
METHOD OF INTER-WORKING BETWEEN IMS AND NON-IMS
(GOOGLE TALK) NETWORKS FOR MULTIMEDIA SERVICES
Zhongwen Zhu and Richard Brunner
PDU Messaging, Ericsson Canada, 8500 Decarie, Montreal, Quebec, Canada
Keywords: Inter-working, IMS, SIP, multimedia, XMPP, 3GPP, CSCF, Google Talk.
Abstract: With the evolution of third generation network, more and more multimedia services are developed and
deployed. Any new service to be deployed in IMS network is required to inter-work with existing Internet
communities or legacy terminal users in order to appreciate the end users, who are the main drivers for the
service to succeed. The challenge for Inter-working between IMS (IP Multimedia Subsystem) and non-IMS
network is “how to handle recipient’s address”. This is because each network has its own routable address
schema. For instance, the address for Google Talk user is xmpp:xyz@google.com, which is un-routable in
IMS network. Hereafter a new Inter-working (IW) solution between IMS and non-IMS network is proposed
for multimedia services that include Instant Messaging, Chat, and File transfer, etc. It is an end-to-end
solution built on IMS infrastructure. The Public Service Identity (PSI) defined in 3GPP standard (3
rd
Generation Partnership Project) is used to allow terminal clients to allocate this IW service. When sending
the SIP (Session Initial Protocol) request out for multimedia services, the terminal includes the recipient’s
address in the payload instead of the “Request-URI” header. In the network, the proposed solution provides
the mapping rules between different networks in MM-IW. The detailed technical description and the
corresponding use cases are present. The comparison with other alternatives is made. The benefits of the
proposed solution are highlighted.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, with the help of 3G IMS network
infrastructure rollout (3GPP, 2007), it is possible for
operators to deploy and offer different multimedia
services, such as Instant Messaging, Chat, and File-
transfer, etc., to their subscribers. However before
deploying a new multimedia service in the network,
operators want to be sure that the new service can
increase ARPU (average revenue per user) in order
to meet their ROI (Return-On-Investment). One of
very important factors for new multimedia services
to succeed is to be compatible with legacy system as
well as to work with existing Internet communities,
e.g. Google Talk (Saint-Andre, 2004). In one word,
the service shall appreciate end users as many as
possible.
In order to make the multimedia service work
across different networks (IMS and non-IMS), the
routing mechanism for Inter-working or Inter-
operability has to be provided. The mapping rules
for the request and response between two different
networks shall be set.
Following the layer concept, the Inter-working
solution can be provided at control layer or service
layer. One of example is BGCF, which provides the
telephone (voice) inter-working service between
mobile phone and traditional fixed line phone at
control layer. However it is difficult to apply this
technique to the multimedia applications that reside
at service layer. The reason is that at control layer,
the information is not enough to differentiate one
service from the others. On the other hand, the
solution is required to have little impact on IMS core
network to facilitate operators to deploy it in the
network.
In the following sections, a new IW solution at
service layer is proposed. The solution introduces
new logics at both terminal and server side. It is
defined as one public service using PSI as a service
identity. It has no impact on IMS core network. The
solution handles any kind of address schema for the
recipient. It provides the mapping rule for all the
requests and responses travelling among different
networks.
251
Zhu Z. and Brunner R. (2008).
METHOD OF INTER-WORKING BETWEEN IMS AND NON-IMS (GOOGLE TALK) NETWORKS FOR MULTIMEDIA SERVICES.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 251-256
DOI: 10.5220/0001932602510256
Copyright
c
SciTePress
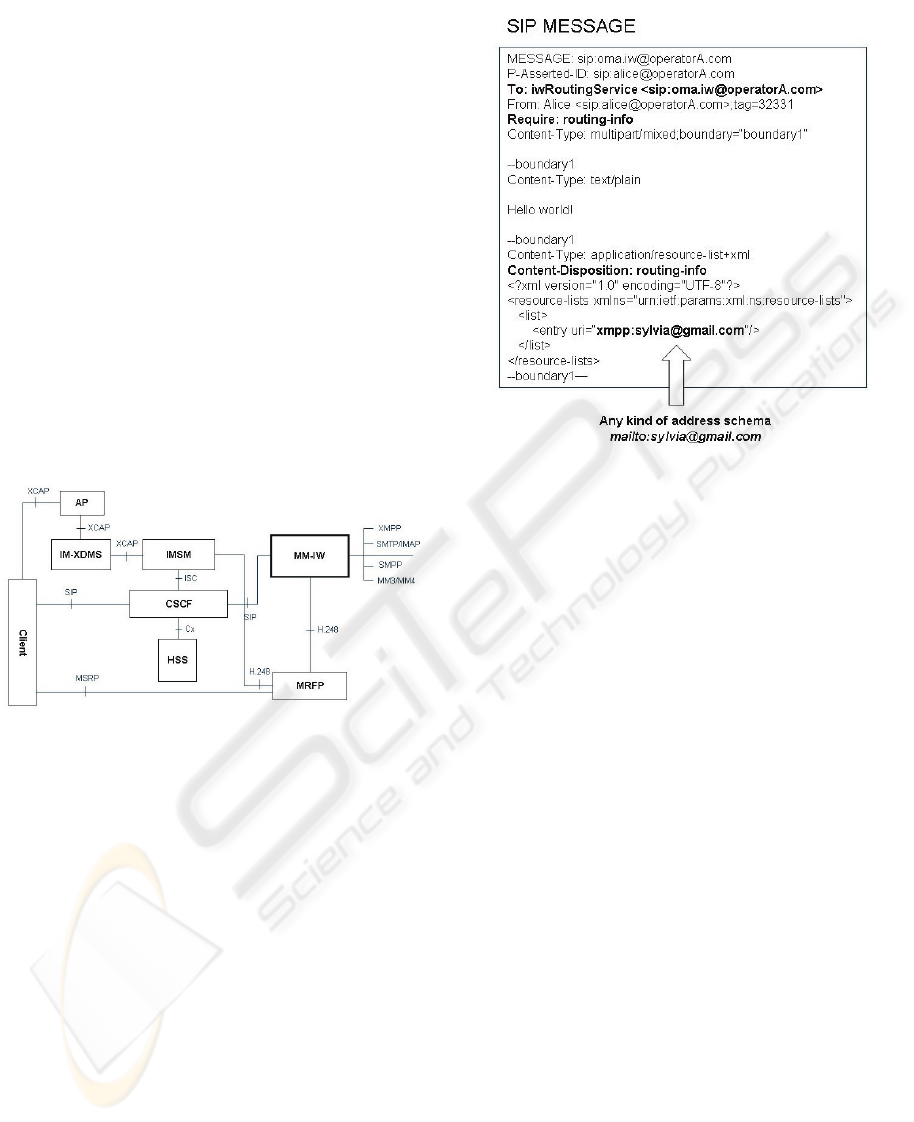
2 MULTIMEDIA
INTER-WORKING SERVICE
The basic concept of the proposed solution is to
introduce a logic function – Multimedia Inter-
working (MM-IW) in IMS network. It provides the
Inter-working service to terminals (end clients) by
publishing its PSI or pre-configured at terminals.
When sending the message to the recipient whose
address is not SIP URI or Tel URI, the terminal shall
send the SIP request directly towards MM-IW
instead of the recipient.
The overall architecture of Multimedia Inter-
working solution is given in Figure 1 by following
3GPP IMS core network structure and IM
Messaging Architecture (OMA, 2007). MM-IW is
the key component in the network to provide the
Inter-working service. It has a SIP stack to receive
and send SIP request and response. It also has the
function to control the media plane, such as MRFP,
via H.248.
Figure 1: Architecture of MM-IW solution.
The main function of MM-IW is to retrieve the
recipient’s address from the incoming request/
response, then construct the outgoing request/
response according to the mapping rules. MM-IW
resides at the edge of different networks. It makes
use of MRFP to handle the multimedia content at
media level in IMS network. On the other hand, it
also handles (convert and construct) the multimedia
content from/towards non-IMS network as shown in
Figure 1 for different protocols, e.g. SMPP, SMTP/
IMAP, XMPP, MM3/MM4, etc.
The example of SIP request, e.g. SIP MESSAGE
referring to (Rosenberg, 2002, Campell, et al. 2002,
OMA-TS 2008), from a terminal to MM-IW is
described in Figure 2. It is based upon the
mechanism provided in (Garcia-Martin, 2007) and
(Camarillo, 2007). “Request-URI” in SIP
MESSAGE is set to PSI for MM-IW, which is pre-
configured or provisioned to the terminal. A simple
and easy version of PSI is proposed hereafter:
sip:oma.iw@operator.com
Figure 2: Example of SIP MESSAGE towards MM-IW.
In addition, “Require” header is used to demand
MM-IW to handle “Content-disposition: routing-
info” stored in the payload of the SIP request in
XML format referring to (Rosenberg, 2007). As
shown in the example, the address of the destination
can be any kind of address schema since this address
shall never be used for routing purpose inside IMS
network.
3 TECHNICAL DESCRIPTION
The proposed Inter-Working solution is an end-to-
end solution based on business logics at both MM-
IW and terminal. The corresponding flows and
mapping rules are described and discussed in detail
in the following subsections. Then the use cases are
given to cover all basic Inter-working scenarios.
3.1 Logic Flows
3.1.1 Logic Flow at the Terminal
(Originating Side)
At the terminal (originating side), when sending SIP
request to the recipient, the end user shall decide if
the request shall be sent to recipient directly (using
normal SIP flow) or through MM-IW. The basic
logics to make such kind of decisions are given in
Figure 3.
SIGMAP 2008 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
252
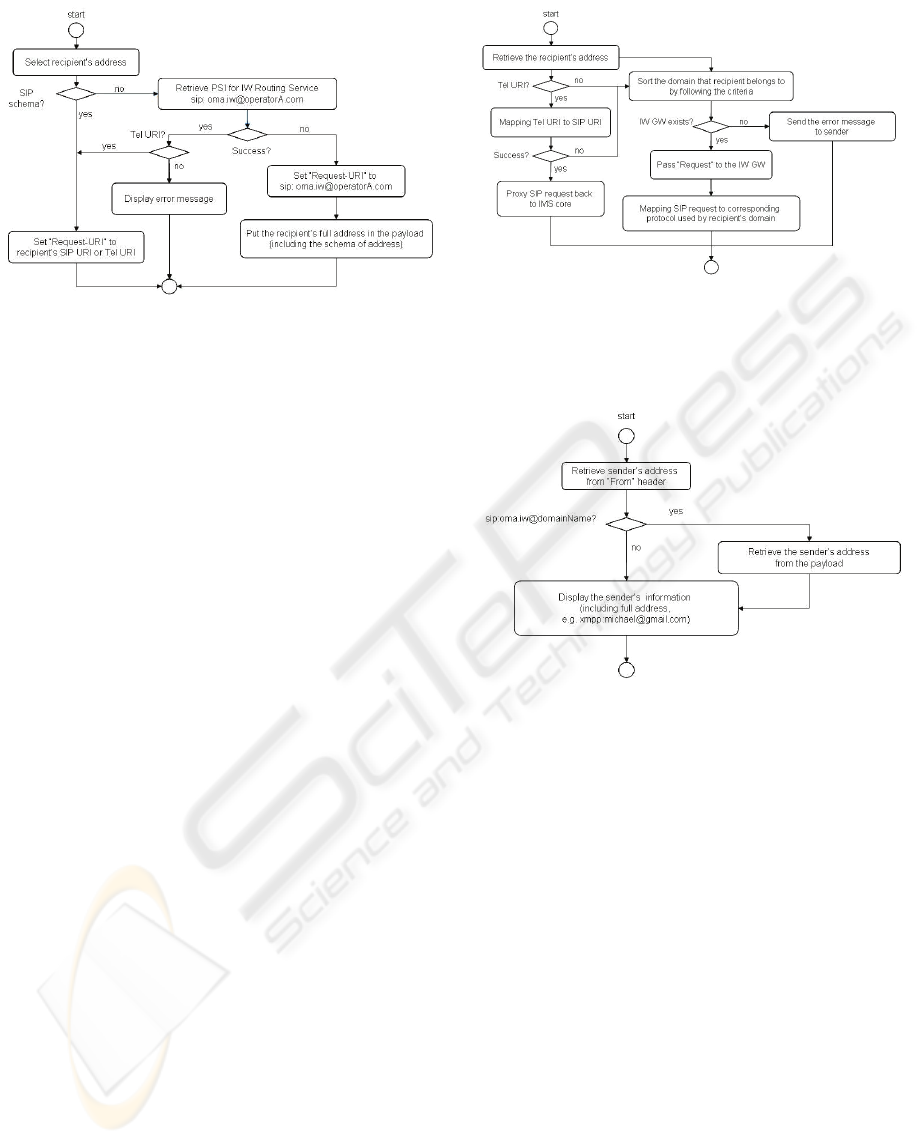
Figure 3: Logic flow at terminal (originating side).
In general, the end user selects a recipient from
his contact list, probably only the name. Then the
terminal retrieves the corresponding address from
the contact list of the sender. It first checks to see if
the address follows SIP schema, which is the pre-
requisite for routing the message in IMS network.
If the recipient’s address is not SIP URI, the
terminal retrieves PSI for IW routing service (MM-
IW), which is set to “Request-URI” in the outgoing
SIP request. Then the recipient’s address as well as
the message input by the sender is put into the
payload of the outgoing SIP request by following the
format given in Figure 2.
In case that PSI can not be retrieved, the terminal
checks if the recipient’s address is Tel URI. If true,
the message is sent out by setting recipient’s Tel
URI in “Request-URI”, which requires IMS core
network (mainly DNS lookup) to resolve the
recipient’s SIP address referring to 3GPP.
At the end, the message is sent to IMS network if
all the steps succeed or the error message is
displayed for the failure cases.
3.1.2 Logic Flow at MM-IW
At MM-IW, when receiving the request, it shall first
decide if the request can be routed back to IMS
network or not according to the mapping between
Tel URI and SIP URI.
If the mapping succeeds, the request shall be
proxy back to IMS network. Otherwise, the request
shall be sent to the IW GW (Inter-Working
Gateway), which maps the SIP request to the
corresponding protocol based upon the recipient’s
address (schema plus content of the address).
If no corresponding IW GW exists, the error
message is sent back to the message sender.
Figure 4: Logic flow at MM-IW.
3.1.3 Logic Flow at the Terminal
(Terminating Side)
Figure 5: Logic flow at terminal (terminating side).
At the terminal (terminating side), when receiving
SIP request, the end user (recipient) shall check to
see if “From” headers in the request presents the
address of MM-IW hosted in the recipient’s or
sender’s operator domain. If yes, the sender
information shall be retrieved from the payload of
the received SIP request. The basic flows to make
such kind of decisions are described in Figure 5
3.2 Mapping Rules
The mapping rules for the message between IMS
and Google Talk are given as an example in Figure 6
and 7.
In the message flow from IMS to Google Talk,
“From” header in the SIP request is mapped to
“From” header in XMPP message format. The
recipient’s address that is stored in payload of the
SIP request is mapped to “To” header in XMPP
message format referring to (Saint-Andre, 2004).
METHOD OF INTER-WORKING BETWEEN IMS AND NON-IMS (GOOGLE TALK) NETWORKS FOR
MULTIMEDIA SERVICES
253
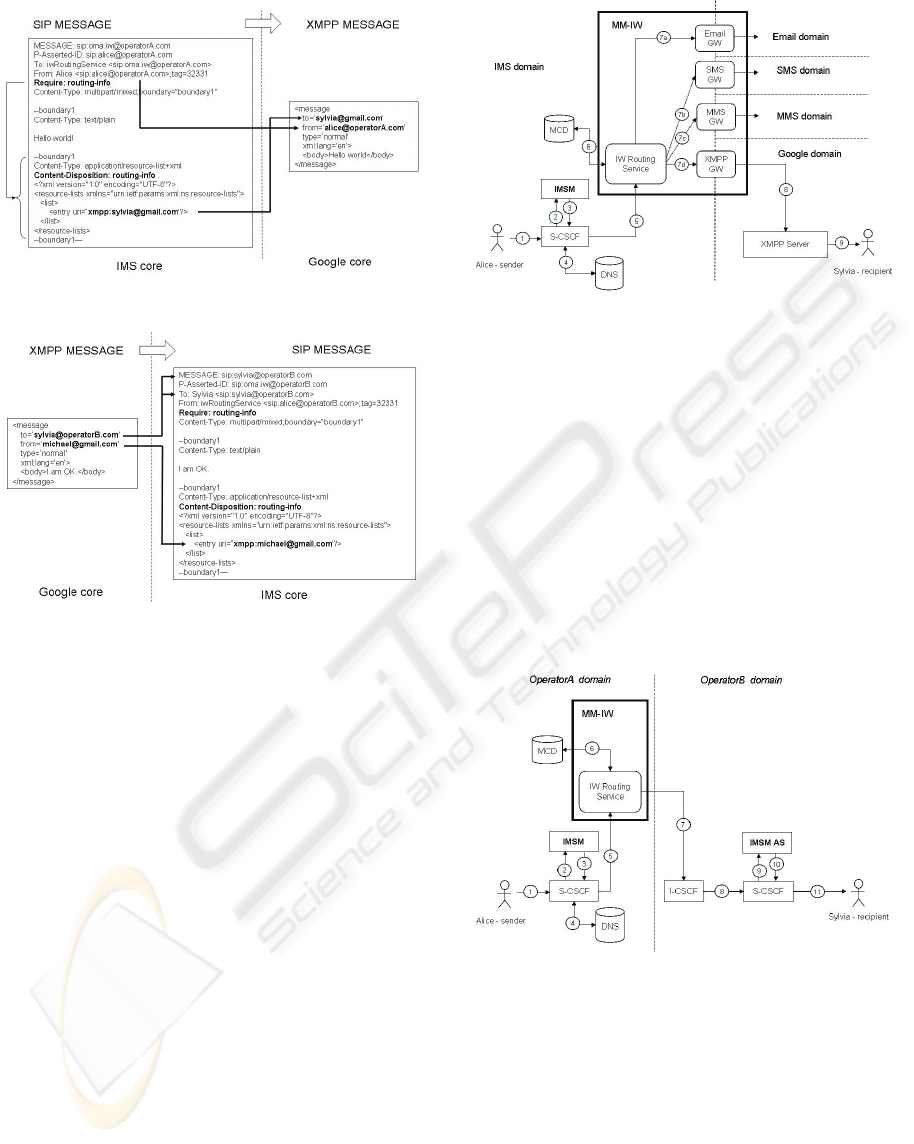
Figure 6: Maps from SIP to XMPP (message).
Figure 7: Maps from XMPP to SIP (message).
In the reverse flow, “To” header in XMPP
message is mapped to both “Request-URI” and “To”
header in the outgoing SIP request. “From” header
in XMPP message is mapped to the resource list
captured in the payload of the outgoing SIP request.
Furthermore, MM-IW shall include its own address
in “From” header as shown in Figure 7 to indicate
the message is injected by MM-IW.
3.3 Use Case Discussion
3.3.1 Flow from IMS to Google (Originating
IW)
This is a basic scenario in which Alice, an IMS user,
sends an Instant Message towards Sylvia who is a
Google Talk user.
The message arrives at S-CSCF for Alice. It is
forwarded to IMS Messaging server (IMSM) based
upon the ISC trigger (IMS Service Control, referring
to 3GPP standard) since it is IM. Then the S-CSCF
routes message towards MM-IW after resolving PSI
to IP address by doing DNS lookup.
Figure 8: Flow from IMS to Google (Originating IW).
IW routing service in MM-IW verifies if the
sender is allowed to use the service by checking the
sender’s profile in user database (MCD). Then the
message is forwarded to XMPP GW since the
recipient is a Google Talk user. Eventually the
message is delivered to the recipient via XMPP
server.
3.3.2 Flow from IMS to IMS using Tel URI
The scenario is that Alice only has Sylvia’s
telephone number. She wants to send IM to Sylvia
using Tel URI instead of SIP URI.
Figure 9: Flow from IMS to IMS using Tel URI.
Since the recipient’s address is Tel URI, the
terminal at originating side puts the recipient’s
address in the payload of the message according to
flow in Figure 3. The message is sent to MM-IW.
IW routing service figures out that the recipient’s
address – Tel URI can be mapped back to SIP URI
(DNS lookup, not shown in Figure 9). Then IW
routing service replaces Tel URI with the found SIP
URI and proxy the message back into IMS network.
SIGMAP 2008 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
254
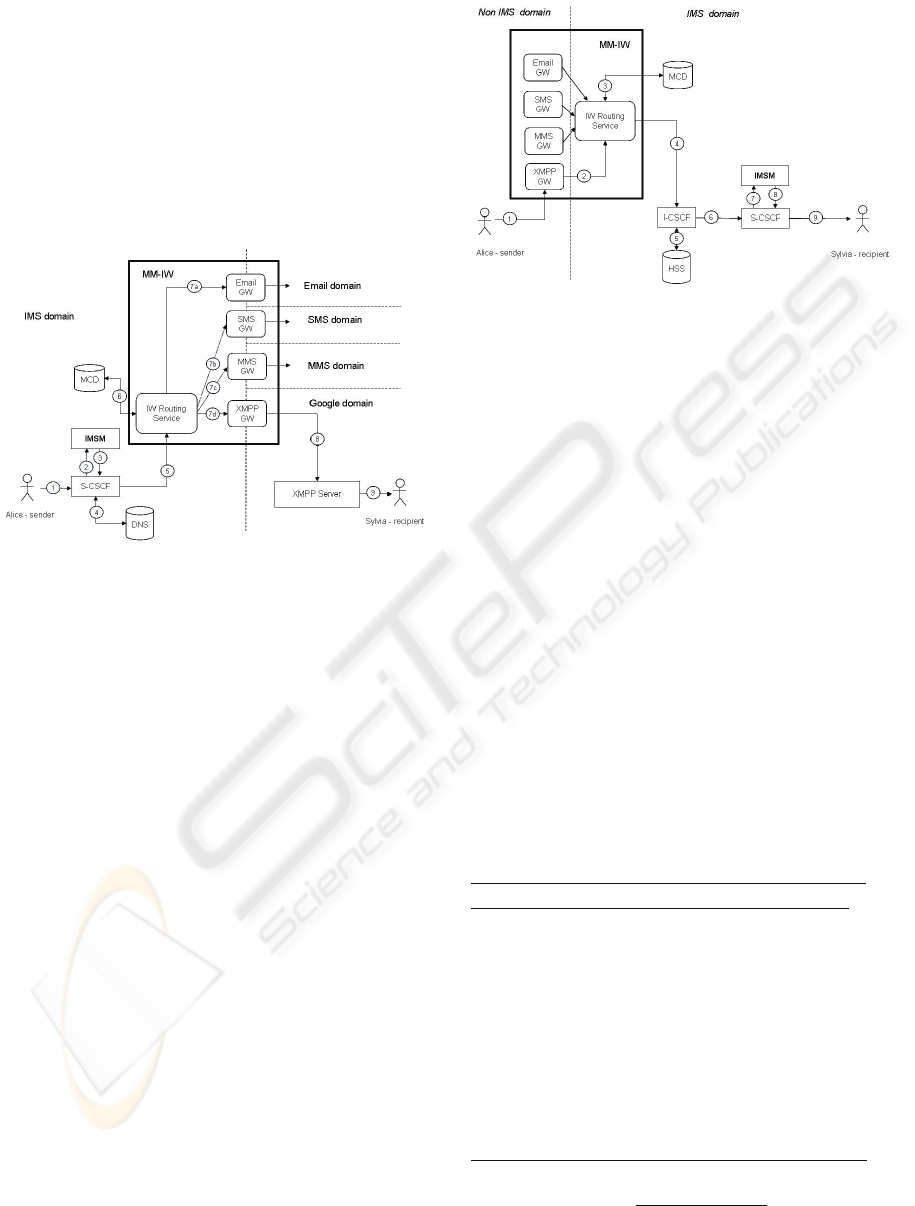
The message is eventually delivered to the recipient
via terminating S-CSCF.
3.3.3 Flow from IMS to Google
(Terminating IW)
The scenario is that Alice sends IM to Sylvia.
However, at that time, Sylvia is “un-registered” in
IMS network but she can be accessed via Google
Talk account. The message shall be delivered to
Sylvia via Google Talk domain.
Figure 10: Flow from IMS to Google (Terminating IW).
Referring to Figure 10, after receiving the
message from the S-CSCF, the terminating IMSM
finds out that the recipient is “un-registered”. IMSM
forwards the message towards MM-IW directly
following step 10. The IW routing service in MM-
IW checks the recipient’s preference in user
database, such as MCD. Then it decides to send the
message to XMPP GW for Google IW.
XMPP GW maps the SIP request to XMPP
message format by applying the mapping rule
referring to Figure 6 and sends the message to the
recipient via XMPP server.
3.3.4 Flow from Google to IMS
The scenario shown in Figure 11 is that Alice wants
to use her Google Talk account to send an IM to
Sylvia.
When the message arrives in XMPP GW, IW
routing service retrieves the recipient’s address. IW
routing service might check if the recipient exists in
the operator domain and the recipient is allowed to
receive the message from Google Talk users.
Figure 11: Flow from Google to IMS.
After the SIP URI is identified for the recipient,
the message is mapped from XMPP format to SIP
request by following the mapping rules shown in
Figure 7.
The IW routing service sends the message to I-
CSCF, which will route the message towards the
terminating S-CSCF after consulting with HSS.
Then the terminating IMSM is involved and the
message is delivered to the recipient.
4 COMPARISON
One of alternative solutions for the inter-working
between IMS and non-IMS network was proposed in
(Costa-Requena et al., 2004). The URI parameter is
used to carry the address schema of the destination.
The example given in their patent publication is for
the interoperability between wireless village client
and IMS client. The address of wireless village (wv)
is mapped to SIP address and vice versa.
wv:bob@operatorB.com
is mapped to
sip:bob@operatorB.com;(user=wv).
The conversion of recipient’s address between two
address schemas is done either at terminal or IMS
network (CSCF, or GW). The solution has the
impact on IMS core network, which is not the case
for the proposed solution.
The other alternative is to encode recipient’s address
in Request-URI of SIP request, such as:
sip:bob@gmail.com.iw.operator.com
The domain name, iw.operator.com
, is provisioned
into DNS, which is used to route the corresponding
SIP request to the IW node. However, this solution
METHOD OF INTER-WORKING BETWEEN IMS AND NON-IMS (GOOGLE TALK) NETWORKS FOR
MULTIMEDIA SERVICES
255

can not carry the information of the destination
scheme, e.g. xmpp.
5 SUMMARY
The proposed MM-IW solution provides the service
to allow end users to send/receive IM to/from their
friends in non-IMS network. In contrast to other
existing IW solutions, it is deployed at service layer
and has no impact on IMS core network. The
solution is well suit for IMS architecture.
The impact on the IMS terminal client is limited
since it only requires verifying the schema of the
recipient against SIP URI at sending side and the
sender’s address at the terminating side. The
proposed MM-IW is neither terminal-based IW
solution nor purely network-based IW solution. It is
the solution that requires the logics from both
terminal and network.
The proposed MM-IW provides the foundation to
bring different messaging users together (IMS or
non-IMS users). It will benefit not only end users
but also operators.
The further investigation on generic mapping
rules among different protocols is under the way.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is fund by Ericsson Canada Inc. under
Ericsson DMMP technology leadership project
(2008).
TERMINOLOGY
Acronym Definition
3GPP 3
rd
Generation Partnership Project
ARPU Average Revenue Per User
BGCF Breakout Gateway Control Function
CSCF Call Session Control Function
DNS Domain Name System
GW Gateway
HSS Home Subscriber Server
I-CSCF Interrogating CSCF
IETF Internet Engineering Task Force
IMAP Internet Message Access Protocol
IMS IP Multimedia Subsystem
IMSM IMS Messaging
ISC IMS Service Control
IW Inter-Working
MCD Messaging Common Directory
MM-IW Multimedia IW
MMS Multimedia Messaging Service
MRFP Multimedia Resource Function
Processor
ROI Return on Investment
SMS Short Messaging Service
SMPP Short Message Peer-to-Peer Protocol
SMTP Simple Mail Transfer Protocol
XMPP Extensible Messaging and Presence
Protocol
REFERENCES
3GPP TS 24.229, 2007 IP multimedia call control protocol
based on Session Initial Protocol and Session
Description Protocol; stage 3. In release 7.
OMA-AD-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0, 2007, Instant Messaging
using SIMPLE Architecture. In version 1.0.
OMA-TS-SIMPLE_IM-V1_0, 2008, Instant Messaging
using SIMPLE. In version 1.0.
Gustafsson A., Lenman A., 2007, Ericsson Enriched
Messaging Architecture. In Ericsson Review No. 2.
Garcia-Martin, M., 2007. Multiple-Recipient MESSAGE
Requests in the Session Initiation Protocol. In draft-
ietf-sip-uri-list-message-01.txt.
Camarillo, G., 2007. Conference Establishment Using
Request-Contained Lists in the Session Initiation
Protocol. In draft-ietf-sip-uri-list-conferencing-01.txt.
Rosenberg, J., 2007. Extensible Markup Language (XML)
Formats for Representing Resource Lists. In RFC
4826
Saint-Andre, P., 2004. Extensible Messaging and Presence
Protocol (XMPP); core. In RFC3920.
Saint-Andre, P., 2004. Extensible Messaging and Presence
Protocol (XMPP); Instant Messaging and Presence. In
RFC 3921.
Saint-Andre, P., 2004. Mapping XMPP to CPIM. In
RFC3922.
Saint-Andre, P., 2004. Internationalized Resource
Identifiers and URIs for XMPP. In RFC4622.
Rosenberg, J., 2002. Session Initial Protocol. In RFC
3261.
Costa-Requena, J. Aarnos, J. And Espigares, I. 2004
Method and Apparatus for Routing Wireless Village
Messages in An Internet Protocol Multimedia
Subsystem, US patent application publication,
US2004/0068584 A1.
Campbell, B. Rosenberg, J. Schulzrinne H. Huitema and
Gurle, 2002, SIP Extension for Instant Messaging,
RFC 3428
SIGMAP 2008 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
256
