
A NOVEL SEGMENTATION METHOD FOR CROWDED SCENES
Domenico Bloisi, Luca Iocchi
Dipartimento di Informatica e Sistemistica, Sapienza University of Rome, Italy
Dorothy N. Monekosso, Paolo Remagnino
Kingston University London, Surrey, U.K.
Keywords:
Stereo vision, Background modeling, Segmentation, Crowded environments.
Abstract:
Video surveillance is one of the most studied application in Computer Vision. We propose a novel method to
identify and track people in a complex environment with stereo cameras. It uses two stereo cameras to deal
with occlusions, two different background models that handle shadows and illumination changes and a new
segmentation algorithm that is effective in crowded environments. The algorithm is able to work in real time
and results demonstrating the effectiveness of the approach are shown.
1 INTRODUCTION
Visual surveillance of dynamic and complex scenes
is currently one of the most active research topics in
Computer Vision. Traditional passive video surveil-
lance is ineffective when the number of cameras ex-
ceeds the ability of human operators to keep track
of the evolving scene. Intelligent visual surveillance
aims to automatically detect, recognize and track peo-
ple and objects from image sequences in order to
understand and describe dynamics and interactions
among them.
There exists (Hu et al., 2004; Heikkil¨a and Sil-
ven, 1999; Haritaoglu et al., 2001; Halevi and Wein-
shall, 1999; Haritaoglu et al., 1999) a wide spectrum
of promising applications for video surveillance sys-
tems, including access control in special areas, human
identification at a distance, crowd flow statistics and
congestion analysis, detection of anomalous behav-
iors and interactive surveillance using multiple cam-
eras, etc.
However, none of the above is able to deal with
all the problems a video surveillance system typically
encounters, namely occlusions, illumination changes,
shadows and tracking failures in crowded environ-
ments.
We present an algorithm that uses two stereo
cameras to deal with occlusions, two different back-
ground models that handle shadows and illumination
changes and a new approach for segmentating even in
a crowded environment.
The paper is organized as follows: after discussing
related work in Section 2, the general architecture of
the algorithm is described in Section 3. In Section 4
we present the segmentation module in general and in
Section 5 we detail our novel segmentation algorithm.
Section 6 shows a series of results obtained by our
approach, while Section 7 provides the conclusions.
2 RELATED WORK
There is extensive literature on tracking people in
crowded scenes and in every case the major difficulty
arises in tracking under occlusions. In (Tsai et al.,
2006) color models and optical flow are used in order
to solve the problem, while in (Gilbert and Bowden,
2007) a global object detector and a localized frame
by frame tracker are combined for dealing with oc-
clusions. However, those papers present only scenes
with up to 4 people. More crowded situations are han-
dled by the method of (Khan and Shah, 2006), where
one of the limitations is its sensitivity to shadows and
only outdoor environments are considered.
In (Bahadori et al., 2007; Darrell et al., 2001; Ioc-
chi and Bolles, 2005) a ground plane view approach is
studied: in order to compute the localization of peo-
ple in the world, a ground plane view of the scene is
computed by projecting all foreground points onto the
484
Bloisi D., Iocchi L., N. Monekosso D. and Remagnino P. (2009).
A NOVEL SEGMENTATION METHOD FOR CROWDED SCENES.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 484-489
DOI: 10.5220/0001792604840489
Copyright
c
SciTePress

ground plane view reference system. This is achieved
by using the stereo calibration information of map
disparities into the sensors 3-D coordinate system and
then the external calibration information to map these
data in a world reference system. However, these ar-
ticles do not deal explicitly with crowded scenes.
In this paper we describe a system architecture
that integrates ground plane view analysis with a
novel segmentation algorithm that is robust to the
presence of many people.
The main difference between our work and (Ba-
hadori et al., 2007) is the number of people detectable.
In (Bahadori et al., 2007) scenes presenting more than
4 people are not considered and for segmenting peo-
ple close to one another a ground plane view ap-
proach is presented. We add to the segmentation mod-
ule a novel method called Height Image algorithm
(see Section 5) explicitly designed for dealing with
crowded environments (i.e., up to 15 people).
More specifically we developed a new algorithm
for segmenting people very close to one another or
even touching each other. The presence of a crowd in
the scene causes a great amount of noise in the 3-D
measures, especially if people are far from the cam-
era. Our height image algorithm (see Section 5) in-
tegrates the 3-D information from the stereo camera
with the background model in order to deal with the
measurement noise.
3 METHOD OVERVIEW
The method is applied to the training of nurses in the
School of Nursing Faculty of Health and Social Care
Sciences at Kingston University London
1
. The aim
is to detect and track people in order to analyze their
behavior.
Data are collected using two commercial stereo
cameras (Videre Design STH-MDCS
2
) each camera
connected to a computing unit (an Intel Core 2 Duo
2,0 GHz CPU Mac mini
3
) through a Firewire connec-
tion. Disparity is estimated with the Videre Design
stereo algorithm (Konolige, 1997) allowing for real
time computation of dense disparity maps.
The main functions of the system are: optical de-
tection and tracking of moving people present in the
field of view of each stereo camera, computing posi-
tion and understanding behaviors of any moving tar-
get observed by a camera, and multi camera informa-
tion fusion. Those tasks are extremely hard to achieve
1
as part of the project ”Visual modeling of people be-
haviors and interactions for professional training”.
2
http://www.videredesign.com
3
http://www.apple.com/macmini
Figure 1: The general architecture of the approach.
due to both the clutter in the scene (up to 15 people)
and the uniform the nurses wear (see Fig. 2). Further-
more the scene is extremely dynamic because both
beds and room screens are frequently moved.
Figure 2: Two different camera views with the resulting seg-
mentation.
The general architecture of the approach is de-
picted in Fig. 1. It is made of three modules: seg-
mentation, tracking and data fusion. In the rest of the
paper we focus only on the segmentation one in order
to detail our novel algorithm specially designed for
dealing with crowded scenes.
4 SEGMENTATION
All the steps our method performs are depicted in
Fig. 3.
First of all, as in (Bahadori et al., 2007), two dif-
ferent background images are computed (see the top
left of Fig. 3): a color intensity background model and
a stereo background model.
A NOVEL SEGMENTATION METHOD FOR CROWDED SCENES
485
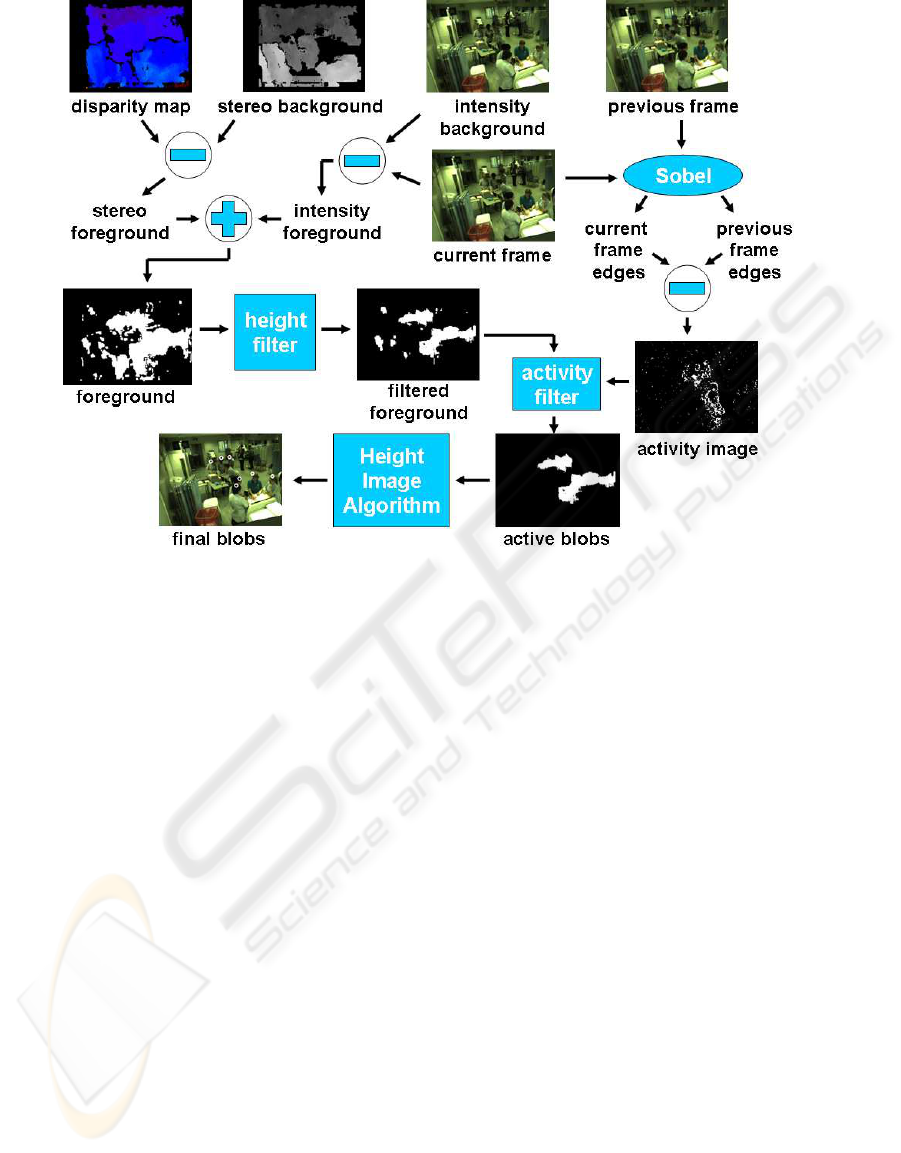
Figure 3: The segmentation algorithm.
Integrating two different backgroundmodels gives
many advantages. The use of the stereo background
is useful in eliminating shadows appearing on walls
and on the ground and in considering as foreground
even people that remains in the same position for long
periods of time. The use of the intensity background
can ”fill the holes” that appear in the disparity map
due to homogeneous color clothes.
A set L of n frames from the left stereo rig is used
to build the intensity background image B which rep-
resents only the static (i.e., non-moving) part of the
scenario. This procedure is carried out continuously
(every 40 seconds) to adapt to changes in the sce-
nario, in fact the intensity background is not fixed but
must adapt to both gradual and sudden illumination
changes (such as sunrays from the windows), artificial
light flickering and changes in the background geom-
etry (such as moved objects like chairs, beds and room
screens).
Our approach to background modelling is based
on a mixture of Gaussians (Friedman and Russell,
1997; Stauffer and Grimson, 2000; Elgammal et al.,
2000): the algorithm computes the histogram for each
pixel (i.e., the approximation of the distribution) in
the RGB color space and it clusters the raw data in
sets based on distance in the color space. The clus-
tering is made online after each new sample is added
to L avoiding to wait until L is full. In this way the
background extraction process is faster because the
computational load is spread over the sampling inter-
val instead of concentrating it after having completely
filled L. In order to correctly manage the fluctuating
artificial light, up to seven clusters (i.e., background
values) for each pixels are considered. Such a solu-
tion allows for representing flickering in the illumi-
nation intensity as well as the natural light from the
windows and it was successfully applied also on out-
door environments.
The stereo background is computed only once ex-
ploiting a set S of n disparity images stored by the
stereo camera when the scene is empty (see for exam-
ple the top left frame in Fig. 5). It can be computed
offline or online (e.g., if the system is activated early
in the morning). In this way the stereo background
represents a 3-D map of the scene observed. The
stereo background is computed exploiting the same
algorithm used for the intensity background but using
disparity images.
From the current frame and the intensity back-
ground an intensity foreground is computed, while
using the current disparity image and the stereo back-
ground we extract a stereo foreground. The final fore-
ground image is obtained merging those two images
(see the left side of Fig. 3).
From the foreground image a set of blobs is ex-
tracted. For each blob a height threshold is applied:
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
486

the part of the blob below 1.40 meters is discarded.
At the end of this process we obtain a filtered fore-
ground image (see the middle of Fig. 3). The activ-
ity filter allows to discard all the inanimate objects
in the scene that are taller than 1.40 meters such as
room screens and opening doors, in fact people even
if standing in the same position perform always light
movements detectable through the Sobel’s operator.
Then we extract a set of blobs from the filtered
foreground image and consider each found blob with
respect to its ”activity”: i.e., subtracting the current
frame edges from the previous frame ones an activity
image is computed (see the right side of Fig. 3). If a
blob covers a part of the activity image with a ”suffi-
cient” number of non-zero points that blob is consid-
ered active: in this way a list of active blobs is stored.
We used 25 as a threshold for considering a blob
as active, but obviously that threshold depends on the
number of frame per seconds the application is com-
puting (our method’s speed is 8 fps, see Section 6).
For each active blob a process called height image
segmentation is carried on in order to segment the ex-
act number of people in the scene, i.e., the final list
of blobs (see the bottom of Fig. 3). The height image
segmentation detailed description is given in the next
section.
5 THE HEIGHT IMAGE
ALGORITHM
The algorithm is detailed in Table 1 and Fig. 4 shows
its input and its output. The input is the list of all
the active blobs present in the scene (see Fig. 4 a), the
output is the final list of people detected (see Fig. 4 c).
The height image (see Fig. 4 b) is a gray scale image
in which the pixel intensity values belonging to the
silhouette of the moving people are a representation
of their height. From each active blob a correspond-
ing height image is formed. This image is used for
segmenting people very close to one another or even
touching each other.
For each blob in the height image a mean value of
the height values is computed and the height image is
updated removing all the pixels belowthe mean value.
A new set of blobs is extracted and the mean value is
recomputed on that new set. The process is reiterated
until we are able to extract the final list of centroids
(see Fig. 4 c) accordingto a predefined thresholdt (we
chose 30 as a useful threshold for 320×240 frames).
Once we have found all the centroids we are able
to extract from the original foreground image a cylin-
der representing the detected person (see Fig. 5 and
Fig. 6).
Figure 4: a) The height image algorithm input. b) The
height image. c) The output.
Figure 5: Head, trunk and legs sections.
6 RESULTS
The algorithm performance in terms of frame per sec-
onds are showed in Table 2.
We recorded 8 hours of training practice in two
different days and with different light conditions. In
order to test the accuracy of our system we visually
examined a set of randomly chosen frames taken from
different moments in the day and compared for each
frame how many people are actually in the camera
field of view (FOV) and how many centroids are lo-
cated by the segmentation algorithm. We cannot use
a benchmark like PETS
4
or similar because does not
exist a benchmark for stereo images.
The error e
i
for each scene i is computed as
e
i
=
| ˆn− n|
n
(1)
where ˆn is the number of detected people and n is the
real number of people in the FOV. The accuracy a
i
for
4
http://www.cvg.cs.rdg.ac.uk/slides/pets.html
A NOVEL SEGMENTATION METHOD FOR CROWDED SCENES
487

Table 1: The height image algorithm.
Height Image Algorithm
Let t be the minimum area for a blob to be
considered of interest, A the set of found
activity blobs, F the final set of the segmented
objects we are searching for and H the set of
height images.
input: t, A
output: F
For each activity blob a
i
∈ A {
1. Find the maximum M
i
and the minimum m
i
height associated to its pixels.
2. Normalize the pixels between 1 and 255.
3. Build a grayscale image h
i
formed from
the pixels in a
i
grey-colored according to the
previous normalization.
4. Add h
i
to H.
}
While H is not empty {
1. Extract an element h
i
from H and find the
centroid C(h
i
).
2. Find the mean value v
i
for the pixel
intensities in h
i
.
3. Erase all the pixels from h
i
that are
below v
i
.
4. Extract from h
i
a set B of blobs such that
{∀ b
j
∈ B : b
j
⊂ h
i
∧ area(b
j
) > t}.
If B is empty then add C(h
i
) to F,
else add every element b
j
∈ B to H.
5. Delete h
i
from H.
}
Table 2: Algorithm speed.
Frame Dimensions Recording FPS
320×240 NO 12
320×240 YES 8
640×480 NO 8
each scene i is
a
i
= 1− e
i
(2)
The average accuracy A is
A =
1
n
n
∑
i=1
a
i
(3)
The result are showed in Table 3, where differ-
ent type of situations are considered depending on
the number of people in the FOV. A comparison with
other similar methods is not easy because those con-
sider quite often up to 3 or 4 people in the scene, while
we examined more crowded situations.
Table 3: Segmentation accuracy.
No. of people No. of samples Accuracy
in the scene considered A
0 to 3 25 0.99
4 to 7 25 0.93
8 to 11 25 0.86
12 to 15 25 0.85
Most of the errors are concentrated in an area of
the FOV far from the camera due to the noise in the
stereo disparity map. Those errors can be avoided
integrating the second camera segmentation on the
same image (see Fig. 2 where people not detected in
a view are detected in the second one).
Figure 6: The tracking results.
As one can expect, performance of segmentation
depends on the height of the camera. In fact, high
cameras retrieves scenes with less occlusions.
7 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In this article we presented a novel approach for seg-
menting crowded environments. The major contribu-
tion of this study is the design of a method able to de-
tect up to 15 people in the scene at the same time. Dif-
ferently from other similar work that considers up to 3
of 4 people in the scene, we presented a real crowded
situation where the system may afford a challenging
task of counting a larger number of people.
Experimental results show the performance of the
system. The results in Table 3 refer only to the seg-
mentation module. We took in account only the er-
ror performed by that module due to the focus of this
paper on segmentation. If the system is considered
in all its parts, the tracking module is able to correct
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
488

the segmentation errors due to the Kalman filter ac-
tion. In fact the segmentation module outputs at 8 fps
while the tracking module can work even at a lower
data rate, thus a number of errors can be corrected.
As future work we intend to improve the integra-
tion between the two different types of background
and to add a series of zigbee sensors to the scene in
order to merge information coming from two different
sources: the stereo cameras and the zigbee sensors.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors thank Susan Rush for helping out in the
design and organization of the data acquisition exer-
cises.
REFERENCES
Bahadori, S., Iocchi, L., Leone, G. R., Nardi, D., and Scoz-
zafava, L. (2007). Real-time people localization and
tracking through fixed stereo vision. Applied Intelli-
gence, 26(2):83–97.
Darrell, T., Demirdjian, D., Checka, N., and Felzenszwalb,
P. F. (2001). Plan-view trajectory estimation with
dense stereo background models. In ICCV, pages
628–635.
Elgammal, A. M., Harwood, D., and Davis, L. S. (2000).
Non-parametric model for background subtraction. In
ECCV ’00: Proceedings of the 6th European Con-
ference on Computer Vision-Part II, pages 751–767,
London, UK. Springer-Verlag.
Friedman, N. and Russell, S. (1997). Image segmentation
in video sequences: A probabilistic approach. pages
175–181.
Gilbert, A. and Bowden, R. (2007). Multi person tracking
within crowded scenes. In Workshop on Human Mo-
tion, pages 166–179.
Halevi, G. and Weinshall, D. (1999). Motion of distur-
bances: Detection and tracking of multi-body non-
rigid motion. Machine Vision and Applications,
11:122–137.
Haritaoglu, I., Cutler, R., Harwood, D., and Davis, L. S.
(2001). Backpack: Detection of people carrying ob-
jects using silhouettes. Computer Vision and Image
Understanding: CVIU, 81(3):385–397.
Haritaoglu, I., Harwood, D., and Davis, L. S. (1999). Hy-
dra: Multiple people detection and tracking using sil-
houettes. In ICIAP ’99: Proceedings of the 10th In-
ternational Conference on Image Analysis and Pro-
cessing, pages 280–285, Washington, DC, USA. IEEE
Computer Society.
Heikkil¨a, J. and Silven, O. (1999). A real-time system for
monitoring of cyclists and pedestrians. Proc. Second
IEEE International Workshop on Visual Surveillance,
June 26, Fort Collins, Colorado, USA, 74-81.
Hu, W., Tieniu, T., Liang, W., and Maybank, S. (2004). A
survey on visual surveillance of object motion and be-
haviors. Systems, Man and Cybernetics, Part C, IEEE
Transactions on, 34(3):334–352.
Iocchi, L. and Bolles, R. C. (2005). Integrating plan-view
tracking and color-based person models for multiple
people tracking. In ICIP (3), pages 872–875.
Khan, S. M. and Shah, M. (2006). A multiview approach
to tracking people in crowded scenes using a planar
homography constraint. In ECCV (4), pages 133–146.
Konolige, K. (1997). Small vision systems: hardware and
implementation. In Eighth International Symposium
on Robotics Research, Hayama, Japan.
Stauffer, C. and Grimson, W. E. L. (2000). Learning pat-
terns of activity using real-time tracking. IEEE Trans.
Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell., 22(8):747–757.
Tsai, Y.-T., Shih, H.-C., and Huang, C.-L. (2006). Mul-
tiple human objects tracking in crowded scenes. In
ICPR ’06: Proceedings of the 18th International Con-
ference on Pattern Recognition, pages 51–54, Wash-
ington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
A NOVEL SEGMENTATION METHOD FOR CROWDED SCENES
489
