
MOBILE BUSINESS EXPERT ADVISOR
Danco Davcev, Marjan Arsic and Dalibor Ilievski
Faculty of Electrical Engineering and Information Technologies
University “Ss Cyril and Methodius”, Skopje, Macedonia
Keywords: Mobile Expert, on-demand knowledge, Web services, XML Agents, Fuzzy logic, Pocket PC.
Abstract: In this position paper, we introduce the service which enables consultations by the Experts and/or web
services via mobile devices. The advanced development of wireless networks and mobile devices with
various connection features made a great substrate for the development of services which are based on
immediate response. One such service is a service for on-demand knowledge. A Helpdesk operator can post
a request for consultation to the Experts and/or web services. The goal is to make knowledge available on
demand at any time and any place. This approach gives faster problem solutions, more productive expert
and/or web services, and high availability of the knowledge.
1 INTRODUCTION
The benefit of mobile devices combined with stable
and cheap wireless networks made new kinds of
services to appear. Experts are becoming more
available than ever. Their services can be easy
utilized and customers will have direct answer to the
required question. In some cases (if appropriate) one
of the XML agents communicates with the necessary
Web services to find the solution of the problem.
Exchange of knowledge and consultation process
among customers and available expert authority via
helpdesk operators are very important aspects of
quick problem solution using the mobile devices.
The goal of the mobile technology is to make
information instantly available to customers. The
new business processes can benefit a lot by using
mobile connection between customers and experts.
The exchange of the various content types of media
data (text, drawing, and sound) will enhance the
efficiency of consultations between the customer
and the expert advisor. It gives benefits in reducing
of costs, avoiding future problems or possible
claims, saving time, increasing profit and customer
satisfaction.
There are many desktop applications that
support multimedia communication among
participants. Communication among several
participants that includes multimedia transfer is at
the beginning of the development and utilization in
the sphere of mobile handheld devices. Hence, new
demands are imposed to these devices: greater
processing power to support real time multimedia
transfer (video stream, voice stream, and file
exchange), greater memory space. Modern feature
rich applications demand space on the screen for
displaying all available features, which could be an
issue when handheld devices are used.
A great consideration should be given to the
readability and utilization of small mobile user
interfaces. In this paper, we present our approach in
creating a Mobile Business Expert Advisor (MBEA)
for demanding and exchanging of various content
types and knowledge on mobile devices. The
interface of our MBEA adapts the dimensions and
visibility of the user controls according to the user’s
preferences and utilization of the controls and also,
the current usage of the specific media contents
within the business process. Our knowledge – based
interface is managed by fuzzy logic and many XML
based agents.
The related work in the second section gives
some comments to similar MBEA-s. The
architecture of our Mobile Business Expert Advisor
is elaborated in the third section, which is the main
contribution of this paper. The fourth section
describes the design of MBEA. Implementation and
Evaluation of MBEA are presented in fifth section.
Finally, in the sixth section we conclude the paper.
203
Davcev D., Arsic M. and Ilievski D. (2008).
MOBILE BUSINESS EXPERT ADVISOR.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 203-208
DOI: 10.5220/0001913202030208
Copyright
c
SciTePress
2 RELATED WORK
The agent-based approach that uses fuzzy logic to
determine importance of certain information is
elaborated in (
David Camacho, 2001). The agents
described in this paper are based on access to the
Web. We use similar approach to determine
importance of user interface features in regards to
user preferences and media contents used in current
session. However, in our approach is used wireless
network access for communication between
handheld devices.
In (Vlado Glavinic, 2007), an intelligent tutoring
system was presented. They use agents to recognize
the device and the way user device connects to the
global network and according to that information, a
learning content is adjusted to the particular device
and sent to the learner’s device. It differs from our
system because we introduced agents whose purpose
is to intelligently adapt the user interface to the
preferences of each user.
Intelligent Mobile Answering Service is given in
(Business Wire, 2006). Customers can use free-form
questions on any subject with natural language
queries. They can send text messages containing
questions in any form just as easy as they send text
message to their friends and receive a specific
answer to their mobile phones. The natural language
queries allow customers to ask questions in the way
they normally express themselves. Unlike this, our
approach is based on resolving business issues in
various format types by the experts.
In (Lu, L. Kitagata, 2003) an agent based
adaptive user interface control for desktop
applications is presented. Although we share similar
ideas, our approach is multi-agent based adaptive
interface which uses fuzzy logic for handheld
devices.
In (Weichang Du, 2006), collaborative
applications can be built using two types of agent
collaborations, agent communications through
XACL and agent visiting. Agents are represented as
XML entities, not programming language entities.
Secondly, agent hosting services are implemented as
web services with published WSDL, not programs in
certain programming languages with published
APIs. Thirdly, although XML agents’ behaviors
have to be coded in some supported programming
languages, the interactions between agents and hosts
in agents’ behavior code are through invoking local
hosts’ web services, which is neutral to
programming languages and host operating systems.
Although we also use XML entities as agents and
we share similar ideas of using web services (when
appropriate), in our approach we use more flexible
protocol for communication among agents which is
based on fuzzy-based knowledge.
In (Pasquale De Meo, 2007), an XML-based
multiagent recommender system for supporting
online recruitment services is proposed. Although
the main purpose of this system is to provide Online
Recruitment Services, it is also agent and XML
based and as a consequence, it can easily cooperate
with company information systems. The so called
ontology of their user agent stores the profile of a
given user concerning the job search. It is different
from our MBEA because we plan to build a general
purpose advisor system (not only for recruitment
services). For the time being, our objective is to have
a self - adaptive system from the point of view of an
efficient communication between user and the
advisor according to the user's preferences and the
current possibilities of the communication system.
In (Zhiyong Weng, 2007) a feasible framework
that combines agent mobility and intelligence for
consumer-oriented e-business applications is
proposed. This framework complements the current
Web-based systems by adding the wireless channel
of mobile agents. In our work the mobile agents use
an adaptive communication protocol based on fuzzy
logic. In addition, our framework includes web
services.
3 MOBILE BUSINESS EXPERT
ADVISOR (MBEA)
ARCHITECTURE
There are three kinds of users like customers,
helpdesk operator and experts. Helpdesk operator is
the link between experts and customers.
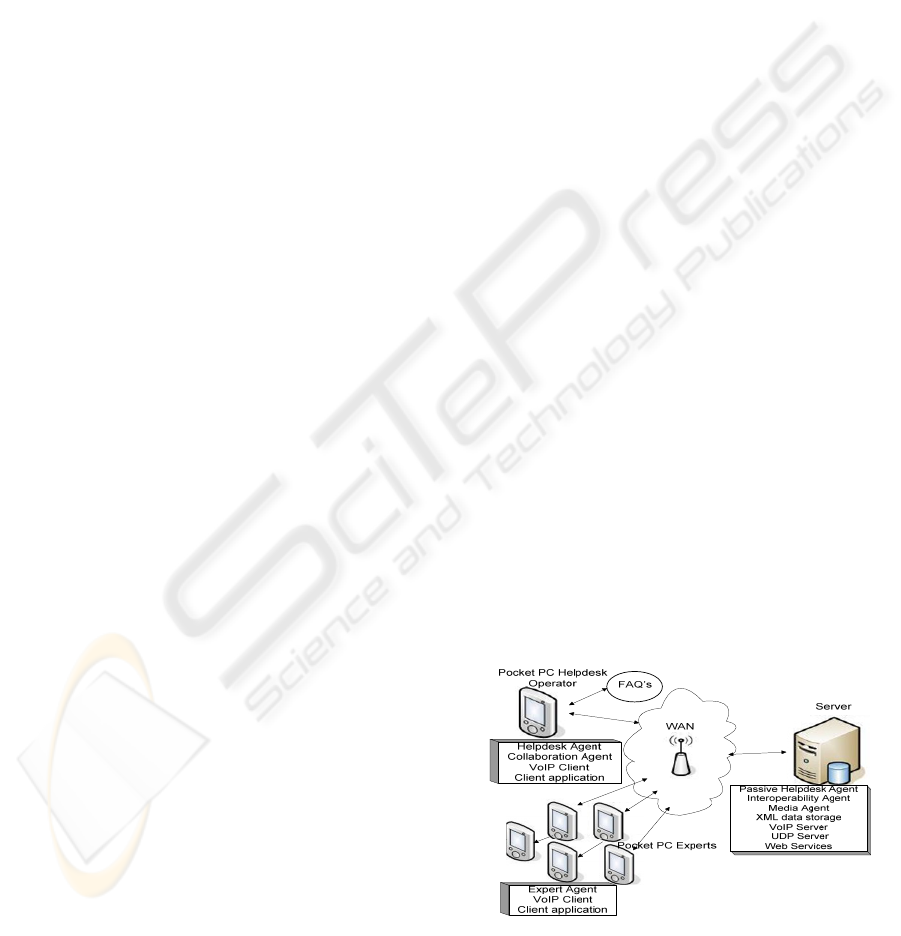
Figure 1: Architecture of the MBEA.
The goal of the helpdesk operator is to response
any kind of requests on demand by the customers in
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
204

appropriate formats (text, draw, VoIP) and to send
the complex requests to the experts and/or web
services which should be resolved by them. Client
applications are implemented on Pocket PCs.
There is only one helpdesk operator and many
experts in one consultation session.
The network communication is realized in a way
that clients send UDP datagrams to the server, and
the server resends the UDP datagrams, according to
the contents of the received message.
The communication protocol between the agents
and the information flow rely on fuzzy logic. In this
case, the fuzzy logic is used for enabling or
disabling (adaptation) some controls depending on
the quality of the service (QoS), i.e. the signal
strength. So, if the signal strength is good, the
features of chat, draw and VoIP will be enabled.
However, for medium signal the VoIP feature will
be disabled. For bad signal, beside the VoIP, the
draw feature should be also disabled, and the only
active communication feature will be chat.
Streams are used for the voice transfer. Desktop
based clients (for both helpdesk operator and
experts) can be also connected to the server.
The Web services are used to find the solution of
the problem using the wireless Internet access. If the
Web services are unable to find the solution, the
Experts are activated. Some types of Web services
are used for the responses. These Web services
support and convert various types of media data.
The experts interface has controls for chat, draw,
VoIP, file upload/download, authority control (VoIP
channel).
The helpdesk operator can give the control over
the interface (or by giving the speaking possibility)
and reclaim the control later. Helpdesk operator has
the role of a moderator in the consultation process.
Figure 1 shows the architecture of the MBEA.
Client applications reside on pocket PCs and they
have three main parts: Helpdesk agent, which
manages operator interaction within the application
and communicates with interoperability agent. VoIP
client serves for the voice transfer, and the client
application represents all the features mentioned
above (chat, draw, voice, file up/download,
communication among clients). Expert Agent
receives and sends the resolved requests using
various file types (like text, image, and voice).
Collaboration Agent calculates the cost of the
corresponding expert’s service. The communication
is realized through wireless area networks
connected to the Internet.
The server contains Interoperability Agent
which redirects the complex request to the Experts
and/or Web services and exchanges reformatted
media types; Passive helpdesk Agent calculates the
helpdesk interface; Media Agent monitors the
media contents (text, image or voice); Experts and
helpdesk preferences are stored in XML data
storage; VoIP Server is responsible for voice
transfer and UDP server application manages the
login, chat, draw and control. For the purpose of
saving the memory and processing power of the
clients handheld devices, Passive Helpdesk Agents
and Media Agent reside on the server side. The
agents are XML based.
4 MBEA DESIGN
In this paper, we describe our approach in
development of a MBEA by using multi XML
agents and fuzzy logic. Helpdesk agent resides on
the client side, and monitors the helpdesk operator’s
interaction by using the features of the application
and communicates with interoperability agent (e.g.
sends the request to the available competent experts
and/or web services, receives the response in
corresponding format and regulates the customers
billing). The triggers that demand helpdesk agent’s
actions are: drawing, sending chat messages, and
communicating using VoIP. This agent is named
Helpdesk because it helps the customers to simply
resolve their requests. At the start of the
communication session, helpdesk agent
communicates with the Passive helpdesk agent and
interoperability agent that reside on the server. The
Passive agent demands the information from the
Media agent about the type of the files to be used for
the particular communication session. This agent is
named passive helpdesk since it waits to be invoked;
it recalculates the interface structure and sends the
data to the helpdesk agent which finally draws the
interface. The Expert Agent receive the requests in
some format (text, file, voice) from the
interoperability agent, concerns about the solution of
the requests, sends the solutions to interoperability
agent, modifies the expert’s profile, checks the QoS
and billing status.
The main tasks of the interoperability agent are:
receiving the requests from helpdesk agent and
forwarding them to the expert agents and/or web
services. Also it exchanges reformatted data files
with helpdesk agent. Media agent monitors the
folder with the data files for the communication
session, and sends this information to the Passive
helpdesk agent. The Passive helpdesk agent
recalculates the helpdesk interface according to the
MOBILE BUSINESS EXPERT ADVISOR
205
information from the Media Agent, the history of
interface affinities (chat_aff, draw_aff, sound_aff,
QoS) for the particular user and the helpdesk agent’s
message about the use of the features. Then, it sends
the corresponding information (for the type of the
helpdesk interface) to the Helpdesk agent which
adapts the helpdesk interface according to this
information. The collaboration Agent calculates the
time session for realization of the expert task and the
cost of the service
Helpdesk and Expert profiles with personal
information about the qualification and the
knowledge for all of them are stored in the XML
database. Additionally a history of affinities is stored
for the helpdesk operator and the experts.
According to the history, Passive helpdesk agent
adapts the helpdesk interface on the beginning of the
communication session.
There are currently three predefined user
interfaces, which can be preloaded on the client’s
device, according to his preferences and the media
contents for the current communication session. The
dimensions and the positions of the controls would
be stored on the helpdesk’s affinity table on the
server. One kind of an interface displays chat on the
larger part of the screen, the second interface has
larger drawing view on the screen, and the third one
has equal space for the chat and the drawing space.
VoIP feature doesn’t occupy much space on the
screen, so the buttons for voice are always displayed
and they will be active if the Signal Strength is
satisfied, i.e. QoS is strong.
Since there is no universal conclusion for making
decisions of which user interface should be
preloaded, fuzzy logic approach is used to model
that kind of the imprecise information.
The interaction made by the helpdesk operator
using the features of the application (chat, draw and
voice feature), is represented as a vector (chat_aff,
draw_aff, sound_aff). A linguistic variable named
RESULT_PREFERENCE is introduced, and it
accepts values from the set of
terms {increase_chat,
increase_draw, the_same}. This variable represents
the visualization of the helpdesk interface, produced
by (1) the helpdesk operator interaction with the
interface; (2) the contents of media folder and (3) the
quality of service of the signal strength that decides
more accurately which interface to be preloaded.
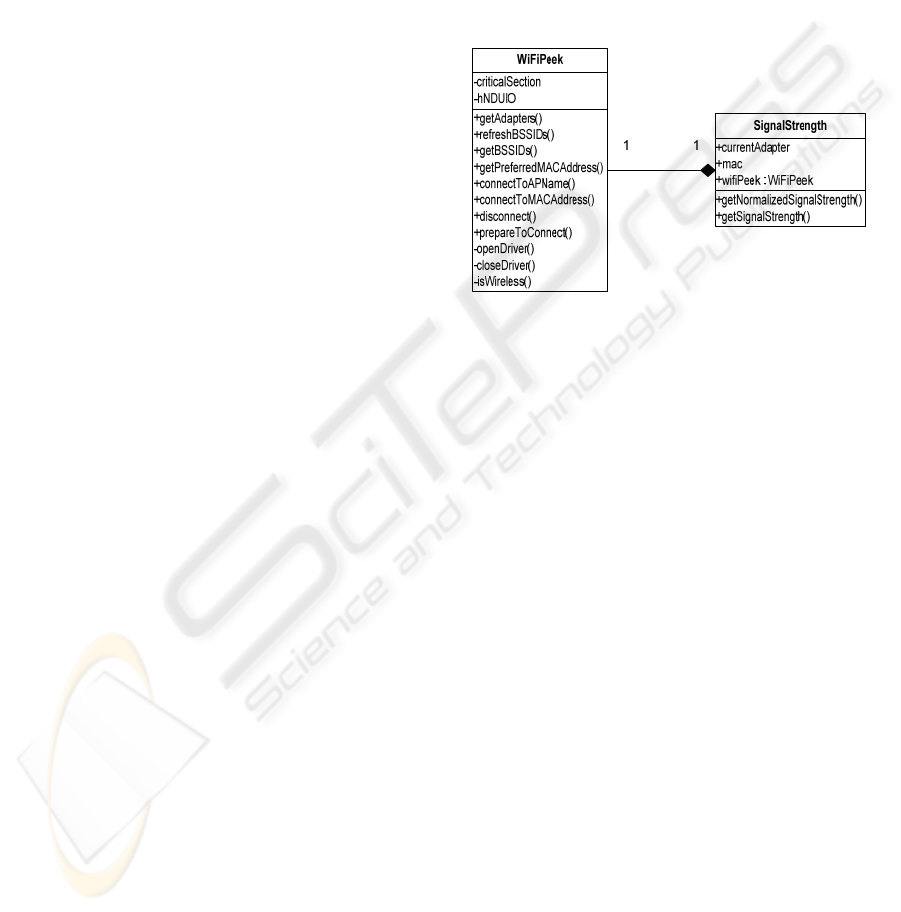
The class diagram for WiFi signal strength is
shown on Figure 2. Two classes are developed,
WiFiPeek and SignalStrength. The WifiPeek class
implements all the Wi-Fi query related elements.
The class uses the NDIS User mode I/O driver
(NDISUIO) to perform Access Point (AP) scanning.
The GetAdapters function can be used to query
names of network adapters. It calls the built-in NDIS
(not NDISUIO) driver. The function fills a buffer
with adapter names separated by commas. The
RefreshBSSIDs function requests that the driver
initiate an AP survey. It takes one parameter: an
adapter name. The GetBBSIDs function returns the
list of available stations, i.e. peers and Access
Points. The function getPreferredMACAddress
returns the MAC address of the connected
(associated) Access Point.
Figure 2: WiFi signal strength – class diagram.
In order to create the MBEA for calculation of the
user interface visual features, the following fuzzy
variables are defined for this expert system: U_A
(user affinity) which presents the most used feature
by the user, i.e. it has the greatest affinity for the
feature; M_P (media profile) presents the profile of
the interface that should be used according to the
media contents; QoS (Quality of Service) presents
the strength of the wireless signal. Output variable
named I (action for interface adaptation) presents the
necessary interface to be preloaded onto the user’s
device screen, according to the input variables.
The linguistic variable Quality of Service (QoS)
accepts values from the set of terms {Strong,
Medium, Weak}.
The linguistic variable U_A accepts values from
the set of terms {Chat, Draw, VoIP} and it has
normalized values of utilization between 0 and 1
(0% to 100%). It is equivalent to the number of
times of usage of the features chat, draw or VoIP
respectively.
The linguistic variable M_P accepts values from
the set of terms {Text, Drawing, Sound}. It has
normalized values of utilization between 0 and 1
(0% to 100%), which is equivalent to the number of
text, drawing and sound files in the media profile
respectively.
In the table 1 is presented the simulation for
fuzzy linguistic values for U_A, M_P and QoS and
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
206

Figure 3: Agents’ collaboration diagram.
the value of I is calculated, based on the fuzzy rules.
The action needed to adapt the interface is described
with the following XML code like the example 1 of
the Table 1.
<IF U_A="DRAW" M_P="DRAWING" QoS="WEAK">
<ASSIGN I="THE_SAME" />
</IF>
In the first example from the Table 1, the draw
affinity is more utilized than chat and VoIP and the
media profile has more drawing objects than text or
sound. It is expected to be increased the drawing
interface, but because the signal is weak and the
drawing features are not supported on such signal,
the interface stay unchanged (the_same). The total
numbers of fuzzy rules are 27, the combination of
the values of all linguistic variables. The next
examples are similar like the first one.
Table 1: Some examples for adapting interface using fuzzy
linguistic variables.
The interaction among agents is shown on the Fig. 3.
5 MBEA IMPLEMENTATION
AND EVALUATION
Applications for Wireless MBEA are developed in
C++ Visual Studio .NET 2008 development
framework with using of the MFC (Microsoft
Foundation Classes) library. Operating systems used
on the pocket PCs are Windows CE, Windows
Mobile. The clients which reside on desktop PCs
and the server use the standard .NET Framework.
Operating system for desktop machines on which the
application is practically deployed, is Windows XP
SP2. The interface adaptation is realized on different
screen resolutions.
The two instances of MBEA interface are shown
on Figure 4 for two different screen sizes of Pocket
PC-s.
The initial feedback of MBEA was given by 20
colleagues in ICT. They were asked to use the
system for stock exchange analysis in last week.
General opinion among participants for the interface
Figure 4: Two instances of MBEA.
MOBILE BUSINESS EXPERT ADVISOR
207

usability, functionality and visibility is average
(80%). Interface is functional and suggestions for
interface rearrangment are mostly done according to
the user needs.
The questions that examine interface usability,
functionality, visibility and provide information for
future upgrades are:
1) Are you satisfied with the way of adaptive
presentation?
2) Can you easily select the parameters of MBEA?
3) Were the results of the MBEA solutions are
clearly displayed?
4) How much the MBEA helped in the business
process?
5) Does the MBEA satisfy the quality of the
service?
The questions are answered with “Yes”, “No” or “I
Don’t Know”. The answers are given in the Table 2.
Table 2: Results of the questionnaire.
Question
Q1 Q2 Q3 Q4 Q5
Average
Percent
Yes 17 15 16 14 18 80%
No 2 3 1 4 1 11%
I don’t know 1 2 3 2 1 9%
6 CONCLUSIONS
This paper presents our approach that uses XML
agents and fuzzy logic in order to achieve adaptive
MBEA. We have developed such mobile system
which determines the features of the interface
according to the contents for the specific session.
Fuzzy logic approach is used for the communication
protocol between XML agents and for interface
adaptation. It can be also used to dynamically
reconfigure the interface according to the
preferences and the type of request. In this way, we
proposed an adaptable MBEA for handheld devices
which brings benefits to the developers of
applications for this software environment, to users
of mobile business systems and at the end, to all
mobile device users. General opinion among
participants for the MBEA usability is positive. In
the future work, we plan to provide an detailed
analysis of the user’s feedback.
REFERENCES
David Camacho, Cesar Hernandez, Jose M. Molina, 2001.
“Information Classification Using Fuzzy Knowledge
Based Agents”, Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, IEEE
International Conference; pp. 2575-2580.
Vlado Glavinic, Marko Rosic, Marija Zelic, 2007.
“Agents in m-Learning Systems Based on Intelligent
Tutoring”, Proc. of the HCI Universal Access in
Human-Computer Interaction, Beijing, China, pp.
578-587.
Business Wire, “AskMeNow Launches Intelligent Mobile
Answer Service 'ASKME'”, CNET Networks, 2006.
http://findarticles.com/p/articles/mi_m0EIN/is_2006_
Sept_25/ai_n16838742 [2008]
Lu, L. Kitagata, G. Suganuma, T. Kinoshita, T., 2003.
“Adaptive user interface for multimedia
communication system based on multiagent” Proc. of
the 17th International Conference on Advanced
Information Networking and Applications,
IEEE
Computer Society, pp. 53- 58.
Weichang Du, Hui Li, 2006. “XML Agents Technology
for Building Collaborative Applications”,
Collaborative Technologies and Systems, CTS
International Symposium, Pages: 289 – 297.
Pasquale De Meo, Giovanni Quattrone, Giorgio Terracina,
Domenico Ursino, 2007. “An XML-Based Multiagent
System for Supporting Online Recruitment Services”,
Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part A, IEEE
Transactions, Volume 37, Issue 4, Pages: 464 – 480.
Zhiyong Weng, Thomas Tran, 2007. “An Intelligent
Agent-Based Framework for Mobile Business”,
Management of Mobile Business, 2007. ICMB 2007.
International Conference, Page: 30
ICE-B 2008 - International Conference on e-Business
208
