
FEATURE-BASED ANNEALING PARTICLE FILTER FOR ROBUST
BODY POSE ESTIMATION
Adolfo L
´
opez and Josep R. Casas
Image Processing Group, Technical University of Catalonia, Barcelona, Spain
Keywords:
Pose estimation, Motion capture, Particle filter.
Abstract:
This paper presents a new annealing method for particle filtering in the context of body pose estimation. The
feature-based annealing is inferred from the weighting functions obtained with common image features used
for the likelihood approximation. We introduce a complementary weighting function based on the foreground
extraction and we balance the different measures through the annealing layers in order to improve the posterior
estimate. This technique is applied to estimate the upper body pose of a subject in a realistic multi-view
environment. Comparative results between the proposed method and the common annealing strategy are
presented to assess the robustness of the algorithm.
1 INTRODUCTION
Markerless human motion capture is a challeng-
ing problem that involves estimating the high-
dimensional configuration of a three-dimensional
non-rigid and self-occluding object. Since a wide
range of applications can be derived from the unobtru-
sive characterization of human activity, this research
area is highly active.
A common model is an articulated body structure
with several degrees of freedom that determine the di-
mensionality of the problem. With these kind of mod-
els one can simply adopt hard kinematic constraints or
can go further restricting the motion, hence confining
the solution to a more tractable subspace at the cost
of generality loss. Regardless of the space in which
we work, human dynamics present multi-modal non-
linear and non-Gaussian statistics. Particle Filters
(Arulampalam et al., 2002) have become a relevant
technique due to their ability to precisely estimate
the statistics of such processes. Several approaches
such as partitioned sampling (MacCormick and Is-
ard, 2000), hierarchical sampling (Mitchelson and
Hilton, 2003) and annealing particle filter (Deutscher
et al., 2000) have been developed to cope with high-
dimensional limitations of the classical Condensation
algorithm (Isard and Blake, 1998).
This paper presents a new annealing particle filter
approach based on the properties of image features.
The feature-based annealing concept exploits the at-
tributes of the weighting functions generated by sev-
eral measures constructed with common image fea-
tures. We empirically show the increased robustness
of our approach testing it under challenging condi-
tions for human motion capture such as limited num-
ber of views and low frame rate.
2 PARTICLE FILTER
Particle Filters (PF) (Arulampalam et al., 2002) are
recursive Bayesian estimators derived from Monte
Carlo sampling techniques which can handle non-
linear and non-Gaussian processes. Commonly used
in tracking problems, they aim at estimating the poste-
rior density p(x
t
|z
t
) by means of a set of N
s
weighted
samples or particles:
p(x
t
|z
t
) ≈
N
s
∑
i
w
i
t
δ(x
t
− x
i
t
) (1)
where w
i
t
is the weight associated to the i-th par-
ticle. This discrete approximation of the posterior
requires the evaluation of weights. This is done by
means of the importance sampling principle (Doucet
et al., 2000), with a probability density function (pdf)
q(x
t
|z
t
) from which we generate samples that can be
evaluated with the posterior (up to proportionality).
This pdf is called the importance distribution.
After a certain time, the variance of the weights
increases, causing what is known as particle degener-
acy. This phenomena causes a degradation in the es-
438
López A. and R. Casas J. (2009).
FEATURE-BASED ANNEALING PARTICLE FILTER FOR ROBUST BODY POSE ESTIMATION.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 438-443
DOI: 10.5220/0001783404380443
Copyright
c
SciTePress

timation. An effective measure for the particle degen-
eracy is the survival rate (Liu and Chen, 1998) given
by:
α =
1
N
s
N
s
∑
i=1
(w
i
t
)
2
(2)
In order to avoid the estimator degradation, the
particle set is resampled. After likelihood evaluation a
new particle set must be drawn from the posterior es-
timation, hence particles with higher weights are re-
produced with higher probability. Once the new set
has been drawn, all the weights are set to
1
N
s
, lead-
ing to a uniformly weighted sample set concentrated
around the higher probability zones of the estimated
posterior.
2.1 Sampling Importance Resampling
The Sampling Importance Resampling (SIR) Particle
Filter proposed in (Gordon et al., 1993) is a method
commonly used in computer vision problems. It is
characterized by applying resampling at every itera-
tion and by defining the importance distribution as the
prior density p(x
i
t
|x
i
t−1
). By introducing these two el-
ements, the computation of weights only depends on
the likelihood.
w
i
t
∝ p(z
t
|x
i
t
) (3)
Consequently, the design of the particle filter is
basically a problem of finding an appropiate likeli-
hood function.
2.2 Annealing Particle Filter
It has been shown in several works that SIR Particle
Filters are a good approach for tracking in low dimen-
sional spaces, but they become inefficient in high-
dimensional problems. Deutscher et. al (Deutscher
et al., 2000) proposed a variation of the SIR frame-
work by introducing the concept of Annealing PF. In
body pose tracking problems, the likelihood approx-
imation is often a function with several peaked local
maxima. Annealing PF deals with this problem by
evaluating the particles in several smoothed versions
of the likelihood approximation. After the weights
are computed via the modified likelihood, particles
are resampled and propagated with Gaussian noise
with zero mean and a covariance that decreases at
every step. Each one of these steps (weighting with
a smoothed function, resampling and propagation) is
called an annealing run. In the last annealing run the
estimation is given by means of the Monte-Carlo ap-
proximation of the posterior mean:
ˆ
x
t
=
N
s
∑
i=1
w
i
t
x
i
t
(4)
The most usual way to smooth the weighting func-
tion is by means of an exponent β < 1 called the an-
nealing rate. In the first layer β is minimum, progres-
sively increasing with each layer, sharpening the like-
lihood approximation. In (Deutscher et al., 2000) a
method for tuning β with the survival rate after each
annealing run is proposed.
The use of a hierarchical model (Canton-Ferrer
et al., 2008) is another possible strategy in order to
have annealing layers due to the exploration in spaces
of increasing dimensionality.
Regarding the likelihood approximation, in
(Deutscher et al., 2000) a matching of the model pro-
jection with foreground segmentation and edges is
proposed. Their flesh model consists of conic sec-
tions with elliptical cross-sections surronding virtual
skeleton segments. Raskin et al. (Raskin et al., 2008)
add the body part histogram as an additional feature.
Other authors use Visual Hull approaches (Lauren-
tini, 1994) to work with voxel data. In that case,
they can use three-dimensional flesh models, like el-
lipsoids (Mikic, 2003) or three-dimensional Gaussian
mixtures (Caillette et al., 2005).
3 OUR APPROACH
3.1 Likelihood Evaluation
For the human body modelling we use an articulated
model, which requires to be fleshed out in order to
evaluate the likelihood of a given pose. In our ap-
proach we cannot rely on a 3D reconstruction that
could be difficult to build and, indeed inaccurate.
Therefore, a projection of the model onto the images
is required. Our proposal is to avoid the computa-
tional cost of projecting the whole set of sampling
points of a 3D flesh model by projecting a reduced set
of points per body part. The flesh model will be a set
of cylinders around all the skeleton segments except
the head, which will be modelled by a sphere (see Fig.
3(a)). Therefore, our reduced set of projected points
will be defined by the vertices of the trapezoidal sec-
tion resulting from the intersection of a plane, approx-
imately parallel to the image plane, with the cylindric
shape modelling the limb (or spherical shape in the
case of the head).
To define an intersecting plane for a given cylin-
der, we compute the vectors going from the camera
center towards each one of the limit points of the limb.
Then the cross product of these vectors with the one
FEATURE-BASED ANNEALING PARTICLE FILTER FOR ROBUST BODY POSE ESTIMATION
439

defined by the principal axis of the limb itself is com-
puted to determine two normal vectors that lie on the
intersecting plane and along which we will find the
key points to project. The head template is handled
with a similar procedure using as limb vector the one
going from the base of the neck to the head center.
Regarding the image features, we propose modi-
fications on a likelihood approximation like the one
proposed in (Deutscher et al., 2000) while keeping
common features that are easy to extract, like fore-
ground silhouettes, edges and detected skin.
• We extract foreground silhouettes by means of a
background learning technique based on Stauf-
fer and Grimson’s method (Stauffer and Grimson,
2000). A shadow removal algorithm (Xu et al.,
2005), based on the color and brightness distor-
tion, is used to enhance the segmentation.
• Edge detection is performed by means of the
Canny edge detector (Canny, 1986). The result is
dilated with a square 5x5 structuring element, and
smoothed with a Gaussian mask. In order to avoid
background spurious edges, we mask the edge de-
tection provided by Canny’s algorithm with a di-
lation of the foreground mask.
• A simple skin detection method based on evaluat-
ing the likelihood ratio between skin and non-skin
hypothesis is performed. The likelihood functions
are estimated by 8-bins color histograms of sev-
eral skin and non-skin samples.
The final likelihood approximation will be a com-
bination of several measures constructed with the
aforementioned features.
N sampling points of the projected flesh model are
matched with the extracted foreground. The weight is
computed as follows:
ω
f l
=
1
N
N
∑
n=1
(1 − I
f
n
) (5)
Since pixel intensities in the foreground masks
(I
f
t
) have 0 or 1 as possible values, the weighting
function is obtained by a normalized sum of the back-
ground pixels falling inside the projected flesh model.
In the case of the head, we add skin detection infor-
mation:
ω
f h
=
1
N
N
∑
n=1
(1 − I
f
n
I
s
n
) (6)
Therefore, the final foreground weight ω
f
is the
averaged sum of all the limbs and head weights.
The proposed weighting function for edges is a
sum of squared differences between the contour pix-
els and the edges of the flesh model aligned with the
axis of the limb:
ω
e
=
1
N
N
∑
n=1
(1 − I
e
n
)
2
(7)
where N stands for the sampling points along the
occluding edges of the projected flesh model.
3.1.1 Foreground Divergence Measure
The proposed foreground matching measure shows
how well the model fits the observation, but does
not evaluate how well the observations are being ex-
plained by the model. Suppose the likelihood p(z
t
|x
t
)
is available and that a given pose generates a pdf. A
measure that can be used to assess the similarity of
the likelihood and the generated pdf is the Kullback-
Leibler divergence. At this point, it is important to
remark that the KL divergence will provide different
results depending on the factor order (except if both
pdfs are identical). We can establish an analogy with
our likelihood approximation. We are trying to de-
termine the mutual information of the model and the
observations. Therefore, we propose to include an ad-
ditional divergence measure between the projection of
the flesh model and the foreground masks to see how
well a particle explains the observations.
ω
d
=
1
N
f
N
f
∑
n=1
(I
f
n
(1 − B
n
)) (8)
This divergence basically consists in measuring
the occupancy of the foreground silhouette (compris-
ing N
f
foreground pixels) by the B
n
pixels of the pro-
jection of a given particle.
3.2 Feature-based Annealing
The foreground matching measure produces a smooth
and flat function (in almost every point) in which
many different poses take considerable degrees of
likelihood. However, foreground matching has the
property of being discriminative with several wrong
states. These properties can be observed in Fig. 1(a),
where the weighting function is shown with actual
data as a function of two angles. The foreground di-
vergence measure is a smooth function that presents,
in general, a broad global maximum (see Fig. 1(b)).
Edge matching is the most determinant measure in
the sense that high values can only be reached when
a particle is very close to the true pose. Nevertheless,
spurious edges can also produce high values of the
likelihood approximation (see Fig. 1(c)).
Since foreground measures produce very broad
functions and edge matching tends to produce peaked
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
440
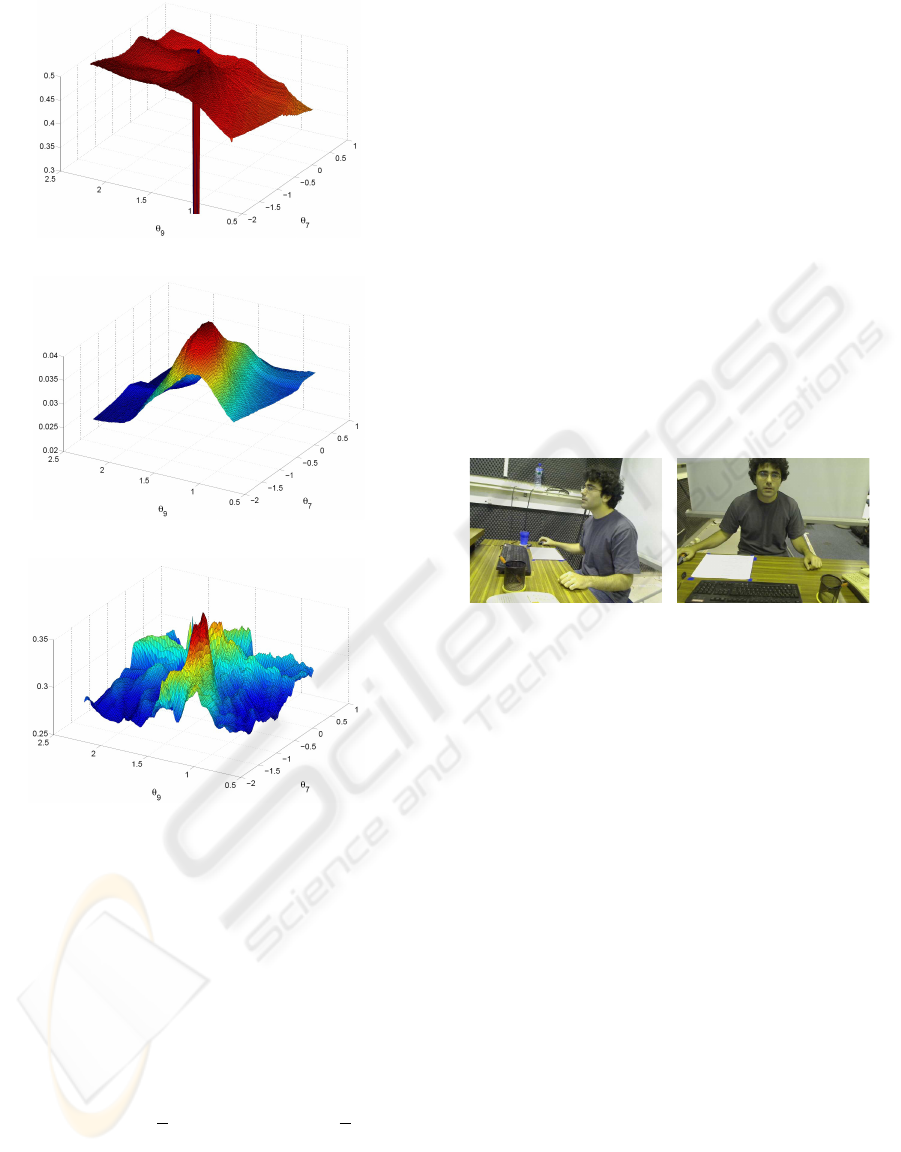
(a) Foreground Matching Weighting
(b) Divergence Weighting
(c) Edges Matching Weighting
Figure 1: Plots of the different feature weightings repre-
sented as functions of two angles of the left arm. The rest
of parameters are set to values close to the true pose.
functions, we can exploit annealing through the de-
scribed attributes of the measures. We propose to use
the annealing rate β not only as exponent of the like-
lihood approximation but also in the final average of
all the measures derived from the image features:
ω = exp
−
C
∑
c=1
(λ
f
c
(
1
β
)ω
f
+ λ
e
c
(β)ω
e
+ λ
d
c
(
1
β
)ω
d
)
!
(9)
where C is the number of views and λ
c
is a weight-
ing coefficient depending on β (allowing to give more
importance to foreground measures in the first layers
and to edge measures in the last layers).
4 RESULTS AND DISCUSSION
4.1 Experimental Setup
We have tested our approach in an office desktop
environment. During approximately two minutes,
three subjects performed several common actions at a
workplace (mouse dragging, writing, typing and pick-
ing objects). Hence, for our tests, we have focused on
the upper body tracking.
Our setup was built under the premise of being
portable, low cost and easy to configure. Two cali-
brated webcams, one frontal and one lateral, record-
ing at 9.5 fps provided the frames onto which our
body model has been projected (see Fig. 2). Both
views are relatively close to the subject, thus the ap-
parent size of some limbs in the image can change
notably depending on their 3D position.
Figure 2: Available views for the experimental setup.
4.2 Body Model
A simplistic articulated upper body model fulfills the
requirements of the described scenario. This model
is based on the kinematic chain framework (Bregler
and Malik, 1998) and comprises a set of joints. In
our case, this set of joints are the base of the neck,
shoulders and elbows with a total of nine degrees of
freedom. In order to set the model in a world position,
a three-dimensional coordinate system built with the
base of the neck as origin and a body orientation are
defined. The world reference point for our model is
set to be the base of the neck (see Fig. 3(a)). There-
fore, the body model defines a thirteen-dimensional
state vector:
x
t
=
{
x
0
, y
0
, z
0
, θ
0
, ...., θ
9
}
(10)
Angle θ
0
is the orientation of the whole body
model while all the other angles are designed follow-
ing hard kinematic constraints.
FEATURE-BASED ANNEALING PARTICLE FILTER FOR ROBUST BODY POSE ESTIMATION
441

(a)
(b)
Figure 3: (a) Articulated upper body model and (b) its pro-
jection for a given particle.
4.3 Experimental Results
3D body part locations (head, shoulders, elbows and
wrists) have been manually annotated in three se-
quences of three different subjects in order to test
the tracker performance. The error is expressed as
the mean distance between the annotated and the esti-
mated joints.
Comparative results between the APF with the
common likelihood approach (comprising edges and
foreground matching) and our proposal are shown in
Fig. 4. In both cases we used the body model and
the projection procedure explained in section 3.1. Fi-
nal mean error obtained by our approach for the three
sequences was 104 mm, 74 mm below the common
case for this difficult scenario. Common likelihood
evaluation makes the tracker vulnerable to track loss,
leading to higher mean error. On the other hand, the
divergence measure and the feature-based annealing
make the tracker more robust under these experimen-
tal conditions.
We found out that some spurious edges due to
clothing and objects caused our tracker to fail in its es-
timation. The apparent motion recorded in the images
was very fast in some of the actions performed, caus-
ing blurs in the image and abrupt translation of body
parts. Since the implemented annealing PF works
0 20 40 60 80
50
100
150
200
250
300
error (mm)
t(s)
APF with Common Likelihood Aproximation
Our approach
Figure 4: Comparative results using 3 layers and 200 parti-
cles per layer with the normal likelihood aproximation and
our proposal.
Figure 5: Tracking samples of a sequence where the subject
types something in the keyboard, picks a pen, writes and
leaves the pen again. The tracker is able to recover the pose
after several errors due to fast apparent motion.
with edges as the most determinant feature and has a
simple propagation model, the algorithm was not able
to track several of these fast motions. However, it was
able to recover some poses after a tracking error.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
We have presented an approach to exploit some com-
mon image features used in annealed particle filter
techniques for human body tracking. We have intro-
duced a foreground divergence measure that allows
us to define a new procedure of annealing based on a
decomposition of the likelihood approximation.
We have tested our proposal with a simple body
configuration and a simplified projection method in a
challenging scenario. A comparison between our pro-
posal and existing methods has been presented. Some
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
442

interesting results have been achieved in such condi-
tions with a low number of particles and layers.
Like in the simple annealed particle filter we have
tried to preserve the tracker generality by only adding
hard kinematic constraints to our model. Conse-
quently, our approach is not able to efficiently track
fast apparent motions due to low frame rates. This
could be attributed to a limitation of the state-space
model and the common propagation model of the
Sampling Importance Resampling framework from
which annealing particle filter is derived.
Future research involves further validation of
feature-based annealing with full body models and
several recording conditions, and the extension of
this study to other image features, including spatio-
temporal features. The introduction of image features
in the propagation scheme to avoid “blind” sampling
with respect to the observations is another possible
research line.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work has been partially supported by the Span-
ish Ministerio de Educaci
´
on y Ciencia, under project
TEC2007-66858/TCM and by the European Commis-
sion under contract FP7-215372 ACTIBIO.
REFERENCES
Arulampalam, M., Maskell, S., Gordon, N., Clapp, T.,
Sci, D., Organ, T., and Adelaide, S. (2002). A
tutorial on particle filters for online nonlinear/non-
GaussianBayesian tracking. Signal Processing, IEEE
Transactions on, 50(2):174–188.
Bregler, C. and Malik, J. (1998). Tracking People with
Twists and Exponential Maps. In Proc. CVPR (1998).
Caillette, F., Galata, A., and Howard, T. (2005). Real-Time
3-D Human Body Tracking using Variable Length
Markov Models. British Machine Vision Conference,
1:469–478.
Canny, J. (1986). A computational approach to edge de-
tection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 8(6):679–698.
Canton-Ferrer, C., Casas, J., and Pardas, M. (2008). Ex-
ploiting Structural Hierarchy in Articulated Objects
Towards Robust Motion Capture. Lecture Notes in
Computer Science, pages 82–91.
Deutscher, J., Blake, A., and Reid, I. (2000). Articulated
body motion capture by annealed particle filtering.
Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2000. Pro-
ceedings. IEEE Conference on, 2:126–133 vol.2.
Doucet, A., Godsill, S., and Andrieu, C. (2000). On se-
quential Monte Carlo sampling methods for Bayesian
filtering. Statistics and Computing, 10(3):197–208.
Gordon, N., Salmond, D., and Smith, A. (1993). Novel
approach to nonlinear/non-gaussian bayesian state es-
timation. Radar and Signal Processing, IEE Proceed-
ings F, 140(2):107–113.
Isard, M. and Blake, A. (1998). CONDENSATION-
Conditional density propagation for visual tracking.
Int. Journal of Computer Vision, 29(1):5–28.
Laurentini, A. (1994). The visual hull concept for
silhouette-based image understanding. Pattern Anal-
ysis and Machine Intelligence, IEEE Transactions on,
16(2):150–162.
Liu, J. and Chen, R. (1998). Sequential Monte Carlo meth-
ods for dynamical systems. Journal of the American
Statistical Association, 93(5):1032–1044.
MacCormick, J. and Isard, M. (2000). Partitioned
Sampling, Articulated Objects, and Interface-Quality
Hand Tracking. Lecture Notes in Computer Science,
pages 3–19.
Mikic, I. (2003). Human Body Model Acquisition and
tracking using multi-camera voxel Data. PhD. The-
sis, University of California, San Diego.
Mitchelson, J. and Hilton, A. (2003). Simultaneous pose
estimation of multiple people using multiple-view
cues with hierarchical sampling. In Proc. of BMVC,
September.
Raskin, L., Rivlin, E., and Rudzsky, M. (2008). Using
Gaussian Process Annealing Particle Filter for 3D Hu-
man Tracking-Volume 2008, Article ID 592081, 13
pages. EURASIP Journal on Advances in Signal Pro-
cessing.
Stauffer, C. and Grimson, W. (2000). Learning Patterns of
Activity Using Real-Time Tracking. IEEE Transac-
tions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,
pages 747–757.
Xu, L., Landabaso, J., and Pardas, M. (2005). Shadow Re-
moval with Blob-Based Morphological Reconstruc-
tion for Error Correction. Acoustics, Speech, and
Signal Processing, 2005. Proceedings.(ICASSP’05).
IEEE International Conference on, 2.
FEATURE-BASED ANNEALING PARTICLE FILTER FOR ROBUST BODY POSE ESTIMATION
443
