
ARCHETYPE ALIGNMENT
A Two-level Driven Semantic Matching Approach to
Interoperability in the Clinical Domain
Jesús Bisbal
Universitat Pompeu Fabra (CISTIB) and CIBER-BBN, Pg Circumvallacio 8, Barcelona 08003, Spain
Damon Berry
Dublin Institute of Technology, School of Electrical Systems Engineering, Kevin Street, Dublin 6, Ireland
Keywords: Electronic health records, Two-level modelling, Archetypes, Interoperability, Semantic interoperability,
Ontologies, Ontology alignment.
Abstract: Semantic interoperability between electronic health record systems and other information systems in the
health domain implies agreement about the structure and the meaning of the information that is
communicated. There are still a number of similar but different EHR system approaches. Some of the newer
approaches adopt the two-layer model approach where a generic reference model is constrained by
archetypes into valid clinical concepts which can be exchanged. The meaning of the concepts that are
represented by an archetype can be conveyed by embedding codes from a commonly recognised
terminology at appropriate points in the archetype. However, as the number of archetypes multiply it will
become necessary to match archetypes from different sources to facilitate interoperability.
This paper describes an approach that supports semantic interoperability between heterogeneous two-level
health information systems by identifying similarities between archetypes. The approach identifies
relationships between ontological terms which have been embedded in pairs of archetypes as a means of
matching these terms. The matched terms can then in turn be used to identify similarities between
archetypes. The limited contextual scope of an archetype simplifies this matching process.
1 INTRODUCTION
Safe interoperability of clinical information systems
(Grimson 2001; Dick 1997) requires that the
information being transferred includes all necessary
context so that it can be appropriately interpreted at
a site (e.g. hospital) that is different from where that
information was originally captured.
Misinterpretations may lead to fatal medical
decisions (Kohn 2000). This requirement has widely
been acknowledged in the medical domain (Grimson
2001). Also, in biomedical research (e.g. genomics),
for example, capturing the context of information
has also been clearly identified as an important
requirement (Goble 2008), but a generic
architectural solution has not emerged, as in the case
of clinical applications.
The traditional software engineering approach to
modelling any domain consists of creating a
(possibly very large) model which contains all the
information that is considered necessary for the
software application at hand. The necessary
information is identified by the user experts that take
part in the project. This approach has repeatedly
been followed in the medical domain, and it has
proved rather unsatisfactory (Garde 2007). The
medical domain is characterized by being (Martinez-
Costa 2008):
1. Large: e.g. a well known clinical taxonomy,
SNOMED-CT, contains over 350.000 atomic
concepts and 1.5 million relationships;
2. Complex: different views of information,
requirements, and granularity, all of which must
be represented in the model; and
3. Open-ended: advances in clinical research
constantly update clinical practice, which in
turn change the type of information that is
considered necessary for a given application.
216
Bisbal J. and Berry D. (2009).
ARCHETYPE ALIGNMENT - A Two-level Driven Semantic Matching Approach to Interoperability in the Clinical Domain.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Health Informatics, pages 216-221
DOI: 10.5220/0001541502160221
Copyright
c
SciTePress
Therefore, instances of a single-model approach
necessarily represent a narrow view of the domain
that needs to be represented, as understood by the
specific set of users that have been involved in the
requirements phase. If a different set of users is
involved, it is likely that a rather different set of
information items will be judged as necessary,
although it will be equally valid.
Currently, it is believed that the most promising
approach to model the clinical domain for
interoperability purposes consists of separating what
is Information, from what is domain Knowledge.
Accordingly, the clinical domain is modelled using
the so-called two-level modelling approach (Grimson
1998; Beale, 2002; Garde 2007). The first level,
referred to as the Reference Model, contains a very
reduced set of building blocks or classes of an object
model, which have a very abstract meaning (i.e.
Element, Item, Entry, Section, Composition, and
Folder). These building blocks are organised in a
hierarchical structure according to a set of generic
constraints. Due to the abstract meaning of these
classes, however, any clinical concept can be
modelled using only this limited set of classes. A
clinical concept (e.g. blood pressure, problem list)
that has been modelled by applying further clinical
constraints to these abstract classes represents the
second level of this architectural approach, the
Knowledge, and is referred to as Archetype.
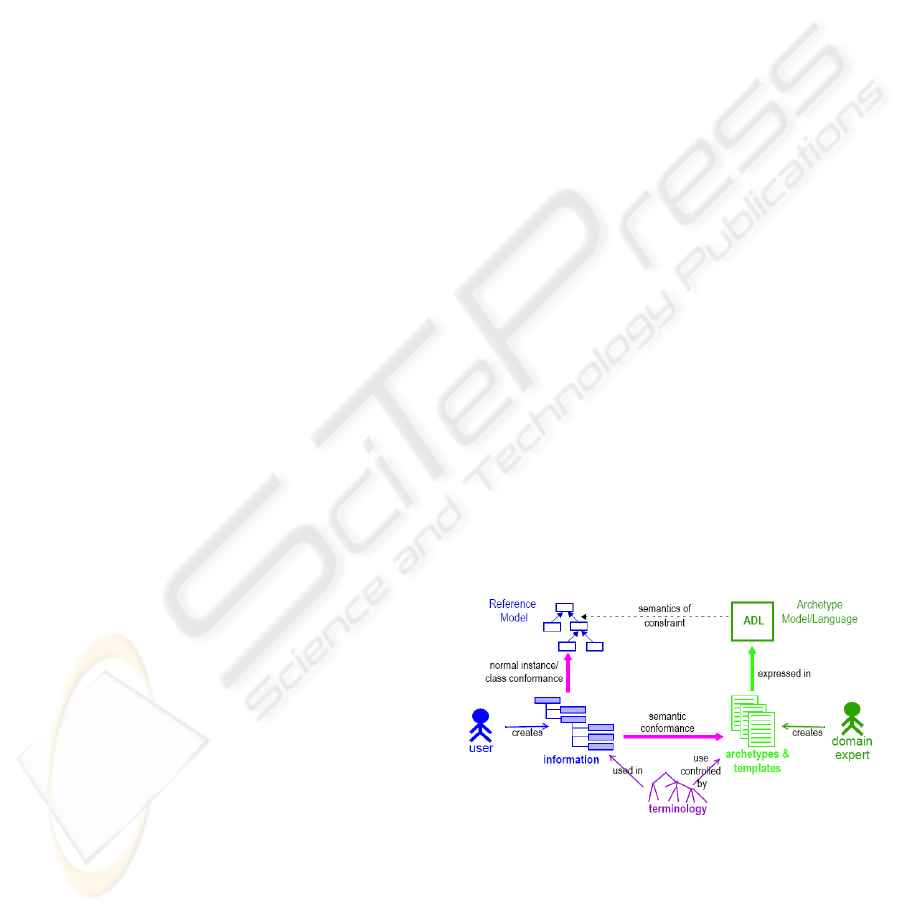
Archetypes are the basis on which interoperability is
performed in the two-level approach. Figure 1 shows
a representation of the actors involved in this
approach, as well as their relationships (Beale 2002).
It must be noted that the two-level modelling
approach is currently being adopted by the major
medical information standardization bodies: CEN
13606 (or EHRcom, http://www.centc251.org/), and
HL7 RIMv3
(http://www.hl7.org/). Additionally, the
OpenEHR
(http://www.openehr.org/) foundation
provides another specification and open source
implementation of this approach. Although attempts
have been made, there is still further work to
harmonise the reference models and archetype
models used by these efforts.
Therefore, for the time being, in order to achieve
semantic interoperability of clinical applications, the
two-level modelling approach does not suffice. At
the very least, a mapping between the different (de
jure or de facto) standards is needed (Dogac 2005;
Martinez-Costa 2008; Iakovidis 2007). However, it
is also quite likely that more sophisticated mappings
between archetypes will also be required. As
described above, archetypes are the unit of
communication between interoperating applications,
as they define the minimum context that must be
considered for safe communication. Thus archetypes
must be agreed upon before communication. It does
not seem feasible, however, to expect that all
professionals of all disciplines will agree on exactly
all details of the archetypes associated to the data
they would like to exchange. If this approach
becomes widely accepted, it is certain that the
number of available archetypes will become very
large (at the time of writing there are aproximately
700 archetypes in OpenEHR). Although archetypes
are annotated with terms from standardised
ontologies (terminologies, taxonomies, etc), there
will still exist differences both at the archetype level,
as well as at the terminology level. Local variations
at the archetype level will stem from specialization
of archetypes for specific purposes and research
projects, and due to competing standards. Also, there
are several widely used terminologies that could be
used to annotate archetypes (e.g. SNOMED-CT,
MeSH, NCI, FMA). Local ontologies are also used
to annotate archetypes. Therefore, a sound and
general process for matching archetypes is essential.
This paper describes a novel approach to address
semantic interoperability in the healthcare domain.
Archetypes are used to scope the context of the
matching process that will allow two independent
healthcare providers to interoperate. It structures the
matching algorithms at two different levels, the
terminology level and the archetype level,
leveraging the most mature research on ontology
matching. The context of archetype will limit the
matching space, to allow for more accurate mapping
results and, due to the nature of archetypes,
ultimately to very high level of automation.
Figure 1: Two-level modelling approach (Beale 2002).
2 RELATED WORK
The two-level modelling paradigm was originally
proposed by the EU-funded project Synapses
(Grimson 1998). Since then, it has evolved (Beale
ARCHETYPE ALIGNMENT - A Two-level Driven Semantic Matching Approach to Interoperability in the Clinical
Domain
217

2002) incorporating additional constraints. This
evolution has not produced a unified approach, but
there are three major players. ISO 13606 and HL7´s
CDA RIMv3 are EU and USA standards. OpenEHR
is promoted by a commercial company
(http://oceaninformatics.biz), and is having a
significant impact. Some research projects aim at
facilitating the interoperability between these
approaches (Iakovidis 2007).
The Artemis project developed a framework to
map archetypes between different standards (Dogac
2005). It defined a syntactic transformation of
(ADL-defined) archetypes into OWL format. The
project developed a tool called OWLmt that was
used to manually define the mappings between the
archetypes, and then automatically map data
instances conforming to the source archetype into
instances conforming to the target archetypes. The
present paper aims at avoiding this manual mapping.
The Poseacle project (Martinez-Costa, 2008) is
taking a software engineering approach for the
semantic transformation of ADL archetypes into
OWL. The final goal is the transformation of one
archetype expressed in one standard into the same
archetype expressed into a different standard. In
contrast, the work presented here aims at aligning
two archetypes (expressed in same or different
standards) that may define similar but not
necessarily the same concepts.
An ontology is the explicit conceptualization of a
domain agreed upon by a community of users
(Martinez-Costa 2008). Due to the large number of
ontologies currently available for many domains and
applications, there is a need to match different
ontologies (i.e. to find equivalences) or to align
them (when the domains only partially overlap). A
large body of research exists on ontology matching
and ontology alignment approaches (Tan 2007).
There are two main categories of ontologies (Garde
2007). ‘Ontologies of reality’ describe real
phenomena, while ‘ontologies of information’
contain the information models of the content to be
stored or communicated. A collection of Archetypes
is an information ontology. The ultimate goal of the
research presented here is to adapt and extend
existing ontology alignment techniques to the
particular case of archetypes, in order to achieve
better quality results and more automation in
semantic interoperability.
3 SYSTEM ARCHITECTURE
As archetypes are the artefacts around which
interoperability is built, there is a need to
automatically map between archetype definitions.
The architecture of the system being implemented to
achieve this goal is shown in Figure 2. The
architecture is clearly separated in two levels.
Archetypes (e.g. blood cholesterol) are used to guide
the alignment process and are used at both levels.
As described in the previous section, the
concepts defined in archetypes using classes from
the reference models are normally annotated using
terms from standard terminologies (e.g. MeSH).
These terminologies must be harmonized before
archetypes can be aligned. However, the alignment
of such ontologies is a significant task by itself.
Thus, a semantic interoperability approach based on
manipulating large terminologies (ontologies) would
suffer scalability (and quality) problems. It should
be noted, however, that archetypes provide a better
context for alignments than general. It is easier to
create mappings if the ontologies to map are smaller
and scoped to the application (Noy 2004). For this
reason, at the upper half of Figure 2, the references
to standard terminologies included in the archetypes
(their ‘annotations’) are extracted.
These references are used to query the standard
terminologies and consistently extract related
concepts (Noy 2004; Jiménez-Ruiz 2007). The
resulting subontologies should be of a reasonable
size, since an archetype must have a limited scope.
Therefore, existing alignment techniques can be
applied to these subontologies (Tan 2007). The
result of this step is a set of alignments between a
few concepts of these standard terminologies. In
some cases there already exists a metathesaurus (e.g.
UMLS) which defines equivalences between terms.
However, in general, especially in research
environments, this will not be the case.
Ont ology
Ali gnment
Ont ology
Ali gnment
(ge ne ric )
( archetyped)
Chol est erol
Archetype
( e.g. C EN 13606)
C holester ol
Ar c h e type
(e. g. OpenEH R)
(r eference models)
Alignments
Histor y
Archetyp es
Re p o s i tory
Archet ypes
R e pos itory
(context / anchors)
Of f -the-shelf tool (e.g .
P r om pt , FOAM)
Aligner–RM wi th
Anc ho r
Ontol ogi es
(Local, M e S H , .. .)
Ontology Interface
(e. g. P rot égé)
Ontologi es
(Local, NCI, ...)
Ont ol ogy Int er face
(e.g. P rotégé)
X
A
B
C1
C2
C3
Extractio n of frames
relevan t to terms used
i n archet yp es
C1’
C2’
C3’
X’
B
A’
Align small p arts o f large o ntologies:
C1 – C1’ (99 %)
C2 – C2’ (95 %)
C3 – C3’ (91 %)
(anchors ) (anchors )
Figure 2: System architecture.
Once this initial step has been performed, the
aligned terms (concepts) are used as anchors (Noy
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
218

2001) to the next alignment module, at the lower
half of Figure 2. Anchors are pairs of already
aligned concepts, and are used to tune the similarity
measures of neighbouring concepts, ultimately
providing better quality alignments. This module
will match the remaining parts of the archetypes and
could be implemented using simply existing
ontology alignment algorithms. However, such an
approach would ignore the additional knowledge
provided by the reference models upon which
archetypes are built. Thus, the objective is to modify
the way alignment algorithms work so that they take
into account the specific characteristics of the
reference models (see Section 4). Once this is done,
this new module (termed in the figure Aligner-RM
with Anchors), would map the archetypes. Such a
mapping approach would fall into what is currently
referred to as Semantic Matching (Giunchiglia
2007). To the best of the authors’ knowledge, this
approach has not been yet investigated in the context
of archetypes, using the specific semantics of their
underlying reference models and hierarchical
structure (tree) of archetype definitions.
The last component of the architecture shown
in Figure 2 refers to the history of alignments
between archetypes successfully performed in the
past. Many existing tools store previous alignments
so that they may be reused in future alignment tasks
(Tan 2007). However, this is always done in a local
and proprietary way. The very nature of archetypes
implies that they must (to a large extend) be agreed
upon by a community. Also, the number of different
archetypes that two different healthcare providers
will be interested in exchanging (aligning) will also
be limited. Finally, there are currently only three
competing archetype models. Considering all these
characteristics, it will be very likely that the same or
very similar alignment tasks are repeatedly
performed by the communities using the two-level
approach. Therefore, the history of previous
alignments is expected to play a very central role in
an archetype-oriented alignment architecture. Given
the limited scope of archetypes and the limited
number of possible alignments, in the long run this
history of alignments should increase the level of
automation that could be achieved.
4 IMPLEMENTATION
The architecture described in the previous section is
currently under development. It has been designed
so that most of its components can be built using
existing open source code publicly available from
recent and current research projects. This approach
reduces the overall development time and increases
the quality of the resulting software, as its
components are updated by the advances of these
research projects.
All ontological components (terminologies and
archetypes) are used in their OWL format. Although
OWL is not yet the only language to describe
ontologies, it is becoming widely accepted. That
being said, existing terminologies, taxonomies and
ontologies have been written in many different
languages. For example, MeSH and NCI have their
own proprietary formalisms (now commonly
expressed also in XML). Biological ontologies are
commonly expressed in OBO. Finally, archetypes
have traditionally been expressed with ADL
(archetype definition language).
However, the current trend is towards expressing
all ontologies in OWL and, without loss of
generality, this is the assumption taken for this
architecture. Particularly, NCI is already available in
OWL format (NCI, 2008), and MeSH can readily be
transformed into OWL (Assem 2004). Finally,
recent developments (Martinez-Costa 2008) argue
for archetypes to be expressed in OWL, and some
example archetypes exist that have already been
semantically mapped into OWL. All of these
contributions are being incorporated into the
implementation of the architecture presented here.
Standard terminologies are too large to be
managed in a single file. Thus the implementation
reported here is storing and manipulating them in an
OWL database, using Protégé (protege.stanford.edu)
ontology management system.
The extraction of subontologies from these
standard terminologies is being implemented using
two of Protégé plug-ins that have this specific
purpose, namely Prompt (Noy 2004) and OntoPath
(Jiménez-Ruiz 2007).
The ontology alignment module shown at the
upper half of Figure 2 is generic; it does not add any
benefits to specialize its behaviour to the
characteristics of the two-level model. Its goal is
simply to align the (small) subontologies extracted
from large standard terminologies. Several possible
open source modules can be reused here. In
particular FOAM (Ehrig 2005) is being used for the
current implementation.
The most innovative contributions of the
architecture being implemented are, on the one hand,
the use of two levels of alignments and, on the other,
the actual mapping of archetypes (module at the
lower half Figure 2. The development of this module
is the only significant implementation effort needed
ARCHETYPE ALIGNMENT - A Two-level Driven Semantic Matching Approach to Interoperability in the Clinical
Domain
219

in order to fully realize and evaluate the architecture
advocated in this paper. Its implementation will
modify existing open source alignment algorithms
(particularly, FOAM). Much research will be needed
in order to fully exploit the specific characteristics of
archetypes and reference models in the
implementation of this module. The current
considerations that are being taken into account,
thanks to the existence of an underlying reference
model, include:
1. Elements of archetypes define value ranges that
the conforming data must satisfy. If these do not
match in both archetypes (intersect, include), it
is possible that the two archetypes may not be
aligned.
2. Archetypes can also express the units in which
measurements are taken. If units are different in
both archetypes, interoperation is jeopardized.
3. The reference models include the concept of
‘certainty’. If terms in archetypes do not satisfy
certainty thresholds, automated interoperation
may not be possible.
4. The building classes of the reference models in
all (three) competing standards of the two-level
modeling approach have abstract semantics.
Although the names of the classes are not
shared between these standards, their semantics
are quite similar. If alignments are to be
performed between archetypes of different
standards, aligning algorithms based on string
similarity measures will fail in this case, as class
names can be very disparate. Dictionary-based
approaches will not be of much help either, as
all names are quite abstract. Model Management
research (Atzeni 2008), see section 5, should be
used to address this issue.
5. Archetypes define a hierarchical organization of
classes from the reference model. The particular
location of a given element of an archetype
inside this hierarchy defines its context and
restrains its extract meaning. Semantic matching
research (Giunchiglia 2007) is being inspired by
the same observations, and it will be specialized
for the case of archetypes.
The evaluation of the current implementation of
the architecture described in Section 3 must show
the benefits of the two-level approach to alignment.
It must compare the performance and quality of
algorithms that do not include knowledge of
reference models. FOAM is being used as the
baseline for comparison purposes. In the evaluation,
archetypes expressed in OWL format (particularly,
cholesterol archetypes are used for the time being,
taken from (klt.inf.um.es/~poseacle/ontologies.html)
have been introduced as input to FOAM. This tool
output a set of alignments (510, if threshold 90%),
both with concepts extracted from the archetypes as
well as from the underlying reference models.
Similarity measures in FOAM do not take into
account the semantics of the abstract classes that
build up the reference models or the constraints
enforced when defining archetypes, like for example
those outlined above.
5 FUTURE WORK
This paper has presented an architecture to facilitate
the interoperability between clinical information
systems that use the so-called two-level modelling.
Archetypes in this modelling paradigm are seen as
the centre of the interoperation process. By
automatically identifying appropriate mappings
between archetypes, semantic interoperability is
greatly facilitated.
This architecture leverages and specializes
results from on-going research projects on ontology
alignment and management, and using the open-
source software these produce.
Future research will be mainly focused on two
areas: (sub)ontology extraction, and archetype-aware
alignment algorithms. Subontology extraction can be
compared to defining a view from a database.
However, due to the richer semantics defined by an
ontology, it must be decided how such a view is
extracted, so that the resulting ontology can be
considered consistent. Existing approaches (Noy
2004; Jiménez-Ruiz 2007) are based on the
definition of the path traversals which identify the
nodes are to be extracted. For archetypes, the nodes
to be extracted are those terms used in order to
annotate the concepts of an archetype.
Regarding archetype-aware alignments, Section
4 has illustrated a few examples of how this will be
implemented. The reference model provides a very
specific source of domain knowledge used to align
archetypes. Particularly, when aligning archetypes
which were built according to different reference
models, there is also a need to map between these
reference models, in addition to between the
archetypes. It should be noted that reference models
are considered by the communities of users as being
reasonably stable. Also, they are not unmanageably
large (by design). Therefore, the best approach to
map between reference models is to leverage on a
databases research field called model management
(Atzeni 2008). In model management, when two
models need to be mapped to each other (e.g. from
HEALTHINF 2009 - International Conference on Health Informatics
220

relational to object-oriented), the constructs (e.g.
table, class) of each model are mapped onto the set
of constructs of a more abstract model, the
supermodel. A set of transformations is applied,
within the supermodel, to the set of constructs that
originated from the source model, in order to
transform them into constructs that can be mapped
into the target model. At the end, the resulting
constructs are mapped from the supermodel back
into those of the target model. Such an approach is
highly flexible as of the set of models and constructs
that it can handle. Changes in the models do not
require changes in the applications that perform
those mappings. Such an approach has not been
applied to map between reference models.
(Martínez-Costa 2008) followed similar ideas but
using software engineering principles instead of
using database techniques.
Finally, as outlined in Section 3, the results
history of previous alignment tasks should also be
used to improve the quality and the automation of
future alignments. Given the current trend (Chung
2007) towards cooperation between communities of
users with similar interests, and given the
community-orientated nature of archetypes, it is
clear that the alignment history between archetypes
should be a resource of such a community. It will be
investigated how alignments between archetypes
developed and used on several sites could be shared
and reused by other sites. These alignments
represent the understanding of all these archetypes
(ontologies), and their equivalences, from the point
of view of the different researchers involved in each
of these mappings. This cumulative knowledge will
be useful when new alignments are to be performed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This research has jointly been funded by the Ramon
y Cajal and the Jose Castillejo (JC2007-00050)
programmes of the Spanish Ministry for Science and
Innovation, and the EHRland project funded by Irish
Health Information and Quality Authority.
REFERENCES
M. van Assem, M. R. Menken, G. et al. ‘A Method for
Converting Thesauri to RDF/OWL’, The Semantic
Web 2004, LNCS 3298, pages 17-31.
P. Atzeni, P. Cappellari, et al. ‘Model-independent schema
translation’, VLDB Journal 17:1347-1370, Nov. 2008.
T. Beale. ‘Archetypes: Constraint-based domain models
for future-proof information systems’, 11
th
OOPSLA
Workshop Behavioral Semantics, pp. 16-32, 2002.
V. Bicer, A. Dogac, et al. ‘Archetype-Based Semantic
Interoperability of Web Service Messages in the
Health Care Domain’, Journal Semantic Web 1, 2005.
K. Chung, L. Hossain, and J. Davis. ‘Individual
performance in knowledge intensive work through
social networks’, 2007 ACM SIGMIS CPR conference
on Computer personnel research, pp 159 – 167.
R.S. Dick, et al., (Eds). ‘The Computer-Based Patient
Record: An Essential Technology for Health Care’,
Institute of Medicine, Revised Edition, 1997.
M. Ehrig, and Y. Sure. ‘FOAM - Framework for Ontology
Alignment and Mapping’, in the Workshop on
Integrating Ontologies, 156, pp. 72-76, October 2005.
S. Garde, E. Hovenga, et al. ‘Expressing Clinical Data
Sets with openEHR Archetypes: A Solid Basis for
Ubiquitous Computing’, International Journal of
Medical Informatics. 76(3): 334-341, 2007.
C. Goble, and R. Stevens. ‘State of the nation in data
integration for bioinformatics’, Journal of Biomedical
Informatics, 41(5):687-693, October 2008.
J. Grimson. ‘Delivering the electronic healthcare record
for the 21st century’. Int. J. Med. Inf. 2001; 111-127.
J. Grimson, W. Grimson, et al. ‘A CORBA-based
integration of distributed electronic healthcare records
using the Synapses approach’. IEEE Trans. Inf. Tech.
in Biomedicine, 2(3):124-138, 1998.
F. Giunchiglia, M. Yatskevich, and P. Shvaiko. ‘Semantic
Matching: Algorithms and Implementation’, Journal
on Data Semantics, LNCS 4601, pages 1-38, 2007.
I. Iakovidis, A. Dogac, et al. ‘Interoperability of eHealth
Systems - Selection of Recent EU's Research
Programme Developments’, Proc. Int. Conf. eHealth:
Combining Health Telematics, Telemedicine,
Biomedical Eng. and Bioinformat. to the Edge, 2007.
E. Jiménez-Ruiz, et al. ‘OntoPath: A Language for
Retrieving Ontology Fragments’, LNCS 4803, pp 897-
914, 2007.
L.T. Kohn,et al. (Ed.). ‘To err is human: Building a safer
health system’, National Academic Press, 2000
C. Martínez-Costa, et al. ‘A Model-driven Approach for
Representing Clinical Archetypes for Semantic Web
Environments’. Journal Biomedical Informatics 2008.
NCI Thesaurus, accessed July 2008 at
http://ncicb.nci.nih.gov/download/evsportal.jsp
N.F. Noy, and M.A. Musen. ‘Anchor-PROMPT: Using
non-local context for semantic matching’, in the
workshop on Ontologies and Information Sharing at
the International Joint Conference on Artificial
Intelligence, pp 63-70, 2001.
N.F. Noy, and M.A. Musen. ‘Specifying Ontology Views
by Traversal’, the Semantic Web Conference – ISWC
2004, LNCS 3298, pp 713-725.
H.Tan and P. Lambrix, ‘A method for Recommending
Ontology Alignment Strategies’, the Semantic Web
Conference. LNCS 4825, pages 494-507, 2007.
ARCHETYPE ALIGNMENT - A Two-level Driven Semantic Matching Approach to Interoperability in the Clinical
Domain
221
