
TOOL OF THE INTELLIGENCE ECONOMIC: RECOGNITION
FUNCTION OF REVIEWS CRITICS
Extraction and Linguistic Analysis of Sentiments
Grzegorz Dziczkowski and Katarzyna Wegrzyn-Wolska
Ecole Superieur d’Ingenieurs en Informatique et Genie des Telecommunicatiom (ESIGETEL)
1,Rue de Port de Valvins 77-215 Avon-Fontainebleau Cedex, France
Ecole des Mines de Paris 35, rue Saint-Honore 77305 Fontainebleau, France
Keywords:
Opinion Mining, Sentiments Analysis, NLP, Recommender System.
Abstract:
This paper describes the part of recommender system designed for movies’ critics recognition. Such a system
allows the automatic collection, evaluation and rating of critics and opinions of the movies. First the system
searches and retrieves texts supposed to be movies’ reviews from the Internet. Subsequently the system carries
out an evaluation and rating of movies’ critics. Finally the system automatically associates a numerical mark
to each critic. The goal of system is to give the score of critics associated to the users’ who wrote them. All
of this data are the input to the cognitive engine. Data from our base allow making correspondences which
are required for cognitive algorithms to improve advanced recommending functionalities for e-business and
e-purchases websites. Our sesystem uses three different methods for classifying opinions from reviews critics.
In this paper we describe the part of system which is based on automatically identifying opinions using natural
language processing knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION AND ISSUE
With the growth of Web, e-commerce has become
very popular. A lot of website offer online sales or
give the possibilities for rating objects online, for ex-
ample the movies. While peoples like to check out the
recommendations of others users before creating their
own opinions those predictions become very useful
for the customers. To predict the potential choice Rec-
ommender System were created (RS). RS allows peo-
ple to do the choice without any personal knowledge
of alternatives. Algorithms for suggestion are based
on the experience and the opinion of other users. It is
helpful to find recommendations from people who are
familiar with the same problem, who have done their
choice in the past, whose perspective we value, or
who are recognized experts (Tarveen and Hill, 2001).
RS provides correspondences between the users
which have similar profile. A new user has to create
his profile. The RS will suggest a new limited choice
based on the similar taste of other users. RS proposes
the choice to the user which is based on correspon-
dences between the users’ tastes. The credibility of
the result of RS can not depend on commercial rea-
sons because it could make people distrustful. The
efficacy of such system depends of the data’s quality
and quantity. For this reason presented system fur-
nishes the users’ profiles which are necessary for al-
gorithms of cognitive engine. The main goal of the
developed system is to collect a huge base of reviews
critics and automatically associate marks which ex-
press sentiments of the writer. For each critic we asso-
ciate a new mark and a user profile. The result of this
treatment is creation of user’s profiles database. Our
system is based on statistic and semantic representa-
tion of documents. Our work is divided on extraction
and filtering the opinion from the text and on assign-
ment the mark to subjective sentences. The extraction
and information filtering consists of the identification
of quite precise information in a text in the natural
language and its representation in a structured form
(Panzienza, 1997).
The relative failure of the generic systems com-
prehension is well-known today. It should however be
recalled that these systems resulting from work of au-
tomatic treatment of the languages of years 1980 re-
ally made it possible to explore this generic approach
of the comprehension of text.. This is pushing a large
218
Dziczkowski G. and Wegrzyn-Wolska K. (2008).
TOOL OF THE INTELLIGENCE ECONOMIC: RECOGNITION FUNCTION OF REVIEWS CRITICS - Extraction and Linguistic Analysis of Sentiments.
In Proceedings of the Third International Conference on Software and Data Technologies - ISDM/ABF, pages 218-223
DOI: 10.5220/0001894402180223
Copyright
c
SciTePress

numbers of researchers to describe natural languages
in the same way as formal languages. Maurice Gross
(Gross, 1997) undertook with his team of the LADL
(French Laboratory for Linguistics and Information
Retrieval) the exhaustive examination of simple sen-
tences of French, in order to have reliable and quan-
tified data on which it would be possible to make rig-
orous scientific experiments. To exploit the linguis-
tic knowledge an application Unitex was created at
LADL (Paumier, 2003). Unitex is an environment of
enhancement used to build formalized descriptions to
broad coverage of natural languages and apply them
as texts of important size in real time. Unitex treat
in real time the texts of several mega-bytes for the in-
dexing of morpho-syntactic reasons, the search for set
phrases or semi-fixed phrases, and the production of
agreements and the statistical study of the results.
Another way to automatically express an opinion
from the text is a use of classifier. The statistics meth-
ods suppose that descriptions of the objects of the
same class are divided by respecting a specific struc-
ture of the class. Learning methods based on an exam-
ple are often used in information’s research on a large
group of text. Problems consist in constituting a rep-
resentative corpus of the field which we operate, and
to find the rules or to constitute an operational model
of this corpus. This model makes the system able to
predict the behaviour to adopt when a new candidate
arrives to classification. There was a lot of research
in classification of reviews to positive and negative
like the works of Turney, Littman, Dave, Lawrance,
Pang, Lee. Classifiers identify the well-known classes
to which belong the objects. The classifiers’ perfor-
mance depends of the model for each class of a base
learning (Turney and Littman, 2003), (Wiebe et al.,
2004).
2 LINGUISTIC RESOURCES
The linguistic resource to achieve the information re-
trieval and extraction are as follows: dictionaries, net-
works of the recursive transitions (local grammar, ta-
bles of lexicon-grammar.
The digital dictionaries employed by Unitex use
formalism of DELA. Numeric dictionaries describe
both the simple words and the complex words of
a language. Dictionaries associate the word with a
lemma and a series of grammatical, semantical and
inflexional codes.
Grammar is a representation of linguistic phenom-
ena by recursive transitions (RTN), formalism close
to that of the finite state automaton. Many studies
have highlighted the adequacy of automats on linguis-
tic problems. A transducer with a finite number of
states is a graph which represents a whole of entry
sequences, and associates sequences produced as an
output. Generally a grammar represents sequences of
words and produces linguistic information like the in-
formation on the syntactic structure.
A local grammar (Kamp, 1981) is an automaton
representation of the linguistic structures witch is dif-
ficult to formalize in lexicon-grammar tables or nu-
meric dictionaries. The local grammars, represented
in the forms of graphs, describe elements which con-
cern the same syntactic or semantic field. The linguis-
tic descriptions grouped together in the form of local
grammars are used for a large variety of automatic
processes applied to the text. Thus various methods
of lexical clarification were developed to implement
grammatical constraints described before using this
type of graph.
The corpora of text are represented by automats,
in which each state corresponds to a lexical analy-
sis. The linguistic phenomena are represented by lo-
cal grammar, and are then translated into finite state
automaton in order to be easily confronted with the
corpora of text.
Tables of lexicon-grammar are matrixes that out-
line the properties of all the simple verbs which are
described by syntactic properties. Each word having
almost unique behaviour, the tables give the grammar
of each element of the lexicon, which is why they
are called lexicon-grammar tables. With Unitex we
can build grammar from such tables. The lexicon-
grammar is a systematic description of the syntactic
and semantic properties of the syntactic factors that
is predicative verbs, nouns and adjectives. It is orga-
nized in groups of tables, which are associated with
the syntactic category like full verbs, verbs supports,
names, etc... A table corresponds to a particular syn-
tactic construction and gathers all the words enter-
ing this construction. Currently lexicon-grammar is
especially developed for the verbs and the predica-
tive phrases (Tarveen and Hill, 2001) (Turney and
Littman, 2003).
3 OVERVIEW OF GENERAL
APPROACH
Our system has modular architecture. The principle
tasks are: collecting the reviews from Internet, check-
ing if the text found is a review, assigning a mark to
the reviews and presentation of results. This paper
is focused on the marking critic’s module and more
precisely of linguistic method of classifying the re-
views. We developed three different methods for as-
TOOL OF THE INTELLIGENCE ECONOMIC: RECOGNITION FUNCTION OF REVIEWS CRITICS - Extraction and
Linguistic Analysis of Sentiments
219
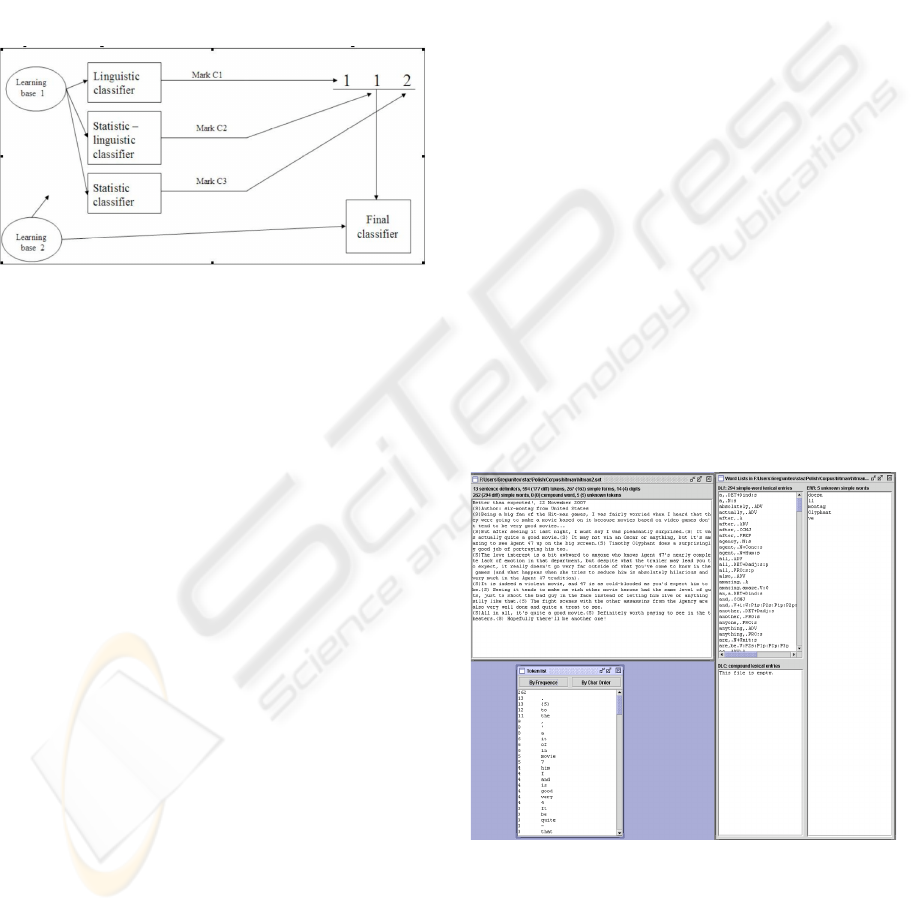
signing a mark to the reviews. These methods are
based on different approach of corpus classification.
For each method we developed a classifier which sep-
arately assigna a mark. At the end we obtained three
marks for one review which can be different. We
use another classifier which will assign the final mark
to the reviews based only on three marks get before
from classifiers (Dziczkowski and Wegrzyn-Wolska,
2007a), (Dziczkowski and Wegrzyn-Wolska, 2007b).
The process of assignment of the mark into the
critic is shown on figure 1.
Figure 1: The process of mark assignment.
For marking reviews we use three different ap-
proaches which are as follows:
• Linguistic classifier: For each sentence of reviews
we assign a rule of grammar that expresses inten-
sity of opinion.
• Statistic-linguistic classifier: Statistic researches
on linguistic data for determine behaviour of re-
views which have the same mark. The futures
are for example: characteristic words, sentence
length, corpus width, detection of negation, char-
acteristics expressions, special and special punc-
tuation. For entire corpus of reviews we calculate
the distance of the characteristics of new reviews
to the characteristics of the groups.
• Statistic classifier: Statistic research based on
classifier of Bayes which is a categorizer of the
probabilistic type founded on the theorem of
Bayes.
The work presented in this paper is foccused on
the linguistic knowledge using linguistic resource de-
scribed in section 2 (Cover, 1991), (Dave et al., 2000),
(Pang and Lee, 2004), (Wang et al., 2003).
4 LINGUISTIC CLASSIFIER
To perform the critics marking we have to get a group
of characteristic already evaluated - a learning base.
On different website we can find film critics with the
mark assigned (e.g. IMDB, Amazon). We used those
data (critics, users, marks) to create our learning base.
We use the scale of marking from 1 to 5. We re-
grouped all the critics by their mark. So we have ob-
tained 5 different groups of film’s critics: a group of
critics with score 1, 2 ... 5. For each group we build a
grammar. Grammar is based on learning base, which
contain about 2000 sentence for each mark’group
(Dziczkowski and Wegrzyn-Wolska, 2007b).
For this part we use a linguistic treatment which
require lexicons and specialized grammar. The de-
velopment of such resources is a long and tiresome
task, which generally requires an expertise on the
field approached and knowledge in data-processing
linguistics like techniques of filtering, categorization
of documents and extraction of information. Com-
prehension is seen as a transduction which transforms
a linear structure, i.e. text (the linear structure) is
transformed into an intermediate logico-conceptual
representation, which is then used to make conclu-
sions. The semantic analysis aims to produce a
structure representing as accurately as possible, a
unit of the sentence, with its meanings and its com-
plexity; then it has to integrate all structures into a
single textual structure. At the end, we obtain a
logico-conceptual representation of the text (Altai,
1992), (Kamp, 1981), (Alshawi, 1992). Semantico-
conceptual structures can be more or less broad,
rich and complex and more or less ambiguous (Dz-
iczkowski and Wegrzyn-Wolska, 2007a).
Figure 2: Linguistic resource: dictionaries.
This part of system was developed with Unitex ap-
plication, the example of linguistic resource used is
shown on figure 2, figure 3 and figure 4. We use a
linguistic analyser Unitex to pre-treatment, to lemma-
tise the words, to add synonyms, to detect negation,
to add semantic classes to the words and at least to
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
220

build complex local grammars. Semantic classes are
associated to the word and show polarity and inten-
sity of the word. For associate semantic classes to the
words we were based on subjective word dictionary -
General Inquirer Dictionary.
Figure 3: Linguistic resource: local grammar.
Figure 4: Linguistic resource: results.
The General Inquirer is a mapping tool. It maps
each text file with counts on dictionary-supplied cat-
egories. It combines the ”Harvard IV-4” dictionary
content-analysis categories, the ”Lasswell” dictionary
content-analysis categories, and five categories based
on the social cognition work of Semin and Fiedler,
making for 182 categories in all. Each category is
a list of words and word senses. Unlike some ar-
tificial intelligence programs that can be applied to
texts within limited topic domains, the General In-
quirer simply maps text according to categories and
does not search after meaning. General Inquirer map-
pings have proven to supply useful information about
a wide variety of texts. But it remains up to the re-
searchers, not the computer, to create knowledge and
insight from this mapped information, usually situat-
ing it in the context of additional information about
the texts’ origins. It contains 1,915 words of positive
outlook, 2,291 words of negative outlook. Below on
figure 5 is an example of General Inquire Dictionary.
Figure 5: General Inquire Dictionary.
The main purpose of linguistic classifier is the assign-
ing of the mark in harmony with sentiments contained
in the review. The assignment of mark is carrying
on sentence by sentence. In order to create rules of
grammar for each mark (in our case the mark from 1
to 5) the study of reviews from the learning base was
perform. In this way 5 grammars was created - one
for each mark. Each grammar contains a lot of rules
- local grammars. For each grammar more than 30
local grammars was created. In order to assign the
mark to the new opinion research is performed sen-
tence by sentence in order to find the rule correspond-
ing to the examined sentence. At the end of this treat-
ment we obtained selected sentences of new reviews
with corresponding rules. To obtain the final mark we
calculate the average of marks corresponding to main
grammars.
The constructions of local grammars were done in
manual way by analysing of reviews sentences with
the same mark associated. The local grammar can not
be to much general cause it makes the research too
much ambiguous. If the local grammars is too much
complex the application is doubtful. The local gram-
mars were created for detection the polarity and inten-
sity of opinion for one sentence. Other classifiers used
in our system perform the statistic classification. In
this classifier we just take care of form of local gram-
mars. Other more statistic futures like typical words,
typical expression, size of sentence the frequency of
characteristic word repetition, the number of punctu-
ation marks are not taken in account. Of course the
TOOL OF THE INTELLIGENCE ECONOMIC: RECOGNITION FUNCTION OF REVIEWS CRITICS - Extraction and
Linguistic Analysis of Sentiments
221
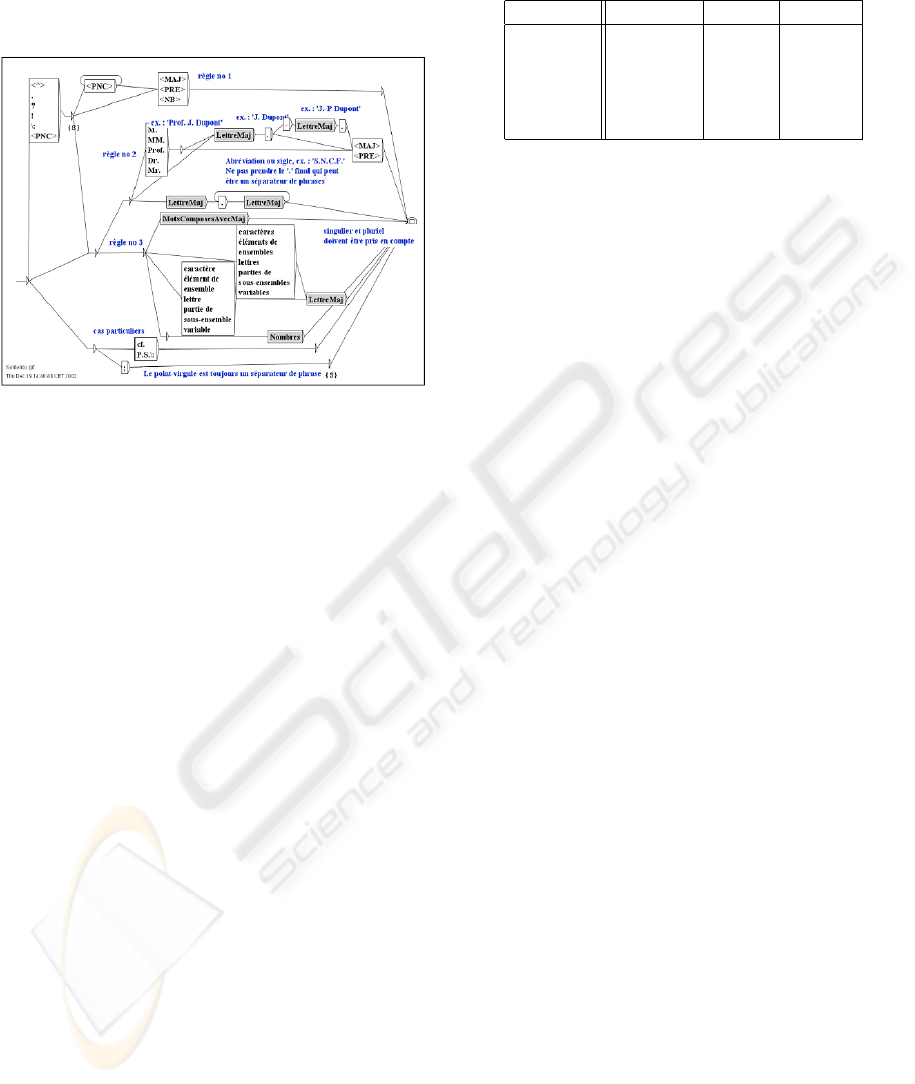
typical words are in dictionaries with semantic classes
and in local grammars, but the grammar must exist for
linguistic treatment. In figure 6 there we show an ex-
ample of local grammar.
Figure 6: Example of local grammar.
The creation of local grammar is a time-consuming
task. And it’s difficult to explain in scientific way
if the local grammars couldn’t be done better or on
which complex level we should stop. The grammars
used in our system were accordant in empiric way.
We start to create local grammars. Then we added the
level of complicity of local grammars and so on. For
each level we effected tests and calculated F-score.
The final result of our rules of grammars is chosen to
provide the best F-score. Unfortunately we can not
be sure that our choice is the most coherent. We took
into consideration that each classifier presented in our
system should have its own futures. In spite of all it’s
important to notify that linguistic classifier gives the
best results.
5 RESULTS
We carried out tests of presented linguistic classifier
for all groups of mark. The corpus of movie reviews
used in test contains 2264 sentences for a mark equal
to 5, 1957 sentences for 4, 1308 sentences for 3, 1925
sentences for 2, and 1835 sentences for 1. The results
are shown in Table 1.
We can see that the better results were obtained
for the extreme opinion - for the movies reviews with
a mark equal to 1 or 5. Results seem to be logical be-
cause extreme emotions are strongest, so it is easiest
to automatically mark and to judge them all. More-
over extreme reviews are most often longest so it sup-
ports the correct assessment. In spite of these im-
provements we made, we are still far from the ideal
Table 1: Experimental results.
Precision Recall F-score
Class 5 * 72.4% 83.4% 76.5%
Class 4 * 70.8% 82.4% 76.1%
Class 3 * 67.8% 71.6% 69.6%
Class 2 * 62.5% 55.9% 59%
Class 1 * 76.3% 84.2% 80.1%
case. According to our test results and since it is
necessary to start from the principle that more com-
plex and complicated grammars are needed, we no-
ticed that the linguistic classifier gives better results
that statistic or statistic-linguistic classifier.
6 CONCLUSIONS
Presented system caries out a collection of movies
critics and automatically assign a mark to each critic.
This system is a support of RS. The goal of our work
is to automate the whole system, particularly to im-
prove the estimation of individual user’s critics. The
system allows an automatically assignment of a mark;
however to increase the research on other fields it will
be necessary to create a linguistic base and a new
analyze of the different elements of the group’s be-
haviour.
We focused ourselves on the automatic search task
of information in a corpus, more precisely on the lin-
guistic analyse of sentiments. Our study was made
on the application ”Unitex” since it’s the tool that
makes it possible to carry out a major search by using
grammars, tables of lexicon-grammar and dictionar-
ies. Our objective was to prepare the data and creation
of complex local grammars.
We succeeded in the creation and the integration
of linguistic classier. This method made possible
to automatically assign a mark to the sentiments in
movies reviews. The adjustment of the linguistic re-
sources like the creation of the complex local gram-
mars or the adaptation of the dictionaries was an im-
portant part of our work to improve the linguistic clas-
sifier. We obtained satisfying results, but it is neces-
sary to specify that there remain several points to be
improved. The solutions from the automatic informa-
tion retrieval presented in this report give an image
of the complexity of this field and highlight the need
for making improvements and especially for opening
several doors in the domain of research.
ICSOFT 2008 - International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
222

REFERENCES
Alshawi, H. (1992). The core language Engine. MIT Press.
Altai, H. (1992). The core language engine. In ACL-MIT
Press Series in Natural language Processing. MIT
Press.
Cover, T. (1991). Elements of Information Theory. John
Wiley.
Dave, K., Lawrance, S., and Pennock, D. (2000). Opinion
extraction with hmm structures learned by stochastic
optimization. AAAI.
Dziczkowski, G. and Wegrzyn-Wolska, K. (2007a). Graph
based system purpose - built for automatic retrieval
and extraction of the electronics data. In Internet and
Multimedia Systems and Applications. ACTA Press.
Dziczkowski, G. and Wegrzyn-Wolska, K. (2007b). Rcss -
rating critics support system purpose built for movies
recommendation. In Advances in Intelligent Web Mas-
tering. Springer.
Gross, M. (1997). The construction of local grammars. In
Finite-State Language Processing. MIT Press.
Kamp, H. (1981). Evenements representations discursives
et reference temporelle. In Langages nb 64.
Pang, B. and Lee, L. (2004). Sentimental education: Senti-
ment analysis using subjectivity summarization based
on minimum cuts. In ACL.
Panzienza, M. (1997). Information extraction (a multidis-
ciplinary approach to an emerging information tech-
nology). Springer Verlag (Lecture Notes in Computer
Science), Heidelberg,.
Paumier, S. (2003). De La reconnaissance de formes lin-
quistique a l’analyse syntaxique. These, Marne-la-
Valee,.
Tarveen, L. and Hill, W. (2001). Beyond recommender sys-
tems: helping people help each other. In HCI in the
millennium. Addison-Wesley.
Turney, P. and Littman, M. (2003). Measuring praise and
criticism: Inference of semantic orientation from as-
sociation. In ACM Transactionon Information Sys-
tems. TOIS.
Wang, Y., Hodges, J., and Tang, B. (2003). Classification
of web documents using a naive baves method. IEEE.
Wiebe, J., Wilson, T., Bruce, R., Bell, M., and Martin, M.
(2004). Learning subjective language. computational
linguistics.
TOOL OF THE INTELLIGENCE ECONOMIC: RECOGNITION FUNCTION OF REVIEWS CRITICS - Extraction and
Linguistic Analysis of Sentiments
223
