
HYBRID PARAMETERIZATION SYSTEM FOR WRITER
IDENTIFICATION
Carlos F. Romero, Carlos M. Travieso, Jesús B. Alonso and Miguel A. Ferrer
Department of Signals and Communications, Technological Centre for Innovation on Communication (CeTIC)
University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Campus de Universitario de Tafira
Ed. de Telecomunicación, Pabellón B. 35017, Las Palmas de G.C., Spain
Keywords: Writer Identification, Graphologist Features, Handwritten Writing, Biometric System, Neural Networks,
Pattern Recognition.
Abstract: In this paper, we present a hybrid parameterization system from classical and graphologist features, as the
existing percentage of cohesion in the writing of each individual, as well as the smaller and greater axes of
the ovals and loops. They have been used on the writer identification together with other parameters applied
to handwritten words. That set of characteristics has been tested with our off-line database, which consists
of 70 writers with 10 samples per writer and as well each sample is composed of 34 words. We have got a
success rate of 96%, applying as classifier Neural Network, and after, the technique of “more voted”
algorithm, with 10 Neural Networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
Nowadays, advances on Computer Science and the
proliferation of computers in the modern society, it
is an unquestionable fact. But the great importance
that continues having the handwritten document and
the own writing, is true.
For this reason and its wide and extented use,
many handwritten documents are exposed to
possible forgeries, deformations or copies, and
generally, with illicit use. The tasks of Graphologist
or Forensic Expert are very hard and tedious, due to
the secuencial and manual work developed, whose
task is to certify and to judge the authenticity or
falsehood of handwritten documents (for example:
testaments) in a judicial procedure.
Nowadays, the Graphologists have to investigate
and use so much time to extract features that allow
to drawing conclusions about the body of writing.
Therefore, they have to work with graph paper and
templates in order to obtain parameters (angles,
dimensions of the line, directions, parallelisms,
curvatures, alignments, etc.). Too, they have to use
magnifying glass with graph paper in order to do
measures of angles and lines.
The motivation of this present work is to develop
an automatic system for the help in this field. It is
possible because our proposal try extracting
information biometric of the writing. The scientific
bases for this idea are from the brain human. If we
try to do writing with the less skilful hand, there will
be some parts or forms very similar to the writing
with the skilful hand, due to those orders are sent by
the brain, and each brain is intrinsic of each person
(Romero et al., 2007).
The act to write is a phenomenon governed by
the brain and integrated in the psychomotricity of
the individual; in contrast to mimic movements, the
handwriting movements are fixed toward a plane
that allows its study and measurement.
The writing like codified and dynamic message
that reflects a certain biometric information of the
individual in its communication with the others is
fundamentally individual, recognizable, univocal
and unique; that it makes possible the people
identification.
Generally, this effect is projected toward the
writing by two types of forces (Romero et al., 2007),
they are:
Conscious or Known: because it can do a
control of the own free will.
Unconscious: because it escapes to control of
the own free will. This is divided into: forces
of type mechanical and emotional, where are
harboured feelings.
449
Romero C., Travieso C., Alonso J. and Ferrer M. (2009).
HYBRID PARAMETERIZATION SYSTEM FOR WRITER IDENTIFICATION.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 449-454
DOI: 10.5220/0001123104490454
Copyright
c
SciTePress

All the persons transmit their writing by their
brain, and simultaneously, the handwritten impulse,
which is the symbolism of the space. It is obtained
the dimensions of the writing, which are adapted of
proportional form, maintaining the size of the text or
a balance to the natural size, if the individual was
forced to write in a reduced space.
Nowadays, the writer identification is a great
challenge because these researches are not as studied
as the identification based on fingerprints, hands,
face or iris (other biometric techniques), due mainly
to the operation of the brain is very difficult of
parameterize. On the other hand, the mentioned
techniques use widely researched biometric
information.
Most of the characteristics implemented until the
moment offer information of the static
characteristics of the writing (Hertel et al., 2003),
(Marti et al., 2001), (Srihari et al., 2001), because
they are limited the formal aspect of the letters, its
form and dimension. These characteristics are easier
to modify or to falsify. Two or three years ago, some
authors are starting to present graphologist features
(Gupta, et al., 2007). In this work is introduced new
graphologist parameters fusioned with some
classical parameters. It will be showed our best
combination of parameters for identification writer
in the next sections.
The proposed characteristics in this paper are not
limited to the aspect nor the static features, because
this present work observes the handwriting writing
like a performance of the movement in the space.
For example, the cohesion and the analysis of the
opening of the ovals and loops, that reflect to use the
graphologist features in the writing, which are
difficult to modify.
As the majority of the works proposed up to
now, on biometric recognition, the framework of the
system depends on the following basic steps.
Image pre-processing and segmentation:
Preparation and modification of images, so
that the module of segmentation produce the
results desired. The segmentation separates
the zones of interest (lines, words or
characters), and it is key for the success or
error of the following analysis (Feature
Extraction).
Feature Extraction: They are qualitative and
quantitative measures that permit to obtain a
significant geometrical characterization of the
style of writing, in order to differentiate
writers among themselves. Pressure, speed,
direction, inclination, cohesion, continuity,
opening of ovals constitutes some of the
graphologist features. The aspect of the letters,
its form and dimension is some of the classical
features. The graphologist features help to be
more discriminating. In this present work, the
most of our graphologist features are
automatically got. In future works, we hope to
reach it.
Classification: A statistical analysis of the
extracted characteristics is carried out, which
will permit the comparison with the samples
of our database, seeking the writer, who
possesses more similarities.
The most references about writer identification
are using geometry features as angles, lengths,
heights, relations between distances, etc., (classical
parameters) (Zois et al., 2000), (Marti et al., 2001),
(Shihari et al., 2001). Besides the most references
use their own databases and with a size, minor to 50
writers (Hertel et al., 2003), (Said et al., 1998), (Zois
et al., 2000), (Marti et al., 2001), (Romero et al.,
2006). For this reason in this present work, we have
introduced new feature extractions, and we have
built a database lager than in the most references.
Figure 1: System of writer identification.
The rest of the paper is organized of the
following way, in section 2, it becomes a brief
description of the building of the database. In section
3 is briefly described the image pre-processing and
the segmentation of the words. In the following
Acquire Images
Pre-processing
Segmentation
Features Extraction
Database
Static
Features
Graphologist
Features
Classification
Training
Mode
Test
Mode
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
450

section, the procedure for the extraction of the
characteristics is explained. Section 5 contents the
used methods for classification. And finally in
section 6, the conclusion of this work is written up.
2 DATABASE
For the building of our database, we have used a
paragraph of 15 lines, on Spanish language. That
text is from “Don Quijote de la Mancha” from
Miguel de Cervantes, and we have used the same
text for each writer. With this size of text, writers
can show their personal characteristics, because they
keep their writing habits.
This database has been built with 70 writers, and
each one has made 10 times this template (paragraph
of 15 lines). The size of paper was DIN-A4 format
(297 mm. × 210 mm). The sheet was written with a
pen of black ink. Each writer of our database had
one week for doing the writing, and therefore, it is
considered like an effect of temporal invariance on
this database.
The creation conditions of our database were the
normalized with the same type of paper (80 gr/m2),
ballpoint pen, and similar place of support (for doing
the writing). Of this way, our work is centred on the
writing and the efficiency of proposed parameters.
In the future work, we are going to change the rest
of variables.
The samples are scanned 200 dpi, obtaining
images on grey scale, with 8 bit of quantification.
Do not add any text to the headers (do not set
running heads) and footers, not even page numbers,
because text will be added electronically.
3 IMAGE PRE-PROCESSING
AND SEGMENTATION
The first step of the image pre-processing consists of
utilizing Otsu’s the method, in order to get the
binarization of the samples (Otsu et al., 1979).
As a result of the binarization, in most cases, the
line of writing remains with irregular aspect. For that
reason, we have implemented other image pre-
processing for skew elimination. We developed a
algorithm in order to detect the maximum projection
of the word, using histogram tool. This permits to
smooth out the baseline, so, the baseline remains
well defined (see figure 2). Besides, it is eliminated
the existing noise in the images after scanning
process, by morphological mathematics.
As previous step to the separation of words or
components connected (by labelling), the detection
and elimination of the punctuation marks (points,
accents and comma) is carried out, by a size
threshold, In particular, we have removed
components connected if they were minor than 60
pixels.
4 FEATURE EXTRACTION
In this present work, we have introduced some new
parameters (graphologist characteristics), and they
have been joined to some classical parameters
(Leedham et al., 2003), (Romero et al., 2007), in
order to improve the previous references.
Handwriting cohesion is called to the percentage
of unions that appear between the letters of the same
one; when saying unions talk about the final strokes
of the letters are continued with the initials of the
following letters without ballpoint pen rises of the
paper.
In order to make an estimation of the cohesion in
the handwriting, the images of the 34 words of each
sample are selected and binarized and their
components connected with connectivity-8 are
labelled to them. As soon as the quantity of
components connected of each word is obtained, it is
proceeded to calculate the average and the variance
of the components connected. Those words have
been selected by their size, the largest.
As for the analysis of the ovals and loops of the
words, segmentation is carried out obtaining an
image where only appears the above mentioned
characteristic (see Figure 2) (Leedham et al., 2003).
The ovals and loops are calculated by labelling, the
closed zones are obtained, and a threshold is
established in order to remove the shortest ovals and
loops, minor than 60 pixels.
Then, it is done the measurement of the minor
and major axes of each ovals and loops from 34
words. Axes are calculated by maximum projection
using histograms. Finally, it is calculated the average
size of the above mentioned axes of the handwriting
sample in analysis.
Also it was studied the eccentricity feature for
both ovals and loops, but it was rejected because it
was producing a decrease of successes rate, because
of the fact that the eccentricity value was very
similar for the inter-classes and intra-classes
relation, and with great variance.
Giving an estimation of the speed, the cohesion
and the oval shapes also it is analyzed particular
features of following letters "a, d, g, q, b, p, o",
HYBRID PARAMETERIZATION SYSTEM FOR WRITER IDENTIFICATION
451
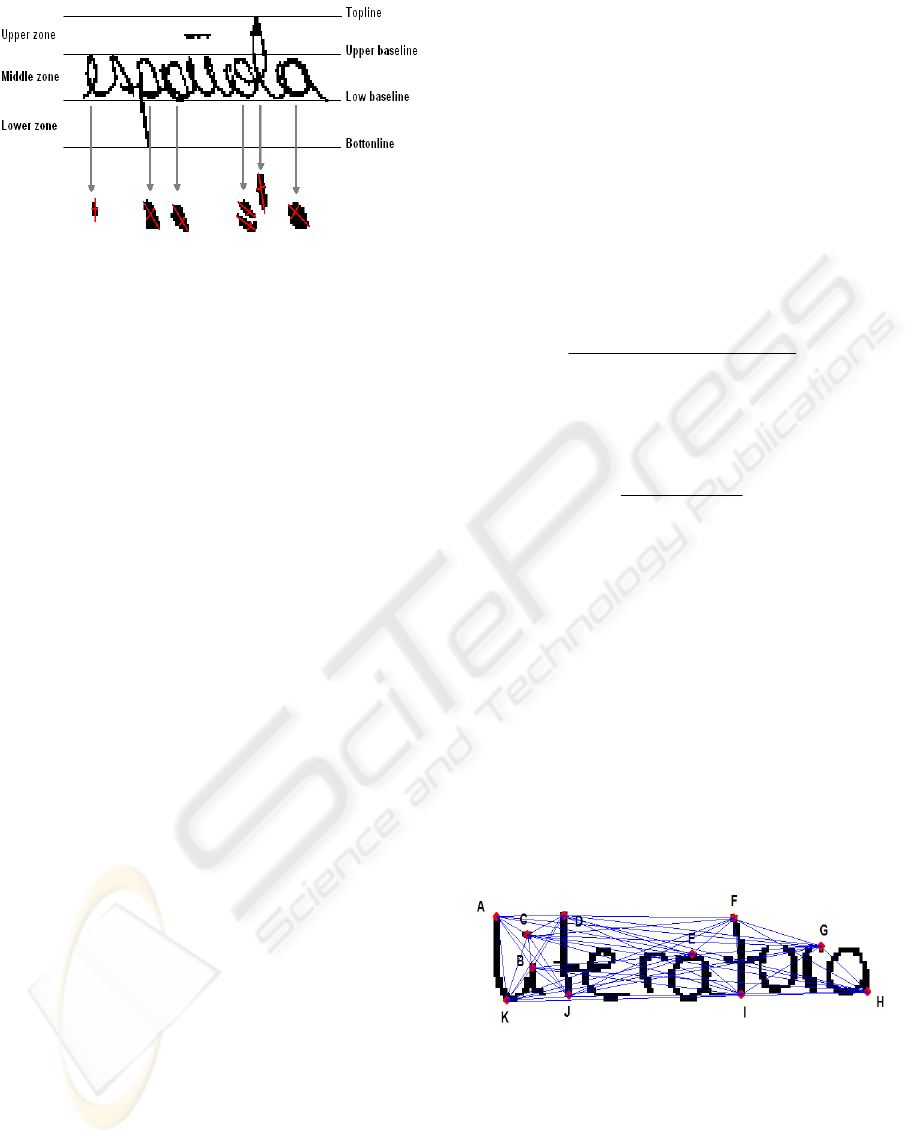
Figure 2: Ovals and loops with its respective major and
minor axes.
which consist on a rounded part or oval that can be
joined or not with the following stroke or with an
ascending or descending. This letters are found by a
labelling of closed area, and non with letter
recognition, because there are writers, who writes
open letters, without loops and ovals.
This new characteristic has been included in the
list of the classical characteristics already developed
in (Romero et al., 2007), (Hertel et al., 2003):
length of the words,
quantity of pixels in black,
estimation of the width of the letters,
height of the medium body of writing,
heights of the ascending and descending,
height relation between of the ascending and
medium body,
height relation between descending and
medium body,
height relation between descending and
ascending,
height relation between medium body and the
wide of writing,
proportionality index.
The quantity of black pixels and the length of
words (horizontal size of the image), they will give
us an estimation of the dimension and thickness of
the line, the wide of letters and the height of the
medium body. Besides these are distinctive
characteristics of the style of writing.
The estimation of the width of letters is carried
out, seeking the row with greater quantity of black to
white transition (0 to 1). It is counted the number of
white pixels between each transition, this result is
averaged.
In order to measure the height of the medium
body of the words, the goal is to determine the upper
and lower baseline through maximums and
minimum values and to measure the distance among
them (see figure 2).
In order to approach baselines of each word, it
was decided to use the adjustment of minimum
mean square error that is based on find the equation
(see expression 1) that better be adjusted to an set of
points "n" (Chin et al., 1997). The equation is the
following:
baxy
+
=
(1)
where the coefficients “a” and “b” determine the
lineal polynomial regression by means of the
following expressions:
∑∑
∑∑∑
==
===
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
⎟
⎠
⎞
⎜
⎝
⎛
−
=
n
i
n
i
ii
n
i
i
n
i
i
n
i
ii
xxn
yxyxn
a
1
2
1
2
111
(2)
n
xay
b
n
i
i
n
i
i
∑∑
==
−
=
11
(3)
Those values of “a” and “b”, based on the
coordinates of minimums or maximums detected in
the contour of the word, are different baselines.
Minimums are to approach the lower baseline and
the maximums for the superior baseline.
The extraction of the proportionality index is
semi-automatic system because the sample of the
word is displayed in the window of the screen and
the operator will mark on the zoomed window, the
interest points using the mouse. This process will be
automated in future works.
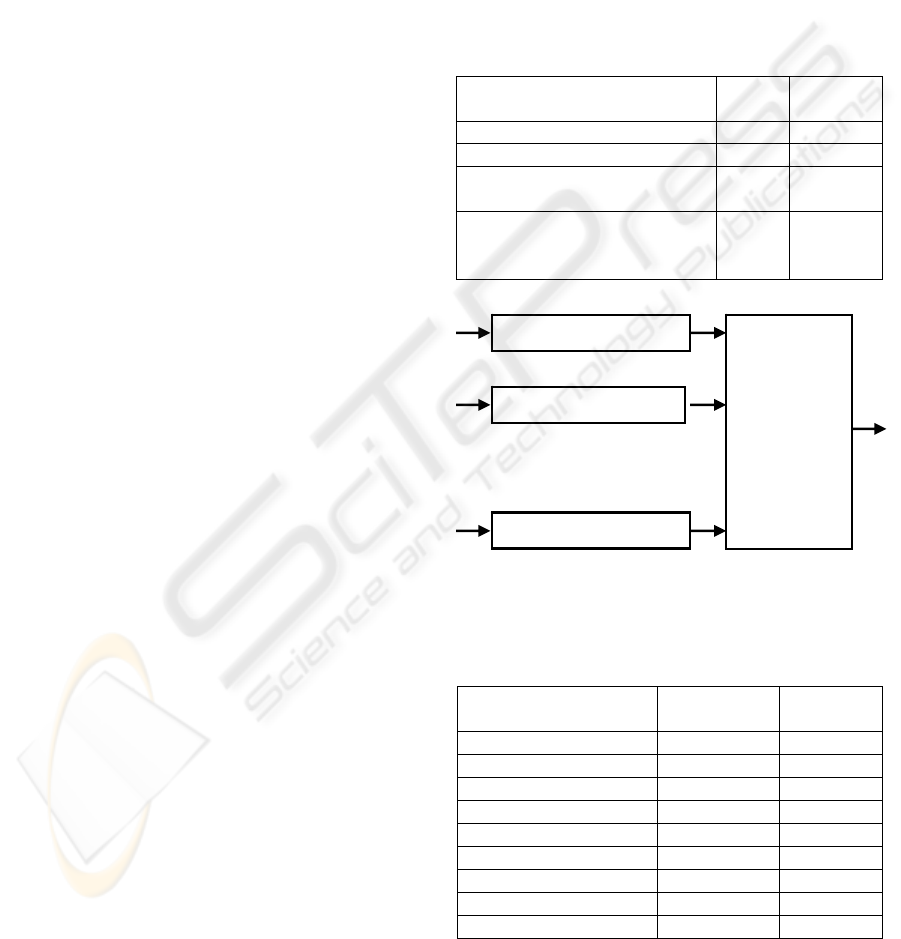
The selection of the points is done with the most
representative sites as they can be the ascending
ones, descendent, terminations, etc.
Figure 3: Segments obtained when points are united.
Then, it is united the marked points (to see
Figure 3); each line formed between two points is
considered as a segment. Next, we measured the
length of each segment obtaining a list of lengths.
Using this list, we calculated the average length
and its variance, obtaining proportionality indexes.
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
452
5 CLASSIFICATION
AND RESULTS
The identification can be seen as a problem of
classification of N classes, in our case N writers.
There are two variations of interest when are
compared the samples: about the writing of a same
writer and between the writings of two different
writers. The variation of a writer among their own
samples should be smaller than the variation among
samples of two different writers.
In order to give solution to this problem, the
methodology of the used identification was
independent supervised classification. Therefore, we
have a system with two modes, training and test
mode.
For the training, we have used the 50% of our
database, and the remainder to carry out the test
mode. That is, five samples have been chosen to
training and other five for the test, since we have 10
samples for each writer. Besides, a total of 34 words
have been extracted from paragraphs, and there will
be 34 words by sample.
Like our parameters depend on words used and
its writer, we have used the same word for this
process; in particular, we have used a set of 34
words from the paragraph of 15 lines. But, the
samples set for training and test mode of these 34
words are different, being obtained from 10 different
samples of each writer. Therefore, this system works
with a close set of words (34 words).
In order to calculate the characteristics, we have
used 170 words (34 x 5 samples/writer) on the
training process. The criterion of selection to choose
the previous 34 words was their length, mayor of 5
letters, because with this length, they offer
information more general than a word with a shorter
size.
Experiments have been carried out in five times,
for which the results are shown by their averaged
rate and their standard deviation (see table 1). In
each time, the training and test samples were chosen
randomly, with an independent training and test of
sample.
As classifier, we have used a Feed-Forward
Neural Network (NN) with a Back-propagation
algorithm for training (Bishop, 1995) (Juang et al.,
1992), where the number of input neurons is given
by the dimension of the vector of features wit 374
parameters (11 parameter x 34 words). And the
number of output neurons is given by the number of
writers to identify.
Too, we have researched with different number
of neurons in the hidden layer, and finally, 180
neurons were used, because they have presented the
better results.
The average success rate for recognition is 93.02
%, with a standard deviation of 0.83. But this result
was improved using the method of the ‘more voted’
algorithm, where we have built a schedule with 10
neural networks (see figure 4), and we have reached
a recognition rate of 96 %, with a standard deviation
of 0. Those results can be observed on the following
table.
Table 1: Comparison of results without new features vs.
with new features.
Features Mean
Standard
Deviation
Classical features 81,08 % 1,52
Classical Features+Cohesion 89,28 % 1,18
Classical
Features+Cohesion+Axis
93,02 % 0,83
Classical
Features+Cohesion+Axis and
using ‘More voted’ Algorithm
96,00 % 0
Figure 4: Classification System with ‘more voted’
algorithm, based on NN.
Table 2: Comparison of results among different published
methods vs. our work.
Author
Number of
writers
Success
Rates
(Said et al., 1998) 40 95,00 %
(Zois et al., 2000) 50 92,50 %
(Marti et al., 2001) 20 90,70 %
(Srihari et al., 2001) 100 82,00%
(Hertel et al., 2003) 50 90,70 %
(Bensefia et al., 2005) 150 86,00 %
(Schomaker et al., 2004) 100 95,00%
(Romero et al., 2007) 30 94,66%
This present work 70 96,00%
It is a difficult to do a comparison between the
different references, because each one uses a
Neural Network
1
‘More
Voted’
Algorithm
Neural Network
2
Neural Network
10
.
.
.
HYBRID PARAMETERIZATION SYSTEM FOR WRITER IDENTIFICATION
453

different database. Therefore, in the table 2 is
showed the number of writer and its success. For
this present work has been obtained a better success
rate with more writers. In the future works, we are
working on the increase of our database and the
creation of novel and discriminative parameter.
6 CONCLUSIONS
For Graphologist or Forensic Experts, the combined
features (classical and novel graphologist
parameters) contribute more reliable information in
order to identify a person.
Therefore in this work, we have developed a
combined parameterization between classical and
novel graphologist characteristics, in order to be
used in the writer identification from handwriting
documents. In fact, the use of these novel parameters
has improved the classical system.
We have used a back-propagation NN for the
classification. And in order to improve results, we
are implemented a ‘more voted’ algorithm. The
success rate is 96% for 70 writers.
The experiments carried out with our database to
evaluate the power of discrimination of the
implemented characteristics, it is allowing us to
show the considerable increase of the success rate
with all the developed characteristics.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This present work has been supported by Education
and Science Ministry from Spanish Government
(TEC2006-13141-C03-01).
REFERENCES
Otsu, N., 1979. A threshold selection method from gray-
level histograms. In IEEE Transaction on Systems,
Man and Cybernetics, Vol. 9, Issue 1, pp 62-66.
Gupta, S., Namboodiri, A.M., 2007. Repudiation
Detection in Handwritten Documents. In Lecture
Notes in Computer Science. Vol. 4642, pp. 356-365.
Leedham, G., Chachra, S., 2003. Writer Identification
using Innovate Binarised Features of Handwritten
Numerals. In Proceeding of the 7th International
Conference on Document Analysis and Recognition.
Vol. 1, pp. 413-416.
Romero, C.F., Travieso, C.M., Alonso, J.B., Ferrer, M.A.,
2007. Using Off-line Handwritten Text for Writer
Identification. In WSEAS Transactions on Signal
Processing. Issue 1, Vol. 3, pp. 56-61.
Hertel, C., Bunke, H., 2003. A Set of Novel Features for
Writer Identification. In Proceedings of the Audio and
Video Based Biometric Person Authentication. pp.
679-687.
Chin, W., Harvey M., Jennings, A., 1997. Skew Detection
in Handwritten Scripts. In IEEE Region 10 Annual
Conference. Speech and Image Technologies for
Computing and Telecommunications. Vol. 1, p. 319-
322.
Bishop, C.B., 1995. Neural Networks for Pattern
Recognition, Oxford University Press.
Juang, B.H., Rabiner, L.R., 1992. Spectral representations
for speech recognition by neural networks-a tutorial.
In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the Workshop
Neural Networks for Signal Processing. pp. 214 – 222.
Said, H.E.S., Peake, G.S., Tan, T.N., Baker, K.D., 1998.
Writer Identification from Non-uniformly Skewed
Handwriting Images. In Proceedings of the 9th British
Machine Vision Conference. pp. 478-487.
Zois, E.N., Anastassopoulus, V., 2000. Morphological
Waveform Coding for Writer Identification. In Pattern
Recognition. Vol. 33, Nº3, pp. 385-398.
Marti, U.V., Messerli, R., Bunke, H., 2001. Writer
Identification Using Text Line Based Features. In
Sixth International Conference on Document Analysis
and Recognition, pp. 101-105.
Srihari, S., Cha, S.H., Arora, H., Lee, S., 2001.
Individuality of Handwriting: A Validity Study. In
Proceedings ICDAR’01. pp 106-109.
Bensefia, A., Pasquet, T., Heutte, L., 2005. Handwritten
Document Analysis for Automatic Writer
Recognition. In Electronic Letters on Computer Vision
and Image Analysis. pp. 72-86.
Schomaker, L., Bulacu, M., 2004. Automatic Writer
Identification Using Connected-Component Contours
and Edge-Based Features of Uppercase Western
Script. In IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence. Vol. 26, No. 6, pp. 787 – 798.
Romero, C.F., Travieso, C.M., Alonso, J.B., Ferrer, M.A.,
2006. Writer Identification by Handwritten Text
Analysis. In Proceeding of the 5th WSEAS int. Conf.
on System Science and Simulation in Engineering. pp.
204-208.
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
454
