
DESCRIPTION LOGIC FOR AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION
OF MAMMOGRAM REPORTS
Amel Boustil
Département d’informatique, Université de Mohamed Bouguerra Boumerdés, 35000, Boumerdés, Algérie
Zaidi Sahnoun
Département d’informatique, Université Mentouri Constantine, Labo LIRE, Constantine 2500, Algérie
Keywords: Semantic Web, Ontology, OWL, Mammogram Report, Concept, Property, Description Logic, Racer, ACR.
Abstract: In this paper, we present a system for automatic classification of mammography reports, based on a
radiological OWL DL ontology. The later describes radiological signs and categories of the BI-RADS
classification established by American College of Radiology (ACR) in the OWL DL language. Our system
is designed firstly to formalize content of mammogram reports written in free text driving by the ACR
Ontology, then to infer relevant classes and corresponding attitude by using subsumption classification.
Classification in our work is based on description logic by using OWL DL ontology and description logical
reasoning system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Mammogram reports written in free text are difficult
to interpret and analyze by programs machines. The
difficulty is due to the informal structure of
mammogram reports. Finding a way to make-up
these reports in a formal content is also a difficult
work (Zweigenbaum, 1994) (Ricky, 2001) due to the
complexity of natural language and medical
knowledge.
In recent years, research in Semantic Web has
been moving from realm to a reality denoting a
vision of a new World Wide Web in which
ontologies are accessed and shared on the basis of
formal representation. Ontologies have become
common on the medical Web (Golbreich, 2004)
(Holger and al, 2004) and it is now possible to
formally reason about them and derive implicit
information. The WWW Consortium (W3C) was
developing ontology web language (OWL) (OWL,
2004), a language for encoding knowledge on Web
to make it understandable to automatic electronic
processing information.
Our aim in this paper is to show how to use a
formal ontology written in OWL language in
medical domain and to provide a helpful tool for
classification of francophone mammogram reports
based on description logics as a foundation of
semantic Web ontology representation language
(Badeer, 2003). In this work we will firstly present
our ontology developed in (Boustil, 2006) which
contains radiological concepts, pathological
concepts and different classes named ACR classes
written in OWL language by using Protégé OWL
(Holger, 2004). ACR Classes are obtained from a
normalized Classification (ACR, 2002) of BI-RADS
System. The second work will be to show how we
use this formal ontology to firstly formalize content
of mammogram report written in free text and
secondly to deduce pathological ACR classes by
classifying formal representation of mammogram
report in our ontology.
Deducing ACR corresponding classes in our
work is based on using Description Logic as
ontology describing language. Here we don’t use
conceptual graphs like in Minelas system
(Zweigenbaum, 1994) or natural language
processing like in MedLee system (Nilesh,1995).
The real difference in our work is in using standards
of Semantic Web for describing sharing knowledge
and also in inference based Description Logic
(Haarsley, 2001). The main idea is to follow trail of
concepts, instances and properties in each statement
of mammogram report written in free text, then to
193
Boustil A. and Sahnoun Z. (2009).
DESCRIPTION LOGIC FOR AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMOGRAM REPORTS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 193-198
DOI: 10.5220/0001538701930198
Copyright
c
SciTePress
determine relations between them by using models
given by our ontology, result to these steps will be
saved in XML file as a formal representation of the
mammogram report. Finally, we use a description
logical reasoning system to classify in our ontology
the XML file rewritten as a new concept.
Description logical reasoning system returns for the
new concept its super concepts corresponding to
ACR class.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows. A brief introduction to BI-RADS Systems
and ACR classification is presented in section 1.
Then we outline how we have constructed ACR
ontology. In the following section, we explain the
main components of our system and how to
construct a formal representation of mammogram
report that will be classified in ACR ontology to
deduce corresponding ACR category. Related work
and future directions are discussed in section 4, and
section 5 concludes with brief summary
2 BI-RADS SYSTEM AND ACR
CLASSIFICATION
Today, breast cancer is the most common form of
cancer for women. Mammography is used to detect a
number of abnormalities of the breasts of
asymptomatic patients. Recently, studies have
demonstrated the benefits of routine mammograms
in terms of early detection of cancer and the
subsequent reduction in mortality (Assessment,
2003).
However, there is a variability between intra and
inter observatory in using lexicon, interpretation and
classification of lesions seen in mammography
images. Rules which establish diagnostic or
prognostic conclusion about morphological
descriptions observed in mammography images
created in examination are published in a
classification system like the ACR classification.
The American College of Radiology (ACR) has
established the Breast Imaging Reporting and
Database System (BI-RADS) (Assessment, 2003) to
guide the breast cancer diagnostic routine. It
standardizes a classification in 6 categories named
and presented in Table1. The aim of this normalized
classification is to standardize structure and lexicon
(ACR, 2002) of mammogram report to reduce errors
in variability of interpretations. We have used this
lexicon to construct our ontology.
Table 1: ACR Categories.
BI-RADS™ Assessment Categories (Assesment, 2003)
ACR 0 Need Additional Imaging Evaluation
ACR 1 Negative
ACR 2 Benign Finding
ACR 3 Probably Benign Finding – Short Interval
Follow-Up Suggested
ACR 4 Suspicious Abnormality – Biopsy Should Be
Considered
ACR 5 Highly Suggestive of Malignancy Appropriate
Action Should Be Taken
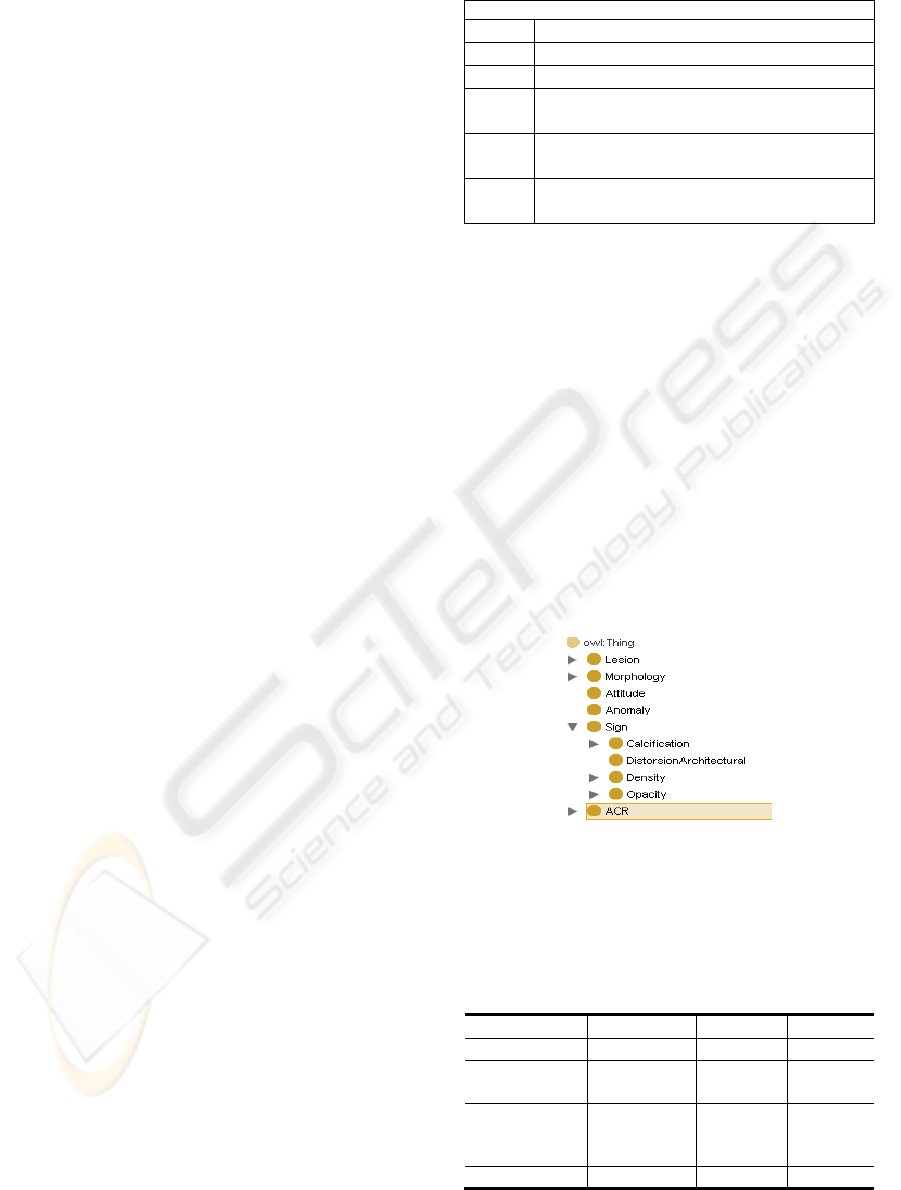
3 ACR OWL ONTOLOGY
A first ontology has been designed and developed in
OWL DL in (Boustil, 2006). It provides the main
concepts, properties and ACR categories relevant to
ACR classification. There are morphologic concepts
like Shape, Margin, Size, Density, Number;
radiological signs like Mass, Calcification,
Architectural distortion and Asymmetric Density;
mammary lesions like cysts, Fibroadenoma,
Carcinoma; and the six categories defined in ACR
classification which are ACR0, ACR1, ACR2,
ACR3, ACR4, ACR5. Figure 1 presents a partial
taxonomy of our ontology developed in Protege
OWL.
Figure1: Partial taxonomy of ACR ontology.
Some concepts are related to others by certain
properties like: hasShape, hasBord, hasSign, etc.
Table 2 gives some properties and its characteristics.
Table 2: Some Properties of Radiological Ontology.
Proprieties Domain Range Inverse
hasAnomaly ACR Anomaly
hasForm Calcification
Mass
Shape
hasSign
hasDensity
hasOpacity
Anomaly
Anomaly
Anomaly
Sign
Density
Mass
IsSign
Of
isSignOf Sign Anomaly hasSign
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
194

ACR categories are described as a defined Class.
So we have defined for each ACR category
necessary and /or sufficient condition of the form
Class ⊆ ClasseExpression where Class is a class
name and ClassExpression is a complex expression
complying with the OWL DL syntax, which can be
interpreted as a necessary condition for an individual
to be an instance of the subclass Class. Equivalence
axiom is represented by Class ≡ ClassExpression
where Class is a class name and ClassExpression is a
complex expression, which can be interpreted as a
necessary and sufficient condition for an individual
to be an instance of the class.
ACR 2: there are Benign Findings which don’t need survey-
llance or complementary examination:
[L1] Round Opacity and macrocalcification (cyst or
fibroadenoma)
[L2] Intramammary lymph nodes
[L3] Mixed density or oily density (lipomas,
harmatomam, galactoceles, oil cysts)
[L4] Macrocalcification without mass (fibroadenomas,
cyst, vascular calcification)…
[L5] …
Figure 2: ACR2 as described in (ACR, 2002).
Each line in ACR 2 as presented in figure 2 is a
subclass of ACR2 and it is described by using other
concepts. As an example Ligne1: Round Mass and
macrocalcification (Fibroadenoma or cyst) is an
anomaly1 if in our report there is a radiological sign
of round mass and macrocalcification (figure 3).
Anomaly1≡Anomaly ∩ ∃ hasSign (RoundOpacity)
∩ ∃ hasSign(MacroCalcification) (1)
Benign Anomaly1 have a necessary and
sufficient condition of: image (mammogram report)
of an anomaly with existence of a radiological sign
of an Opacity round, and Macro Calcification.
A cyst or fibroadenoma gives also anomaly1.
(Kyste U Fibroadenoma) ⊆ Anomaly1 (2)
Figure 3: Anomaly1 in Protégé Plug-in.
The same method is used to deduce the other
anomalies and the existence of one of the eight
Benign Anomaly listed in figure2 deduces the ACR2
Class as described in (3). Also, (4) means that ACR2
deduces no surveillance or complementary
examination.
ACR2 ≡ Anomaly1 U Anomaly2 U Anomaly3 U
Anomaly4 U Anomaly5 U Anomaly6 U
Anomaly7 U Anomaly8 (3)
ACR2 ⊆ ACR ∩ not(ComplementaryExaman U
Surveillance) (4)
Figure 4: ACR2 in protégé Plug-in.
ACR3, ACR 4, ACR 5 are written in the same
manner but ACR1 is a particular case because it
represents image described in (5) which don’t
contain any of the four radiological signs.
ACR1≡
ACR ∩ not (∃ hasSign(Mass ∩
Calcification ∩ Architectural_Distorsion ∩
Asymetry_of_density) (5)
We need additional imaging evaluation like in
ACR0 when we are not in the other well identified
classes (6)
ACR0 ≡ ACR ∩ not (ACR1 U ACR2 U ACR3 U
ACR4 U ACR5) (6)
We have used Racer (Haarsley, 2001) in Plugin
OWL (Holger, 2004) to find out hidden
dependencies, inconsistencies, and to compute the
overall multiple hierarchies’ classification, from the
class and properties logical definitions and
inclusions. We incrementally fixed them and revised
the ontology until it was proved to be globally
consistent. In the following section we will explain
how to use this ontology to classify mammogram
report.
DESCRIPTION LOGIC FOR AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMOGRAM REPORTS
195

Structural analysis
Lexical analysis
Inference analysis
Conclusion: ACR Class
XML file
Semantic analysis
Racer
Formal
representation o
f
report in XML
Useless
Words
ACR
OWL
Ontology
Unknown
Words
Mammogram
report
3 APPLICATION
The main idea of our system resides in comparing
formal representation of francophone mammogram
report to our formal ontology by using subsumption
reasoning. In other terms classify this formal
representation in the hierarchy of concepts of our
ontology and deduce ACR class and the procedure
to follow in treatment.
Figure 5: Global description of our system.
Formal representation is obtained by extracting
classes, instances, properties from mammogram
report by using ACR ontology and some techniques
of natural languages like in (Ricky, 2001). But
contrary of the approach presented in (Ricky, 2001),
classification reasoning in our system is based on
description logic and is done by using Racer. The
different components of our application are
presented in figure 6.
Figure 6: Architecture of our Application.
3.1 Structural Analysis
Because mammogram reports are written in free
text, structural Analysis identifies in this phase the
different structures of mammogram report: Entitle,
dates, information patients, Findings, Conclusions,
etc. To facilitate this analysis we focus our work
only on findings section. Others parts will be treated
as future work.
3.2 Lexical Analysis
In this step, the system identifies the individual
sentences within Findings section by using end-of-
sentence markers.
The aim of this analysis is to extract types of
each word by looking up to the radiological
ontology and the useless word (like: il, mais, avec).
Any words that remain unknown after this process
are inserted into a separated file. A medical language
expert is responsible for later studying of these
words and for a new modification of our ontology.
The different steps followed by the current analyzer
are:
• Step1: split the text to sentences separated by
point.
• Step2: split each sentence to words.
• Step3: find type of each word (concept,
instance, property, useless word, unknown
word).
We must here download our OWL Ontology and
access it by using Jena API. Result of this phase is a
mediate XML file containing a list of sentences
represented by list of words:
<Text>
<sentence number=’1’>
<Concept name=’..’ presence=’..’ />
<Property name=’..’ />.
<Instance name=’..’ />.
</sentence>....
</Text>
3.3 Semantic Analysis
The aim of this phase is to find links between
concepts and properties by using ACR ontology. For
example, if lexical analysis returns the following
sentence (as a list of term)
Opacité
ronde MacroCalcification ovale mixte
The semantic analysis will conclude that there are:
• Opacity where the shape is round and the
density is mixed (hasDensity is a property
where its domain can be only opacity)
• MacroCalcification where the form is oval
Classifier
Result: ACR Class and Procedure of
treatmen
t
Mammog
ram report
Formal
Ontology
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
196

Opacité Ronde Macrocalcification Ovale Mixte
Figure 7: Example of logical relationships
that can be
inferred from a sentence.
The difficult work here is to determine Domain
of each property. For this reason, we have developed
an algorithm to find Domain of properties; the
algorithm will be very simple if each sentence
contains only one concept. In the other case and
because we perform a francophone report, our
algorithm tries to find the nearest concept in the left
of the current property; otherwise it seeks for the
nearest concept in the right of it, and in each attempt
it tests if this concept can be a Domain of the current
property by asking Jena.
Result of this Analysis is an XML file of the form:
<Concept name=’Opacity’ presence=’yes’>
<hasForm>Shape_round</ hasForm >
<hasDensity> Density_mixed </hasDensity>
</Concept>.
<Concept name=’Macrocalcification’presence
’yes’>
<hasForm>Shape_oval</hasForm>
</Concept>.
3.4 Inferential Analysis
From the result of the previous analysis which
represents a formal description of mammogram
report saved in XML file we will determine a Racer
Query. Inferential analyzer asks Racer to classify
Query as a new class in ACR ontology to determine
the number of anomaly and finally it asks also Racer
for super Class of corresponding anomaly to
determine ACR category.
The Racer query equivalent to previous XML file is:
Query = (AND
((Anomaly)
(AND (Concept
1
(SOME R
11
Concept
11
)…
(SOME R
1n
Concept
1n
) ))
…
(AND ( Concept
m
(SOME R
m1
Concept
m1
)…
(SOME R
mn
Concept
mn
)))
)
Query generated for the previous example is:
AND ((Anomaly)
(AND (Opacity,
(SOME hasForm ShapeRound)
(SOME hasDensity DensityMixe)))
(AND (MacroCalcification,
(SOME hasForm ShapeOval)))
)
This corresponds to:
Anomaly ∩ ( opacity ∩ (∃ hasForm ShapeRound) ∩
(∃ hasDensity DensityMixe)) ∩ (Macrocalcification
∩ (∃ hasForm ShapeOval)) (7)
From the Query, we ask Racer to classify it as a
new concept in our ontology then to determine super
class of this new concept. Racer will return the
number of ACR categories and attitude to follow in
treatment. Racer will deduce that :
(7) ⊆ Anomaly1 ⊆ ACR2.
4 RELATED AND FUTURE
WORKS
In (Ricky, 2001), authors use a simple lexicon about
thoracic radiology reports in lung
cancer patients’
domain. They use also natural language machine and
statistical techniques to classify their reports. There
haven’t notion of formal ontology in their
architecture and the aim was to structure radiological
report by looking to a simple lexicon manually
developed. However, our system is based on formal
ontology developed in OWL DL language and our
aim is to use this ontology in structuring radiological
reports and also in classification of them by using
subsumption reasoning. Advantages of our approach
are the use of a formal OWL ontology where we can
easily verify consistency and checking errors by
using Racer. Also all step of analysis of
mammogram report depends largely to the model
given by the ontology, and deduction of ACR
classes depends largely to our conceptual approach
to the ontology given by ACR classification.
We have also followed the same method used to
define Dialysis and Transplantation Ontology in
(Golbreich, 2004) in declaring necessary and
sufficient condition. But in our application we have
used these conditions in definition of ACR Classes
in the aim to resolve a problem, not only to define a
formal ontology.
Medlee systems (Nilesh, 1995) and Minelas
(Zweigenbaum, 1994) use conceptual graph
approach and techniques of natural language
hasForm
hasDensity
hasForm
Instance
of shape
Concept
Instance
of shape
Instance
of Density
Concept
DESCRIPTION LOGIC FOR AUTOMATIC CLASSIFICATION OF MAMMOGRAM REPORTS
197

processing in performing medical reports written in
free text. Our work is different in using standards of
semantic web like OWL DL and our aim is oriented
to give a real application of semantic web than to
process medical natural language. Here we don’t use
expert systems based on first order logic because we
want to give a real use of formal ontologies based
description logic in medical domain. Description
logic is a sub set of First Order logic where the
complexity of proof is inferior than in First
Logic(Tsarkov, 2003).
The current project has been under development.
Each of the five modules shown in Figure 6 is being
developed as a simple application in order to give
more attention to inferential analysis. All code has
been written
in the JAVA programming language.
All access to ACR ontology is done by Jena API and
we had used Racer as description reasoning system.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In the current Work, we have presented a system to
automatically classify mammogram report by using
a formal mammary radiological ontology developed
in OWL DL language which uses radiological signs
and an ACR normalized classification. Each ACR
Class is declared in our ontology by some necessary
and/or sufficient conditions which are used by Racer
to classify formal representation of mammogram
report in this ontology. Formal representation is
obtained after different analysis of mammogram
report written in free text and using some techniques
of natural language and subsumption reasoning. The
current project has been under development and we
are waiting to test it on many real mammogram
reports.
REFERENCES
ACR classification, 2002. ANAES : Service des
recommandations et références professionnelles.
http://www.has-
sante.fr/portail/upload/docs/application/pdf/ACR.pdf
Assessment Categories, 2003. BI-RADS®
MAMMOGRAPHY. Fourth Edition.
Baader, F. Calvanese, D., McGuinness, D., Nardi, D. et
Patel-Schneider, P., 2003. The Description Logic
Handbook : Theory, Implementation and Applications.
Cambridge University Press.
Boustil Amel, Sahnoun Z., Mansouri Z., Golbreich C.,
2006. Classification des compte-rendus
mammographiques à partir d'une ontologie
radiologique en OWL. Extraction et gestion de
Connaissances (EGC'2006), RNTI, Vol. 1:199-204,
Cepadues-Editions, ISBN 2.85428.677.4.
Golbreich C., Mercier S.. 2004. Construction of the
dialysis and transplantation ontology, advantages,
limits, and questions about Protégé OWL. 7th
International Protégé Conference, Bethesda.
Haarslev V. and Möller R., 2001. Description of the
RACER System and its Applications. In Proceedings
International Workshop on Description Logics (DL-
2001), Stanford, USA, 1.-3. August, pages 131–141.
Holger, K., 2004. The Protégé OWL Plugin. 7th
International Protégé Conference, Bethesda. 2004.
Holger, K., Olivier, D., Mark A, Musen, 2004. Weaving
the Biomedical Semantic Web with the Protégé OWL
Plugin. First International Workshop on Formal
Biomedical Knowledge Representation, Whistler,
Canada.
Nilesh L., Jain D.Sc, Carol Friedman, 1995. Identification
of Findings Suspicious for Breast Cancer Based on
Natural Language Processing of Mammogram
Reports. Proc AMIA Annu Fall Symp. 829-33.
OWL Web Ontology Language Reference, 2004. W3C
Recommendation 10 February. http://www.w3.org/
TR/owl-ref/
Ricky K., Taira, G. Stephen Soderland, and Rex M.
Jakobovits, 2001. Automatic Structuring of Radiology
Free-Text Reports, Radiographics, 21:237-245.
Tsarkov, D., Horrocks, I., 2003. DL reasoner vs. rst-order
prover. Proc. of the 2003 Description Logic Workshop
(DL 2003) volume. pp. 152159.
Zweigenbaum P., Consortium Menelas, 1994.
MENELAS: An Access System for Medical Records
Using Natural Language. Computer Methods and
Programs in Biomedicine, 45: 117-120.
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
198
