
EFFICIENT SOURCE CODING IN A THRESHOLDING-BASED ECG
COMPRESSOR USING THE DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM
Carlos Hernando Ramiro, Manuel Blanco Velasco, Eduardo Moreno-Mart´ınez
Fernando Cruz Rold´an and Jos´e S´aez Landete
Departamento de Teor´ıa de la Se˜nal y Comunicaciones, Universidad de Alcal´a, Madrid, Spain
Keywords:
ECG compression, Electrocardiogram, Entropy, Maximum compression ratio, Source coding, Thresholding,
Wavelet transform.
Abstract:
The aim of electrocardiogram (ECG) compression is to achieve as much compression as possible while the
significant information for diagnosis purposes is preserved in the reconstructed signal. The source coding stage
allows us to modify the compression ratio without quality degradation through a lossless encoder. In this work,
the performance of this stage is analyzed in a compression scheme that has already presented good results
among those from the state of the art. The compressor is based on discrete wavelet transform, thresholding
and two-role encoder. The study consists of fixing all the stages except the source coding one in order to
obtain an upper compression ratio bound. The assessment is based on the entropy of the independent symbols
and the minimum expected length of the codewords. The results reveal a gap to improve the compression
ratio, so from the previous entropy study an alternative compression method is proposed. For this purpose
the symbols probabilities are analyzed through the normalized histogram. Thus, a Huffman encoder instead
of the two-role one is applied in the new compressor to attain the maximum compression ratio. In this way a
significant improvement is obtained without decreasing the original retrieved quality.
1 INTRODUCTION
The electrocardiogram (ECG) provides essential in-
formation to cardiologists for diagnosing. Therefore,
ECG processing has been a topic of great interest
and is most commonly used in applications such as
monitoring. Since 1961, when Holter (Holter, 1961)
introduced new techniques to monitor continuously
the electrical activity of ambulatory patients, ECG
recording techniques have gone through constant evo-
lution. The current ECG recording systems allow to
gather long-term signals with a duration of several
hours in a simple, inexpensive and non-invasive way.
Then the amount of ECG data increases considerably
and compression becomes a necessity in order to pro-
vide storage and transmission solutions.
With this in mind, many compression schemes
have been proposed during the past decades. A short
summary of them can be found in (Blanco Velasco
et al., 2004b). Among them, the lossy compression
techniques achieve great compression results at the
expense of some distortion in the original signal. The
point is that the lost information must be the irrelevant
from the diagnosis view (e.g. noise, lowest power fre-
quencies, etc.), which in terms of the ECG means that
the morphology of the reconstructed signal does not
change significantly. Recently, several thresholding-
based compression algorithms using signal decompo-
sition techniques have been developed (Abo-Zahhad
and Rajoub, 2002; Benzid et al., 2003; Chen et al.,
2006; Blanco Velasco et al., 2004b; Blanco Ve-
lasco et al., 2004a; Benzid et al., 2007; Blanco Ve-
lasco et al., 2007), because they yield attractive per-
formance and low computational cost. The typical
block diagram of this kind of compressors is shown
in figure 1. Although some of them utilize modern
techniques for the decomposition of the original sig-
nal such as nearly-perfect reconstruction cosine mod-
ulated filter banks (N-PR CMFB) (Blanco Velasco
et al., 2004b; Blanco Velasco et al., 2004a) or wavelet
packets (WP) (Blanco Velasco et al., 2007) with good
results, most of them are based on the discrete wavelet
transform (DWT), which play an interesting role in
the ECG data compression applications owing to their
easy implementation and efficiency (Abo-Zahhad and
Rajoub, 2002; Benzid et al., 2003; Chen et al., 2006;
259
Ramiro C., Velasco M., Moreno-Martínez E., Roldán F. and Landete J. (2009).
EFFICIENT SOURCE CODING IN A THRESHOLDING-BASED ECG COMPRESSOR USING THE DISCRETE WAVELET TRANSFORM.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 259-264
DOI: 10.5220/0001533502590264
Copyright
c
SciTePress

x[n]
y[n]
c[n]
SIGNAL
DECOMP.
THRESHOLDING
y [n]
th
y[n]
^
PCM
QUANTIZATION
SOURCE
CODING
Figure 1: Block diagram of a typical thresholding-based
compressor using signal decomposition.
Benzid et al., 2007).
In this paper, the study is focused on the
thresholding-based compressors using DWT. The
source coding stage of this kind of compression
schemes is analyzed in order to obtain the maximum
compression ratio (CR
max
). For this purpose the rest
of the blocks presented in figure 1 are fixed utilizing
the compression scheme proposed in (Benzid et al.,
2007). Then the statistical analysis of the indepen-
dent symbols used in the source encoder is performed
and an upper bound of the compression ratio is de-
rived. Provided that some gap exists for source co-
ding, we propose a new strategy to increase the com-
pression ratio. Therefore a new compression scheme
that yields better compression ratio (CR) is proposed.
2 THRESHOLDING-BASED
COMPRESSORS
This type of compression schemes takes advantage
of a signal transformation into a domain where the
contribution of some coefficients to the reconstruc-
ted signal morphology is less important than others.
A common technique would be to cancel the less
significant wavelet coefficients, producing large runs
of zeros. These bursts of zeros favor the compres-
sion through source coding implementation. Thus the
original sample values are discarded and the quality of
the retrieved signal is degraded. To perform this pro-
cedure, a threshold value must be determined. This
parameter fixes the edge between the deleted samples
and the significant ones. The threshold depends on
quality and compression requirements whatever the
aim is. Then the threshold can be fixed beforehand
(Abo-Zahhad and Rajoub, 2002; Benzid et al., 2003;
Chen et al., 2006) or be adjusted according to the de-
sired results (Blanco Velasco et al., 2004b; Blanco
Velasco et al., 2004a; Benzid et al., 2007; Blanco Ve-
lasco et al., 2007).
The significant coefficients are quantized through
pulse code modulation (PCM). Finally, a lossless en-
coder is applied to the full sequence that includes the
successions of zeros and the quantized significant co-
efficients altogether. This coding procedure consists
of two main steps:
• Determining the independent symbols to repre-
sent the original signal that will be later encoded.
• Selecting the codewords that will encode each one
of those symbols.
In this study, tests with this kind of compre-
ssors are carried out using the MIT-BIH Arrythmia
Database. As measurement criteria to evaluate the
quality of the retrieved signal two parameters are
used. One is the percentage root-mean-square diffe-
rence (PRD), which is defined as:
PRD =
v
u
u
u
u
u
u
u
t
N
∑
n=1
(x[n] − ˆx[n])
2
N
∑
n=1
(x[n])
2
× 100, (1)
where x[n] is the original ECG signal and ˆx[n] is the
reconstructed one. Since the PRD is strongly depen-
dent on the signal mean value, high mean values can
mask the real quality performance assessment. To
avoid this, we also use the modified criterion as fo-
llows:
PRD1 =
v
u
u
u
u
u
u
u
t
N
∑
n=1
(x[n] − ˆx[n])
2
N
∑
n=1
(x[n] − ¯x[n])
2
× 100, (2)
where ¯x[n] is the signal mean value. Furthermore,
it is established in (Zigel et al., 2000), that if the
PRD1 value is between 0 and 9, the quality of the
reconstructed signal is either ‘good’ or ‘very good’,
whereas if the value is greater than 9, its quality group
cannot be determined.
Moreover the CR value is calculated as follows:
CR =
b
x
b
c
, (3)
where b
x
is the amount of bits used to represent the
original ECG signal x[n] and b
c
is the total number of
bits obtained after the source encoder block to repre-
sent c[n].
3 COMPRESSION METHODS
The first compression scheme used in this work is
based on that of proposed in (Benzid et al., 2007). It
utilizes discrete wavelet transform (DWT) and thres-
holding. The threshold is obtained through an itera-
tive approach that finishes when the PRD reaches the
PRD target (PRD
target
) as is proposed in (Blanco Ve-
lasco et al., 2004a). The compressor consists of the
following main steps:
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
260

1. Choose the PRD
target
and apply the DWT, up to
the fifth level and with the mother wave “bior4.4”.
2. Threshold the wavelet coefficients with an ite-
rative algorithm in order to match the PRD
target
within a tolerance of 1%.
3. Quantize in PCM the nonzero wavelet coeffi-
cients. The quantization resolution B is chosen in
an adaptive way. The value of B is increased until
the PRD matches the PRD
target
, with a tolerance
of 10%.
4. Lossless source coding of the thresholded and
quantized coefficients by means of the two-role
encode (TRE) technique, which consists of the
following:
(a) A baseline of 2
B
is added to the significant coe-
fficients. Then each of them is coded with B+1
bits.
(b) The runs of zeros are also coded also with B+ 1
bits. The minimum encodable length is 1 and
the maximum is 2
B
− 1, this way these code-
words are different from those used in the pre-
vious point. Thus longer successions of zeros
must be represented with more than one code-
word.
The other compression scheme differs from the
first one in the 5th stage. In this case, the lossless
source coding is carried out with a Huffman encoder
(Skretting, 1999) although using the same symbols as
obtained with the TRE method. Thus shorter code-
words are assigned to less probable symbols and the
expected length of the codeword is reduced since the
symbol probabilities are different. In the Huffman en-
coder, the logarithmic encoding and the iterative se-
quence splitting options have been disabled in order to
preserve the original independent symbol set. There-
fore a fair comparison analysis between the compre-
ssion and quality results of both methods can be done.
4 UPPER COMPRESSION RATIO
BOUND ACHIEVEMENT
The CR
max
that can be achieved with a lossless source
encoder is studied in order to obtain an upper com-
pression bound. To do so, the entropy of the indepen-
dent symbols used as input in the source coding stage
is analyzed.
The source entropy defines a boundary to the ex-
pected length of any instantaneous code (Cover and
Thomas, 2006):
Teorema 1. The expected length L of any instanta-
neous D-ary code for a random variable X is greater
than or equal to the entropy H
D
(X), with equality
when D
−l
i
= p
i
, where p
i
is the symbol i probability
and l
i
its corresponding codeword length.
L ≥ H
D
(X). (4)
The procedure to derive CR
max
in the compressor
schemes described in section 3 consists of the follo-
wing steps:
1. The independent symbol set used to encode is
chosen. The independent symbols are defined as
those that present a biunique relationship with the
final codewords. In our case the full symbol set
includes two different subsets:
• The runs of zeros with length less or equal than
2
B
− 1.
• The significant coefficients, which are quan-
tized with B bits.
Thus the independent symbol set consists of
2
B+1
− 1 different symbols, as the value 0 is use-
less because there are not successions of zeros
with this length.
2. The probability mass p(x) of the random variable
X is calculated. Then the entropy is derived, con-
sidering the binary alphabet D = {0, 1}:
H(X) = −
∑
x∈H
p(x) log p(x). (5)
3. The CR is obtained as a result of two independent
compression processes: PCM quantization stage
and source coding. For PCM quantization, the
compression ratio CR
1
only depends on the re-
solution B used. The lower B, the greater CR
1
.
On the other hand, the compression ratio of the
source coding CR
2
can be improved without mo-
difying the quality of the retrieved signal. Accor-
ding to theorem 1, the entropy establishes a bound
to the expected length L of the codeword and con-
sequently to CR
2
as follows:
CR
2
=
B
L
≤
B
H
. (6)
Therefore, the relation
B
H
can be considered as the
upper bound of CR
2
(CR
2max
).
4. To obtain CR
max
, the CR
1
value is also needed. It
follows this equation:
CR
1
=
B
x
B
=
11
B
, (7)
where B
x
is the original sample resolution, whose
value is 11 for this database, and B refers to the
quantization resolution.
5. Finally the CR
max
value can be calculated apply-
ing the following equation:
CR
max
= CR
1
·CR
2max
. (8)
EFFICIENT SOURCE CODING IN A THRESHOLDING-BASED ECG COMPRESSOR USING THE DISCRETE
WAVELET TRANSFORM
261

5 EXPERIMENTAL STUDY
Tests are carried out using signals from the MIT-BIH
Arrythmia Database. Files in the database contain two
leads sampled at 360 Hz with 11 bits per sample of
resolution. The signal length taken is 182 seconds,
that is 65520 samples per signal. This value is very
close to the two to a power 2
16
(65536), which allows
us to speed the DWT computing up. Moreover the
1024-baseline added to each lead for storage purposes
is removed before processing.
A statistical study with the signal 117 is firstly
done. The independent symbols used as input in
the source encoder are obtained and the normalized
histogram is calculated. Moreover the reconstructed
waveform is derived and the error signal is calcu-
lated as the difference between the original and the
retrieved samples. The PRD
target
as well as the qua-
lity and compression results are presented in table 1.
Figure 2 shows the histogram. Two graphs are ob-
tained because the whole set of symbols is split into
two groups as explained in section 4. Note in the his-
togram of figure 2 that symbols in the run of zeros
have null probability while others are clearly much
more likely. Symbols with null probability which
does not need any codeword, so it is not necessary
to encode them. Also shorter as possible codewords
must be assign to the more frequent symbols.
Moreover the first 4096 samples of the original,
retrieved and error signal are shown in figure 3. The
cardiologists actually diagnose through visual analy-
sis of the ECG, so both waveforms must look as si-
milar as possible. In this case, taking into account the
great upper compression bound obtained, an optimal
visual quality of the reconstructed signal is attained.
Furthermore the error is equally distributed over time,
so cannot mask significantly any part of the signal by
accumulation.
Table 1: Upper compression bound for signal 117.
Signal PRD
target
B CR
max
PRD PRD1
117 2 7 17.24 2.12 8.01
The first compression study is also carried out
with the signal 117. Several values of B are taken
in order to check the efficiency of the adaptive quanti-
zation technique. The results are shown in table 2. As
can be seen, the criterion to select B holds for B = 7,
which is that of chosen by the adaptive quantization
procedure in table 1. This strategy permits to reduce
the value of B, and as a result increases the CR, in
a dynamic way according to the nature of each ECG
signal. So the adaptive quantization algorithm is re-
0 20 40 60 80 100 120
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
Símbolos
(a)
140 160 180 200 220 240
0
0.01
0.02
0.03
0.04
0.05
0.06
0.07
0.08
Símbolos
(b)
Figure 2: Normalized histograms of signal 117 for
PRD
target
= 2. (a) Runs of zeros (b) Significant coefficients.
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
−400
−200
0
200
n
Amplitude
Original 117 signal
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
−400
−200
0
200
n
Amplitude
Reconstructed 117 signal
0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 3000 3500 4000
−20
−10
0
10
20
Error signal
n
Amplitude
Figure 3: Compression waveform of signal 117 for
PRD
target
= 2.
vealed as efficient and valuable to be included in the
quantization stage of the proposed method. Also the
compression ratios are greater and closer to the upper
bound for all the tested B values.
Another study is performed with the dataset com-
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
262
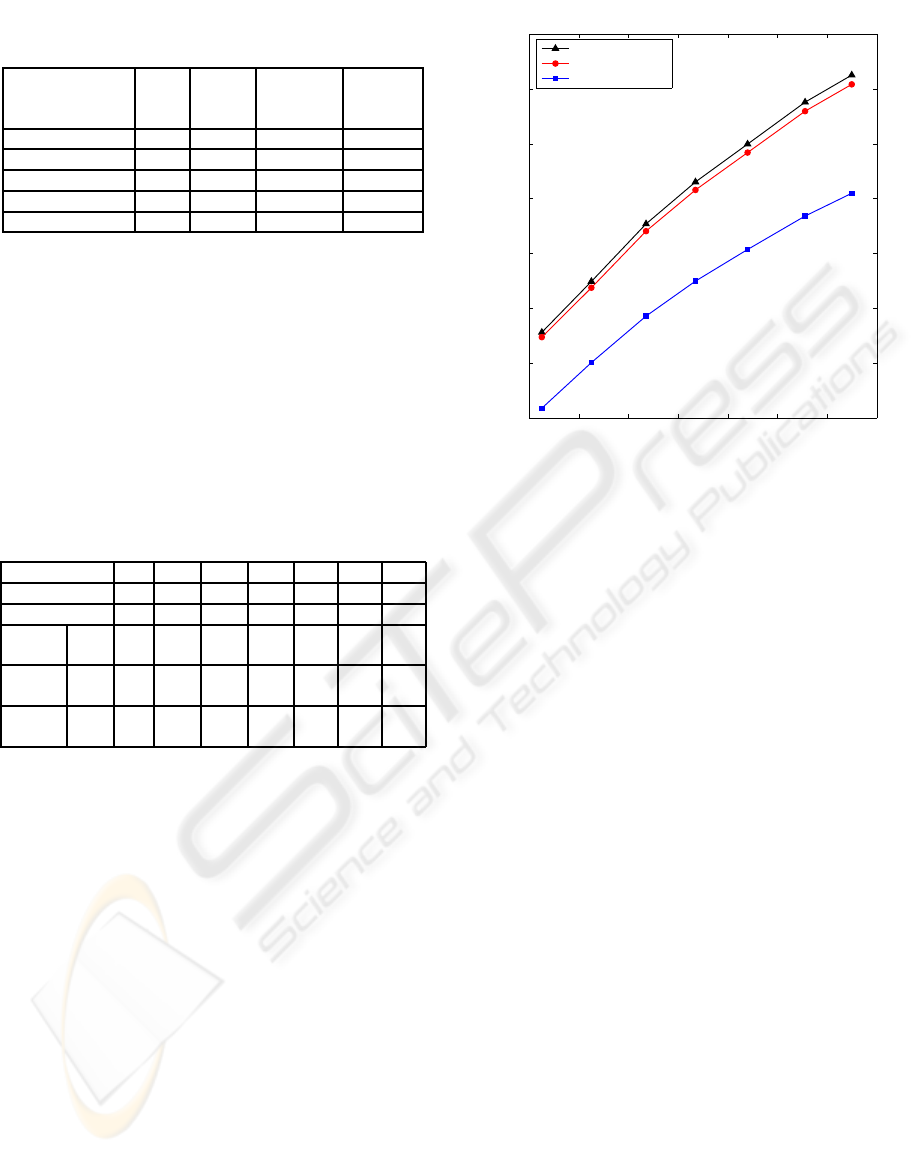
Table 2: Quality and compression results as a function of B
for the 117 signal.
PRD
target
= 2 PRD CR
max
CR TRE
method
CR
prop.
method
B = 6 2.44 18.68 14.68 18.40
B = 7 2.12 17.24 13.65 16.96
B = 8 2.02 15.73 12.38 15.36
B = 9 2.00 14.33 11.25 13.81
B = 10 1.99 13.11 10.28 12.36
posed of the records 100, 101, 102, 103, 107, 109,
111, 115, 117, 118 and 119. In this case diffe-
rent PRD
target
values are taken, which can be seen in
table 3. In the table 3 we show the averaged CR, PRD
and PRD1 of the whole dataset for different PRD
target
.
The obtained PRD1 values, except the last one, are all
under 9, which stands for good quality of the recons-
tructed signal. The CR as a function of PRD is shown
in figure 4. As can be seen in the graphic, our methods
yields better compression ratio in the full range.
Table 3: Compression and quality results for the signal set.
PRD
target
2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5
PRD 2.13 2.63 3.18 3.67 4.20 4.78 5.25
PRD1 3.77 4.64 5.64 6.51 7.41 8.42 9.27
Comp.
limit
CR
max
9.12 10.98 13.08 14.61 15.99 17.52 18.51
TRE
method
CR 6.35 8.02 9.71 10.99 12.14 13.37 14.20
Proposed
method
CR 8.95 10.75 12.82 14.31 15.68 17.19 18.17
As was said above, several symbols with null
probability can be noticed in the runs of zeros his-
togram, meanwhile other symbols are clearly more
frequent than any other. In the TRE method, same
length codewords are used for every symbol, but it
does not take advantage of the different symbols pro-
babilities. As a result, figure 4 shows that the com-
pression ratios derived with this technique are signifi-
cantly lower than the maximum ones. On the other
hand, the proposed compression scheme takes ad-
vantage of the different probabilities through a Huff-
man encoder. Thus shorter codewords are assigned to
more probable symbols so the expected length of the
generated code decreases and consequently the com-
pression performance improves. In this way we ob-
tain CR values closer to the upper bounds.
2 2.5 3 3.5 4 4.5 5 5.5
6
8
10
12
14
16
18
20
PRD
CR
Compression limit
Proposed method
TRE method
Figure 4: Compression comparative study results.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this work a thresholding-based compression
scheme using DWT is proposed. The results show
a better performance than similar compressors in the
state of the art. The entropy analysis of the indepen-
dent symbols used to encode is carried out and the
upper compression ratio bound is derived. The CR
max
calculation is revealed as an effective tool to evalu-
ate the compression bound that a specific scheme can
provide. In this work, the TRE method has been
analyzed as it has demonstrated good performance
among those in its category. The analysis of the upper
CR bound tells us that there is still a gap for the im-
provement. Therefore, a Huffman encoder (Skretting,
1999) is applied as source coder attaining better re-
sults for a wide range of PRD values. The obtained
CR values keep very close to the upper bound. There-
fore, an optimal result has been obtained for this par-
ticular scheme.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been supported in part by Grant PR-
2007-0216 from the Ministerio de Educaci´on y Cien-
cia, in part by the Fondo de Investigaci´on San-
itaria under Project PI052277, in part by Comu-
nidad Aut´onoma de Madrid and Universidad de Al-
cal´a through project CCG07-UAH/TIC-2034, in part
by the Fundaci´on de Investigaci´on M´edica Mutua
EFFICIENT SOURCE CODING IN A THRESHOLDING-BASED ECG COMPRESSOR USING THE DISCRETE
WAVELET TRANSFORM
263

Madrile˜na and in part by grant “Introducci´on a la In-
vestigaci´on” from Universidad de Alcal´a held by Car-
los Hernando–Ramiro.
REFERENCES
Abo-Zahhad, M. and Rajoub, B. A. (2002). An
effective coding technique for the compression of
one–dimesional signals using wavelet transforms.
Medical Engineering and Physics, 24(3):185–199.
Benzid, R., Marir, F., and Bouguechal, N.-E. (2007).
Electrocardiogram compression method based on the
adaptative wavelet coefficients quantization combined
to a modified two-roled encoder. IEEE Signal Pro-
cessing Letters, 14(6):373–376.
Benzid, R., Marir, F., Boussaad, A., Benyoucef, M.,
and Arar, D. (2003). Fixed percentage of wavelet
coefficients to be zeroed for ECG compression. Elec-
tronics Letters, 39(11):830–831.
Blanco Velasco, M., Cruz Rold´an, F., Godino Llorente,
J. I., and Barner, K. E. (2004a). ECG compression
with retrieved quality guaranteed. Electronics Letters,
40(23):1466–1467.
Blanco Velasco, M., Cruz Rold´an, F., Godino Llorente, J. I.,
and Barner, K. E. (2007). Wavelet packets feasibility
study for the design of an ECG compressor. IEEE
Trans. on Biomedical Signal Processing, 54(4):766–
769.
Blanco Velasco, M., Cruz Rold´an, F., L´opez Ferreras,
F.,
´
Angel Bravo Santos, and Mart´ınez Mu˜n´oz, D.
(2004b). A low computational complexity algorithm
for ECG signal compression. Medical Engineering
and Physics, 26(7):553–568.
Chen, J., Ma, J., Zhang, Y., and Shi, X. (2006). ECG com-
pression based on wavelet transform and Golomb cod-
ing. Medical Engineering and Physics, 42(6):830–
831.
Cover, T. M. and Thomas, J. A. (2006). Elements of Infor-
mation Theory. John Wiley & Sons, New York, 2nd
edition.
Holter, N. J. (1961). New methods for heart studies. Sci-
ence, 134:1214–1220.
Skretting, K. (1999). Arithmetic Coding and
Huffman Coding in Matlab. (online)
http://www.ux.uis.no/∼karlsk/proj99.
Zigel, Y., Cohen, A., and Katz, A. (2000). The Weighted
Diagnostic Distortion (WDD) measure for ECG sig-
nal compression. IEEE Transactions on Biomedical
Engineering, 47(11):1422–1430.
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
264
