
STUDY OF THE PROPERTIES OF BIOTIN-STREPTAVIDIN
SENSITIVE BIOFETS
Thomas Windbacher, Viktor Sverdlov, Siegfried Selberherr
Institute for Microelectronics, TU Wien, Gußhausstraße 27–29/E360, A-1040 Wien, Austria
Clemens Heitzinger, Norbert Mauser
Wolfgang Pauli Institute and Department of Mathematics, University of Vienna, Nordbergstrasse 15, A-1090 Wien, Austria
Christian Ringhofer
Department of Mathematics, Arizona State University, Tempe, AZ 85287, U.S.A.
Keywords:
BioFET, Field-effect biosensor, Biotin-streptavidin, Simulation, Multi-scale problem, Interface conditions.
Abstract:
In this work the properties of a biotin-streptavidin BioFET have been studied numerically with homogenized
boundary interface conditions as the link between the oxide of the FET and the analyte which contains the bio-
sample. The biotin-streptavidin reaction pair is used in purification and detection of various biomolecules; the
strong streptavidin-biotin bond can also be used to attach biomolecules to one another or onto a solid support.
Thus this reaction pair in combination with a FET as the transducer is a powerful setup enabling the detection
of a wide variety of molecules with many advantages that stem from the FET, like no labeling, no need of
expensive read-out devices, the possibility to put the signal amplification and analysis on the same chip, and
outdoor usage without the necessity of a lab.
1 INTRODUCTION
Today’s technology for detecting tumor markers,
antigen-antibody complexes, and pathogens is time-
consuming, complex, and expensive (Pirrung, 2002),
(Shinwari et al., 2006). For instance, a typical proce-
dure to detect a given DNA complex is to increase the
concentration by RT (reverse transcription) or PCR
(polymerase chain reaction), followed by a process
step that will add a label to the DNA enabling detec-
tion by light or radiation. After all these steps the
sample is applied to a microarray. The microarray
consists of an array of spots, and every single spot
is able to detect a different type of molecule. After
the reaction has taken place the array is read by an
expensive microarray reader.
Replacing the above sensing mechanism by an
electrical detection has several benefits. First, the op-
tical microarray reader becomes superfluous. Detec-
tion by FET (field-effecttransistor) makes the integra-
tion of amplifying and analyzing circuits on the same
chip possible, thus saving also equipment. The ad-
vanced development of semiconductor process tech-
nology allows mass production of such devices, de-
creasing the price dramatically. Various kinds of reac-
tion pairs are possible and have been studied, like de-
tection of DNA (Fritz et al., 2002), (Hahm and Lieber,
2004), (Gao et al., 2007), cancer markers (Zheng
et al., 2005), proteins, e.g. biotin-streptavidin (Im
et al., 2007), (Cui et al., 2001), (Gupta et al., 2008),
(Stern et al., 2007), albumin (Park et al., 2008), and
transferrin (Girard et al., 2006). In these papers dif-
ferent device types and materials were investigated
and provided different solutions for each problem. In
principle, every molecule that is charged in the solute
and that can be bound to the surface layer can be de-
tected by a BioFET. The field of applications is very
wide and spans from DNA sequencing, point of care
applications, to controlling environmental pollution
and the spread of diseases. The BioFET can be easily
integrated into the chip environment. By putting a mi-
crofluidic channel above the functionalized gate of the
24
Windbacher T., Sverdlov V., Selberherr S., Heitzinger C., Mauser N. and Ringhofer C. (2009).
STUDY OF THE PROPERTIES OF BIOTIN-STREPTAVIDIN SENSITIVE BIOFETS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices, pages 24-30
DOI: 10.5220/0001430700240030
Copyright
c
SciTePress

BioFET the chip can be turned into a mini-laboratory
- the lab on chip. This enables better control of the
environmental parameters (e.g. local pH or detecting
the amount of a special protein) and gives the possi-
bility of local measurement (e.g. how a cell reacts to
a stimulus), thus providing a complete lab-on-a-chip.
However, there are still many problems to overcome
and a lot of research is needed. For instance, an in-
teresting way to avoid problems by poor isolation be-
tween device and solution has been shown by (Kim
et al., 2006).
2 METHOD
A BioFET consists of several parts: a semiconduc-
tor transducer, a dielectric layer, a biofunctionalized
surface, and the analyte (Figure 1). The semiconduc-
tor transducer is a conventional FET. The dielectric
layer is the gate oxide, and the biofunctionalized sur-
face contains immobilized biomolecule receptors at-
tached, so it is able to bind the desired molecule. The
analyte is in an aqueous solution. If a target molecule
binds to a receptor, the local charge density at the sur-
face changes and thus the potentialin the semiconduc-
tor. The conductivity of the channel of the field-effect
transducer is changed.
The binding of the target with the receptor hap-
pens at the Angstrom length scale, while the semi-
conductor device is in the micrometer length scale.
Thus a proper way of combining the semiconductor-
solution interface is crucial.
Analyte
p
nn
Oxide
Reference Electrode
DrainSource
Figure 1: Schematic diagram of a BioFET.
Transport in a FET with a gate length of
1µm, is usually modeled via the drift-diffusion ap-
proach (Tang and Ieong, 1995), (Selberherr, 1984).
The aqueous solution is described by the Poisson-
Boltzmann equation.
ε
0
∇· (ε
Ana
∇ψ(x, y)) = −
∑
σ∈S
σ q c
∞
σ
e
−σ
q
k
B
T
(ψ(x,y)−ψ
µ
)
(1)
k
B
denotes Boltzmann’s constant, T the temperature
in Kelvin, and σ ∈ S, where S contains the valences
of the ions in the electrolyte. ε
0
describes the permit-
tivity of vacuum, and q the elementary charge. ψ
µ
is
the chemical potential. c
∞
σ
is the ion concentration in
equilibrium, while ε
Ana
≈ 80 is the relative permittiv-
ity of water.
The sum describes the carrier densities arising
from the Boltzmann model. Assuming sodium-
chloride as salt, which is a 1 : 1 salt, the expression
given in (1) can be reduced to
ε
0
∇· (ε
Ana
∇ψ(x, y)) = 2q c
∞
σ
sinh(
q
k
B
T
(ψ(x, y)− ψ
µ
)).
(2)
The charge on the surface due to chemical reaction
of the H
+
and OH
−
was modeled at pH = 7 with the
site-binding model (Shinwari et al., 2006):
Q
Ox
= q N
S
[H
+
]
b
K
a
e
−
q
k
B
T
Ψ(x,y)
−
K
b
[H
+
]
b
e
q
k
B
T
Ψ(x,y)
1+
[H
+
]
b
K
a
e
−
q
k
B
T
Ψ(x,y)
+
K
b
[H
+
]
b
e
q
k
B
T
Ψ(x,y)
.
(3)
N
S
denotes the surface binding site density, while K
a
and K
b
are the equilibrium constants for charging the
surface positively and negatively, respectively. [H
+
]
b
describes the positive hydrogen ion concentration of
the bulk and is corrected to the activity of the hydro-
gen concentration by the e
q
k
B
T
Ψ(x,y)
terms.
The biomolecules are modeled in a physics-based
bottom-up approach. By calculating the charge and
dipole moment for a single molecule (see for ex-
ample Figure 2, (Poghossian et al., 2005)), a mean
charge density and a mean dipole moment density
of the boundary layer is obtained. This bridges
the gap between the Angstrom length scale of the
biomolecules and the micrometer dimensions of the
FET (Heitzinger et al., 2008a), (Heitzinger et al.,
2008b), (Ringhofer and Heitzinger, 2008), (Wind-
bacher et al., 2008).
The link between the gate oxide and the aque-
ous solution is realized by two interface conditions,
(Heitzinger et al., 2008a), (Heitzinger et al., 2008b),
(Ringhofer and Heitzinger, 2008), (Heitzinger and
Klimeck, 2007),
ε
0
ε
Oxid
∂
y
ψ(0−, x) − ε
0
ε
Ana
∂
y
ψ(0+, x) = −C(x), (4)
ψ(0−, x) − ψ(0+, x) = −
D
y
(x)
ε
Ana
ε
0
. (5)
The x-axis is parallel oriented to the oxide sur-
face, while the y-axis points into the liquid. ψ(0−)
describes the potential in the oxide, while ψ(0+) re-
lates to the potential in the solute. The first equation
describes the jump in the field, while the second in-
troduces a dipole moment which causes a shift of the
STUDY OF THE PROPERTIES OF BIOTIN-STREPTAVIDIN SENSITIVE BIOFETS
25
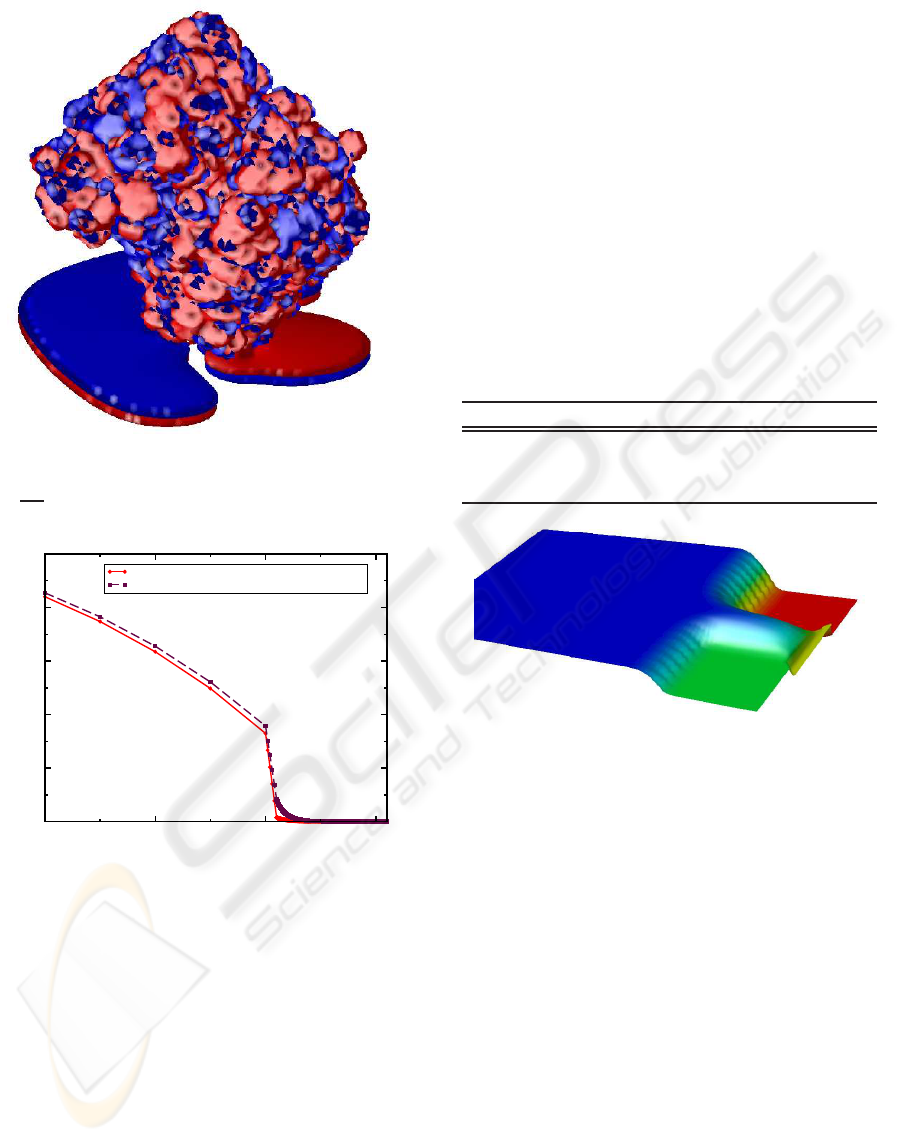
Figure 2: Biotin-streptavidin complex (http://www.pdb.org)
on the oxide surface. Two iso-surfaces for plus and minus
0.03
k
B
T
q
˚
A
2
are shown.
-2e-07
-1e-07
0
1e-07
y [m]
-0.2
0
0.2
0.4
potential profile [-V]
SiO2 Water and salt
SiO2 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 10nm
Figure 3: Potential profile at the interface (from left to right:
semiconductor, oxide, solute).
potential taken into account by adjusting the potential
in the analyte (Figure 3).
3 SIMULATION
Three different types of dielectric were simulated.
SiO
2
as a reference, Al
2
O
3
, and Ta
2
O
5
as possi-
ble high-k materials, with relative permitivies of 3.9,
10, and 25 respectively. As solute 1mMol sodium-
chloride at pH = 7 was considered. The parameters
for the site-binding model can be found in Table 1
(Landheer et al., 2005). For each dielectric the un-
prepared state (just water and salt), the prepared state
(water, salt, and biotin), and the bound state when
the chemical reaction has taken place (water, salt,
and biotin-streptavidin) were calculated for two dif-
ferent mean distances between molecules (λ = 10nm,
λ = 15nm). The data used for calculating charge and
dipole moment of biotin and streptavidin are obtained
from http://www.pdb.org (1SEW.pdb, Figures 2, 12).
The potential distribution across the device is shown
in Figure 4 and output curves were calculated for ev-
ery parameter combination mentioned above, assum-
ing a 100% binding efficency. The potential of the
reference electrode is set to 0.4V so that the FET will
be in moderate inversion as proposed by (Deen et al.,
2006).
Table 1: The parameters needed for the site-binding model
using different dielectric.
Oxide pK
a
pK
b
N
S
[cm
−2
] Reference
SiO
2
−2 6 5 · 10
14
(Bousse, 1982)
Al
2
O
3
6 10 8 · 10
14
(Bousse, 1982)
Ta
2
O
5
2 4 10 · 10
14
(Bousse et al., 1991)
Figure 4: Potential profile for Ta
2
O
5
water, salt, and biotin-
streptavidin at λ = 10nm average distance. Blue denotes
−1V while red stands for 1V.
4 RESULTS
Figures 5, 6, and 7 show a decrease in the output cur-
rent for biotin attached to the surface in comparison
to the unprepared surface. This downward shift for
the bound state in comparison to the unbound state is
due to the increase of negative charges at the interface,
which is also confirmed by the difference between the
curves for λ = 10nm and λ = 15nm, since for 10nm
the molecules are more dense than by 15nm.
As can be seen in the Figures 5, 6, and 7 the bigger
the ε
r
of the dielectric the bigger is the output current.
Thus high-k materials deliver stronger output signals.
According to (Deen, 2007) however, higher ε
r
dielec-
tric constants may lead to higher trap densities and
thus to a decreased signal-to-noise ratio. Therefore a
trade-off between bigger output signal and signal-to-
noise ratio has to be met. Figure 8 shows the output
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
26
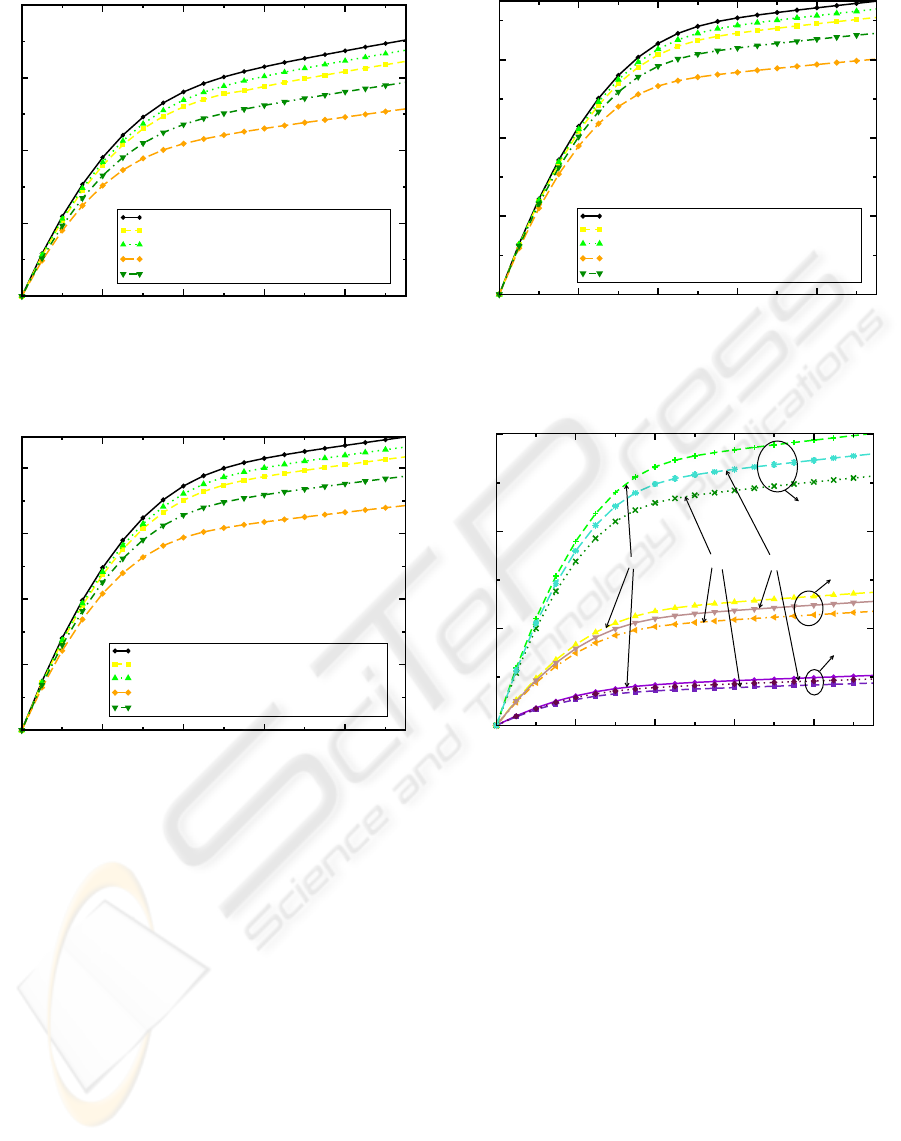
0 0,2 0,4
0,6
0,8
source to drain voltage [V]
0
10
20
30
40
drain current [A/m]
SiO2 Water and salt
SiO2 Water, salt, and biotin 10nm
SiO2 Water, salt, and biotin 15nm
SiO2 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 10nm
SiO2 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 15nm
Figure 5: Output curve for SiO
2
for unprepared, prepared
but unbound, and bound state at λ = 10nm and λ = 15nm,
respectively.
0 0,2 0,4
0,6
0,8
source to drain voltage [V]
0
20
40
60
80
drain current [A/m]
Al2O3 Water and salt
Al2O3 Water, salt, and biotin 10nm
Al2O3 Water, salt, and biotin 15nm
Al2O3 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 10nm
Al2O3 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 15nm
Figure 6: Output curve for Al
2
O
3
for unprepared, prepared
but unbound, and bound state at λ = 10nm and λ = 15nm,
respectively.
curves as a function of dielectric and molecule ori-
entation (0
◦
means perpendicular to the surface and
90
◦
means lying flatly on the surface) leading to the
lowest output curves for 0
◦
followed by 90
◦
and the
curves without dipole moment for each group. Fig-
ures 10 and 11 show the small signal resistance as a
function of dielectric and molecule orientation, dis-
playing smaller values for higher relative permittivity
ε
r
. A slightly larger differential resistance is observed
for perpendicular molecule orientation, in agreement
with the previous results shown in Figures 5, 6, and 7.
This is expected, because biomolecules are inhomo-
geneously charged. Therefore they possess a dipole
moment which enters into the boundaryconditions (5)
and there should be a difference in the output curves
of the BioFET for different orientation angles in rela-
tion to the surface.
0 0,2 0,4
0,6
0,8
drain to source voltage [V]
0
50
100
150
drain current [A/m]
Ta2O5 Water and salt
Ta2O5 Water, salt, and biotin 10nm
Ta2O5 Water, salt, and biotin 15nm
Ta2O5 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 10nm
Ta2O5 Water, salt, and biotin-streptavidin 15nm
Figure 7: Output curve for Ta
2
O
5
for unprepared, prepared
but unbound, and bound state at λ = 10nm and λ = 15nm,
respectively.
0 0.2 0.4
0.6
0.8
drain to source voltage [V]
0
50
100
150
drain current [A/m]
SiO2
Al2O3
Ta2O5
no dipole moment Angle 0
Angle 90
Figure 8: Output curves for SiO
2
, Al
2
O
3
, and Ta
2
O
5
for
calculation without dipole moment, angle 0
◦
(perpendicular
to surface), and angle 90
◦
(parallel to surface).
In the biochemical community there is an ongo-
ing discussion, if the orientation of the biomolecule
is relevant for sensing. Several papers have shown
contradictory results (Oh et al., 2005), (Wacker et al.,
2004), (Kusnezow et al., 2003), (Peluso et al., 2003),
(Turkova, 1999). All these papers are based on optical
detection. Although more study is needed, we men-
tion that for optical detection it is more important to
choose the linking molecule in a way that the reaction
is not hindered by steric effects (receptors block each
other) or the binding sites are blocked or even broken
by the crosslinker. In the case of a BioFET, however,
a field-effect as working principle is used. Thus it is
important to have a linker that is as short as possible,
to be close to the surface. To increase the signal-to-
noise ratio, the linker should have as little charge as
possible. For example, in order to detect streptavidin,
STUDY OF THE PROPERTIES OF BIOTIN-STREPTAVIDIN SENSITIVE BIOFETS
27
-1e-07
-5e-08
0
y [m]
-0.4
-0.2
0
0.2
potential profile [-V]
Al2O3 no dipole moment
Al2O3 Angle 0
Al2O3 Angle 90
Figure 9: Potential profile for biotin-streptavidin at λ =
10nm from left (semiconductor) to right (oxide).
0,2 0,4
0,6
0,8
source to drain voltage [V]
0
0,02
0,04
0,06
0,08
0,1
0,12
SiO2 biotin 10nm
SiO2 biotin 10nm Angle 0
SiO2 biotin 10nm Angle 90
Al2O3 biotin 10nm
Al2O3 biotin 10nm Angle 0
Al2O3 biotin 10nm Angle 90
Ta2O5 biotin 10nm
Ta2O5 biotin 10nm Angle 0
Ta2O5 biotin 10 Angle 90
small signal resistance [Ω m]
Figure 10: Small signal resistance for SiO
2
, Al
2
O
3
, and
Ta
2
O
5
for calculation without dipole moment, angle 0
◦
(perpendicular to surface), and angle 90
◦
(parallel to sur-
face) at biotin only.
biotin is used as a binding agent. A biotin molecule is
attached to the surface with a neutral linker. Strepta-
vidin then binds to biotin thus forming a bound state.
The charge difference between the unbound state of a
biotin alone, which is negatively charged with a sin-
gle elementary charge and the bound state of biotin-
streptavidin, which is negatively charged with five el-
ementary charges, is large enough for detection. We
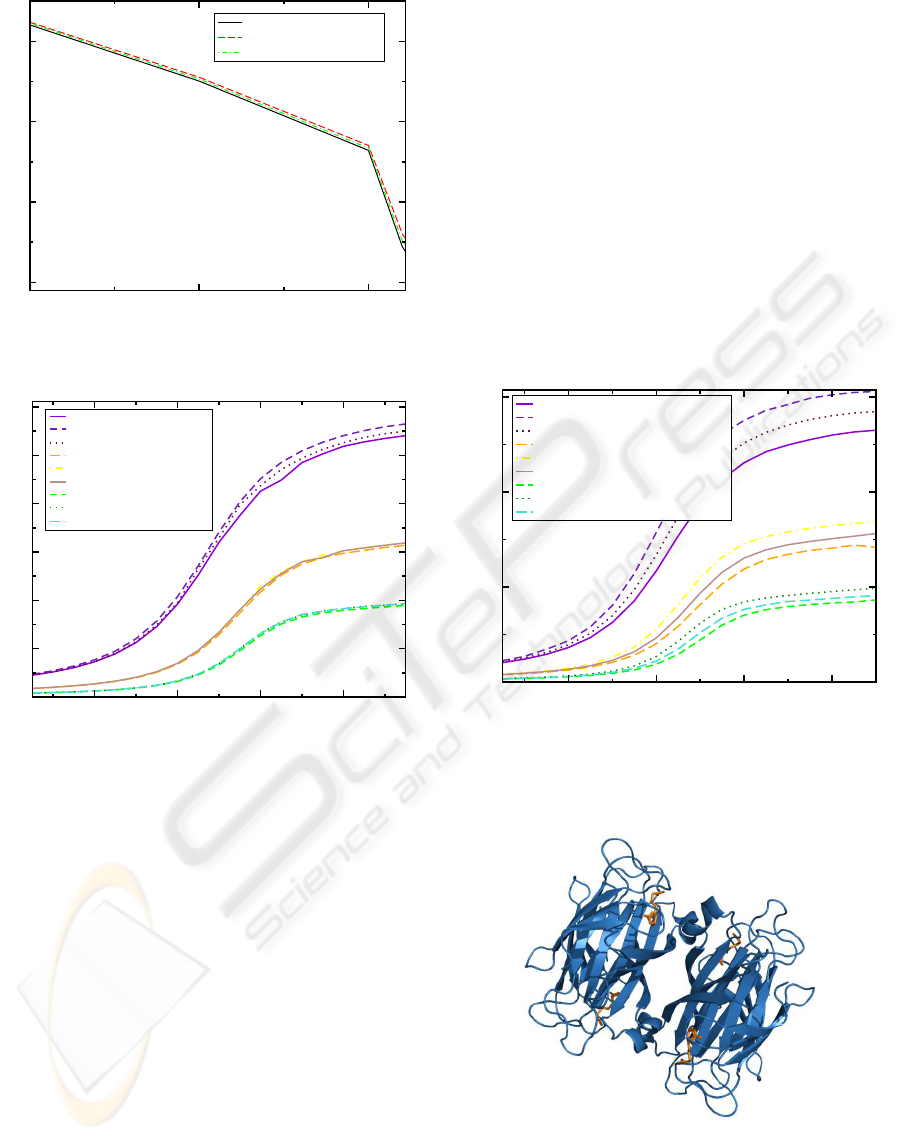
also note that due to the tetrameric nature of strepta-
vidin it has four sites to bind biotin as shown in Figure
12. Therefore, the linker binding biotin to the surface
should be short enough in order to prevent binding
several biotin molecules to a single molecule of strep-
tavidin .
5 CONCLUSIONS
The model shows a strong dependence on surface
charges and indicates a detectable shift in the thresh-
old voltage depending on their orientation related to
the surface. The bound state (streptavidin-biotin)neg-
atively charged with five elementary charges com-
pared to the unbound state (biotin) negatively charged
with one elementary charge leads to a reduced con-
ductivity, when hybridization has taken place. Also
the shift of the threshold voltage and output char-
acteristics due to different molecule orientations
(0
◦
...perpendicular to surface, 90
◦
...lying flat on sur-
face) can be seen. This shows the usefulness of
the simulation method for the design of efficient
BioFETs.
0,2 0,4
0,6
0,8
source to drain voltage [V]
0
0,05
0,1
0,15
SiO2 biotin-streptavidin 10nm
SiO2 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 0
SiO2 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 90
Al2O3 biotin-streptavidin 10nm
Al2O3 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 0
Al2O3 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 90
Ta2O5 biotin-streptavidin 10nm
Ta2O5 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 0
Ta2O5 biotin-streptavidin 10nm Angle 90
small signal resistance [Ω m]
Figure 11: Small signal resistance for SiO
2
, Al
2
O
3
, and
Ta
2
O
5
for calculation without dipole moment, angle 0
◦
(perpendicular to surface), and angle 90
◦
(parallel to sur-
face) at bound state (biotin-streptavidin).
Figure 12: Scheme of the tetrameric protein streptavidin
and biotin.
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
28

REFERENCES
Bousse, L. (1982). The Chemical Sensitivity of Elec-
trolyte/Insulator/Silicon Structures. PhD thesis.
Bousse, L., Mostarshed, S., Van Der Shoot, B., De Rooij,
N. F., Gimmel, P., and Gopel, W. (1991). Zeta po-
tential measurements of Ta
2
O
5
and SiO
2
thin films.
Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 147(1):22–
32.
Cui, Y., Wei, Q., Park, H., and Lieber, C. M. (2001).
Nanowire nanosensors for highly sensitive and selec-
tive detection of biological and chemical species. Sci-
ence, 293(5533):1289–1292.
Deen, M. J. (2007). Highly sensitive, low-cost integrated
biosensors. In SBCCI 2007: 20th Symposium on Inte-
grated Circuits and System Design, page 1.
Deen, M. J., Shinwari, M. W., Ranu´arez, J. C., and
Landheer, D. (2006). Noise considerations in field-
effect biosensors. Journal of Applied Physics,
100(7):074703–1 –074703–8.
Fritz, J., Cooper, E. B., Gaudet, S., Soger, P. K., and Man-
alis, S. R. (2002). Electronic detection of DNA by
its intrinsic molecular charge. In PNAS, volume 99,
pages 1412–1416.
Gao, Z., Agarwal, A., Trigg, A., Singh, N., Fang, C., Tung,
C., Fan, Y., Buddharaju, K., and Kong, J. (2007). Sil-
icon nanowire arrays for label-free detection of DNA.
Analytical Chemistry, 79(9):3291–3297.
Girard, A., Bendria, F., Sagazan, O. D., Harnois, M., Bihan,
F. L., Sala¨un, A., Mohammed-Brahim, T., Brissot, P.,
and Lor´eal, O. (2006). Transferrin electronic detec-
tor for iron disease diagnostics. IEEE Sensors, pages
474–477.
Gupta, S., Elias, M., Wen, X., Shapiro, J., and Brillson,
L. (2008). Detection of clinical relevant levels of
protein analyte under physiologic buffer using planar
field effect transistors. Biosensors and Bioelectronics,
24:505–511.
Hahm, J. and Lieber, C. M. (2004). Direct ultrasensitive
electrical detection of DNA and DNA sequence vari-
ations using nanowire nanosensors. Nano Letters,
4(1):51–54.
Heitzinger, C., Kennell, R., Klimeck, G., Mauser, N.,
McLennan, M., and Ringhofer, C. (2008a). Modeling
and simulation of field-effect biosensors (BioFETs)
and their deployment on the nanoHUB. J. Phys.:
Conf. Ser., 107:012004/1–12.
Heitzinger, C. and Klimeck, G. (2007). Computational as-
pects of the three-dimensional feature-scale simula-
tion of silicon-nanowire field-effect sensors for DNA
detection. Journal of Computational Electronics,
6:387–390.
Heitzinger, C., Mauser, N., and Ringhofer, C. (2008b).
Multi-scale modeling of planar and nanowire field-
effect biosensors. submitted.
http://www.pdb.org.
Im, H., Huang, X. ., Gu, B., and Choi, Y. . (2007).
A dielectric-modulated field-effect transistor for
biosensing. Nature Nanotechnology, 2(7):430–434.
Kim, D., Park, J., Shin, J., Kim, P., Lim, G., and Shoji, S.
(2006). An extended gate FET-based biosensor inte-
grated with a Si microfluidic channel for detection of
protein complexes. Sensors and Actuators, B: Chemi-
cal, 117:488–494.
Kusnezow, W., Jacob, A., Walijew, A., Diehl, F., and Ho-
heisel,J.D. (2003). Antibody microarrays: An evalua-
tion of production parameters. Proteomics, 3(3):254–
264.
Landheer, D., Aers, G., McKinnon, W., Deen, M., and
Ranu´arez, J. (2005). Model for the field effect from
layers of biological macromolecules on the gates of
meta-oxide-semiconductor transistors. journal of ap-
plied physics, 98(4):044701–1 –044701–15.
Oh, S. W., Moon, J. D., Lim, H. J., Park, S. Y., Kim, T.,
Park, J., Han, M. H., Snyder, M., and Choi, E. Y.
(2005). Calixarene derivative as a tool for highly
sensitive detection and oriented immobilization of
proteins in a microarray format through noncovalent
molecular interaction. FASEB Journal, 19(10):1335–
1337.
Park, K., Lee, S., Sohn, Y., and S.Y, C. (2008). BioFET
sensor for detection of albumin in urine. Electronic
Letters, 44(3).
Peluso, P., Wilson, D. S., Do, D., Tran, H., Venkatasub-
baiah, M., Quincy, D., Heidecker, B., Poindexter, K.,
Tolani, N., Phelan, M., Witte, K., Jung, L. S., Wagner,
P., and Nock, S. (2003). Optimizing antibody immo-
bilization strategies for the construction of protein mi-
croarrays. Analytical Biochemistry, 312(2):113–124.
Pirrung, M. C. (2002). How to make a DNA chip. Angew.
Chem. Int. Ed., 41:1276–1289.
Poghossian, A., Cherstvy, A., Ingebrandt, S., Offenh¨ausser,
A., and Sch¨oning, M. J. (2005). Possibilities and lim-
itations of label-free detection of DNA hybridization
with field-effect-based devices. Sensors and Actua-
tors, B: Chemical, 111-112(SUPPL.):470–480.
Ringhofer, C. and Heitzinger, C. (2008). Multi-scale mod-
eling and simulation of field-effect biosensors. ECS
Transactions, 14(1):11–19.
Selberherr, S. (1984). Analysis and Simulation of Semi-
conductor Devices, volume Springer of ISBN: 3-211-
81800-6.
Shinwari, M. W., Deen, M. J., and Landheer, D. (2006).
Study of the elecrolyte-insulator-semiconductor field-
effect transistor (EISFET) with applications in biosen-
sor design. Microelectronics Reliability.
Stern, E., Klemic, J., Routenberg, D., Wyrembak, P.,
Turner-Evans, D., Hamilton, A., LaVan, D., Fahmy,
T., and Reed, M. (2007). Lable-free immunodetection
with CMOS-compatible semiconducting nanowires.
Nature Letters, 445(1):519–522.
Tang, T.-W. and Ieong, M.-K. (1995). Discretization of
flux densities in device simulations using optimum ar-
tificial diffusivity. IEEE Transactions on Computer-
Aided Design of Integrated Circuits and Systems,
14(11):1309–1315.
Turkova, J. (1999). Oriented immobilization of biologically
active proteins as a tool for revealing protein interac-
tions and function. Journal of Chromatography B:
STUDY OF THE PROPERTIES OF BIOTIN-STREPTAVIDIN SENSITIVE BIOFETS
29

Biomedical Sciences and Applications, 722(1-2):11–
31.
Wacker, R., Schroder, H., and Niemeyer, C. M. (2004).
Performance of antibody microarrays fabricated by ei-
ther DNA-directed immobilization, direct spotting, or
streptavidin-biotin attachment: A comparative study.
Analytical Biochemistry, 330(2):281–287.
Windbacher, T., Sverdlov, V., Selberherr, S., Heitzinger, C.,
Mauser, N., and Ringhofer, C. (2008). Simulation
of field-effect biosensors (BioFETs). In Proc. Simu-
lation of Semiconductor Processes and Devices (SIS-
PAD 2008), pages P18/1–4, Hakone, Japan.
Zheng, G., Patolsky, F., Cui, Y., Wang, W. U., and Lieber,
C. M. (2005). Multiplexed electrical detection of
cancer markers with nanowire sensor arrays. Nature
Biotechnology, 23(10):1294–1301.
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
30
