
TYPICAL PROBLEMS WITH DEVELOPING MOBILE
APPLICATIONS FOR HEALTH CARE
Some Lessons Learned from Developing User-centered Mobile Applications
in a Hospital Environment
Andreas Holzinger, Martin Höller, Marcus Bloice
Institute of Medical Informatics, Statistics and Documentation (IMI), Research Unit HCI4MED
Graz University Hospital, Auenbruggerplatz 2/V, Graz, Austria
Berndt Urlesberger
Department of Neonatalogy, Graz University Hospital, LKH-Universitätsklinikum, Austria
Keywords: Mobile applications, touch screens, human-computer interaction, information systems.
Abstract: This paper provides an overview of the experiences gained during the design, development and
implementation of mobile applications for use within the clinical domain. Current problems and issues that
arose during the development of the software are documented and discussed. Medical professionals'
opinions, both medical doctors and nurses, and their input were coupled with front end development (user
interface design) and back end development (software engineering) to decide on the most optimum
development path and to select the most appropriate environments. Most of all, this project can be seen as a
further example that User-Centered Development (UCD) is necessary, however it is not sufficient when
developing mobile, cross-platform, and future-proof applications for medicine and health care.
1 INTRODUCTION
During the past few years, improvements in the
technology of touch screens, further miniaturization,
lower power consumption, and longer battery life
has made it possible to design and produce better
mobile computers, tablet PCs, and small mobile
devices such as PDAs or smart phones. The market
for such mobile computing devices is rapidly
expanding whilst at the same time the technological
performance of these devices is steadily increasing,
(Antinisca Di & Cecilia, 2007). In this paper we
concentrate on discussing the lessons learned during
the development of specific user-centered software
for tablet PCs and define the tablet PC as our mobile
computing device (Prey & Weaver, 2007). However,
although mobile computers have been available for a
relatively long time in hospitals (Forman &
Zahorjan, 1994), different studies show that health
care professionals are reluctant to use poorly
designed mobile systems, as the patient care
workload is very time constrained and can be
extremely hectic (Brekka, 1995), (Holzinger &
Errath, 2007). Mobile computer user satisfaction is
certainly an issue and this has not been researched
extensively (Ozok et al., 2008). Obviously, all
aspects of Human–Computer Interaction (HCI) and
Usability Engineering (UE) are of growing
relevance, and must be especially considered when
in the process of developing software for medical or
health care purposes (Holzinger, 2007). This has
resulted in a set of commonly accepted development
practices, such as User-Centered Development
(UCD) (Holzinger, Searle & Nischelwitzer, 2007),
(Holzinger, Sammer & Hofmann-Wellenhof, 2006).
Although such considerations are important, we
must accept that for an application to work well, all
aspects must be taken into account, and there is the
potential danger that HCI professionals and usability
engineers tend to discount the underlying aspects of
software engineering (SE) (Thimbleby, 2007).
235
Holzinger A., Höller M., Bloice M. and Urlesberger B. (2008).
TYPICAL PROBLEMS WITH DEVELOPING MOBILE APPLICATIONS FOR HEALTH CARE - Some Lessons Learned from Developing User-centered
Mobile Applications in a Hospital Environment.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 235-240
DOI: 10.5220/0001909102350240
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 MOBILITY IN HEALTHCARE
There are several areas of healthcare where mobile
computers are necessary. On top of this, each area
has its own unique requirements. In order to
differentiate between them, we form two distinct
sections: a) Round Assistance, which consists of
help, or assistance, that a doctor might require when
doing routine “rounds” of the wards to check the
patients’ progress, etc.; and b) On-call Assistance,
which consists of help or assistance that a doctor
may need while on call-duty. These are not routine
check-ups on patients; rather they are performed as
and when deemed necessary by medical
professionals who are on call-duty.
Two main clinical situations exist which
determine whether or not a Patient Data
Management System (PDMS) is used in the unit,
Again, this depends on a number of factors. Wards
that use such PDMSs face specific problems (Junger
et al., 2001).
However, any pros of automatic data storage are
also faced with cons: a) overloading the medical
professional with data b) communication difficulties
that occur with patient details. In both of the above
cases, these problems will ensure that the future
worth of mobile applications is secured.
All PDMSs have basic operation centers, which
are generally PCs that are within a distance of two to
three meters from the patient. There, the majority of
the medical operations are performed (data
observation, decision finding, drug prescription).
Due to the huge amount of data available to the
medical professional using the PDMS, it is difficult
to gain a quick overview of the patient’s situation.
Details can be found within the PDMS, but
overviews are difficult to get. Switching between
different patient details on the same computer/screen
requires a lot of time and is actually not especially
helpful.
One solution to this problem may be a set of two
to three screens, on which data is displayed. Another
solution would, of course, be the use of a mobile
device, which communicates with the PDMS (via
WLAN, for example).
A problem which is often encountered when
doing rounds on the medical wards is that any
discussion of a patient’s medical needs is often
centered on the PC display belonging to the patient.
Most often, one person sits while others stand
around in a circle in order to view the display. This
situation presents several problems, not least the
difficulty in seeing smaller details on the screen
(which does, of course, depend on the number of
persons within group) and, furthermore, the situation
is conducive to a communicative environment. An
optimum solution to this problem would be to use
mobile devices, which would aid communication
and ease data visualization.
PDMSs are often located within intensive care
units; units with standard care patients do not have
PDMSs (this is due to the fact that in this case
monitoring data does not have to be stored
continuously). In such circumstances mobile
applications could be used as information servers
during a round (displaying laboratory data, etc.).
Here mobile applications are essential.
In both the above scenarios the mobile device
has to have a screen size and display resolution
suitable for graphical data presentation. Therefore
only tablet PCs or laptops are appropriate. Due to
hospital budget shortages, duties-on-call have
become more common. In such a situation a senior
doctor is available by phone. Data presentation using
mobile applications eases decision finding and is
beneficial to the senior doctor. In such cases, mobile
devices such as PDAs or smart phones may also be
appropriate. However, this is true only in very
specific circumstances.
3 METHODS AND MATERIALS
Within our project the prototype of a mobile system
for visualizing a patient’s overall status during ward
rounds was developed for the intensive care unit of
the department of neonatology at Graz University
Hospital, which is amongst the largest in Europe.
An automatic patient monitoring system stores a
huge amount of various data at fixed intervals of 15
minutes for each patient. The measured data consists
of vital signs, administered medications, expulsions,
and so on.
The problem for the medical professionals was
twofold: 1) The system’s user interface for viewing
and analyzing the data is, however, very cluttered
and containing extreme large amount of data in a
unstructured way. Although a graphical timeline plot
is provided, doctors often have to analyse the raw
numeric data. The average time spent on the analysis
of one patient is between 5 and 15 minutes,
depending on the doctor’s experience. 2) The system
is non mobile, requiring the medical professionals to
proceed to the stationary PC’s.
The aim of our project was not only to provide
mobility but also to significantly reduce the time
spent on information perception, so the raw data
only has to be analyzed if the patient is not in a good
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
236
condition. This is accomplished by providing instant
visual feedback about the patient’s status using a
combination of star plots and traffic light metaphor.
3.1 Device
The device used for the prototype was an LE1600
tablet PC by Motion Computing, which supports
stylus and finger input. Extensive experiments about
the differences between finger versus stylus input
have already been undertaken (Holzinger et al.,
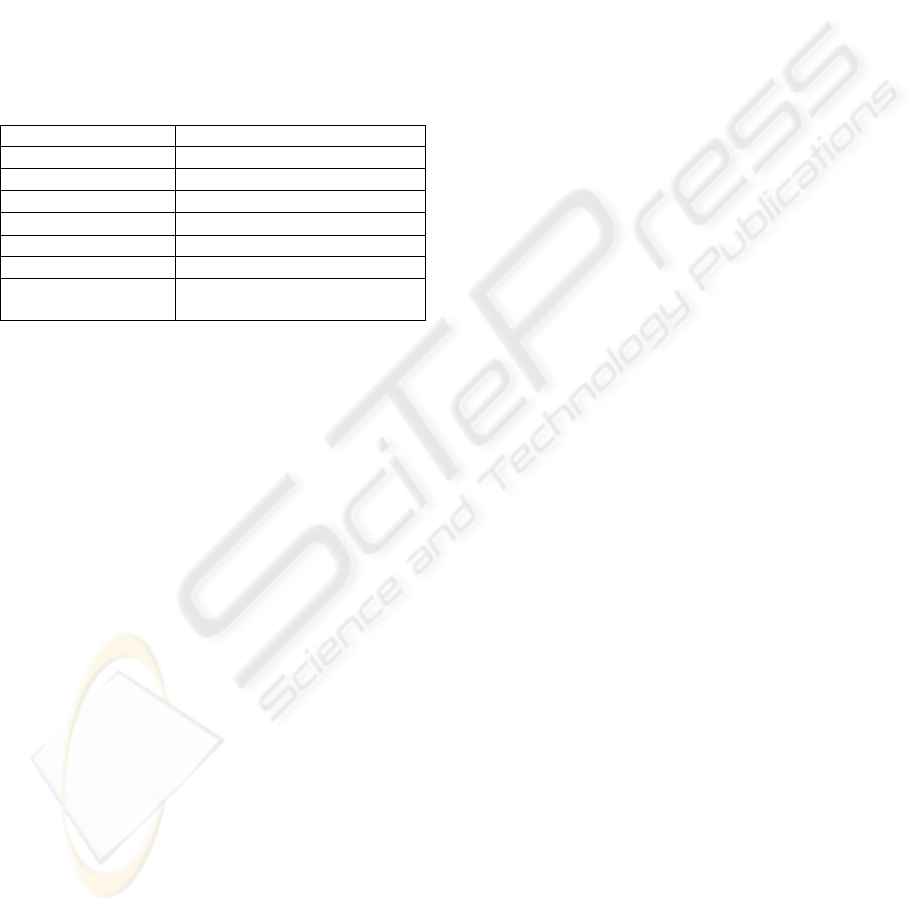
2008b). Table 1 contains the technical specifications
of this device.
Table 1: Technical specifications of the LE1600.
CPU
Intel Pentium M at 1.6 GHz
Memory
1 GB
Display size
12.1” XGA LCD
Display dimensions
247 mm x186 mm
Display resolution
1024 px × 768 px
Hard disk size
60 GB
Weight
1.4 kg
Physical
dimensions
296 mm x 240 mm x 18.7 mm
3.2 Software
The software was written using Java 1.5 and the
Swing user interface toolkit, where we had quite
positive experiences from former projects
(Holzinger et al., 2008a). Basically, services should
be adapted at runtime to the features of the device.
Also, end users should at any time specify that
services are delivered to match certain parameters.
For example, end users may request that an image be
printed while specifying a particular resolution,
format and/or number of colours (Stefano, Claudia
& Luigi, 2007).
3.2.1 Visualization Front-end
The front end is based on so called “visualization
modules”. Each module is created and configured by
the medical doctor. It reflects a subset of the
available data, containing interrelated values. The
doctor chooses which values are contained within
the module. The module “Circulation” for example
would contain heart rate, blood pressure, oxygen
saturation, etc. For each of these values the medical
doctor sets three intervals for defining the alarm
states of good, mediocre and bad. Each module has
an overall alarm state, which can too be good,
mediocre or bad. This overall alarm state is defined
by the individual values’ alarm states.
If, for example, value A is bad, the overall alarm
state of the module becomes bad too. In the
visualization the alarm state is represented using the
traffic light metaphor, i.e. the background of the star
plot is filled with green, yellow or red .
3.2.2 Database Interface
The database in question was an Oracle 8i database,
for which there are JDBC drivers available. Java
Database Connectivity is an API (Application
Programming Interface) which allows database-
independent connectivity between the Java
programming language and a wide range of
databases, including Oracle 8i (Oracle, 2008).
Oracle have available a JDBC compliant driver
for this database which allowed for relatively quick
development of the interface between the Java
program and the patient data.
Of course, speed was also an issue – without
good response times the software would not be
useful as a way of accessing data quickly and easily.
However, in this regard JDBC and Oracle perform
extremely well. Database and driver support,
therefore, was not a technological issue when
developing the application; however it was a factor
which played a role in deciding which programming
language to chose. It is also worth pointing out that
were the JDBC drivers not available, this would
have led to an extremely long development cycle
and may not have been possible at all.
This is an absolutely crucial aspect that must be
considered when developing mobile applications
that access an external database: your programming
language/platform/database combination must have:
a) the ability to perform the required task and,
less obviously,
b) should have available quality drivers and
libraries to ease development.
4 LESSONS LEARNED
4.1 General
As already mentioned in the introduction, mobile
devices have increased in capability by many factors
over the past few years, in terms of both features,
such as integrated cameras, and raw processing
power. Coupled with the fact that mobile devices
now contain many of the attributes that constitutes a
PC, several software development platforms have
become available by various vendors, most notably
TYPICAL PROBLEMS WITH DEVELOPING MOBILE APPLICATIONS FOR HEALTH CARE - Some Lessons
Learned from Developing User-centered Mobile Applications in a Hospital Environment
237

Google, Microsoft, and Sun Microsystems, among
others. However, their usefulness in the area of
medicine must be discussed.
Interestingly, the proliferation of mobile phones,
and jointly, the popularity of games for mobile
phones have cemented Java’s position as the
environment of choice for developing mobile
applications for small devices.
Having said this, developing applications in the
area of medicine requires that a platform inhibits far
different attributes than those platforms used to
develop mobile games. In this section, we discuss
the problems, and currently available solutions for
developing real-world, cross-platform solutions for
mobile devices.
4.2 Currently Available Cross
Platform Development
Environments
In the classical development world, if you wish to
develop a piece of software you must usually first
decide on the device on which you will develop your
application. Palm, for example, offer an SDK for
their devices which eases the development of
applications. Therefore, software developed for
Palm devices can only be run on Palm OS.
Limiting yourself to one single platform
seriously diminishes your potential market when
selling your software, or, in the case of the medical
profession, may demand redevelopment (if, for
example, a device or platform is no longer available
when inventory is recycled). Cross-platform
development, in many respects, eases this as you can
develop software that runs on any device where the
runtime environment is available (Bishop &
Horspool, 2006).
Since Java’s philosophy of “write once, run
anywhere” was incepted, several vendors have
delivered cross platform languages.
Microsoft has developed .NET, and its Micro
Edition competes with Java’s Mobile Edition in the
mobile domain. A new player in this area is Google,
who, along with 30 other technology companies, is
currently touting the Android platform (Android,
2008). If a doctor or medical professional were to
carry a device with them at all times, it would
suffice to say that the device must just be portable.
Tablet PCs have the advantage of having high
system resources, large screens, and most run the
ubiquitous Windows operating system.
On Windows, there are any number of cross-
platform development environments that one could
choose from, varying from the obvious, to the
slightly more abstract yet equally capable
alternatives (such as Adobe’s Air, and Microsoft’s
Silverlight).
4.3 Java SDK
Creating game applications using the Java SDK
seems to be the de facto way of producing
applications for small devices, but here we must
judge its worth as a platform for more serious
application development.
A number of aspects of the Java SDK were
analysed. For example, Java has been known to
render fonts very poorly on screen, and has been a
topic of discussion for quite some time, with various
workarounds and techniques available to cure the
problem. Another severe restriction is the missing
support for floating point numbers in MIDP (Mobile
Information Device Profile) versions prior to 2.0,
though there exist third party workarounds for this
problem. So long as the mobile device is MIDP 2
compliant, this is no longer an issue, however this is
something which must be ascertained before
development begins and could potentially be an
issue in the future lifecycle of your software.
4.4 Alternatives to Java - AJAX
AJAX is a term used to describe a number of
currently available technologies that when combined
form a framework with which you can build
desktop-like applications for the web (Turner &
Wang, 2007).
The often touted examples are Google’s AJAX
applications such as Gmail, Calendar or Maps – they
allow drag & drop, ‘refreshless’ updating of
information, and offer a desktop like and feel.
Of course, being AJAX applications, they can
run on any supported browser such as Firefox,
Safari, or Internet Explorer, eliminating the need for
the developer to worry about which operating
system the user is running, as long as the operating
system itself supports the browser. This has the
added advantage that most of the high-end
technology can reside on a server rather than on the
user’s device. An AJAX application can therefore
access an Oracle database, without the programmer
having to worry about Oracle drivers being available
for their framework/operating system combination
One of AJAX’s advantages stems from the very
fact that it was conceived as an internet platform – it
is geared towards users implementing a point and
click device rather than a keyboard. This bodes well
for small devices, as input is generally carried out
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
238

using a stylus rather than a keyboard. Using Google
Maps on a traditional PC, for example, it is possible
to find your street and house without having to input
a single character into the keyboard (assuming some
knowledge of geography). Creating applications,
therefore, using AJAX geared towards mobile
devices that utilize styli should demand no extra
effort of the part of the programmer; in fact the
inverse is true – it should be more instinctive to
generate applications that do not require keyboard
input.
4.5 Java Limitations
Java’s Runtime Environment (i.e. the Java Virtual
Machine) is not platform independent. It is simply a
runtime which is available on a (diminishing)
number of platforms. Its source code, however, is
platform independent, but this is also true of C/C++
code, often referenced as being platform specific.
Consider the following example in Java:
for (int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
System.out.println("Number: " + i);
}
And the following code written in C++.
for(int i = 1; i <= 10; i++)
{
cout << "Number: " << i << endl;
}
Both these source codes are transferable between
platforms. The C++ code requires that a compiler is
available for the platform that you want to run your
code on, but the same is true of Java – it requires
that a Java VM is available on the machine you wish
to run your code on.
The main difference is that the compiled output
is not transferable, but the code is. Of course,
programs are far more complicated than this, and
even primitive types, such as integers, vary in size
from C++ compiler to C++ compiler. And Java’s
compiled output is transferable from one platform to
another, without even the need to recompile,
something impossible to achieve with a C++
compiled application. However, this still begs the
question: is Java useful as a platform in the medical
domain where usage on mobile or small devices is a
must? The authors thinks so. While Java’s Virtual
Machine is available only for Windows, Mac OS
and Linux\UNIX, these are only operating systems
available for tablet PCs as of the time of writing. It
also seems very unlikely that another operating
system will appear in the foreseeable future.
One more thing to consider, however, is that Java
is not available for Windows Mobile or Palm
(discontinued since the 12
th
of January, 2008). It is
therefore the author’s opinion that AJAX could still
be considered the most optimal solution in creating
cross platform applications. However, it is unlikely
that PDAs have the required resolution and screen
size required to view patient information effectively.
Of course, that is not to say AJAX cannot run on
tablet PCs, this is certainly what AJAX was
designed to do. Consider also the quickly changing
medical field – AJAX applications when run, by
definition, are always up to date (this, however, is
also true of Java’s Webstart). Therefore, ruling out
AJAX altogether would be foolish, it certainly has
its niche, but perhaps not in the medical domain, or
rather not in our specific area of patient care in the
medical field.
4.6 NET
Microsoft’s .NET framework is as platform
independent as Java, in the sense that the runtime
can be ported to any platform. Currently Microsoft
only supplies a runtime for the Windows line of
operating systems, but because Microsoft submits
the specification for the Common Language
Infrastructure to both ECMA and ISO, it is an open
standard. Therefore, it is possible for third parties to
create implementations of the framework on other
platforms. This is currently the goal of the Mono
project, which aims to port the framework to Linux.
However, for our requirements in the medical
domain, we required a far more concrete
implementation, and Java officially releases several
versions of its framework, something that ruled out
.NET at this time for our purposes.
Again, inter-platform operability was an absolute
requirement for us, as potentially many different
machines and platforms would be using the software
across the university hospital, and because we have
no control over what devices the hospital purchases
for its medical professionals.
4.7 Chosen Platform
The decision was made to opt for Java as the
language of choice. The medical domain demands
unique considerations that eventually ruled out most
platforms that are currently available. Several years
from now, .NET may be a contender, and AJAX was
certainly a consideration. However, AJAX lacks the
maturity and robustness required for the purposes of
this project, and Java’s large library meant
TYPICAL PROBLEMS WITH DEVELOPING MOBILE APPLICATIONS FOR HEALTH CARE - Some Lessons
Learned from Developing User-centered Mobile Applications in a Hospital Environment
239

development could be performed as rapidly as
possible. It can be seen that the field of medicine
demands far more considerations when developing a
piece of software. Everything must be considered,
from screen resolution, platform availability, speed,
portability, library capability, and supported
technologies. Java’ maturity, concrete standards
(such as the JDBC API) and wide ranging third party
support makes it the choice for medical software
development.
5 CONCLUSIONS
It is clear that special considerations must be made
when developing applications in the medical
domain, especially if these applications should be
platform independent, future proof, and mobile.
There are a plethora of frameworks, environments,
and programming languages available, each with
their own specific advantages and disadvantages but
only some are suitable for the medical domain. By
reading this paper, it should be possible to save
anyone a lot of research and work if you they are
considering writing a cross platform, portable
application in the medical domain. Almost all
considerations were taken into account, from screen
resolution, doctors’ wishes, language suitability, and
operating system capability. By working close to
medical professionals, UI experts, and software
engineers, it was possible to ascertain what special
considerations must be taken into account when
working in this field. By analysing these
considerations, a number of concrete factors could
be defined which eventually led to development path
and programming environment that was chosen.
REFERENCES
Android (2008), Open Handset Alliance, Online available:
www.openhandsetalliance.com/android_overview.htm
l, last access: 2008-06-10
Antinisca Di, M., Cecilia, M. (2007) Performance analysis
and prediction of physically mobile systems. 6th
international workshop on Software and performance.
Buenos Aires, ACM, 129-132.
Bishop, J., Horspool, N. (2006) Cross-platform
development: Software that lasts. Computer, 39, 10,
26-35.
Brekka, T. (1995) Select mobile computers tailored to
healthcare environment. Health Management
Technology, 16, 13, 48, 50.
Forman, G., Zahorjan, J. (1994) The Challenges of Mobile
Computing. IEEE Computer, 27, 4, 38-47.
Holzinger, A. (Ed.) (2007) HCI and Usability for
Medicine and Health Care: Third Symposium of the
Workgroup HCI&UE of the Austrian Computer
Society, USAB 2007, LNCS 4799, Berlin, Heidelberg,
New York, Springer.
Holzinger, A., Emberger, W., Wassertheurer, S. & Neal,
L. (2008a) Design, Development and Evaluation of
Online Interactive Simulation Software for Learning
Human Genetics. Elektrotechnik &
Informationstechnik (e&i), 125, 5, 190-196.
Holzinger, A., Errath, M. (2007) Mobile computer Web-
application design in medicine: some research based
guidelines. Univ Access in the Information Society
International Journal, 6, 1, 31-41.
Holzinger, A., Höller, M., Schedlbauer, M., Urlesberger,
B. (2008b). An Investigation of Finger versus Stylus
Input in Medical Scenarios. ITI 2008: 30th
International Conference on Information Technology
Interfaces, June, 23-26, 2008, Cavtat, Dubrovnik,
IEEE, in print.
Holzinger, A., Sammer, P., Hofmann-Wellenhof, R.
(2006) Mobile Computing in Medicine: Designing
Mobile Questionnaires for Elderly and Partially
Sighted People. Springer LNCS 4061. Berlin, New
York, Springer, 732-739.
Holzinger, A., Searle, G., Nischelwitzer, A. (2007) On
some Aspects of Improving Mobile Applications for
the Elderly. In: Stephanidis, C. (Ed.) Coping with
Diversity in Universal Access, Research and
Development Methods in Universal Access, LNCS
4554. Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, Springer, 923-
932.
Junger, A., Michel, A., Benson, M., Quinzio, L. A., Hafer,
J., Hartmann, B., Brandenstein, P., Marquardt, K.,
Hempelmann, G. (2001) Evaluation of the suitability
of a patient data management system for ICUs on a
general ward. International Journal of Medical
Informatics,
64, 1, 57-66.
Oracle (2008), Oracle 8i. Online available:
http://java.sun.com/javase/technologies/database last
access: 2008-06-10
Ozok, A. A., Benson, D., Chakraborty, J., Norcio, A. F.
(2008) A comparative study between tablet and laptop
PCs: User satisfaction and preferences. International
Journal of Human-Computer Interaction, 24, 3, 329-
352.
Prey, J., Weaver, A. (2007) Tablet PC technology: The
next generation. Computer, 40, 9, 32-33.
Stefano, C., Claudia, R., Luigi, U. (2007) A Java mobile-
enabled environment to access adaptive services. 5th
international symposium on Principles and practice of
programming in Java. Lisboa, Portugal, ACM, 249-
254.
Thimbleby, H. (2007) User-Centered Methods Are
Insufficient for Safety Critical Systems. In: Holzinger,
A. (Ed.) USAB 200, LNCS 4799. Berlin, Heidelberg,
New York, Springer, 1-20.
Turner, A., Wang, C. (2007) AJAX: Selecting the
framework that fits - The right tools make the
difference. Dr Dobbs Journal, 32, 6, 40-42.
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
240
