
Search Algorithm and the Distortion Analysis
of Fine Details of Real Images
Sai S. V. and Sorokin N. Yu
Institute of Information Technologies, Pacific National University
Tikhookeanskaya str., 136 Khabarovsk, Russia
Abstract. This work describes a search algorithm and a method of the
distortions analysis of fine details of real images based on objective criteria.
1 Introduction
Nowadays for the quality analysis of coding and transfer of images various static and
dynamic test tables are used. Methods of measurement of the test table signals or
subjective estimations allow for estimating distortions that appear during the image
compression, for example, under JPEG, JPEG 2000 or MPEG standards.
It is known, that the distortions are essentially shown on fine structures with low
contrast during image compression with losses. In test tables such structures include:
stroke patterns such as stroke wedges and zoned lattices, groups of parallel strokes,
color strokes, thin lines, fine single details, etc. However, as practice shows, contrast
of test tables (hence, fine structures) has a high value, which does not allow
estimating distortion of details with a low contrast.
For a full rating of coding quality real test photos or video images are used
additionally to test tables. The rating of quality of real images is carried out by
subjective methods or with the help of root-mean-square deviations.
Until now the most reliable way of image quality estimation is the method of
subjective estimation, which allows for estimating serviceability of a vision system on
the basis of visual perception of the decoded image. Procedures of subjective
estimation demand a great amount of tests and a lot of time. In practice, this method is
quite laborious and restricts the control, tuning and optimization of the codec
parameters.
The most frequently used the root-mean-square criterion (RMS) for the analysis of
static image quality does not always correspond to the subjective estimation of fine
details definition since a human vision system processes an image on local
characteristic features, rather than averaging it elementwise. In particular, RMS
criterion can give "good" quality estimations in vision systems even after elimination
of fine details in a low contrast image after the digital compression.
A number of leading companies suggest hardware and software for the objective
analysis of dynamic image quality of MPEG standard [1]. Examples are: Tektronix
PQA 300 analyzer, Snell & Wilcox Mosalina software, Pixelmetrix DVStation
device. Principles of image quality estimation in these devices are different.
S. V. S. and N. Yu S. (2008).
Search Algorithm and the Distortion Analysis of Fine Details of Real Images.
In Image Mining Theory and Applications, pages 58-64
DOI: 10.5220/0002338700580064
Copyright
c
SciTePress

As an example, PQA 300 analyzer measures image quality using the “Just Noticeable
Difference – JND” algorithm developed by Sarnoff Corporation. PQA 300 analyzer
carries out a series of measurements for each test sequence of images and basing on
the JND measurements it forms a common PQR estimation, which is close to
subjective estimations. Snell & Wilcox firm offers a PAR method (Picture Appraisal
Rating) for the objective analysis of image quality. PAR technology systems control
artifacts created by compression under MPEG-2 standard. The Pixelmetrix analyzer
estimates a series of images and determines definition and visibility errors of block
structure and PSNR in brightness and chromaticity signals.
The review of objective methods of measurements shows that high contrast
images are usually used in test tables, while distortions of fine details with low
contrast that are mostly common after the digital compression are not taken into
account.
It is necessary to note that there exists a lack of practical objective methods of
measurement of quality of real images: analyzers state an integrated rating of
distortions as a whole and do not allow for estimating authentically distortion of local
fine structures of images.
Thus, the problem of finding the objective criteria of the analysis of fine details
distortions of images nowadays is considered important.
[5] and [6] describe methods for the definition analysis of fine details of the test
table image. In these works mathematical models and definition rating criteria in
equal-contrast color space are described, and a synthesis algorithm of test tables for
static and dynamic images is proposed.
In the present article the original method of the distortions analysis of fine details
of real images by objective criteria is offered.
2 Search Algorithm of Fine Details
Detailed descriptions of the search algorithms of fine details are presented in well
known literature, e.g., (Pratt, 2001) and (Gonzalez, Woods, 2002). These overviews
show that in most cases the criteria of the fine details recognition do not take into
account the threshold values of the visual contrast.
Consider our developed search algorithm of fine details of the image.
In the first stage the image is broken into blocks of size 3×3 pixels.
In the second stage for each pixel of the block a transformation of primary color
signals (RGB) into equal color space
***
VUW
(Wyczecki, 1975) is carried out:
1725
31
−=
/*
YW
,
)(13
**
o
uuWU −=
,
)vv(WV
o
**
−=13 ,
where
*
W
⎯ is the brightness index;
*
U and
*
V ⎯ are the chromaticity indices; u
and v are the chromaticity coordinates in Mac-Adam diagram (Mac Adam, 1974);
o
u = 0,201 and
o
v = 0,307 are the chromaticity coordinates of basic white color.
In the third stage the contrast of the block in the normalized equal color space is
calculated:
5959

2
*
th
*
2
*
th
*
2
*
th
*
V
V
U
U
W
W
K
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
=
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
,
(1)
where
)(3
*
min
*
max
*
WWW −=
Δ
, )(3
*
min
*
max
*
UUU −=
Δ
and )(3
*
min
*
max
*
VVV −=
Δ
are the
values of block contrast on brightness and chromaticity indices, determined by the
number of the minimum perceptible color difference (MPCD);
*
th
W
Δ
,
*
th
U
Δ
,
*
th
V
Δ
are
the thresholds according to brightness and chromaticity indices for fine details.
Threshold values on brightness and chromaticity indices depend on the size of fine
details, background color coordinates, time period of object presentation and noise
level.
For fine details with sizes not exceeding one pixel the threshold values are
obtained experimentally.
In particular (Sai, 2003), for fine details of the test table located on a grey
background threshold values are approximately
6
*
≈
th
W
Δ
MPCD and
72
**
≈≈
thth
UU
ΔΔ
MPCD.
In the fourth stage we exclude from the analysis the blocks with high contrast and
those blocks that have invisible (by eye) changes of brightness and chromaticity.
Thus, the remaining blocks have contrast that satisfies to the following condition:
52
≤
≤
K
Δ
.
(2)
The distinctive feature of the algorithm is that the thresholds of visual perception of
fine details contrast of the image depend on the average brightness of the analyzed
block. In particular, the contrast change on light blocks of the image will be more
visible than on dark ones.
The given condition can be taken into account with the help of adjusting
coefficients during the computation of the thresholds. For example, for the brightness
threshold:
**
*
th
W
th
WkW
ΔΔ
⋅= ,
(3)
where
1
*
≈
W
k
Δ
for the grey blocks ( 9070
*
<< W ), 1
*
<
W
k
Δ
for the light blocks
(
90
*
≥W
), and 1
*
>
W
k
Δ
for the dark blocks (
70
*
≤W
).
In the fourth stage (using the standard binary masks) the recognition of the block
with the following attributes is carried out: a “dot object”, a “thin line”, a “structure
fragment”. As a “structure fragment” the “chess field” fragment is selected.
For one block of size 3×3 pixels the quantity of such masks including their
inversion will be equal to 12. Some examples of binary masks are shown in Figure 1.
Fig. 1. Examples of binary masks.
For recognition of attributes the image of the block will be transformed to the binary
form as follows: for each i-th pixel of the block the following condition is checked:
6060

1
***
*
<
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
+
⎟
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎜
⎝
⎛
2
th
*
i
2
th
*
i
2
th
i
V
V
U
U
W
W
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
Δ
,
(4)
where
)WW(W
*
min
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
, )UU(U
*
min
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
, )VV(V
*
min
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
are the
differences of the coordinates for the comparison of pixel’s color coordinates with the
minimal value; or
)WW(W
*
max
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
, )UU(U
*
max
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
, )VV(V
*
max
*
i
*
i
−= 3
Δ
are the differences of the coordinates for the comparison of pixel’s color coordinates
with the maximal value.
If the condition (4) is fulfilled the decision on membership of the pixel to the
minimal or to the maximal value is taken. We assign the level of one to the maximal
values and level of zero to the minimal values. If the condition (4) is not fulfilled for
an i-th pixel, this block is excluded from the further analysis.
After that the binary block of the image is compared to the binary image of the j-th
mask with the help of a simple equation:
∑
=
−=
9
1i
i,jij
)MaskIb(M .
(5)
The decision is made that the given block refers to the image of the j-th mask in case
if the computed value (5) is equal to zero. The decision about exclusion of the current
block from the analysis is made if the value (5) is not equal to zero for all masks.
Thus, the offered search algorithm allows for allocating fine details in the test real
image for the further analysis of their reproduction quality in the decoded image.
3 Distortion Analysis
Consider a method of the distortion analysis of fine details of a real image. For the
analysis we used two digital images. The first image is in the BMP format and is
considered as a reference image received from a scanner or a digital camera. We
assume that on the output of the image source the image with a high quality of fine
details is formed. The second image (also in the BMP format) is received after
processes of compression and decoding of the first image.
In the first stage the search algorithm of fine details of the reference image is
carried out.
On the second stage for each found j-th block the deviation of the maximal value
of color coordinates is computed:
(
)
(
)
(
)
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
++=
2
*
2
*
2
*
max
iiij
VUW
ε
,
(6)
where i = 1…N; N = 9 is the number of elements in the block and
6161
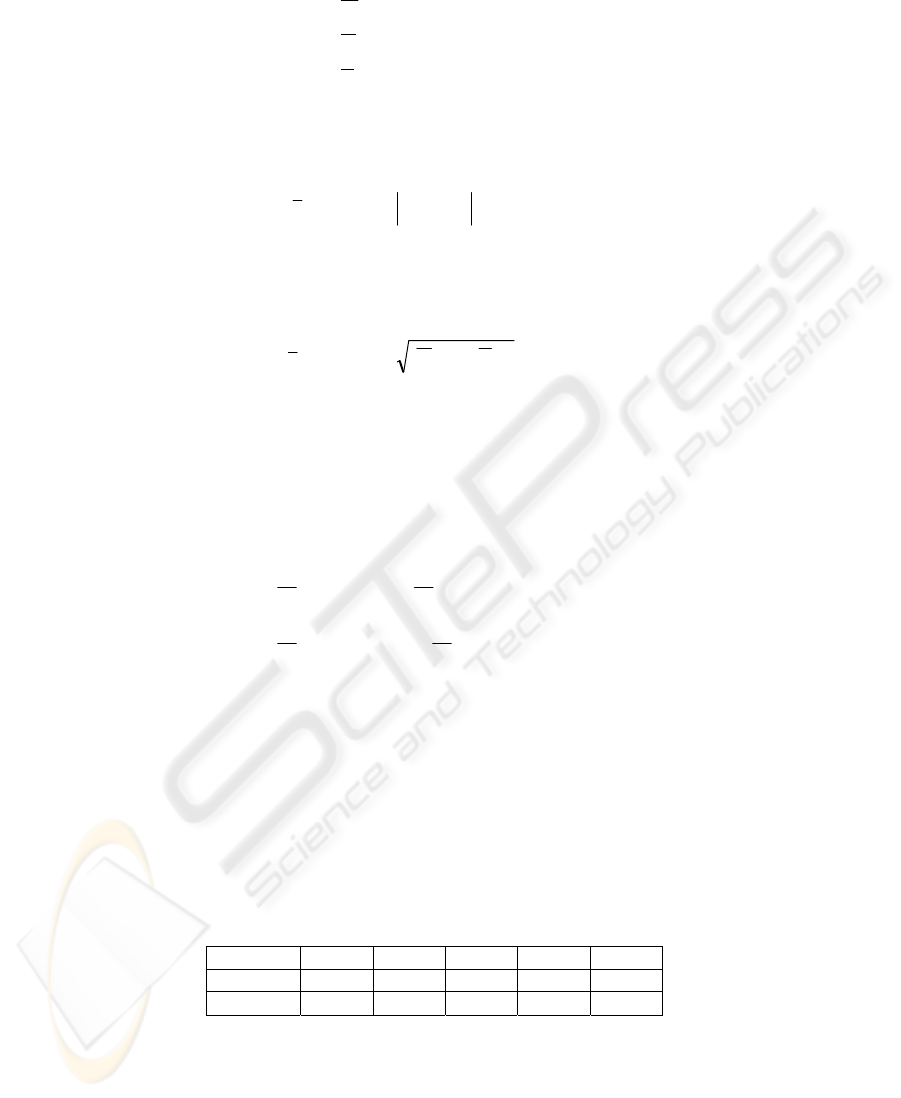
****
****
****
/)
~
(3
,/)
~
(3
,/)
~
(3
thiii
thiii
thiii
VVVV
UUUU
WWWW
Δ
Δ
Δ
−=
−=
−=
are the normalized to thresholds deviations on brightness and on chromaticity.
In particular if the block is analyzed only on brightness the expression (6) will be
transformed into:
(
)
***
)(
/
~
3max
thiiWj
WWW
Δε
−= ,
(7)
where
*
i
W
~
is the value of brightness of the i-th pixel in the image block after the
compression.
If the block is analyzed on chromaticity we obtain:
(
)
(
)
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
+=
2
*
2
*
),(
max
iiVUj
VU
ε
.
(8)
Expression (8) determines the maximal error of color transfer of fine details in the
block.
Here it is necessary to note that in the compression standards the most complete
information on fine details is contained in the brightness component. Therefore, a
separate calculation of the errors on brightness and chromaticity is justified.
In the third stage the average values of deviation on brightness and on
chromaticity for all image blocks are calculated:
∑
∑
−
=
−
=
=
=
1
0
),(
,
1
0
)(
**
*
;
M
j
VUj
VU
M
j
Wj
W
εε
εε
,
(9)
where M is the number of blocks in the image, which contain fine details found by the
search algorithm.
In the fourth stage using the error value (9) the quality rating of fine details for
transfer and reproduction in the analyzed image is established.
The ten-point scale of quality, used in Adobe Photoshop 5.0 system, during the
realization of JPEG compression algorithm is chosen.
Table 1 contains experimental dependencies of the error (9) on brightness from the
quality rating R for test images "Lena" and "Barbara". For the analysis the blocks with
average brightness in the range (
9070
*
<< W ) were used.
Table 1. Dependency of the error on the brightness.
R 1 3 5 7 9
“Lena” 1,00 0,80 0,78 0,39 0,16
“Barbara” 0,92 0,72 0,67 0,41 0,21
Figure 2 contains a fragment of the test image "Barbara" (top) and the found blocks
with fine details (bottom). On Figure 3 a fragment of the test image with a high
6262

quality rating is shown. On Figure 4 a fragment of the test image with a low quality
rating after an execution of the JPEG algorithm is shown.
For an illustration of distortions in Figures 3 and 4 the differences of brightness in
the blocks of the first and second images are shown (bottom pictures).
Experimental results of research of the error dependences for other test images
have shown that for support of a high quality rating (
6>R ) the average value of the
coordinates deviation of fine details on brightness should not exceed 50 % from
threshold value:
5,0≤
W
ε
.
Fig. 2. Fragment of the test image. Fig. 3. High quality (R = 7).
Fig. 4. Low quality (R = 1).
6363

4 Conclusions
The values of contrast (1) or errors (9) are estimated by a normalized number to visual
thresholds. This is an advantage of the developed search algorithm and of the method
of the distortion analysis. Therefore, the user can make objective decisions about the
presence of fine details in images with a low contrast using expressions (2), (4) and
(5) or about the visibility of distortions on values of the error (9).
In conclusion it is necessary to note that the developed search algorithm and the
method of the distortion analysis of fine details of real images can be used not only
for the error analysis of the JPEG algorithm, but also for any other compression
algorithm of static images. In this case, it is enough to compare the received value of
the error
ε
to the quality rating (Table 1).
The method is also applicable for the distortion analysis of fine details of images
in the basic I-frames of dynamic video sequences used in the MPEG standards.
The high quality reproduction of fine details of images is an important task for
design of vision systems in various applications. The authors hope that the algorithm
and the method offered in this work will help designers of vision systems to solve this
task more efficiently.
References
1. Glasman, K., 2004. MPEG-2 and Measurements. In “625”, No. 1.
2. Gonzalez, R.S., Woods, R.E., 2002. Digital Image Processing. Prentice Hall.
3. Mac Adam, D.L., 1974. Uniform Color Scales. In JOSA, Vol. 64.
4. Pratt, W.K., 2001. Digital Image Processing. Wiley.
5. Sai, S.V., 2003. The Quality of Transmission and Reproduction of Fine Details in Color
Television Images. Dalnauka, Vladivostok.
6. Sai, S.V., 2007. Methods of the Definition Analysis of Fine Details of Images. Chapter in
the book: Vision Systems: Applications, G. Obinata and A. Dutta (eds.), Advanced Robotic
Systems, Vienna, Austria.
7. Wyszecki, G., 1975. Uniform Color Scales: CIE 1964 U*V*W* Conversion of OSA
Committee Selection. In JOSA, Vol. 65.
6464
