
Simulation and Execution of Service Models
using ISDL
Dick Quartel
Telematica Instituut
PO Box 589, 7500 AN Enschede, The Netherlands
Abstract. This paper presents a technique and tool to simulate and execute ser-
vice models specified in the Interaction System Design Language (ISDL). This
language allows one to model the interacting behaviour of a service, at succes-
sive abstraction levels, and from the perspective of the different roles a system
can play in the service. A distinction is made between basic and composite
modelling concepts. Simulation is performed on the basic concepts of ISDL. In
this way, any composite concept that is defined as a composition of the basic
concepts can be simulated. Composite concepts can be added as shorthands to
ISDL. An example is the operation concept. In addition, ISDL allows model
elements to be stereotyped, such that they can be handled differently by the
simulator. The paper shows how web-service operations can be modelled in this
way, and be executed as part of the simulation of a web-service composition.
1 Introduction
Service-orientation is an emerging paradigm to handle complexity and promote re-use
in IT systems. Also at business level, service-orientation is being introduced in com-
bination with service delivery models as “Software as a Service” (SaaS) 26 to deal
with changing business requirements or to exploit new business opportunities. For
example, using a service as unit of functionality to structure business processes gives
more flexibility to outsource parts of the business, and thus to focus on core compe-
tences. Furthermore, new services can be introduced more easily and quickly by com-
bining existing services that are, possibly, provided by other business organisations.
To support the modelling, composition and analysis of services, we have devel-
oped a conceptual framework, called COSMO 23. In this framework, we define a
service as “the establishment of some effect through the interaction between two or
more systems”. This definition captures two main characteristics of a service. Firstly,
a service involves interaction between systems, typically service users and providers.
This interaction represents (part of) the external behaviour of the involved systems,
and abstracts from their internal functioning. Secondly, the interaction should provide
some value to the systems. This value is called the effect of the service.
The COSMO framework defines concepts to model services according to the defi-
nition given above, i.e., modelling their interacting behaviour and effect. These con-
cepts are structured along three axes as depicted in Fig. 1. The horizontal axis distin-
Quartel D. (2008).
Simulation and Execution of Service Models using ISDL.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Architectures, Concepts and Technologies for Service Oriented Computing, pages 52-64
DOI: 10.5220/0001899100520064
Copyright
c
SciTePress

guishes four aspects, i.e., information, behaviour, structure and quality, representing
categories of service properties that can be modelled. This classification corresponds
to aspects found in frameworks for enterprise architectures like GRAAL 9 and Ar-
chiMate 14. The diagonal axis distinguishes the roles of the systems involved in a
service: the user, provider and integrated role. The integrated role abstracts from the
distinction between a user and provider by considering interactions as joint actions,
thereby focusing on what the user and provider have in common.
The vertical axis distinguishes three reference abstraction levels at which a service
can be modelled: a goal models a service as a single interaction, where the interaction
result represents the effect of the service as a whole; a choreography refines a goal by
modelling a service as a set of multiple related, more concrete interactions; and an
orchestration implements a choreography as a composition of sub-services with a
central coordinator that invokes and adds value to these sub-services. During the
development of a service, these levels can be applied recursively. For example, an
orchestration may be designed by first identifying (internal) sub-goals, and subse-
quently refine these goals into choreographies of the sub-services being used.
Fig. 1. The COSMO framework.
Multiple models may be created during service development. These models have to
be analysed for consistency, such as the interoperability between different system
roles and the conformance between successive abstraction levels 24. The aim of this
paper is to present another analysis technique, namely simulation. Simulation is a
valuable technique in assessing correctness, but also to get insight in the interacting
behaviour of services. The simulation technique presented in this paper is based on
the Interaction System Design Language (ISDL). This language is used to model the
behaviour aspect of services, and allows bindings with existing languages, such as
UML/OCL (21) and OWL/SPARQ (16,22), to model the information aspect.
In addition, a tool called Grizzle has been developed to edit and simulate ISDL
models. This tool assumes Java as the information modelling language. An advantage
of using Java is that it facilitates the execution and implementation of ISDL models.
However, it also means that a mapping has to be defined from the information model-
ling language(s) being used to Java.
This paper is further structured as follows. Section 2 presents the behaviour and in-
formation concepts underlying ISDL. Section 3 explains how models constructed
from these concepts are simulated using Grizzle. Section 4 describes an extension to
53

Grizzle that enables the execution of choreographies and orchestrations of web ser-
vices. And section 5 discusses related work and presents our conclusions.
2 Service Modelling Concepts
This section presents concepts for modelling the information and behaviour aspect of
services. First, we present the basic concepts that represent the elementary service
properties and thereby determine the expressive power of ISDL. Next, we describe
how the basic concepts can be combined into composite concepts to facilitate the
modelling of frequently occurring compositions of service properties.
2.1 Basic Information Concepts
The effect of a service refers to elements in the subject domain of the systems in-
volved in a service. This subject domain comprises the entities and phenomena in the
real world that are identifiable by the systems. We use an information model to model
a system’s subject domain. This information model consists of
• individuals that represent the entities and phenomena from the subject domain;
• classes that represent the types of the entities and phenomena; and
• properties that represent the possible relations between classes and individuals.
Since these concepts underlie description logics 2, we often use OWL-DL in combi-
nation with SPARQL to represent information models and pre- and post-conditions
on the state of an information model.
In this paper, we use UML class diagrams to represent information models. The
concept of class maps to a UML class, the concept of property to a UML association,
and the concept of individual to a UML class instance (or object). To represent pre-
and post-conditions on the state of an information model, a natural choice would be
OCL. However, to facilitate execution of these conditions during the simulation of
service models, we have to map the UML class diagrams and OCL conditions onto
Java. We have implemented this mapping using the Octopus tool 19, but its explana-
tion is outside the scope of this paper. In fact, by using proper naming conventions
Java expressions may be easier to understand than OCL expressions. For these rea-
sons, we have chosen in this paper to represent conditions on the state of an informa-
tion model directly in Java.
2.2 Basic Behaviour Concepts
The behaviour of a service consists of the interactions between the systems involved
and the relationships between these interactions. To model this behaviour the con-
cepts of interaction and causality condition are introduced. In addition, we introduce
the concept of action as a useful abstraction of an interaction.
54

Interaction Concept. An interaction represents an activity in which two or more
systems produce some common result in cooperation. The interaction concept only
considers the possible result that can be produced, and abstracts from how this result
is achieved. Consequently, an interaction is considered an atomic activity that either
occurs and establishes the same result for all involved systems, or does not occur for
any of the systems and therefore does not establish any result.
Each system may have different expectations of or responsibilities in the estab-
lishment of the interaction result. This is modelled by defining an interaction as the
composition of two (or more) interaction contributions, one for each involved system.
An interaction contribution represents the participation of a system in the interaction,
by defining the constraints this system has on the possible interaction result. For ex-
ample, Fig. 2(i) depicts a purchase interaction between a customer and a retailer.
Interaction contributions
buy and sell represent the participation of the customer and
retailer in this interaction, respectively. The associated text boxes define the informa-
tion attribute of the interaction contributions, which consists of a declaration part
(upper part of the text box) and a constraint part (lower part of the text box). The
declaration part defines the type of interaction result by referring to some class in the
information model, followed by the attribute name. The constraint part defines the
result constraints that must be satisfied by the interaction result, which are repre-
sented by Java expressions. In this case, both the customer and retailer want to estab-
lish a purchase order as the interaction result. The customer wants to pay a maximal
price of 650 (say) Euro, and wants the order to be delivered within 5 (say) days. The
retailer, however, is only willing to accept orders with a minimal price of 500 Euro
and needs more than 2 days to deliver. The constraint “
o.article = ...” denotes that the
customer should define the article it wants to order. The retailer requires that this
article should be in its catalogue. The associated information model is presented later
in Fig. 4(ii).
Fig. 2. Purchase interaction.
The purchase interaction can only occur if the constraints of both the customer and
the retailer can be satisfied. In case multiple results satisfy the constraints, only a
single result (individual) is established. Since the interaction concept abstracts from
how to select the result, the result is assumed to be selected non-deterministically.
Action Concept. An action represents an activity that is performed by a single sys-
tem. Similar to an interaction, an action has an information attribute defining the type
of the action result and the constraints on this result. The action concept can be used
to model an interaction from the perspective of an integrated role, i.e., abstracting
from the distribution of responsibilities over the user and provider roles, thereby
considering the systems that perform these roles as a single system. This role is useful
as an intermediate step during design and facilitates certain types of analyses. Fig.
55

2(ii) depicts an action that models the purchase interaction from an integrated per-
spective. The result constraints are equal to the conjunction of the constraints of con-
tributions
buy and sell, since the purchase can only occur if all constraints are satisfied.
Causality Condition Concept. Relations between activities can be modelled in dif-
ferent ways, e.g., in terms of state transitions or temporal relations. We model rela-
tions in terms of causality relations. A causality relation defines for each activity a so-
called causality condition, which defines how this activity depends on other activities.
An activity is enabled, i.e., allowed to occur, if its causality condition is satisfied.
Three basic conditions are distinguished, as depicted in Fig. 3: (i) enabling condition
a to define that some activity a must have occurred before another activity b can oc-
cur, (ii) a disabling condition
¬
a to define that activity a must not have occurred be-
fore nor simultaneously with another activity
b, or (iii) a start condition to define that
an activity is allowed to occur from the beginning of a behaviour and is independent
of other activities. These basic conditions can be combined using the (v) conjunction
(and-) and (vi) disjunction (or-) operators to represent more complex causality condi-
tions.
a b
int i
int i
i = a.i+1
a.i < 5
a b
(i) enabling
a b
(ii) disruption
b
(iii) start (iv) reference
a
b
a
b
(v) and (vi) or
Fig. 3. Basic causality conditions.
Fig. 3(iv) also shows that some action b that is enabled by another action a may refer
to the result of
a. In this case the result constraint of b defines that its result is equal to
the sum of the integer value of
a and the value 1. In addition, a so-called causality
constraint is linked to the enabling relation of
b, which defines that b is only enabled
if the result value of
a is smaller than 5. Compared to a result constraint, a causality
constraint is only concerned with the results of actions that enable
b and not with the
attributes of
b itself. The conjunction of the causality condition that a must have oc-
curred and the causality constraint
a.i<5 defines a pre-condition for the occurrence of
b. Instead, the result constraint i = a.i+1 defines a post-condition on b.
Behaviour Concept. To represent multiple related activities, the behaviour concept is
introduced. A behaviour is associated with some system and defines the activities that
are performed by this system, including the relationships between these activities.
The activities that can be defined are actions and/or interaction contributions. A be-
haviour is graphically expressed as a rounded rectangle. Fig. 4(i) depicts as an exam-
ple a choreography between a customer, retailer, payment provider and shipper. The
integrated perspective, as shown in
Fig. 4(iii), makes clear that all interactions occur
in sequence. Although the customer is willing to contribute to interactions
pay and
deliver concurrently, the composite behaviour of the retailer, payment provider and
shipper enforces that the order should be paid before it is delivered. Behaviour
Shipper
also illustrates the instantiation of a sub-behaviour
s, in this case a recursive instantia-
tion since the type of s is
Shipper. This means that after an order has been delivered, a
new instance of behaviour
Shipper can be executed.
56

2.3 Composite Concepts
The basic concepts introduced above can be composed into so-called composite con-
cepts to model frequently-used combinations of service properties. Several composite
concepts have been added to ISDL to facilitate the modelling of services. Here we
present some of them: activity relations, operations and behaviour repetition.
Customer
Payment provider
Retailer
select
checkout
select
checkout
notify
notify
paypay
ship
Order o, Address a
o.article = select.la;
o.price = sum(select.la)
List<Article> la
List<Article> la
Payment p
p.mark = checkout.o.id
la = ...
Order o,
Address a
a = ...
Shipper
deliverdeliver
ship
ShippingNote n
ShippingNote n
n.address = checkout.a;
n.order = checkout.o
ShippingNote n
ShippingNote n
n = ship.n
n.address =
checkout.a;
n.order =
checkout.o
Payment p
p.amount =
checkout.o.price;
p.mark =
checkout.o.id
Payment p
Payment p
p = pay.p
+id : string
+price : double
-deliveryPeriod : int
Order
+amount : double
+mark : string
Payment
+price : double
Article
ShippingNote
Address
1..n article
Shipper s
shipdeliver
select checkout pay notify ship deliver
(i) purchase choreography
(iii) purchase choreography - integrated
(ii) information model
order1
1
address1
Fig. 4. Example of a choreography.
Activity Relations. The basic conditions from Fig. 3 can be combined using the
conjunction (and) and disjunction(or) operators to represent more complex causality
conditions. In this way common relations between activities can be modelled. Fig. 5
depicts the (shorthand) notation for choice, disruption, interleaving and concurrency
relations, including their rewriting in terms of basic causality conditions.
Fig. 5. Common activity relations.
Operations. The basic interaction concept is not supported by communication mid-
dleware. Most middleware assumes the less expressive concept of message passing.
Fig. 6(i) models message passing as a send interaction followed by a receive interac-
tion.
Fig. 6(ii) depicts a shorthand notation for this model, which hides the role of
middleware. This shorthand is used in
Fig. 6(iii) to model an operation as a composi-
tion of three instances of message passing: the sending of an invocation, and the re-
turn of either an invocation result or a fault message.
Fig. 6(iv) depicts a shorthand
notation for an operation. The reply-return part and the fail-catch part are optional,
i.e., either one or both parts can be omitted, e.g., to model a one-way operation.
57
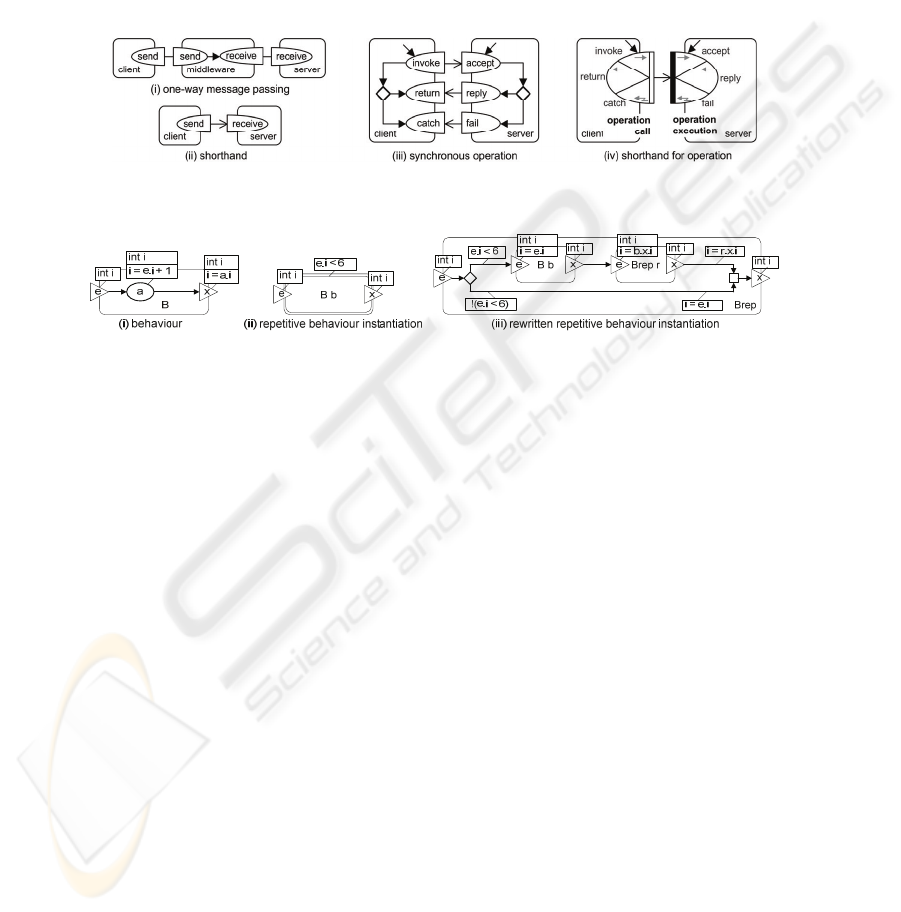
Behaviour Repetition. Fig. 7(ii) depicts the notation for the repetitive instantiation of
behaviour
B, as defined in Fig. 7(i). The meaning of repetitive instantiation corre-
sponds to the while construct of programming languages, with “
e.i < 6” representing
the while constraint. The triangles labeled
e and x represent so-called entry and exit
points, which are syntactical constructs to link a behaviour (instantiation) to other
behaviours or activities. Entry and exit points may have parameters to pass informa-
tion from one behaviour to another. Fig. 7(iii) shows how the composite concept of
repetitive behaviour instantiation can be rewritten to the basic concepts using recur-
sive behaviour instantiation (the choice can be rewritten using Fig. 5(ii)).
Fig. 6. Message passing and operation.
Fig. 7. Repetitive behaviour instantiation.
3 Simulation of Service Models
Simulation of an ISDL model is performed on the basic concepts as presented in
sections 2.1 and 2.2. This reduces the complexity of the simulator, but requires that
composite or specialized concepts have to be rewritten to the basic concepts. These
rewritings have been automated using transformations, which are executed automati-
cally upon the start of a simulation. Therefore, a requirement on the introduction of
new composite concepts in the ISDL language is that such a transformation is de-
fined. This also enforces consistency and compliance with the language.
The simulator that is part of the Grizzle tool captures the semantics of ISDL faith-
fully. Essentially, the simulator has to check for each simulation step which activities
are enabled. Two aspects of the ISDL semantics are highlighted here: its causality and
interaction semantics. For an elaboration on this, we refer to 25.
Causality Semantics. ISDL has a causality-based semantics, which allows one to
model causal dependencies between activities. In the absence of any causal depend-
encies, activities are considered independent and therefore can occur concurrently.
This has the following consequences for simulation:
• an activity
b and its result can only be referred to by another activity a, if a caus-
ally depends on the occurrence of
b, i.e., a depends directly or indirectly on ena-
bling condition
b. In contrast, an interleaving semantics would allow an activity
58

to refer to any activity that temporally preceded the occurrence of this activity.
Furthermore, the disjunction (or-) operator can be used to define alternative
causal dependencies that are established at run-time. Therefore, the simulation
status maintains the causal dependencies among the activities that have been exe-
cuted, i.e., which activities have enabled the occurrence of some activity. For ex-
ample, if
a refers to the result of b, but b does not enable a in the currently simu-
lated behaviour execution, then
a is not enabled. In fact, this is reported as a
modelling error, since a well-defined behaviour should not allow such a situa-
tion;
• a disabling condition
¬
b for some activity a defines a mutual dependency be-
tween
a and b, since the disabling condition imposes that both a and b can not oc-
cur simultaneously, which is a symmetrical condition. Because of this symmetry,
activity
b also depends on activity a. Two cases can be distinguished:
-
b depends on the non-occurrence of a through condition
¬
a; e.g., in case of a
choice relation between
a and b (see Fig. 5(i));
-
b depends on the non-occurrence or occurrence of b through condition
¬
a ∨
a
; e.g. in case of a disruption or interleaving relation between a and b (see
Fig. 5(ii) and (iii)). Note that
¬
a ∨ a is not equivalent to ‘true’ (like in boolean
algebra) or the start condition, since this would imply that
a and b are inde-
pendent.
Therefore, the simulation status maintains whether some activity
a has been caused by
the non-occurrence of some activity
b, i.e., disabling condition
¬
b, to enforce the
mutual dependency between
a and b. For example, assume that a has occurred. In this
case, activity
b could only occur later on during the simulation if it depends on a cau-
sality condition involving enabling condition
a.
Interaction Semantics. An interaction represents a kind of negotiation in which the
interaction contributions represent the negotiation constraints. The following basic
types of negotiation are distinguished:
• value matching, in which all involved contributions require one specific result
value of some type. For example, in Fig. 4(i) the retailer and payment provider
want to establish a payment with a specific mark to identify the paid order. A
similar constraint should be modelled for the price that has been paid;
• value passing, in which one contribution proposes a single result value of some
type and all other contributions accept all or multiple values of this type. For ex-
ample, in Fig. 2(i) the retailer accepts any article from the customer as long as it
is in its catalogue;
• value generation, in which none of the contributions propose a particular result
value, but instead accept all or multiple values of some type. For example, in Fig.
2(i) the constraints on the delivery period allows multiple values, i.e., the values
3 and 4, to be established.
Value generation is difficult to implement without making assumptions about the
Java types that are used to represent the interaction result type. In this case, the simu-
lation user is supposed to propose a value when selecting an interaction for execution.
Subsequently, the validity of this value is assessed against the constraints. An excep-
tion is the time attribute for which value generation is supported through the defini-
59

tion of a specific Java type. The time attribute allows one to model time constraints,
but is not considered further in this paper.
Now considering the simulation of some behaviour B, each simulation step consists
of the following sub-steps:
1. a preparation step, which determines the activities of B that are enabled, based
on the current simulation status;
2. the user interaction step, which colours the activities in the editing window.
Enabled activities are coloured green and executed activities are coloured yellow.
The user can select one of the enabled activities for execution;
3. the execution step, which executes the selected activity, and updates the simula-
tion status accordingly. After this step, the simulation returns to step 1.
Fig. 8 depicts the Grizzle tool in simulation mode. The editing window displays the
behaviour model and the colouring of activities. The simulation window displays the
simulation tree, which represents the hierarchy of super/sub-behaviours and their
activities that have been executed.
Fig. 8. Simulation window.
60

4 Execution of Service Models
The simulator provides two interceptors to invoke external application code during
the simulation of some activity:
• a preparation interceptor at the beginning of the preparation step; and
• an execution interceptor at the end of the execution step.
These interceptors are used to associate real web-service invocations with opera-
tion calls that have been stereotyped as web-service calls. Stereotype information can
be added to each activity and behaviour in ISDL. The stereotype information that has
to be defined for a web-service call comprises the location of the WSDL document,
the namespace URI, the port type name, and optionally the name of the operation in
case it differs from the name of the operation in ISDL. The Grizzle tool provides a
WSDL import function, which enables a user to import a WSDL specification. The
user can choose to either import a single operation, single port type or all port types.
Furthermore, the user may choose whether the web service should be considered from
a client or server perspective. Accordingly, a behaviour model is generated that repre-
sents the user (client) or provider (server) role of the web service in terms of opera-
tion calls or operation executions, respectively, including stereotype information. In
addition, an information model is generated consisting of Java classes that represent
the information types that are referred to by the operations in the behaviour model.
The transformation of WSDL to ISDL and Java is implemented using JAXB and
JAX-WS 13. Fig. 9 depicts an example of an operation call that models a web-service
invocation.
Fig. 9. Operation call stereotyped as web-service call.
In order to invoke the real web-service, stub-code is linked to the execution intercep-
tor of the
invoke part of the operation call. Upon execution of the invoke part in the
simulator, a request message is sent to the web-service. The content of this message is
defined by the attributes and constraints of the
invoke part. The stub-code is generated
automatically using JAX-WS. In addition, code is linked to the preparation intercep-
tor of the
return and catch parts of the operation call, to check if a response or fault
message has been returned by the web-service to the stub-code. If so, the
return or
catch part is enabled in the simulator, respectively. The contents of the response and
fail messages are represented by the attributes of the
return or catch parts of the opera-
tion call. This enables us to perform real web service invocations and incorporate the
results that are returned in the simulation. Fig. 10(i) illustrates the process of simulat-
ing a web-service operation call.
61
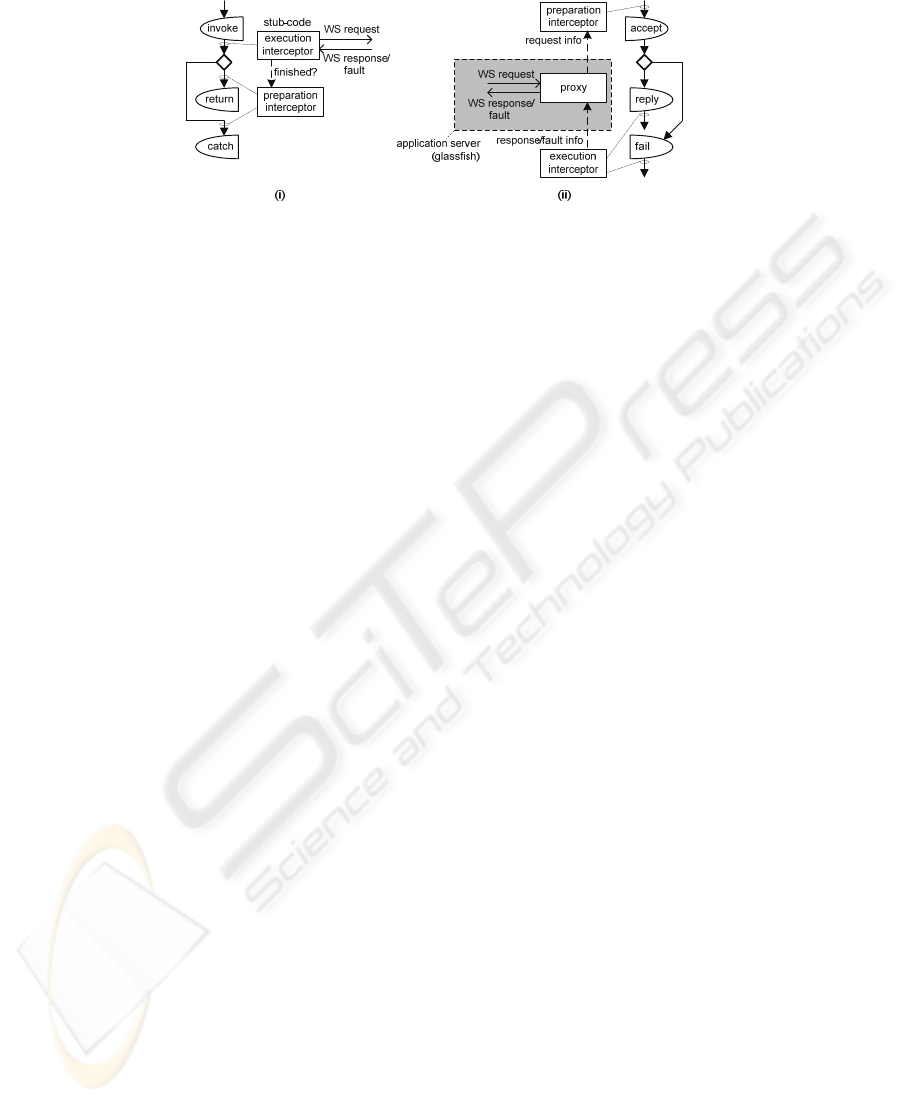
Fig. 10. Simulation of web-service operations.
Besides web service calls, the interceptors are used to enable external web-clients to
invoke a modelled web-service operation execution (see Fig. 6(iv)). A web service
proxy is automatically generated and deployed in an application server, again using
the aforementioned stereotype information. This proxy is responsible for handling the
reception of the invocation request and the return of the invocation result. In between,
the proxy delegates the calculation of the invocation result to the simulator, i.e., to the
preparation interceptor of the
accept part of the operation execution, which indicates
to the user that the operation is enabled. Subsequently, the proxy waits till the user
requests the simulation of the
accept part, followed by either the reply or fail part of the
operation execution. During these simulations steps, the result of the web-service
operation is determined based on the attribute constraints of the
reply and fail parts.
The resulting response or fault information is returned to the proxy by the execution
interceptor of the
reply or fail part of the operation execution, respectively. Fig. 10(ii)
illustrates the process of simulating a web-service operation execution. The applica-
tion server and simulator communicate via TCP.
The support for real web service calls and executions, allows one to use the simu-
lator as an orchestration engine in which a modelled orchestration can be executed by
simulating its ISDL model. This is particularly useful for testing purposes. However,
the simulator does not support important properties of an execution environment,
such as performance, monitoring, etc. Therefore, we can transform an orchestration
model to a BPEL specification that can be deployed on a standard BPEL engine 8.
5 Related Work and Conclusions
To support the modelling, composition and analysis of services, we have developed
the COSMO framework. There are a number of related conceptual frameworks, such
as WSMO 5, OWL-S 15, W3C’s Web Services Architecture 28, and SeSCE 6.
Among these frameworks, we consider OWL-S and WSMO as the most prominent
ones, both in terms of their expressiveness and the extent of usage and reference by
the research community. A comparison with these frameworks can be found in 23.
WSMO uses BPMO (Business Process Modelling Ontology) 4, which extends and
restricts the use of BPMN 20 to facilitate the graphical modelling of the behaviour of
web services. WSMO is mainly supported by two integrated development environ-
ments (IDEs), namely WSMO studio 31 and Web Service Modeling Toolkit 29.
62

These IDEs consist of several tools, e.g., for creating WSMO elements and reasoning
ontologies. All WSMO elements are specified as ontologies in the Web Service Mod-
eling Language (WSML) 30. To our knowledge no support is currently available
from these IDEs for the simulation of the behaviour of web services.
A few tools are available that support the modelling and analysis of service behav-
iours in OWL-S. 10 and 27 have developed an editor that supports the visual creation
and modification of OWL-S specifications. Composite processes are modelled using
a notation based on UML Activity diagrams. 18 have defined an execution semantics
for process models in OWL-S through a mapping onto Petri Nets. This mapping al-
lows for the analysis of process models, such as simulation, reachability analysis and
deadlock detection. The ISDL tool Grizzle also supports a mapping to Petri Nets, in
particular CPN Tools 7. Currently, this mapping is limited to services modelled from
an integrated perspective.
The relationship between the frameworks referred above and COSMO has been dis-
cussed in 23. In particular, COSMO is considered strong in behaviour modelling, at
multiple abstraction levels. To exploit and explore this strength, we have developed a
simulator for ISDL, which allows one to simulate service models. Simulation is based
on the basic, i.e., elementary concepts of ISDL. Composite concepts can be simulated
if they are defined as a composition of basic concepts. Typically, frequently-used
composite concepts are added as shorthands to ISDL. An example is the operation
concept. In addition, ISDL allows model elements to be stereotyped, such that they
can be handled differently by the simulator. In this way, web-service operations can
be modelled and executed as part of the simulation of a web-service choreography or
orchestration. The stubs and proxies that are required to support the execution of the
web-service operations are generated automatically.
In our future work, we want to extend ISDL with shorthands for some workflow 1
and interaction patterns 3. Furthermore, we will extend the simulator to support addi-
tional bindings with information modelling languages, in particular OWL and
SPARQL.
Acknowledgements
This work is part of the Freeband A-MUSE project (http://a-muse.freeband.nl), which
is sponsored by the Dutch government under contract BSIK 03025.
References
1. van der Aalst W, ter Hofstede A, Kiepuszewski B and Barros A. ‘Workflow Patterns’. In:
Distributed and Parallel Databases, 14(3), 2003, pp. 5-51.
2. Baader F, et al. The Description Logic Handbook: Theory, Implementation and Applica-
tions. Cambridge University Press. 2003. ISBN 0521781760.
3. Barros A, Dumas M and ter Hofstede A. Service Interaction Patterns. In: Proceedings of
the 3rd International Conference on Business Process Management, 2005, pp. 302-318.
63

4. Belecheanu R, et al. Business Process Ontology Framework. Deliverable 1.1. Project IST
026850 SUPER, 2007.
5. de Bruijn J, et al. Web Service Modeling Ontology (WSMO) – W3C Member Submission 3
June 2005. http://www.w3.org/Submission/WSMO/.
6. Colombo M, Di Nitto E, Di Penta M, Distante D, Zuccalà M. Speaking a Common Lan-
guage: ‘A Conceptual Model for Describing Service-Oriented Systems’. In: Proc. of the 3
rd
International Conference on Service-Oriented Computing (ICSOC), 2005, pp. 48-60.
7. CPNTools - Computer Tools for Coloured Petri Nets.
http://wiki.daimi.au.uk/cpntools//cpntools.wiki.
8. Dirgahayu T, Quartel D and van Sinderen M. Development of Transformations from Busi-
ness Process Models to Implementations by Reuse, In: 3th International Workshop on
Model-Driven Enterprise Information Systems, 2007, pp. 41-50.
9. van Eck P, Blanken H, Wieringa R. Project GRAAL: Towards Operational Architecture
Alignment. In: Int. Journal of Cooperative Information Systems 13(3), 2004, pp. 235-255.
10. Elenius D, et al. The OWL-S Editor – A Development Tool for Semantic Web Services. In:
Proc. of the Second European Semantic Web Conference (ESWC), 2005, pp. 78-92.
11. ElipseUML. http://www.eclipsedownload.com/.
12. ISDL. http://ctit.isdl.utwente.nl.
13. JAX-WS and JAXB. http://java.sun.com/webservices/technologies/index.jsp.
14. Jonkers H, et al. Concepts for Modelling Enterprise Architectures. In: International Jour-
nal of Cooperative Information Systems, vol. 13, no. 3, 2004, pp. 257-287.
15. Martin D, et al. OWL-S: Semantic Markup for Web Services - W3C Member Submission 22
November 2004. http://www.w3.org/Submission/OWL-S.
16. McGuinnes D and van Harmelen F. OWL Web Ontology Language Overview – W3C Rec-
ommendation 10 February 2004. http://www.w3.org/TR/owl-features/.
17. Milanovic N and Malek M. Current Solutions for Web Service Composition. In: IEEE
Internet Computing, Vol. 8, No. 6, 2004, pp. 51-59.
18. Narayanan S. and McIlraith S. ‘Simulation, verification and automated compostion of web
services’. Proceedings of the 11
th
International Conference on World Wide Web, 2002, pp.
77-88.
19. Octopus tool. http://www.klasse.nl/octopus/index.html.
20. OMG-BPMN, 2006. Business Process Modeling Notation Specification. dtc/06-02-01.
21. OMG-OCL. (2006) Object Constraint Language – Version 2.0. formal/06-05-01.
22. Prud’hommeaux E and Seaborne A. SPARQL Query Language for RDF - W3C Proposed
Recommendation 12 November 2007. http://www.w3.org/TR/rdf-sparql-query/.
23. Quartel D, Steen M, et al. COSMO: a conceptual framework for service modelling and
refinement. In: Information Systems Frontiers, 9 (2-3), 2007, pp. 225-244.
24. Quartel D and van Sinderen M. On interoperability and conformance assessment in service
composition. In: Proceedings of the Eleventh IEEE International EDOC Enterprise Com-
puting Conference (EDOC 2007), 2007, pp. 229-240.
25. Quartel D, et al. On Architectural Support for Behaviour Refinement in Distributed Sys-
tems Design. Journal of Integrated Design & Process Science, 6 (1), 2002, pp. 1-30.
26. SaaS. http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/SaaS.
27. Scicluna J, Abela C and Montebello M. ‘Visual Modeling of OWL-S Services’. Proceed-
ings of the IADIS Internation Conference WWW/Internet, 2004.
28. W3C. Web Services Architecture W3C Working Group Note 11 February 2004.
http://www.w3.org/TR/ws-arch/.
29. Web Service Modeling Toolkit. http://sourceforge.net/projects/wsmt.
30. Web Service Modeling Language, at http://www.wsmo.org/wsml/.
31. WSMO (Web Service Modeling Ontology) Studio. http://www.wsmostudio.org/.
64
