
INTRUSION DETECTION AND PREVENTION SYSTEM USING
SECURE MOBILE AGENTS
Muhammad Awais Shibli
1,2
and Sead Muftic
2
1
NUST School of Electrical Engineering and Computer Sciences, Rawalpindi, Pakistan
2
Department of Computer and System Science DSV, The Royal Institute of Technology (KTH)
Stockholm Sweden, SU/KTH, DSV, Borgarfjordsgatan 15, SE-164 40 Kista, Sweden
Keywords: Intrusion Detection and Vulnerability Assessment, Intrusion Detection & Prevention, Secure Mobile
Agents, Mobile System Security, Mobile Code & Agent.
Abstract: The paper describes design and architecture of the intrusion detection and prevention system based on
secure mobile agents along with the analysis of commercial products and current research efforts in the area.
Once system will be operational it will be the first comprehensive real–life application using mobile agents
that will not only provide security to network resources but also provide security and protection to the
mobile agents system itself. The system efficiently solves several problems with the existing IDS/IPS
solutions: it can detect new vulnerabilities, it can process and filter large volumes of logs, it reacts to
intrusions in real–time, provides protection against unknown attacks, supports and improves IDS/IPS
commercial products by different vendors, and handles software patches. The system not only improves the
existing IDS/IPS solutions, but it also eliminates several of their core problems. In addition, it is self–
protected by full encryption, both mobile agents and their platforms, and therefore not vulnerable to attacks
against its own components and resources.
1 NETWORKS SECURITY
PROBLEMS
1.1 Intrusions and Damages
Security and protection of computer networks and
their resources is one of the most important IT
activities today. Most organizations no longer take
for granted that their deployed networks and
applications are secure and therefore use all kind of
protection tools and products. But, even after
installing various protection mechanisms,
performing continuous monitoring of security logs,
and running extensive penetration tests, network and
hosting security personnel spend considerable time
chasing incidents, preventing penetrations or solving
problems after intrusions and damages. More or less
everybody has already realized that the “secure the
perimeter” approach does not prevent the tide of
incidents, intrusions and damages, because current
techniques and products do not provide effective
solutions (Stev2006). In spite of all the efforts, we
are almost daily witnessing intrusions, damages,
stolen data and valuable Government and/or
corporate information.
Over the last several years, the trends and styles
of intrusions have been changing (CERT, 2007).
Intrusion profiles have enhanced from simple
methods like tracing passwords, social engineering
attacks (Bishop, 2005), and exploiting simple
software vulnerabilities to more sophisticated
methods, like exploiting protocol flaws, defacing
web servers, installing snifter programs, denial of
service attacks, distributed denial–of–service
attacks, or developing command and control
networks using compromised computer to launch
attacks. CERT Coordination Center confirmed in the
“Recent CERT/CC Experiences Vulnerability
Report” (CERT, 2008) that there has been
significant
exponential increase in discovered
vulnerabilities: 171 in 1997 to 7236 in 2007. This
increase in vulnerabilities and intrusion profiles has
also dramatically increased the number of security
incidents in past few years. These statistics show an
alarming situation in which expertise of intruders is
increasing, complexity of network and system
administration is increasing, ability to react fast
107
Awais Shibli M. and Muftic S. (2008).
INTRUSION DETECTION AND PREVENTION SYSTEM USING SECURE MOBILE AGENTS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Security and Cryptography, pages 107-113
DOI: 10.5220/0001930201070113
Copyright
c
SciTePress

enough is declining significantly and along this,
vendors continue to produce software with inherent
vulnerabilities. In addition to direct attacks and
penetrations by humans (hackers or insiders), one of
the additional rising problems in today's networks is
the existence of malicious bots and bot networks
(Security, 2007). Most botnets are created to conduct
malicious actions such as conducting Denial of
Service (DoS) attacks, stealing user identities,
installing keyboard loggers to record keystrokes, or
generating e-mail spam.
2 CURRENT SOLUTIONS AND
THEIR WEAKNESSES
2.1 Conceptual Solutions
Several ID/IP research solutions and many products
emerged in the past, which provide protection
against intrusions at host or network level. These
traditional solutions like antivirus, firewall, spy-ware
and authentication mechanisms provides security to
some extent, but still face the challenge of inherent
system flaws, OS bugs and social engineering
attacks. Back in 1980, James Anderson (James,
1980) proposed the concept of intrusion detection.
Then in 1988, three IDS models have been proposed
based on the approach to detect intrusions: Anomaly
Detection, Misuse Detection, and Hybrid Detection
(Denning, 1987). Anomaly Detection based IDS
produces high rate of false positives. Misuse
Detection produces smaller number of false
positives, but the problem is that signature databases
need to be regularly updated as their detection
capability is based on them.
One of the major problems with current IDSs is
that they cannot detect and respond to new attacks in
real time, because most of them for that require
updates of attack signatures usually provided by
network administrators. It is very
difficult for
network administrators to analyze large logs
generated by network traffic, to identify the attack,
and to respond to it in a real time. The consequence
is new, often distributed attacks, based on the
window of opportunity for an attacker, because
of
the delay in attack identification and response by
network administrators (CERT, 2007). Our system
based on mobile agents solves very effectively this
problem.
Another serious problem with the current ID/IP
systems is that they produce large logs, which
cannot be used and utilized efficiently. With so
many security solutions available, both open source
and commercial products, the problem is not to
obtain security related data, but rather to be able to
reasonably process too much data. Those solutions,
in order to be effective, report several thousand
‘events’ a day, the number rising to near ludicrous
totals in secure areas of government, commerce and
also open university infrastructures. This quite
clearly raises a number of issues. It becomes near
impossible to analyze every logged snippet of
information due to the sheer volume of collected
data. Consequently, more critical attacks may go
unnoticed security administrators either never
process relevant attacks data or process them too
late. Security analyst must have an almost
superhuman speed, capabilities and understanding of
the information being presented (Read, et al., 2007).
In addition, it is generally accepted today that
software has inherent security vulnerabilities (Bruce,
et al., 2004). Usually system and network
administrators do not discover these vulnerabilities
in real time, because of the large size of their
networks and their inability to have access to all the
information about the discovered vulnerabilities. In
fact, it should be advantageous that, as soon as the
patch is released, it is installed where it is required.
Our system is capable to detect new vulnerabilities,
report existing vulnerabilities and also automatically
fetch and distribute patches to their target machines.
2.2 Commercial and Open Source
Products
In this section we review some commercial and open
source products. There are many other IDS/IPS
products, but they are not as advanced as the
reviewed products and also they are all based on the
same protection principles as here described
products.
SNORT is an open source cross-platform
lightweight network intrusion detection tool used for
network traffic monitoring in order to detect
suspicious network activities. It has rules based
logging to perform content pattern matching and
detects a variety of attacks and probes, such as
buffer overflows, stealth port scans, CGI attacks,
and etc. However its rules database should be
updated regularly in order to protect against new
threats. (Snort, 2008).
Cisco
provides an extensive set of security features
in their different security products, such as Defeat
Distributed Denial-of-Service Attacks, Cisco
Intrusion Prevention System (IPS) sensors, and etc.
SECRYPT 2008 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
108

However, common for all solutions and products is
that Cisco is still using common security solutions to
protect networks. Those security solutions fail to
provide adequate level of protection, because of ever
increasing security incidents. The main reason is still
using the traditional signature–based approach for
many products. (Cisco, 2007)
nCircle provides security risk and compliance
management solutions. They have number of
products. Major deficiency of their products is that
they are still using existing static methods to provide
protection of network resources and do not provide
preventive and automatic response capability with
their solutions. (nCircle, 2007)
Reflex Security's Intrusion Prevention™ solutions
provide end-to-end enterprise network protection.
Reflex IPS applies packet inspection with signature,
anomaly and rate-based algorithms to inspect and
control network traffic flows. This detection
methodology already proved to produce either high
rate of false positives or false negatives, and thus
eventually does not provide effective and efficient
secure protection against ever-increasing threats.
(Reflex, 2007)
Nessus™ is a vulnerability scanner that provides
couple of good features like efficient discovery of
vulnerabilities, network configuration and auditing,
asset profiling etc. However, the major problem with
Nessus is that it requires significant involvement of
security administrators. (Nessus, 2007).
2.3 Current Contributions from
Research Community
Some of the research efforts, made by research
community in this area, are following:-
(Stolfo, et al., 1997) “The Java Agents for Meta-
learning (JAM)”. This Project deals with the concept
of
Meta learning for distributed data mining, using
intelligent agents. It has two components: local fraud
detection agent, that learns how to detect fraud and
provides intrusion detection capability, and a secure
integrated meta-learning system, that combines the
collective knowledge acquired by individual local
agents. Data mining, like neural networks and other
single-point learning applications, does not enable
knowledge sharing among agents. The meta-learning
approach tries to reduce this limitation by integrating
a number of remote agents.
(Ssaka, et al., 1999) The Information-technology
Promotion Agency (IPA) in Japan has developed an
IDS called the Intrusion Detection Agent system
(IDA). The IDA is a multi-host based IDS. Instead
of analyzing all of the users' activities, IDA works
by watching specific events that may relate to
intrusions, IDA gathers information and analyzes the
information, and decides whether or not an intrusion
has occurred..
(Balasubramaniyan, et al., 1998) AAFID, proposed
at Purdue in 1998, is an agent based hierarchal
architecture for IDS. It’s simply hierarchal
decomposed the traditional IDS into light-weight
autonomous cooperating agents, which can easily be
reconfigured. Autonomous agents used in AAFID
project are static and special purpose agents which
are only used to dynamically reconfigure IDS
components. The other thing worth noticing is that
AAFID is based on hierarchal architecture which is
vulnerable to direct attacks. If any of the internal
nodes is compromised, the whole branch is disabled.
Secondly, the transfer of huge logs across the
hierarchy also overloads network traffic.
(Zhang, et al., 2004) Intrusion Prevention System
Design (IPSD) presents an idea of integrating the
isolation function of firewall with the detection
capability of IDS. Combination of both will provide
a new concept of intrusion prevention system. Both
firewall and IDS will use the merits of each other to
provide tightly coupled solution
that can react to
network changes in a more effective manner.
(Ko, et al., 1994) “Automated detection of
vulnerabilities in privileged programs by execution
monitoring” (ADVPP) worked on detection of
vulnerability exploitations in privileged programs by
monitoring audit trails. Their work is based on the
assumption that a privileged program is more likely
to exploit vulnerability.
3 THE SOLUTION – SECURITY
SYSTEMS BASED ON MOBILE
AGENTS
The analysis of the current situation and the root
causes of the current problems, indicates that there
are essentially two main reasons for those problems
today:
a) Humans (system and network operators) are slow
to detect vulnerabilities, process logs and react to
intrusions in real time. They have no time to follow
discovery of new vulnerabilities due to diversified
locations and structure of their announcements, and
INTRUSION DETECTION AND PREVENTION SYSTEM USING SECURE MOBILE AGENTS
109

they are slow to react to on–going attacks in real
time, since most of the time they are even not aware
of those attacks. b) Software is always produced by
humans using a manual process, which is prone to
errors and vulnerabilities.
3.1 The Solution
The system described in this paper uses an
innovative approach to eliminate the first essential
problem: secure mobile agents – i.e., active entities
that can migrate from one network node to another
by transferring their code and by eventually also
preserving their reached execution state. The
approach comprises the concept, the set of
components and an effective architectural solution
for building secure network systems using mobile
agents, The system performs the following four
functions in the network: (a) autonomous detection
of vulnerabilities on different host (in a distributed
network) before an attacker can exploit them, (b)
monitoring, retrieval and installation of patches; (c)
protection of hosts by detecting attempts of
intrusions and responding to them in real time, and
(d) tasks related to security management.
Network protection and prevention of intrusions
works best when it is designed into the system
architecture instead of added on later. This system is
based exactly on such approach: the architecture,
components and all protocols of the system are using
secure mobile agents. Those agents monitor the
network, react timely and more accurately to various
intrusion attempts, and thus mitigate or greatly
reduce vulnerabilities. The system also enforces
different types of security polices: access control and
authorization policies. Mobile agents are used to
monitor, synchronize, update and enforce those
policies. Thus, a network is flexible for
changes in
security policies or real-time threat situations.
There are numerous research papers are reports
emphasizing and suggesting security for mobile
agents and their platforms. The proposed system
utilizes most of those ideas and in addition uses
encrypted software modules, thus completely
immune to any type of illegal modification or attack.
It may be also emphasized that in spite of all
research papers and ideas published so far, to the
best of our knowledge there is still not a single,
useful and effective application based on mobile
agents. The described system represents one such
application.
It is expected that mobile agents, as the new
computing paradigm, will show several advantages
compared to the current network security
technologies and products: Efficient discovery of
vulnerabilities; Accurate and prompt monitoring of
events, filtering and analysis of system logs, and
intelligent decisions for local (host) or global
(network) interventions; Reactions in real–time to
undesirable, illegal or unauthorized events;
Simplified network security management. Because
of these effects and advantages, it is expected that
the network security system based on mobile agents
will improve effects of security products and
technologies used in current computer systems and
networks.
3.2 Prerequisites of the Proposed
Solution
In order to have realistic solution, we will address
following major prerequisites of the proposed
system in our future research and development.
3.2.1 Security of the Mobile Agents System
Since mobile agents roam and execute through an
entire network, it is important to provide complete
protection of agents and all their resources. At the
same time, it is equally important to protect agent
platform against malicious agents. This will be
achieved through two combined approaches. The
first one is the IDP system described in the previous
section. Besides all other network resources, it will
also protect mobile agents and agent’s platforms,
since mobile agents platform is also one of the
network resources. The other approach will be to
apply various standard security mechanisms and
services in order to protect mobile agents, their
baggage, communication messages, control
structures and platforms against various accidental
and intentional threats. In that context, security
services for secure computing and secure handling
of data applied to mobile agents systems will also be
addressed. Therefore, besides IDP, comprehensive
network security system will provide to mobile
agents system security services, such as
confidentiality and integrity of resources, access
control to resources, authentication and
authorization of users and other active components,
protection and non–repudiation of transactions, etc.
3.2.2 Security Infrastructure for Mobile
Agents
The large–scale intrusion detection and prevention
systems and various security services in a
SECRYPT 2008 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
110

networking environment, could only be provided by
a comprehensive network security infrastructure.
The principles, functions and topology of such an
infrastructure for standard security services are
known, based on, for instance, PKI, secure
XML/Web, federation, various protocols, and other
security standards.
We will adopt those solutions and will use for
protection of mobile agents too. But, more
important, they will be extended with new research
results specific to the security infrastructure for
mobile agents.
There will be two main standard components of the
infrastructure:-
a) Infrastructure Components for Secure
Mobile
Agents System: - In this group we will
introduce components that support creation of
mobile agents (“Agents Factory”), validation
and appraisal of their functions, structure and
trust (“Appraisal Authorities”), their adoption,
packaging into teams, recovery, sharing,
discovery of their services, etc.
b) Infrastructure Components for the IDP
System: -
This group includes Vulnerabilities
database server, Patches server, IDP log servers,
Intrusion server etc.
4 THE FUNCTIONS OF THE
SYSTEM
4.1 Vulnerabilities Analysis
The first function of mobile agents is to assist
network and system administrators to analyze their
installed IT components in the network and to detect
potential vulnerabilities. For this purpose mobile
agents use three techniques: -(a) vulnerabilities
reported and identified in various vulnerability
databases; (b)Their own testing of new, undetected
vulnerabilities; and (c) Creating and using
sophisticated Snort vulnerability rules.
To perform this function a team of mobile agents is
assembled and launched, manually or automatically
– prescheduled, to scan vulnerabilities at remote
hosts in a network. Mobile agents reach remote host,
get their profile, and bring back the results. These
profiles are then compared with entries in the
vulnerability databases (NVD, OSVDB). At the
same time the agents handle software patches for
those vulnerabilities, as explained in the next
section.
4.2 Intrusions Detection
The second function of mobile agents is to detect
any malicious activity in the network. For this
purpose mobile agents provide three groups of
functions: - (a) Analysis of large volume of data in
various logs generation of effective reports. (b)
Detection of and reaction to host based intrusion
attempts in real time. (c) Detection of and reaction in
real time of distributed intrusion attempts.
To perform these functions different teams of
mobile agents are assembled and launched, among
them a team capable to analyze logs generated by
sensors like, Snort, Osiris, and Microsoft Windows
firewall on remote hosts. Mobile agents reach
remote host, analyze logs and in case of serious
problems report back to the security administrator.
At the same time, the second team of mobile agents
reach remote host, stays there and continuously
monitors and analyzes Snort. In case of any
suspicious activity, they immediately call other
agents for reinforcements. Finally, the third team of
mobile agents detects activities below intrusion
threshold, but cannot be ignored. Agents analyze
systems log, infer and correlate information from
different hosts, all with an intension to identify
distributed intrusion attempts.
4.3 Intrusions Response
The third function of mobile agents in our system is
to timely react to reinforcement requests in case of
intrusion attempts. In this case a team of mobile
agents is automatically dispatched to the remote host
under attack. The team is fully aware of the type of
the attack, as triggered by the static agents that
discovered the attack, and what are the required
reactions and responses. Mobile agents can act on
their own behalf or they can also coordinate, instruct
or guide individual tools on remote hosts to apply
the response appropriately. One of the immediate
actions the agents perform is to close the port being
used for an attack. They also immediately update
local firewall configuration tables. In addition, they
migrate to other hosts in order to perform the same
preventive action(s) in case of a distributed attack.
INTRUSION DETECTION AND PREVENTION SYSTEM USING SECURE MOBILE AGENTS
111
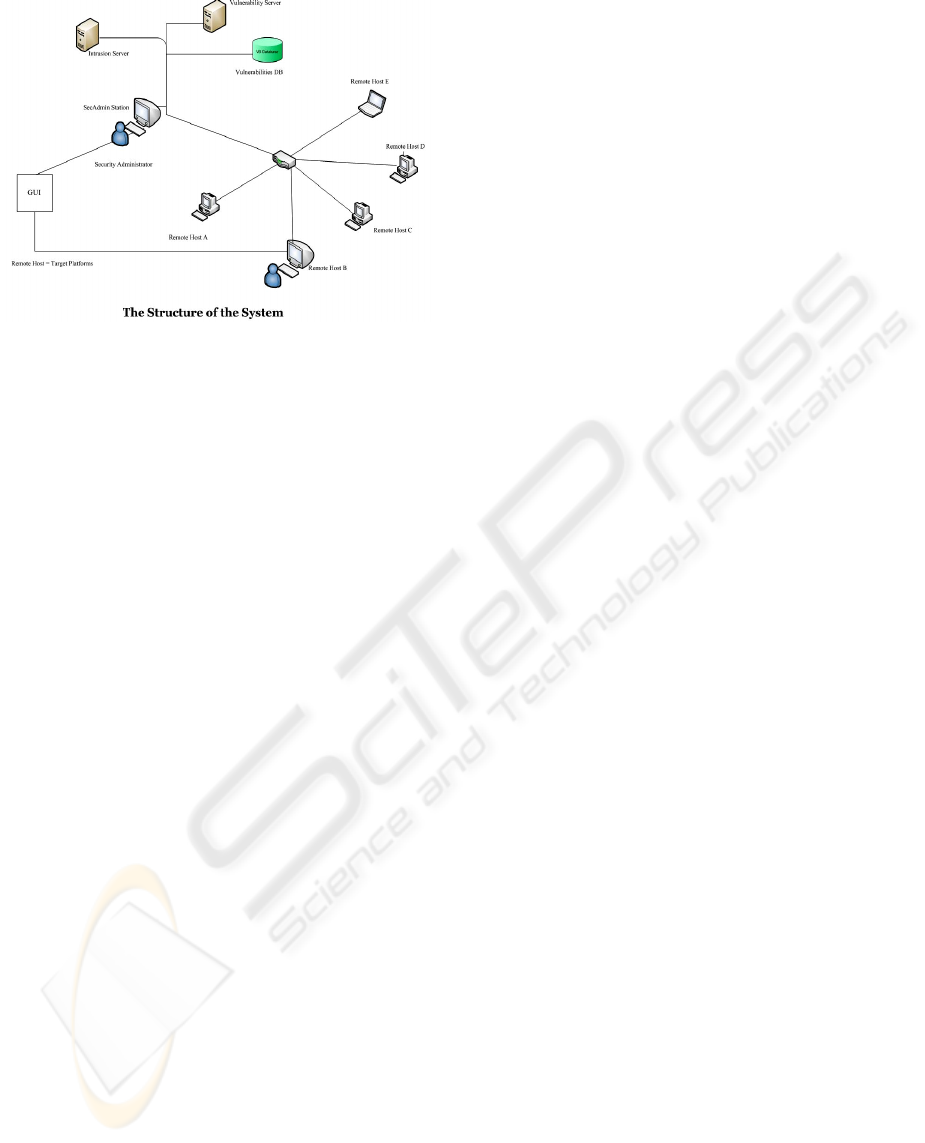
Figure 1: The Structure of the System.
4.4 Network Security Management
The fourth function of mobile agents is to assist
network administrators by keeping the network up
to-date against new potential threats. For this
function a team of mobile agents is launched, which
roam through the network, visit different systems,
analyze and install different services or security
software. For this purpose mobile agents use the
following techniques. (a) Connectivity and status of
remote hosts are checked and reported; (b)
Configuration of remote hosts are checked and
recorded; (c) Security configuration management
related tasks are applied; (d) Mapping of Snort rules
and identified vulnerabilities.
In order to perform this function, a team of mobile
agents is automatically assembled and launched,
they interact with system logs and tools installed at
remote hosts, and perform desired security
management related tasks.
5 THE COMPONENTS AND THE
STRUCTURE OF THE SYSTEM
The overall structure of the system has five
components.
5.1 Management Station
Management station is the component of the system
used by the mobile agents manager
(agents owner)
to perform various management functions with
mobile agents. It provides GUI to the agents’
manager to perform various tasks, like launching of
agents, communicating with agents, and receiving
reports from agents. Moreover, the same station is
also used to manage two servers, vulnerabilities
database server and intrusions server.
5.2 Mobile Agents Platforms
Mobile agents’ platform is installed at each server
and at each workstation where mobile agents can
arrive and execute. They have the following two
sub–components:
Agents server: a platform used to accept and execute
different agents and to provide environment for their
execution;
IDS/IPS components: used to detect attacks and
malicious activities on them. IDS/IPS components
include Snort, Osiris, Nessus™ and firewall.
5.3 Mobile Agents
Mobile Agents are the key component of the system.
Different teams of mobile agents are manually or
automatically launched from the management
station. They perform their designated tasks at
remote hosts and bring back their results to the
management station. Or, they reside at remote hosts
and continuously perform their monitoring and
analyses tasks.
5.4 Management Servers
Our system has two types of management servers:
(a) Intrusion Server: used to response for a
reinforcement requests from different agents, in case
of an attempt of an intrusion. (b) Vulnerabilities
Server: used to collect up-to-date information about
different vulnerabilities and patches. It also hosts
vulnerabilities database. It is used to launch and
response to different mobile agents teams requests
for vulnerability analyses at target platforms.
5.5 Vulnerabilities Database
Vulnerabilities database contains up-to-date
information about all the latest vulnerabilities. The
information about different vulnerabilities is
continuously updated from various sources, like
OSVDB, NVD, Security Focus, and Nessus™
vulnerabilities. Agents’ manager can also manually
add new vulnerabilities into the database in order to
further strengthen the vulnerability database.
The components and the structure of the system are
shown in the last page figure:
SECRYPT 2008 - International Conference on Security and Cryptography
112

6 CONCLUSIONS AND
BENEFITS
The described system shows all benefits, as
expected, for detection and prevention of attacks and
penetrations. It automates and simplifies
maintenance of various system components at
remote hosts, it provides more efficient reaction and
protection against attacks in real time, and it
simplifies management of distributed intrusion
detection and prevention systems.
Contrary to the current commercial products
available in the market, based on closed and
proprietary approach, the system is compatible with
multiple ID/IP products and can be easily applied to
such products for their interoperability, combined
use, and improved maintenance and administration.
Finally, the system is more efficient than existing
solutions, since it minimizes human interventions
and decisions. It is based on the open architecture
and specifications, so it can also be easily extended
by creating and deploying new agents and teams.
The system is fully operational and has already
shown all its benefits in its early tests and initial
deployments.
REFERENCES
Balasubramaniyan Jai et al., An architecture for intrusion
detection using autonomous agents (Conference)//
Computer Security Applications Conference.-
Phoenix, Arizona: IEEE, 1998. - Vol. 7. - pp. 13-24.-
0-8186-8789-4.
Bishop Matt Malicious Logic (Book Section)//
Introduction to Computer Security.- (s.l.): Addison
Wesley, 2005.- 0-321-24744-2.
Bruce Potter and McGraw Gary Software Security Testing
(Article)// IEEE Security and Privacy.- 2004.- pp. 32-
35.
CERT “CERT/CC Statistics 1988-2007 (Online)// CERT
Coordination Center.- 2007.- May 2008.- http://
www.cert.org/stats/.
Cisco Security - Products & Services - Cisco Systems
(Online)// CISCO.- 2007.- October 2007.-
http://www.cisco.com/en/US/products/hw/vpndevc/.
Denning Dorothy An Intrusion-Detection Model
(Journal)// IEEE Transactions on Software
Engineering.- (s.l.): IEEE Press Piscataway, NJ, USA ,
1987. - 2 : Vol. 13. - pp. 222-232. - 0098-5589.
James Anderson Computer Security Threat Monitoring
and Surveillance (Report).- Washington US: NIST,
1980.
Jansen Wayne and Karygiannis Tom Mobile Agent
Security (Report)/ Computer Security Division ;
National Institute of Standards and Technology. -
Gaithersburg, MD 20899, USA: NIST, 1999.- 800-19.
Ko Calvin, Fink George and Karl Levitt Automated
detection of vulnerabilities in privileged programs by
execution monitoring (Conference) // 10th Annual
Computer Security Applications Conference.- 1994.-
Vol. 5.- pp. 134-144. - DOI:10.1109/CSAC.1994
.367313.
Muftic Sead and Chang J Intrusion-Detection System
based on Mobile Agents (Report). - Washington DC
USA : The George Washington University, 2005.
nCircle nCircle, “Proactive Network Security (Online)//
nCircle. - 2007. - October 2007.
Nessus http://www.tenablesecurity.com/nessus/ (Online)//
NESSUS.- 2007. - October 2007. - http://
www.tenablesecurity.com/nessus/.
NIST National Vulnerability Database (Online)// NIST. -
2007. - October 2007. - http://nvd.nist.gov/.
OSVDB The Open Source Vulnerability Database
(Online)// OSVDB. - 2007. - October 2007. -
http://osvdb.org/.
Read H and Blyth A DS Data Visualization: Potential and
Challenges(Report). – (s.l.): ENISA Quarterly, 2007.
Reflex Network Security Switch, Intrusion Prevention
System and Policy (Online)// REFLEX. - 2007. -
October 2007.- http://www.reflexsecurity.com/.
Security Department of Homeland Cyber Security
Research and Development (Report). – (s.l.): Depart-
ment of Homeland Security, Science and Technologies
Division, 2007.
Snort Snort – the de facto standard for intrusion
detection/prevention (Online)// SNORT.- 2007-
October 2007.- http://www.snort.org/.
Steven John Adopting an Enterprise Software Security
Framework (Journal)// IEEE Security and Privacy.-
(s.l.): IEEE, 2006. - 2 : Vol. 4. – pp 84-87
INTRUSION DETECTION AND PREVENTION SYSTEM USING SECURE MOBILE AGENTS
113
