
EFFECT OF SURFACE ELECTRODE ORIENTATION ON
INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR FEATURE
EXTRACTION OF SURFACE MOTOR UNIT ACTION
POTENTIAL
Jun Akazawa
1
, Takaharu Ikeuchi
1
, Takemasa Okamoto
1
, Ryuhei Okuno
2
Masaki Yoshida
3
, Tetsuo Sato
4
and Kotaro Minato
4
1
School of Health Sciences and Medical Care, Meiji University of Integrative Medicine
Honoda, Hiyoshi-cho, Nantan-shi,6290392 Kyoto, Japan
2
Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Setsunan University
17-8 Ikedanaka-machi, Neyagawa-shi, 5728508 Osaka, Japan
3
Department of Biomedical Engineering, Osaka Electro-Communication University
1130-70 Kiyotaki, Shijonawate-shi. 5750063 Osaka, Japan
4
Graduate School of Information Science, Nara Institute of Science and Technology
8916-5 Takayama, Ikom-shi, 6300192 Nara, Japan
Keywords: Electromyogram, Motor Unit, Model, Independent Component Analysis.
Abstract: Recently, application of Independent Component Analysis (ICA) has been reported for effective decomposi-
tion of surface electromyogram (SEMG) signals into a train of surface motor unit action potentials
(SMUAPs) of a single motor unit (MU). Results of ICA were not always sufficient as the feature extraction
of SMUAP at first dorsal interosseous muscle (FDI). The purpose of this study is to propose an effective
method for feature extraction of SMUAP by simulation study of focusing on the effects of electrode orienta-
tion. SEMG signals were created with the model and application of ICA was applied to the signals. The
present study showed that the useful and actual method of ICA application was to repeat measurement of
SEMG signals with varying the electrode orientation, and then to select the better signals for the feature ex-
traction by executing ICA algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
In the field of sports science and rehabilitation, elec-
tromyogram (EMG) observed with the surface elec-
trode, rather than the invasive needle electrode, is
often used to investigate behaviors of the motor
units (MUs). Then the surface EMG (SEMG) could
be decomposed into a train of surface motor unit
action potential (SMUAP) of a single motor unit.
Subsequently, such factors as waveform of the
SMUAP, firing rates, recruitment, de-recruitment,
territory of the MUs could be examined.
Recently a few researches have been reported: Xu,
Xiao, and Chi (Xu et al., 2001) were proposed the
method using the artificial neural network. Bonato,
Erim, and Gonzalez-Cueto (Bonato et al., 2001)
were proposed the method using the method in the
area of time frequency. Recently, Independent Com-
ponent Analysis (ICA) (Bonato et al., 2001) algo-
rithm has been applied to the decomposition method
for large muscles such as biceps brachii muscle by
Maekawa, Arimoto, Kotani, and Fujiwara (Maekawa
et al., 2002), Nakamura, Yoshida, Kotani, Akazawa,
and Moritani (Nakamura et al., 2004), and Gonzalo,
Okuno, and Akazawa (Gonzalo et al., 2005). While
we applied to first dorsal interosseous muscle (FDI),
results of ICA were not always sufficient as the
feature extraction of SMUAP. It was difficult to
separate SMUAPs because several types of
SMUAPs appeared in the single ICA component.
421
Akazawa J., Ikeuchi T., Okamoto T., Okuno R., Yoshida M., Sato T. and Minato K. (2009).
EFFECT OF SURFACE ELECTRODE ORIENTATION ON INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR FEATURE EXTRACTION OF SURFACE
MOTOR UNIT ACTION POTENTIAL.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing, pages 421-425
DOI: 10.5220/0001777704210425
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The purpose of this study is to propose an effec-
tive method for feature extraction of SMUAP by
simulation study of focusing on the effects of elec-
trode orientation.
2 METHOD
2.1 Experimental Set-up
The subject put his hand on the desk horizontally
where the thumb and the fingers were loosely fixed
except the index finger. The isometric adductor
torque of the index finger was measured with strain
gauge. SEMG signals were obtained with eight-
channel bipolar surface electrodes array shown in
Fig. 1. The electrode was placed over the FDI. Each
electrode was stainless wire of 1 mm diameter, a
pair of electrodes was placed with inter-electrode
spacing of 2.54 mm and each pair was placed in
parallel with spacing 2.54 mm. The SEMG signal
was amplified with the gain 60 -80 dB and the cut
off frequency 800 Hz.
The subject was instructed to keep the constant
force of 5% maximal voluntary contraction (MVC)
by watching the force output displayed with bright
lines on the oscilloscope. Both the isometric force
and the eight-channel SEMGs were A/D converted
at the 10 kHz sampling frequency. Informed consent
was given to each subject.
Figure 1: Eight-channel bipolar surface electrodes.
2.2 SEMG Model
Spatial information such as MU territory, muscle
fiber and electrode, is shown in Fig. 2 (a). In the
present study, Griep’s tripole model (Griep et al.,
1982) was used to calculate the action potential
generated on the skin surface by the excitation of a
single muscle fiber.
As shown in Fig. 2, the axis x is defined to be
perpendicular to the skin surface, the axis z is the
moving direction of excitation of the muscle fiber
and the axis y is direction orthogonal to x and z. The
distance between the electrode and the axis of mus-
cle fiber is x
n
in the x-axis, and y
n
in the y-axis. The
distance between the electrode and each point cur-
rent source is z
ni
(i = 1, MU, 3) in the z-axis at t = 0
(the time beginning of excitation of the muscle fiber)
and z
ni
+ v t at the time t, where v is the conduction
velocity of excitation. The action potential of a sin-
gle muscle fiber monitored at the electrode is given
as
∑
=
+++
=Φ
3
1
2
22
)(
2
1
),,,(
i
ninn
i
M
ninn
vtzyx
I
tzyx
πσ
(1)
where
M
σ
is conductivity of the volume conduc-
tor and I
i
the strength of the point current source.
Assume that individual muscle fibers within the
MU are all identical in their characteristics and dif-
ferent in their locations and the number of muscle
fibers is N, the potential at the electrode is given by
∑
=
Φ=Φ
N
n
ninnnMU
tzyxx
1
),,,()(
(2)
Figure 2: Illustration for the SEMG generation model.
(a) Spatial relation between the electrode and the muscle
fiber; (b) Electrode angle θ.
3 RESULTS
3.1 Simulation
<Parameters for tripole model> As to the tripole
model, following parameters were used; conduc-
tivity of the volume conductor was
M
σ
=
0.16
)(
11 −−
Ω m
(Disselhorst-klug et al., 1998), point
current was I
1
)(4.0 A
μ
=
, I
2
)(5.0 A
μ
−=
, and
I
3
)(1.0 A
μ
=
(Griep et al., 1982). The distance be-
tween I
1
and I
2
was 0.45 mm, and that between I
2
and I
3
was 1.8 mm (Griep et al., 1982). The conduc-
tion velocity v was 3.5 (m/s) (Disselhorst-klug et al.,
1998).
<Location of MU> Because we estimated that
territories of single MU of FDI were mostly square-
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
422
type (Akazawa et al., 2005), squared territory model
is used here. As shown in Fig. 2 (a), W is the width,
T is the thickness, xmuc is the distance from skin
surface to the top of the MU, and ymuc is the center
of the MU. For the simplicity only two groups of
MU were used; the number of small-sized group was
hundred and that of large-sized group was ten. Dis-
tribution of the size was Gaussian. Mean values of
W and T were 10 mm, and 10 mm respectively for
the large-sized MU, and 1 mm and 1 mm for the
small-sized MU. The thickness of skin surface/fat
tissues was assumed to be 2.0 mm and the width of
FDI was 2.0 cm.
<Firing Rates> The firing rates of MUs in isome-
tric contraction were examined statistically by Cla-
mann (Clamann, 1969). His finding that the distribu-
tion was Gaussian was applied to the present model.
Because the isometric contraction to be studied in
the present study was approximately 5% MVC, the
mean firing rate was assumed to be 7 Hz for all the
MUs. It was showed that at the low force level of
isometric contraction, firing of individual MUs is
statistically independent (Kanosue et al., 1979). This
results was applied to the present model concerning
to the firing time of MUs.
<Electrode > The position of each electrode is
fixed with the actually used electrode in Fig. 1. Si-
mulation was executed with changing the electrode
angle θ up to 40 degree. Orientation of only the one
large-sized MU was changed from zero to certain
value for understanding clearly the effect of elec-
trode angle, while electrode angle of other MUs is
zero.
<Effects of Electrode Orientation on ICA > Ef-
fects of changing the electrode angle were examined
by simulation study; firstly eight-channel SEMG of
1 (s) duration were created by the model of SEMG
generation, and then ICA was applied to the SEMG.
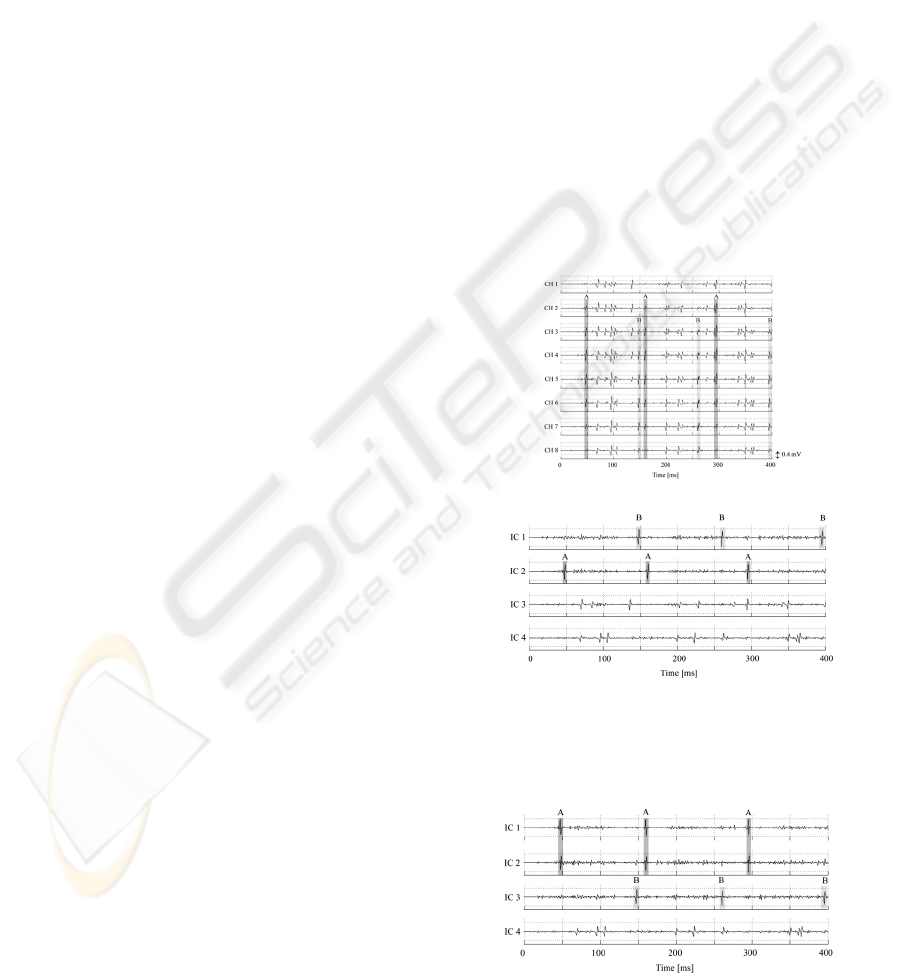
Eight channel SEMG of the model with the elec-
trode angle of 0 degree is shown in Fig. 3 (a). The
output signals which are obtained by applying the
ICA algorithm to the SEMG signals in Fig. 3 (a) are
shown in Fig. 3 (b).
Clear signals (SMUAP-like signals) with almost
the same waveform are apparently found on the first
component IC 1, while very small amplitudes of
signals are found in IC 1 component. Judging from
the time of appearance, these SMUAP-like signals in
IC 1 correspond to the SMUAP marked with B in
Fig. 3 (a); MU corresponds to this SMUAP is re-
ferred to as MU (B). Furthermore, no SMUAP-like
signals are found at the same time in other compo-
nents IC 2, IC 3, and IC 4. These results mean that
feature of MU (B) is extracted by ICA explicitly.
Similarly the same type of SMUAP-like signals are
also found in IC 2 in Fig. 3 (b), which correspond to
MU (A) in Fig. 3 (a).
The effect of electrode angle was examined. Fig.
4 shows thus obtained component of ICA. SMUAP-
like signals are found at the same time in IC 1 and
IC 2. The angle between the electrode and the MU is
10 degree. On the other hand, clear SMUAP-like
signal is found in IC 3, which corresponds to the
MU of the electrode angle of 0 degree. When the
electrode angle changes to 30 degrees, SMUAP-like
signals appear in all the ICA components from IC 1
to IC 8. This result implies that SMUAP amplitude
of the MU (A) in SEMG signal is so large that the
SMUAP-like signal appears in two or more compo-
nents of ICA. Executing these simulations, we found
that as the electrode angle increased, the number of
components in which SMUAP-like signals of the
same MU appeared was increased, and the number
of MUs the SMUAP-like signal of which appeared
in one component was also increased.
(a)
(b)
Figure 3: SEMG and ICA. (a) SEMG signals. (b) The
output signals obtained by applying ICA algorithm to
SEMG signals.
Figure 4: Results of ICA with electrode angle of 10 degree.
EFFECT OF SURFACE ELECTRODE ORIENTATION ON INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR
FEATURE EXTRACTION OF SURFACE MOTOR UNIT ACTION POTENTIAL
423

3.2 Result with Consideration of
Electrode Orientation
Apart from insufficient, we tried to obtain better
results with repeating measurement three times with
changing the electrode orientation. Isometric con-
traction was at 5% MVC and the duration 15 (s).
The result of ICA is shown in Fig. 5 (a) and the
corresponding measured SEMG in Fig. 5 (b). In IC
1, SMUAP-like signals marked with × could be
found clearly; briefly the corresponding MU is
called MU 2. The larger amplitude signal marked
with open circle ○ was also found in IC 1; the cor-
responding MU is called MU 1. In IC 3, a large
amplitude SMUAP-like signal marked by ● was
found. This MU might correspond to MU 1 because
of appearance at the same time in both IC 1 and IC 3.
Consequently the feature extraction of MU 2 was
effectively sufficient in IC 1, and small amplitude
signal corresponding to MU 3 was found in IC 2 as
shown with triangle △. Focusing attention on IC 1
and IC 3, MUs marked by ● and ○ are the same
MU 1. This conclusion could be supported by com-
paring the SEMG signal in Fig. 5 (b) with ICA in
Fig. 5 (a). SMUAPs of MU 1 are clearly seen from
CH 1 to CH 6 in Fig. (b) and those of MU 2 from
CH 3 to CH 5. It should be noted that both SMUAPs
of MU 1 and MU 2 in CH 5 are very similar in the
shape, which means that decomposition of SMUAP
is difficult in judging from only the SEMG signal.
4 CONCLUSIONS
In this study, effects of electrode orientation on the
result of ICA was analyzed with simulation study
and actual voluntary isometric contraction of FDI.
Obtained results were as follows. When the long
axis of the eight-channel electrode was perpendicu-
lar to the long axis of muscle fiber, the result of ICA
was best in terms of the feature extraction of
SMUAP; large amplitude of SMUAP-like signals of
the single MUs appeared in one component of ICA.
As the orientation of the electrode changed apart
from this direction, unexpected results of ICA were
obtained; i.e., large amplitude of SMUAP-like sig-
nals of the single MUs appeared almost at the same
time in other components of ICA, and SMUAP-like
signals of different MUs appeared in one component.
Figure 5: Result of ICA (a) and measured SEMG (b) at
5% MVC of isometric contraction.
REFERENCES
Xu, Z., Xiao, S., and Chi, Z.: ART2 neural network for
surface EMG decomposition, Neural Computing &
Applications, vol. 10(1), (2001) 29-38.
Bonato, P., Erim, Z., and Gonzalez-Cueto, J.: Decomposi-
tion of superimposed waveforms using the cross time
frequency transform, Proc. 23rd Ann. Int. Conf. IEEE
EMBS, Istanbul, (2001).
Hyvarinen, A., Karhunen, J., and Oja, E.: Independent
component analysis, Hoboken: John Wiley and Sons,
The publishing company. London, 2
nd
edition, (2001).
Maekawa, S., Arimoto, T., Kotani, M., and Fujiwara, Y.:
Motor unit decomposition of surface EMG using mul-
tichannel blind deconvolution, Proc. XIVth Congress
of ISEK, Vienna, (2002) 38-39.
Nakamura, H., Yoshida, M., Kotani, M., Akazawa, K., and
Moritani, T.: The application of independent compo-
nent analysis to the multi-channel surface electromyo-
graphic signals for separation of motor unit action po-
tential trains: part I-measuring techniques, J Electro-
myogr Kinesiol., vol. 14, (2004) 423-432.
Gonzalo, A., Okuno, R., and Akazawa, K.: A decomposi-
tion algorithm for surface electrode-array electromyo-
grams, IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology
Magazine, vol. 24(4), (2005) 63-72.
Griep, P., Gielen, F., Boom, H., Boon, K., Hoogstraten, L.,
Pool, C., and Wallinga-De-Jonge, W.: Calculation and
registration of the same motor unit action potential”,
EEG and Clinical Neurophysiol., vol. 53, (1982) 388-
404.
Disselhorst-klug, C., Silny, J., and Rau, G.: Estimation of
the relationship between the noninvasively detected
activity of single motor units and their characteristic
pathological changes by modeling, J Electromyogr
Kinesiol., vol. 8, (1998) 323-335.
Akazawa, J., Sato, T., Minato, K., and Yoshida, M.: Me-
thod of estimating location and territory of motor units
in human first dorsal interosseous muscle with multi-
channel surface electromyograms, JSMBE, vol. 43(4),
(2005) 595-604. (in Japanese)
BIOSIGNALS 2009 - International Conference on Bio-inspired Systems and Signal Processing
424

Clamann, HP.: Statistical Analysis of Motor Unit Firing
Patterns in a Human Skeletal Muscle, Biophys J., vol.
9(10), (1969) 1233–1251.
Kanosue, K., Yoshida, M., Akazawa K, and Fujii, K.: The
number of active. motor units and their firing rates in
voluntary contraction of human brachialis muscle, Jpn.
J. Physiol., vol. 29, (1979) 427-443.
EFFECT OF SURFACE ELECTRODE ORIENTATION ON INDEPENDENT COMPONENT ANALYSIS FOR
FEATURE EXTRACTION OF SURFACE MOTOR UNIT ACTION POTENTIAL
425
