
MOBILE APPLICATIONS IN THE GERMAN HEALTH
INSURANCE SYSTEM TO IMPROVE THE MARKET POSITION
Michael Malik, Dirk Frosch-Wilke, Sebastian Beck, Christian Hartmann
Timo Sturm and Thomas Wieben
Institute of Business Informations Systems,Kiel University of Applied Sciences, Sokratesplatz 2, Kiel, Germany
Keywords: M-Business, Mobile applications, Health insurance, Location based services.
Abstract: Mobile end devices and applications play a growing role in business processes, especially in industry,
commerce and service. But even in different branches, which are significant for their high intensity in
competition – for example the German health insurance system –first preparations are taken to create an
interface for the customer and thus advantages in competition. In many cases these projects are not included
in the context of corporate strategy. This “paper” shows on the basis of a specific project with the health
insurer IKK-Direkt, how mobile applications in the health sector can be introduced, so that technical
restrictions are regarded and additional benefits to the customer are offered, consequently achieving a higher
competitive position for the company.
1 INTRODUCTION
Technological advancements in mobile
communication enable new ways of doing business
(mobile business) (Stafford, 2003). In (Lehner,
2003) mobile business is defined as the application
of mobile technologies to improve or extend
business processes and open new market segments.
Schierholz et al. characterized interdependencies
between the strategic premises and the processes
selected for being supported by mobile technology
(Schierholz, 2005).
The German health insurance sector is strictly
regulated by legislation. The basis for the benefits of
the health insurance system is the Sozialgesetzbuch
V (SGB V), part of the social code of law. The
Sozialgesetzbuch V obliges all German compulsory
health insurance companies to an identical catalogue
of benefits, so called Regelleistungen. These
benefits include for example medical treatments,
preventive treatments and therapeutic measures and
cover 95% of the overall benefits of the compulsory
health insurance companies. (Polixea, 2006)
Because of this widely identical catalogue, a
differentiation to other competitors through special
offers for benefits is only possible in a limited
extent. Concurrently, the income structure of the
health insurance companies is being unified by
legislation. The possibility of the companies to
define the premium rate independently and thus
passing on cost benefits to their customers through a
lower premium rate is vanquished by the
introduction of the unified premium as part of the
health reformation 2009. Consequently, companies
try to differentiate themselves from their
competition by offering additional services that are
outside of the actual catalogue of benefits, for
example online portals in which customers can
change their address without bureaucratic
complexity.
This paper will introduce an approach to how
potential and actual customers can be given
additional benefit by the use of mobile applications
and thus increasing the competitive position of the
health insurance company.
Furthermore, possibilities are presented on how
the mobile internet can be implemented in the
workflow of a health insurance company and which
mobile services are recommendable for health
insurance companies. Hence, the structure of the
paper is as follows: At first, the specialties of the
German health insurance system are outlined, since
these set the regulative framework that has to be
followed by the business strategies of the health
insurance companies. Subsequently, a general
overview of the current use of mobile services in the
117
Malik M., Frosch-Wilke D., Beck S., Hartmann C., Sturm T. and Wieben T. (2009).
MOBILE APPLICATIONS IN THE GERMAN HEALTH INSURANCE SYSTEM TO IMPROVE THE MARKET POSITION.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 117-122
DOI: 10.5220/0001378901170122
Copyright
c
SciTePress

health sector will be given. On this basis a concept
for the development of mobile services is drafted
and technical possibilities for the implementation of
the concept are elucidated.
This publication shows a portfolio of potential
mobile services for health insurance companies and
their integration into a general concept.
2 THE GERMAN HEALTH
INSURANCE SYSTEM
The compulsory health insurance system was
introduced 1883 in Germany as the first social
insurance in Europe and is alongside the pension,
accident, nursing and unemployment insurance a
part of the German social security system. Today,
almost 85% of German citizens in Germany are
members of the compulsory health system (German
Federal Health Monitor, 2007).
Up to an annually adjusted income limit (in 2008
the limit was set at a yearly income of 48.150 €),
every employee is a member of a compulsory health
insurance (The Press and Information Office of the
German Federal Government, 2007). About 218
compulsory health insurances existed in Germany by
the beginning of 2008 (Haufe, 2008). Employees
who earn more than the income limit three years in
consequence can select between compulsory or
private health insurance (§6 SGB V). Self-employed
can become a voluntary member in one of the
insurances mentioned above. Pensioners,
unemployed, apprentices and students are under
certain circumstances bound in an obligatory
membership in a compulsory health insurance.
The premium rates for the health insurance are
paid by employees and employers in equal shares.
For unemployed family members (spouse/ children),
no additional rates have to be paid (family
insurance) (German Ministry of Health, 2008)
3 ABOUT THE PROJECT
The vision of the presented project is the location
and time independent use of health insurance
benefits by members. By providing a mobile
interface and mobile applications the insurer offers
customers and potential customers additional
benefits which leads to a rise in member satisfaction
and offers the final incentive for new contracts.
Mandatory prerequisite for the strategic
positioning of mobile services in the health sector is
the adjustment of the technical affinity of the target
group of (potential) customers.
In the considered project the target group
consists of employed people aged between 20 and
50 years with a higher education. This group is,
based on their age, featured with good health and,
based on their higher education, in a good financial
status. The technical ability to reasonably use the
mobile interface with a mobile device permits the
application of such an interface.
4 AN APPROACH TO
IMPLEMENT A MOBILE WEB
PRESENCE FOR A HEALTH
INSURANCE COMPANY
4.1 Mobile Services in the German
Health Sector
Currently there are three compulsory health
insurance companies in Germany that possess a
mobile web presence. These mobile portals differ
considerably in extent and offered services.
Health insurance company No. 1 that operates its
portal for a longer time already, uses a commercial
product (CMS) for operation that covers the
adaptation of the web pages for the variety of
display solutions of different devices. Navigation
works very fast and easy. Different services like a
search for pharmacies, physicians or provider for
medical devices and disposables are offered. These
services are realised in cooperation with several
commercial service provider. The use of images is
widely avoided.
A second health insurance company offers a
mobile web presence which includes only static/
regional content. Navigation is slower, due to larger
images and long texts. No mobile services are
offered. The technical adaptation is covered by the
same product that is used by the first described
company.
Health insurance company No. 3 brought their
portal online during the period of the project
(December 2007). Information about the technical
background is unknown. The provided mobile
services and the navigation are similar to the
presence of the first described company, while the
use of images is increased. Although this results in
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
118
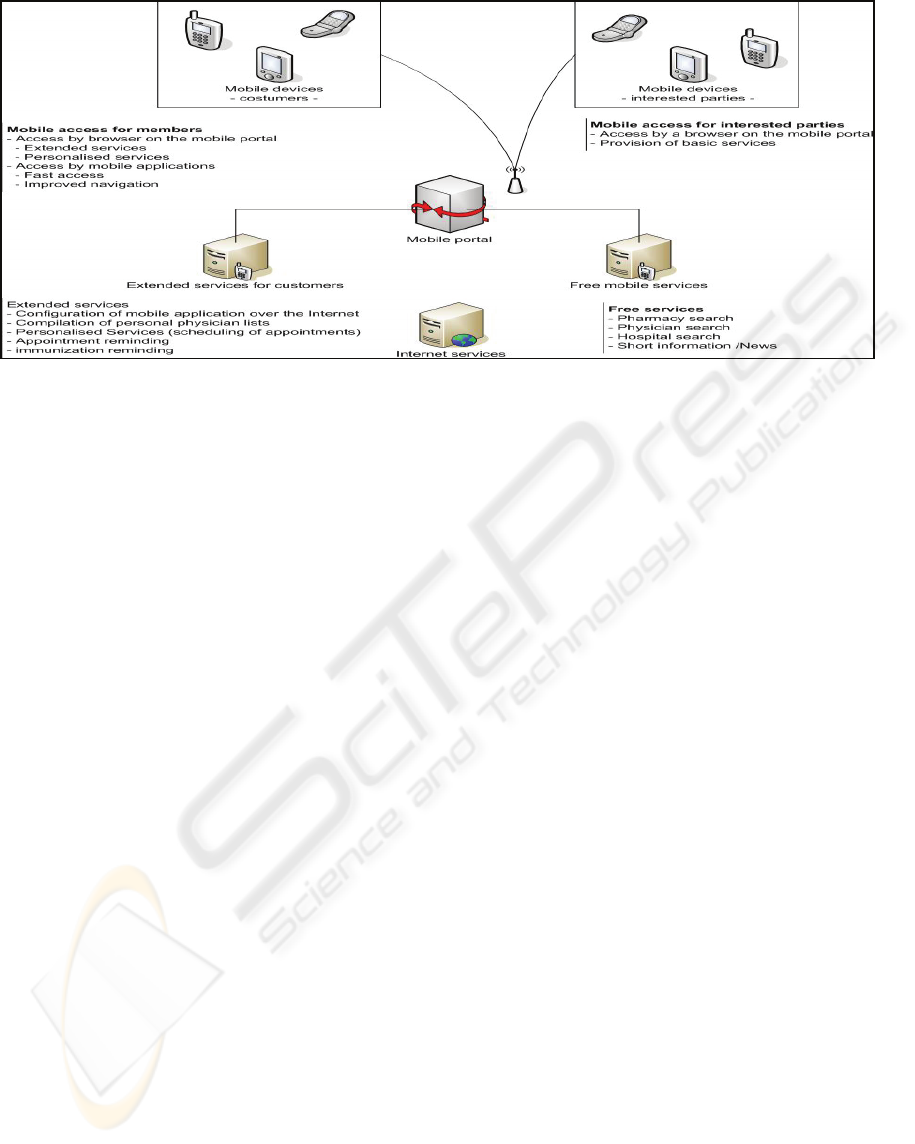
Figure 1: Application environment.
improved clarity, it raises the data traffic and thus is
slowing the page reproduction.
In other branches mobile web presences are far
more advanced. For example big mobile portals
provide several services as news, navigation or
address search. Furthermore, special mobile
solutions are offered, e. g. mobile online banking, by
several banking institutes.
4.2 Draft of a Mobile Solution for a
Health Insurance Company
The development of a three-step realisation plan is
based on the classification of mobile services into an
application environment and a realisable
implementation in several steps in practice.
The first step of the plan consists of a basic
implementation and provision of mobile services
through a mobile portal. In this step, a basic
introduction of the company is included, as well as
the presentation of the advantages this company for
customers and potential customers. This static
content is extended by the basic features of the
information system (pharmacy/ physian search) and
a news portal, which presents the current news of the
health insurance in a mobile format. Already
included in this step is the support by a CMS, to
provide the editors with a tool to easily maintain the
web presence. The provision of step 1 is targeted at
customers of the company and those who have been
adverted to the mobile website. Personalising the
services with a login is not a feature of this phase.
The information systems as well as additional
services (appointment reminding) that are only
provided to members serve as a basis for the second
step. Therefore, a possibility has to be created to
personalize the portal through a personal login
which can be activated by the company. With this
offer, an additional benefit for members will be
achieved. Simultaneously, the second step is based
on the services and offers of the previous step.
Furthermore, these services are accessible for all
user groups free of charge.
Step three describes the next extension:
Advantages for members are extended and by the
use of a Java-application dealing with the different
services is enhanced. Through this, a faster and more
comfortable handling of the services is achieved. By
installing a local application on the mobile device,
access to further interesting features becomes
possible. As an example, “location based services”
enable locating the approximate location of the
mobile device through cell phone antennas. This
could be hence the basis for the information system.
After the implementation of these services, a
foundation stone for an extensive mobile portal
should be created.
4.3 Content Management Systems
Requirements for Mobile Services
The requirements of a content management system
(CMS) for mobile devices orientate themselves on
the technical restrictions which are inherent in
mobile devices. These are:
smaller displays
less arithmetic performance
less storage capacity (Caus, 2007:16)
smaller and/or reduced controls.
MOBILE APPLICATIONS IN THE GERMAN HEALTH INSURANCE SYSTEM TO IMPROVE THE MARKET
POSITION
119

The appropriate CMS must provide solutions to
comply with these exemplarily specified
requirements or work against them.
The simplest solution to fulfil these requirements
would be the setup of an independent mobile
platform which would be suitable for most mobile
terminals. In this case, complex images, diagrams,
animations or style sheets would not be used. A
further possibility is the use of separate style sheets
that enables the mobile device to load the particular
mobile style sheet (handheld) and thus to form the
web page for mobile devices. Through the use of the
command “display:none” in the style sheet, the
device is given the possibility not to load images and
content in general. However, in praxis this approach
was not approved. Frequently this indication is
ignored by the mobile device and the conventional
screen style sheet is loaded.
The most mature solution at present is the use of
multi template output, or generic template output.
The page is then adapted to the respective device at
run-time.
The correct recognition whether and which
mobile device requests the page is a needed
requirement.
Three possibilities exist for the recognition:
Recognition by the user agent included in the
mobile browser smaller displays
Recognition of the mobile device through the
URI to the UAProf of the mobile device
which is sent by the device included in the
request of the page
By user decision
The recommendation is the combination of
several possibilities, enabling the user to choose
between a specially modified page for mobile
devices or the conventional page. The CMS
recognises the mobile device by user agent or
UAProf and provided a modified page for mobile
devices. In this page, it offers the user the change to
the conventional web page.
Common to all solutions, the XHTML mobile
profile (XHMTL MP) should be supported. XHTML
MP is a superset of the XHTML basis standard that
defines the requirements for pages to adapt to
mobile devices.
4.4 Selection of Possible CMS
In the study for the health insurance company four
CMSs were taken into closer consideration.
4.4.1 eWeb
eWeb is a closed source system by the eCONNEX
AG and is already in use in the company. Choosing
eWeb would save training costs and avoid media
breaks. However, multi template output is not
featured by the product which is to be rated as a
disadvantage. Therefore, other CMSs were taken
into closer consideration.
4.4.2 Typo3
Typo3 is an advanced content management system
on open source basis. In the internet community, it is
widely used and due to its ability of workflow
automation, user rights assignment and the multi site
management it is also used by professionals.
Because of the popularity of Typo3, extensions for
the recognition of mobile devices already exist. A
disadvantage is the enormous training effort for
customizing.
4.4.3 Joomla
The CMS Joomla is due to its easy handling very
popular. Possibilities to recognise mobile devices
already exist. However, the range of features does
not match up to the professionalism of Typo3.
4.4.4 Wap2Go
Wap2Go is an extension of the CMS PHPNuke.
With the goal of providing content of PHP Nuke
sites for mobile users, Wap2Go creates an advanced
impression. For example the format of images
(PNG, JPG, GIF) can be selected or deactivated.
However, several unsettled issues exist, therefore a
professional use would be problematic. It is not -
known whether device recognition is featured. Also
the source code is only developed and maintained by
one single developer which is to be seen as a risk.
4.4.5 Recommendation
The authors recommend a further examination of
Typo3, especially the training effort. If this effort is
acceptable for the company, the use of Typo3 for the
mobile web presence is recommended. The decision
is mainly based on the presence of device
recognition and multi site management.
Once the training for the open source system is
successfully accomplished, a second step could be
the migration of the existing web presence from
eWeb to Typo3.
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
120

4.5 Prototype
Accompanying this study a prototype was produced
in which the obtained findings were put into practice
and which represents the first stage of the
development plan.
The main topics are general information, recent
news, pursuing services like specialised search
engines and the possibility to order further
informative documents.
Potential Clients are mainly interested in
information about the health insurance, its services
and its fees. Therefore these points are represented
in the prototype on the first two positions. If the
information that can be found following these two
points is not sufficient, users can find phone
numbers, e-mail addresses and postal addresses to
contact the company directly by following the menu
item “Contact”. The users then can select the
medium they prefer most.
Figure 2: Prototype.
To keep a mobile internet portal interesting for
potential and existing customers, it is important to
offer additional benefit. In case of this prototype,
this target shall be reached by news and the
possibility to search for physians and pharmacies in
the surrounding area. The prototype only uses static
HTML pages to show how the search machines will
work. In the final version, the information entered
by the user will be sent to a web service offered by a
service provider that sends a response with the
addresses of the relevant physians and pharmacies.
During the project, requests to some potential
service providers were sent to request the conditions
for using their web services. Unfortunately, the
service providers reacted either very late or not at
all, so it was impossible to create a prototype that
uses web services.
The search engines should be able to work with
two different kinds of geographic information: the
postal code or a combination of a street and a town.
Generally, the user has one of these available or is
able to obtain them.
A further possibility is to combine all three fields
because in bigger towns a street name may occur
more than once. In this case, the combination of the
postal code, the street name and the town will
provide better results.
The layout of a mobile internet portal has to be
very simple, clear and should be reduced to the most
important points. The homepage should not begin to
scroll on most of the common devices. Complicated
colour schemes and alignments should be used very
carefully, because every mobile device has its own
browser and every browser shows the page
somewhat differently. The corporate design would
possibly be displayed in a warped manner if the
design of the page is too difficult to render.
Important for the prototype is the position of the
logo which is displayed on every page and the
possibility to access the “Impressum”, a mandatory
legal page in Germany, from each page.
4.6 Summary and Outlook
This paper gives an outline summary of the German
health insurance system and the current application
of mobile solutions in this industry. Furthermore, an
approach is described how a statutory health
insurance company can implement a mobile
interface for (prospective) customers and how such a
concept can be realised.
Due to the current technical progress the
development of mobile services will proceed rapidly
in medium-term. Most new mobile phone models
are equipped with large displays. With these mobile
phones, it is possible to navigate on web pages
without larger visual problems (e.g. iPhone). If this
trend carries on and the resolution sizes of mobile
displays and processing speeds continue to increase,
the question is whether special offers on mobile
websites, that provide more than contact
information, are necessary. The only “bottleneck” is
perhaps data traffic and costs for mobile data
exchange (Caus, 2007:32). However, data speed is
increasing more and more while the prices keep on
falling. In addition, unlimited data traffic plans
become more common.
Also the improvement of content management
systems in managing content for mobile use is
making progress.
In concern with the development and integration
of content for mobile users, the question of the core
MOBILE APPLICATIONS IN THE GERMAN HEALTH INSURANCE SYSTEM TO IMPROVE THE MARKET
POSITION
121

competence of the health insurance company arises.
Certainly, the core competence does not lie in
services like a pharmacy or physician search. For
this reason, a self-developed implementation should
not be aimed for. In fact, a health insurance
company should focus on a collection of services
that are rather embedded into or linked from the
website of the company. In this field, the company
collects a range of health-related services that can be
interesting for (potential) customers. Thus it is the
aim that members and potential members will start
their search for information in the health area at the
health insurance company’s website. With the help
of personalised services, members can gain
additional benefit and potential members are being
given a reason to join.
REFERENCES
Caus, T., Hagenhoff S., 2007. Endgerätetechnologien, in
Arbeitsbericht 01/2007, Institut für
Wirtschaftsinformatik, Georg-August-Universität
Göttingen, Innovative Geschäftsmodelle für das
mobile Internet – Eine Fallstudienuntersuchung,
http://webdoc.sub.gwdg.de/ebook/serien/lm/arbeitsberi
chte_wi2/2007_01.pdf
German Federal Health Monitor 2007, Table: ”Number of
members and jointly insured family members of the
statutory health insurance on July 1st of the respective
year. Classification: years, age, sex, type of statutory
health insurance, group of persons insured”
(26.04.2008)
German Ministry of Health 2008, Themenschwerpunkt
Gesundheit ,
http://www.bmg.bund.de/cln_040/nn_600116/DE/The
menschwerpunkte/Gesundheit/gesundheit-
node,param=.html__nnn=true (27.04.2008)
Haufe 2008, Rudolf Haufe Verlag GmbH & Co KG
Sozialversicherungen,
http://www.haufe.de/SID101.OmD6q0hg4eY/sozialve
rsicherung/topIssueDetails?view=themeName&objectI
ds=1200386135.21 (27.04.2008)
Lehner, F. 2003. Mobile und drahtlose
Informationssysteme: Technologien,
Anwendungen,Maerkte. Springer.
Polixea 2006, POLIXEA Deutschland GmbH
http://www.polixeaportal.de/index.php/Lexikon/Detail
/id/123754/name/Leistungskatalog+-+GKV
(27.04.2008)
Schierholz, R.; Kolbe, L.; Brenner, W. 2005. Strategy
Alignment of Moble Solutions in Customer-Oriented
Processes. In. Wirtschaftsinformatik, 47 (2005) 1, pp.
17-24.
Stafford, T.F., Gilleson, Mark L.2003. Mobile commerce:
what it is and what it could be. In: Communications of
the ACM, 46 (2003) 12, pp 33–34.
The Press and Information Office of the German Federal
Government 2007, Neue Rechengrößen in der
Sozialversicherung für 2008,
http://www.bundesregierung.de/Content/DE/Artikel/2
007/10/2007-10-17-neue-rechengroessen-in-der-
sozialversicherung-fuer-2008.html (27.04.2008)
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
122
