web application through the internet.
As was said earlier, agents will communicate
amongst each other by a speech acts-based agent
language. Nevertheless, the user agent can’t
communicate directly with the facilitator agents so
his messages will have to be supported by a web
format (in this case XML format), and later
translated by the facilitator agent to its original
format.
However, a user interface is not an agent. So
how will the agent interact with it? And how can the
page developer or designer guarantee that the page
will have the expected behaviour? To communicate
with the user agent, and so the agent knows what to
do in any given user input, the designer has to
announce in the HTML page what he wants to be
done. A way of doing so, and taking advantage of
the fact that the agent is in AJAX, is through
JavaScript methods. The designer will mark the
HTML page with JavaScript methods parameterized
in a way that is closest to a speech acts-based agent
language. In order to do so, a custom language must
be agreed on between the agent developer and the
designer.
On the other hand, the agent’s response will be
in the form of information presented in the page.
This is a more peaceful interaction, since the agent
already knows what the designer is looking to
achieve, and has information about the current user,
and the current state of the page, it will make a plan
that will finally resume to using AJAX properties
and techniques such as DOM and Dynamic HTML
(DHTML) to manipulate the page’s appearance.
Essentially, pages are the designer or engineer’s
way of communicating with the agent that will be
attributed to the user, and the agent’s response to
those markings will be presented as formatted
information on the page.
3 MAPPING BETWEEN
ABSTRACTION LAYERS
Agents and Multi-agent systems are at a higher level
of abstraction than the commonly used paradigms
such as object-orientation and service-oriented
architectures. However, being at a higher level
doesn’t mean that agents are about “out with the old
in with the new”, in fact they are both something old
and something new. Something new because of their
autonomy, reactivity, proactivity, adaptability and
social ability, as discussed before, and something old
because they make use of all the other abstraction
layers, when they access a data source, when they
invoke an object method, when they call for a
predicate, etc.
This suggests a mapping between the agent and
Multi-Agent layer, that are in a knowledge level
(Newell, A., 1981), and the service layer (which is
made out of objects, web services, remote procedure
calls, etc), that is on a service level.
TOWARDS A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR WEB APPLICATIONS
197
In a Model-Driven Architecture (Miller, J.,
Mukerji, J., 2003) one has the platform independent
model (PIM), which is not binding to any specific
platform but describes the system in as much detail
as possible, and the platform specific model (PSM),
which is the mapping from the PIM to the specific
technologies used to implement the various parts of
the systems. This mapping is achieved by defining a
set of transformation rules, which are to be applied
before the system is up and running and that
implements the modelled system over the desired
specific platform.
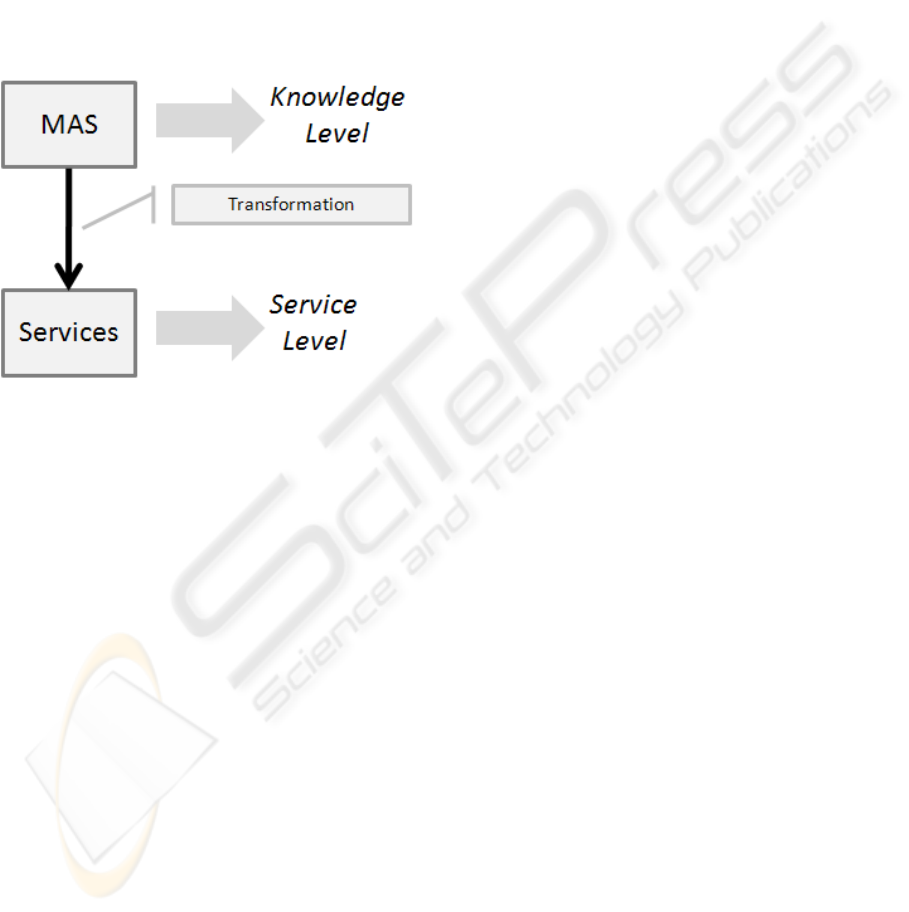
Figure 4: Layer Mapping Diagram.
Figure 4, shows a model-driven view to the
mapping in this scenario, where the Multi-Agent
System is the platform independent model, and the
Services are the platform specific model. In this case
the mapping isn’t made before the system is up and
running, in fact it is made while the system is
running and online.
While the system is running, the agents will
make plans to achieve their objectives and try to
follow them. Those plans, created dynamically and
at runtime, will have primitive and non-primitive
activities. Like a service, an activity is a behaviour
activation or execution to achieve a goal output.
Moreover, an activity (non-primitive) might be a
hierarchy of other activities, as a service might be a
composition of several other services. These
matching characteristics verify that by way of
services one can integrate agents and multi agent
systems with the lower level abstraction layers.
Clarifying, when an activity is non-primitive, it
will expand to other activities and possibly lead to
communication amongst agents in order to satisfy
them, but when it is primitive it will directly match
to an action. This action might go from accessing a
database, to adding two operators, to finding the
closest route between two points, and these actions
may be implemented in a stored procedure, an object
method or a predicate, which can be accessed via
services.
Services allow for the publishing of agents as
service providers that others can use and build upon.
Agents act as wrappers that involve services,
transforming them into rule based “knowledge
services” (Tenenbaum, J., 2005).
4 DISCUSSION AND RELATED
WORK
In this article, a Multi-Agent architecture for the
development of web applications is presented. Other
attempts and different approaches have come before,
that can in some ways relate to this work.
Andrea Bonomi et al (Bonomi, A., Vizzari, G.,
Sarini, M., 2006), propose an evolution from current
web development techniques to an approach using
agents. In this work web sites are interpreted as
graph–like spatial structure composed of pages
connected by hyperlinks, which they represented as
a Multi-Agent system in an Agent Server. The
objective was to keep track of users moving around
the web site, by having agents representing users at
server-side associated with the page that the user
was currently viewing. Also in this work, the term
User Agent is introduced, as the agent that is sent to
the browser and that, with the information related to
the user’s behaviour in a web site, adapts the output
to the browser. This approach still includes the
notion of web server and has the particularity of
keeping user’s session state in a form of an agent,
with the objective of tracking its steps.
In their work, Alexander Pokahr and Lars
Braubach (Pokahr, A., Braubach, L., 2007), use a
model-view-controller pattern to approach these
issues, but only introduce the Multi-Agent paradigm
at server side, in the controller. The interaction
between user and server is still made by a HTTP
request and the response in JSP format, which is the
view. Still, some interesting notions are mentioned
in the controller, such as the coordinator agent and
the application agent. The first one receives it input
from the servlet and communicates with the
application agent.
In another related work, by Hai Jin et al (Hai Jin,
Li Qi, Yong Zhou, Yaqin Luo , 2006), a
combination of WebOS, Grid and Agent technique
is presented as a way to build a virtual computer in a
distributed environment. The intention is to provide
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
198

a way for user to build Web applications. In this
work, as in the one before, there are no agents at
client-side, instead they are a part of the Gridows
Virtual Computer. In this virtual computer there are
various kinds of agents with distinct concerns
(Gateway Agent, Process Agent, Application Agent,
Storage Agent, etc), which can be interpreted as
specifications and different implementations of the
Service Agents or of the Facilitator Agents presented
in this paper.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, an agent model is presented with the
characteristics that allow the agents to be the
foundation of a Multi-Agent system to support the
particular nature of Web applications. An adaptation
of the common three tier architecture is used, with
the intervening entities being agents and Multi-
Agent societies. Because of the particularity of web
applications, three distinct agents are proposed, each
with its concerns.
Despite the definition of different kinds of
agents, the great advantage to this approach is that it
is adaptable and autonomous, in a sense that there
are no constraints in respect to the number of agents
in any function, and that this decision to increase or
decrease the number or agents has no impact to the
programmer or engineer. Multi-agent systems sort
things out via their communication capabilities.
Moreover, at server-side, there might even be agents
that are both facilitators and service agents, and what
was proposed as being agents in this paper can in
fact be Multi-Agent Systems that organize around a
similar objective and cooperate to achieve that goal.
Also, a model-driven approach is presented, in
which agents are the platform independent
components that map to services, which are the
platform specific components. This approach makes
clear that agents have not only the potential to be
autonomous and proactive and intelligent, but also
can act as integrators of all the lower layers of
abstraction, and doing so without human interaction.
Future research will aim at further refining the
infrastructural aspects of the model, namely the
support for agent coordination and dynamic service
composition.
REFERENCES
Bonomi, A., Vizzari, G., Sarini, M., 2006. A
Heterogeneous Multi-Agent System for Adaptive Web
Applications. In Proceedings of the 7th WOA 2006
Workshop From Objects to Agents. http://
ftp.informatik.rwthaachen.de/Publications/CEUR-
WS/Vol-204/P03.pdf
Erl, T., 2005. Service-Oriented Architecture: Concepts,
Technology, and Design, Prentice Hall.
Garrett, J., 2005. Ajax: A New Approach to Web
Applications. http://adaptivepath.com/ideas/essays/
archives/000385.php
Hai Jin, Li Qi, Yong Zhou, Yaqin Luo , 2006. Gridows:
The Great Integrator for Web Applications. In
Proceedings of the 2006 International Conference on
Hybrid Information Technology - Volume 02.
Hasan, J., 2006. Expert Service-Oriented Architecture in
C# 2005, APRESS.
Jennings, N., Wooldridge, M., 1998. Applications of
Intelligent Agents. In Jennings, N., Wooldridge, M.
(Eds.), Agent Technology - Foundations, Applications,
and Markets. Springer.
Miller, J., Mukerji, J., 2003. MDA Guide Version 1.0.1,
OMG. http://www.omg.org/cgi-bin/doc?omg/03-06-01
Morgado, L., Gaspar, G., 2000, A Social Reasoning
Mechanism Based on a New Approach for Coalition
Formation, Proceedings of the 15th European Meeting
on Cybernetics and Systems Research..
Newell, A., 1981. The Knowledge Level. In AI Magazine.
https://www.aaai.org/aitopics/assets/PDF/AIMag02-
02-001.pdf
O'Reilly, T., 2005. What is Web 2.0: Design Patterns and
Business Models for the Next Generation of Software.
http://www.oreilly.com/pub/a/oreilly/tim/news/2005/0
9/30/what-is-web-20.html
Pokahr, A., Braubach, L., 2007. An Architecture and
Framework for Agent-Based Web Applications. In
Multi-Agent Systems and Applications V, 5th
International Central and Eastern European
Conference on Multi-Agent Systems, CEEMAS 2007,
Proceedings. Springer.
Tenenbaum, J., 2005. AI Meets Web 2.0: Building the
Web of Tomorrow, Today. wiki.commerce.net/
images/a/a2/CN-TR-05-07.pdf
Vossen, G., Hagemann, S., 2007. Unleashing Web 2.0:
from concepts to creativity, Morgan Kaufman
Publishers.
Wooldridge, M., 2002. An Introduction to Multi-agent
Systems, John Wiley & Sons.
Kephart J., Chess D., 2003, The Vision of Autonomic
Computing, IEEE Computer 36(1).
TOWARDS A MULTI-AGENT ARCHITECTURE FOR WEB APPLICATIONS
199
