
COMBINED 3D AND MULTISPECTRAL FRESCO
DOCUMENTATION OF THE VILLA OPLONTIS, POMPEI
High-Resolution and High-Performance Digitization of Cultural Heritage
Bernd Breuckmann
Breuckmann GmbH, Torenstr. 14, 88709 Meersburg, Germany
Hubert Mara
Vienna University of Technology, Institute for Computer Aided Automation
Pattern Recognition and Image Processing Group, Favoritenstr. 9/183-2, 1040 Vienna, Austria
Zs´ofia V´egv´ari
Tondo Bt., Haj´ogy´ari sziget 3231036 Budapest, Hungary
Keywords:
3D Computer Vision, 3D Acquisition, Multispectral Analysis, Documentation, Cultural Heritage, Archaeol-
ogy, Fresco.
Abstract:
Motivated by cultural heritage, industry, medicine we are developing 3D-scanners and post-processing sys-
tems for rapid and precise documentation of surfaces with curvature. By constantly increasing resolution and
accuracy of our system we can enable the documentation of small deviations of even flat surfaces – like fres-
cos. This enables documentation of important features for restoration like small fractures or topology of paint-
strokes for scientific research. The 3D-documentation can be done in-situ, radiation-free and contact-free us-
ing a structured (coded) light-source and a digital camera. Using light for documentation of colourful painted
surface lead to the integration of colour-filtering techniques to ”see thru” the first layer(s) of paint. This ap-
proach, typically known from photography, is used to reveal under- drawings of paintings. While photographs
suffer from lens distortion lacking a precise scale, we can provide the height of paint-layers in µm in a properly
calibrated scale. This method has already been successful tested on synthetic data and medieval paintings and
statues, which cover not all painting techniques known to art historians. Therefore we conducted experiments
in Pompei to determine the capabilities of our system for fresco paintings. Results shown in this report cover
traditional close-range 3D-acquisition for larger fields of view (m
2
) and multi-spectral 3D-acquisition for paint
layers having a field of view of ≈ 600cm
2
. Regarding performance – having a tremendous amount of frescos
– we could show that 3D-acquisition can be done in ≈ 15 minutes per m
2
. Multi-spectral 3D-acquisition can
be applied in a similar fast manner by using expert-knowledge to narrow down the areas of interest.
1 INTRODUCTION
Motivated by the challenges in archaeology and espe-
cially archaeometry (Leute, 1987), we are developing
different kinds of contact- and radiation-free systems
for field application. These fully-automated (Kam-
pel and Sablatnig, 2003) and semi-automated sys-
tem (Lettner et al., 2006) help archaeologists to get
efficiently and accurate their daily work done. On the
other hand-side gives us this kind of work interesting
challenges as there often exists no ground truth about
these human-made objects of Cultural Heritage.
Having at least a decade of experience in inter-
and trans-disciplinary projects (Sablatnig et al.,
1991), this paper presents state-of-the-art methods
and hardware for in-situ rapid and high-resolution 3-
dimensional documentation of painted surfaces. As
test-case we choose the Villa Oplontis (Carcavallo,
1980) – also known as Villa Poppaea – with hundreds
of square-meters of walls decorated with roman fres-
cos (Clarke, 1991) of high-value for art-history.
Our Topometrical HighDefinition 3D-surface scan-
615
Breuckmann B., Mara H. and Végvári Z. (2009).
COMBINED 3D AND MULTISPECTRAL FRESCO DOCUMENTATION OF THE VILLA OPLONTIS, POMPEI - High-Resolution and High-Performance
Digitization of Cultural Heritage.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 615-620
DOI: 10.5220/0001800306150620
Copyright
c
SciTePress

ners are optimized for the requirements of arts
and cultural heritage. Our scanners allow the 3-
dimensional digitization of art objects and paintings
with state-of-the-art spatial resolution of 10µm and
accuracy ≈ 2µm in height/depth. As cultural heritage
objects are often colourful objects, the colour is ac-
quired as so-called texture-map. The benefit of this
texture-map compared to photography is the corre-
spondence between 3D coordinates and colour infor-
mation. This is important e.g. for long-time surveys
of colour degradation. Depending on the cultural her-
itage application our 3D-scanners can be tailored us-
ing a wide-selection of fields of view, triangulation
angles and resolution. Using 5 Megapixel cameras
we can achieve up to 2.400 dpi (dot per inch) for flat
objects. As all our systems consist of robust modules
they can be adjusted by the user for a wide variety of
applications ranging e.g. from laboratories and muse-
ums to field-use at archaeological excavations.
The 3D-models recorded with our systems can be
used for virtual reality visualization; documentation
and archiving; and for scientific analysis. Typical ex-
amples for using 3D-models of our partners in cul-
tural heritage are:
• Documentation and archiving of art objects.
• Virtual reconstruction of art objects.
• Virtual presentation in museums and in the inter-
net.
• Manufacturing and rapid prototyping of scaled
copies and replicas.
• Scientific analysis of palaeontological and archae-
ological findings.
• Quantitative mapping of damages on sculptures
and monuments.
• Generation of Identity Cards and Digital Finger-
prints.
• Manufacturing of tailored transportation pack-
ages.
2 ACQUISITION
Conducting two different experiments, we used to dif-
ferent Breuckmann HighDefinition 3D-scanners for
acquisition. The first experiment concerned the rapid
documentation of large areas of frescos covering hun-
dred of square-meters, while maintaining high accu-
racy for restoration planning and long-time surveys
of weathering effects. Related work about the virtual
restoration of weathered ancient laws of Ephesos can
be found in (Kalasek et al., 2008), while an alternate
use of multispectral 3D-survey can be found in (Mara
et al., 2007). Figure 1 shows these two different 3D-
scanners in standard configuration.
(a) (b)
Figure 1: (a) AsmartSCAN-3D scanner and (b) optoTOP-
HE scanner either for a large field of view (top) and a small
field of view (bottom).
The main features of the triTOS-3D/smartSCAN-3D-
scanner by Breuckmann GmbH are: two digital
colour cameras, each one with 1.4 Megapixel; syn-
chronous acquisition of 3D-shape and colour (texture-
map); and a variable field of view (FOV): between
90mm and 650mm image diagonal.
For the performance biased experiments in room
10 of the Villa Oplontis a field of view having a
600mm image diagonal was used. This particular field
of view maximises the acquired area and therefore
performance enabling the acquisition of expected de-
tails of the frescos. These details are seams and cor-
rections introduced at the time of painting; modern
restoration artefacts; and cracks due to weathering.
This setup covered an area of 480 × 360mm per ac-
quisition having a spatial resolution of 0.35mm and a
depth/height resolution of ≈ 20µm.
As 3D-acquisition using the principle of struc-
tured light (Cosmas et al., 2001) works better in
darker environments, while colour acquisition re-
quires brighter illumination the best solution are con-
trollable lights, which are supported by our system.
As this is a well approved method and due to time and
space constraints of this field-trip we decided to use
simple Halogen lamps already on-site. Even with this
quality drawback the texture maps of the 3D-models
are sufficient for most documentation and analysis
tasks. For a full-scale 3D-acquisition campaign we
advice to use controllable lights as we expected, that
future scientific analysis and restoration will have a
noticeable benefit using state-of-the-art illumination.
The 3D-acquisition and the post-processing were
done using the OPTOCAT software-package by
Breuckmann. As the single 3D-scans have to be
stitched, they were also aligned and registered (Besl
and McKay, 1992; Chen and Medioni, 1992) using
the geometry of the surfaces. Finally all 3D-scans
were merged, resulting in a single (polygonal) 3D-
mesh(Hoppe et al., 1992). We have to stress, that
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
616

the result - the polygonal mesh - is scaled with the
accuracy depending on the calibration of the scanner
and its field of view. For our experiments using the
triTOS-3D system with a field of view (600mm) typi-
cally has an accuracy of 100µm or less.
2.1 The New Prototype - A Modified
optoTOP-HE 3D-Scanner
This novel prototype is also known as MSS-3D multi-
spectral 3D-scanner. It is developed as cooperation
between Breuckmann and Tondo. It was first intro-
duced in (V´egv´ari and Breuckmann, 2008) for an ap-
plication in art history, where previously hidden sig-
nature of a famous artist could be revealed. At present
day the MMS-3D allows 3D-acquisition of objects
with painted surfaces in different wavelength from
near Infrared to Deep Blue.
Similar to the previous setup only one 1.4
Megapixel monochrome camera is used for acquisi-
tion having a smaller field of view with 100mm im-
age diagonal. This small field of view was chosen
to maximize the spatial resolution to 60µm and a
depth/height resolution of 5µm. For the optimal scan-
ning distance of the fresco this corresponds to a planar
resolution of ≈ 400dpi.
3 EXPERIMENTS
Having a time frame of a few working hours for these
preliminary experiments, the experts selected two im-
portant points of interests. The first experiment was
the acquisition of opposing frescos with mirrored con-
tent in room 10 – the Triclinio (formal dining room).
This was a two-folded task as these frescos cover sev-
eral square-meters and therefore the first part was to
demonstrate a fast and easy work-flow. The second
part concerns the fact that one of the opposing frescos
is supposed to be from a later period and/or another
workshop, which require a highly focused inspection
on points of interest, which for our examples were the
bird in the lower area as this artistic painting requir-
ing a highly skilled craftsperson, which means a high
probability to find characteristic workshop features.
The second experiment was the acquisition of the
faded fresco under the arch in room 11 – the Cubicu-
lum (sleeping room) – to determine its current state. It
was excavated and documented by a drawingin a very
well preserved state in the 1960’s. As it has suffered
heavy weathering in the last 4 decades, by today only
small fractions are barely preserved. Furthermore it is
difficult to access for human inspection as well as for
other means like photography as it is located near the
ceiling in a dark environment(as preventive measure).
Both tasks split into the followingwork-flow. First
the complete fresco is 3D-acquired using a regular
3D-scanner (triTOS-3D). Secondly specific areas of
interest are selected using expert knowledge and 3D-
acquired in higher resolution with our new prototype
multi-spectral 3D-scanner (MSS-3D). The following
sections show results for these two steps of our two
experiments.
3.1 White Light 3D-Acquisition
Figure 2 show a photograph of a part of the acquired
area and our 3D-scanner. Figure 3 shows a visualisa-
tion of the polygonal mesh (3D-model) with texture-
map. Figure 4 shows the same polygonal mesh with-
out texture-map. We have to mention that the heights
and depths of the surface details (z-values) were mag-
nified by a factor of 5 for this visualization.
Figure 2: Fresco on the west wall with triTOS-3D scanner
Note: the bird on the left-hand-side was also acquired using
the MSS-3D multi-spectral scanner.
(a) (b)
Figure 3: Visualisation of the recorded 3D-data of the (a)
west and (b) east wall with texture-map.
An alternative visualisation of the 3D-mesh of the
fresco is shown in Figure 5. The Figure shows the
height as a pseudocolor plot, where the different
colours represent different z-values according to the
corresponding colour-scale (bar top-left). The refer-
ence (z = 0 or xy-plane) is estimated as best-fit plane
of the surface. As the surface was globally smoothed
using the low frequency domain the colours in the
Figure show the global deviation of the shape of the
COMBINED 3D AND MULTISPECTRAL FRESCO DOCUMENTATION OF THE VILLA OPLONTIS, POMPEI -
High-Resolution and High-Performance Digitization of Cultural Heritage
617
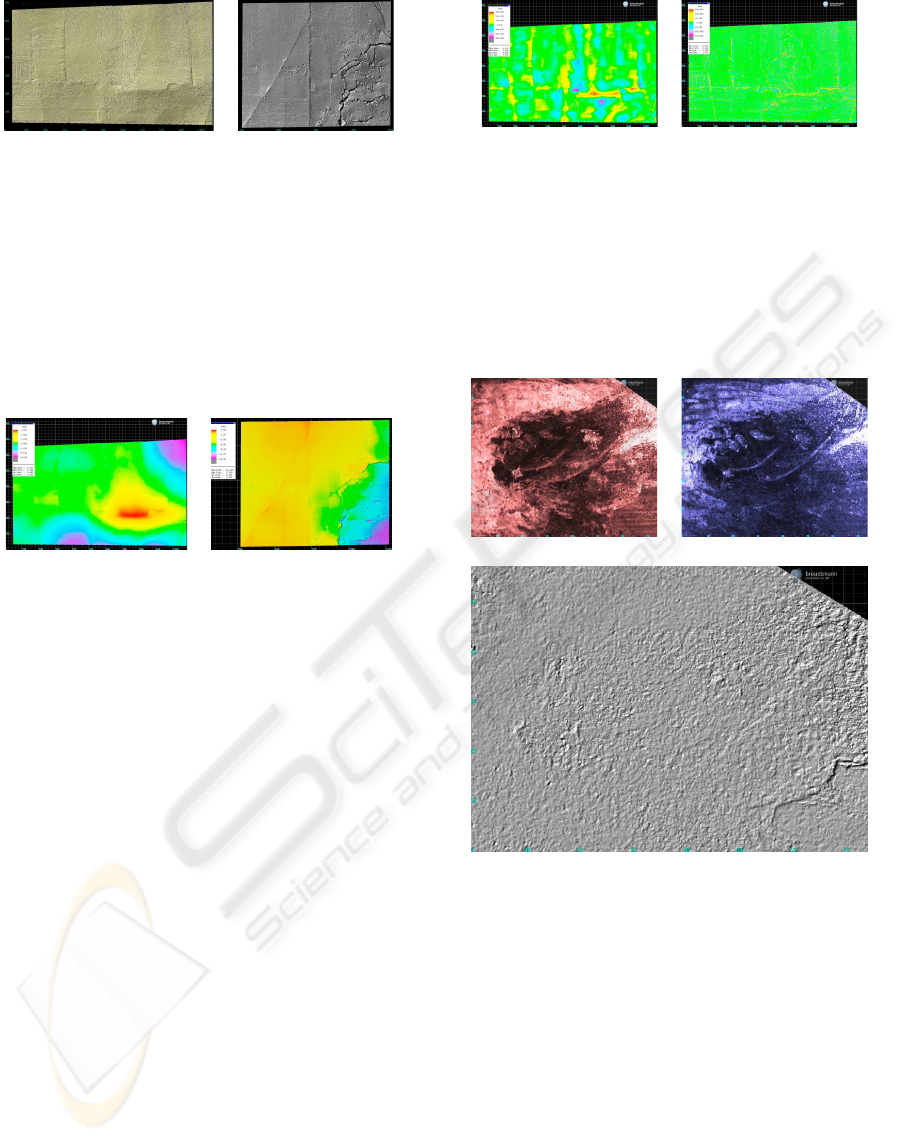
(a) (b)
Figure 4: 3D-data (fresco relief) without colour (z-values
magnified by a factor of 5).
fresco to an ideally flat plane. The deviation can be
introduced by three reasons: First of all and trivial:
man-made objects are never flat. Secondly the devi-
ation could have been introduced during restoration.
Finally it can also be a sign of weathering like water
dispersing into the wall. Practically combinations are
very likely.
(a) (b)
Figure 5: Pseudocolor plot of the height/depth (compared
to a flat plane in the low frequency domain) for the (a) west
and (b) east wall.
A second possibility is a comparison to a curved
surface described by a polynomial function having
higher degrees. Figure 6a shows for example using
a degree of 13. This curved surface is also used as
reference like an ideal plane and aligned using the
same best-fit algorithm. This approach mainly shows
the medium frequency parts of the z-values.
The third possibility is to show only high fre-
quency parts adapted using high pass filters – remov-
ing the low frequency domain (see Figure 6b).
However, the best choice of visualization using
different references and filters depends on the appli-
cation. Regarding our experience of previous appli-
cations for cultural heritage domain a best practice
guide for daily fieldwork will be determined consid-
ering e.g. The London Charter (Beacham et al., 2006;
Ogleby, 2007).
3.2 High-Resolution Multispectral
3D-acquisition
Bird on the west wall. As the east and the west
fresco in room 11 contain a painting of a bird, we
acquired its plumage using the MSS-3D as it has the
most artistic details. Figure 7a,b shows the 3D-scans
(a) (b)
Figure 6: West wall: (a) Comparison with a curved surface
of degree 13, medium frequency domain. (b) Visualization
of the high frequency domain of the 3D-mesh.
using an Infrared and a dark blue filter ”close ultra-
violet”. Figure 7c shows the difference in height be-
tween these two scans. In the lower right corner an
additional layer of paint can be detected having an
average height of 40µm.
(a) (b)
(c)
Figure 7: 3D-mesh of the birds plumage acquired using (a)
Infrared and (b) dark-blue filters. The texture-map shows
the reflection of the filtered light. (c) Difference of height
between the Infrared and dark-blue 3D-meshes. The lower
right corner shows a height of 40µm of an additional layer
of paint. No texture-map is shown.
4 RESULTS
An area of about 1.000 × 600mm has been digitized
by 3D-acquisiton of 6 overlapping areas on the west
wall of room 10. The empiric overlap typically is
≈ 15% depending on surface details. The total ac-
quisition time for this area was 15 minutes. Using -
as previously proposed - controlled lights will only
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
618
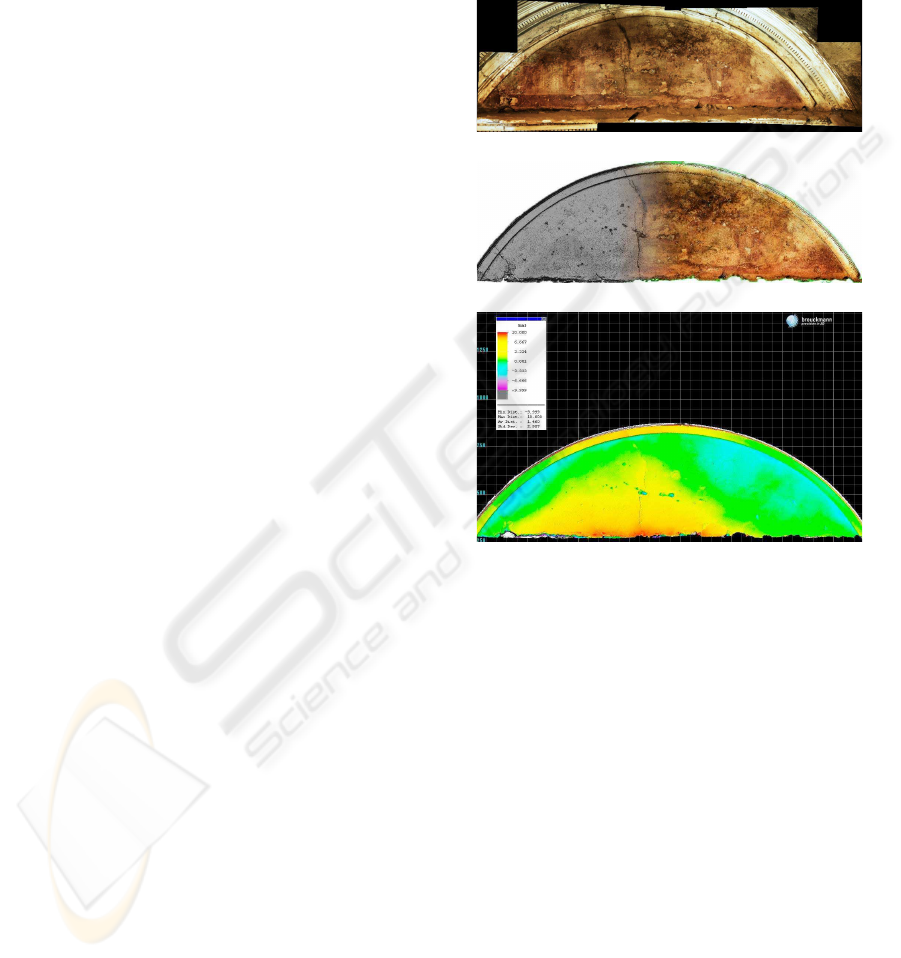
slightly affect the time for setting up the 3D-scanning
equipment, which typically require 15-30 minutes
(per room and/or day). On the opposite (west) wall a
slightly larger area of 1.000× 900mm has been digi-
tized by 3D- acuqisition of 9 overlapping areas within
20 minutes.
The same performance, while maintaining the
high-resolution in the µm- range was demonstrated
for the weathered fresco in room 11. The arc-shaped
fresco under the ceiling in a height of 3m was dig-
itized by 3D-acquisition of 15 overlapping areas re-
quiring half an hour. Due to the lack of photographic
illumination the texture-map of the fresco acquired by
the 3D-scanner lacks proper colour representation in-
cluding highlights from the halogen lamps. To over-
come this we took 9 extra photographs with a Nikon
D300 (at 18mm f/3.6, 12 Megapixel Camera-RAW)
to estimate a panoramic image, which has been used
as alternative texture-map. This procedure shows
an alternate way for colouring a 3D-mesh in case a
higher resolution for the texture-map is required. Al-
ternatively old manual drawings or photographs can
also be mapped for comparison. In this case we
can use the mapped drawing as an overlay to deter-
mine the parts of the fresco lost during the last four
decades. The whole documentation including setup
of the hardware, post-processing and the acquisition
of one multispectral 3D-Image was done in less than 4
hours. Half of the working-time – for post-processing
– can be done in a remote location. Figure 8a shows
the stitched panoramic image of the fresco used as
texture-map. Figure 8b shows the final 3D-mesh with
and without texture-map. Figure 8c shows the dis-
tance in comparison to a flat plane.
Beside high-resolution and high-preformance, we
could also give the experts of archaeology a pre-
cise and therefore objective measurments of impor-
tant features. Just to mention a few, theses features
are anicent traces of the paint-process (seam), paint-
strokes of ancient corrections of the images as well
as modern changes from restauration. Especially for
these features the possibility of ”seeing thru” of layers
of paint proofed valuable for determination of draw-
ing styles, which is important for classification e.g. of
workshops or time-periods.
Another concern is the comparison to other types
and generations of 3D-scanners. For the application
of fresco documentation an in-situ comparison was
not possible due to budget and time constraints. Hav-
ing experience of more than a decade of documenta-
tion of small objects – typically ceramics (Sablatnig
and Menard, 1997) – we can assess that 3D-scanners
no older than three years (e.g. used for (Lettner et al.,
2006)) cannot reach the accuracy shown in this paper
by a factor of 10 or more. This means the level of
required accuracy (Shannon, 1948) for frescos is not
met. Vice versa we can assess that this newgeneration
of 3D-scanners will extend the documentation of any
other type of painted surface known in Cultural Her-
itage (e.g. fine-ware ceramics) by adding information
of the height of a the paint.
(a)
(b)
(c)
Figure 8: (a) Panoramic image used as texture-map, (b) 3D-
mesh (left) without and (right) with texture-map and (c) 3D-
data compared to a flat plane of the fresco in room 11.
5 CONCLUSIONS AND
OUTLOOK
We could show that even large frescos having several
square meters in size can be done in reasonable time,
e.g. during one or two excavation seasons (of typi-
cally 2-4 weeks). It has to be stressed that this is not
only a course documentation, which could be done
by photographs, because we achieve a resolution and
accuracy in m scale. This enables not only the doc-
umentation of the artistic content, it also enables the
documentation of the production technique of frescos
like seams and paint strokes, as well as it reveals mod-
ern, but old restoration attempts. As also degenera-
tion features like cracks or bended surfaces are docu-
mentation we can propose a degeneration prediction,
COMBINED 3D AND MULTISPECTRAL FRESCO DOCUMENTATION OF THE VILLA OPLONTIS, POMPEI -
High-Resolution and High-Performance Digitization of Cultural Heritage
619

which can focus and optimize restoration in an accu-
rate predictive way.
For future work we also propose a cooperation us-
ing mid-range 3D-scanners to embed the highly accu-
rate fresco 3D-scans within a proper 3D-model of the
complete site. This will answer all the preservation
questions from an architectural point of view as well
as for preservation of the frescos themselves in reality
and virtual reality.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
We thank Prof. John R. Clarke from the Univer-
sity of Texas for the invitation to the Villa Oplontis
and his expert advises. We also thank him and his
team for providing in-situ organization of the admin-
istration and infrastructure. Finally we thank the EC
funded CHIRON project (EU contract No. MEST-
CT-2004-514539) under supervision of Prof. Franco
Niccolucci for partially funding this work.
REFERENCES
Beacham, R., Denard, H., and Niccolucci, F. (2006). An in-
troduction to the london charter. In et al., M. I., editor,
The e-volution of Information Communication Tech-
nology in Cultural Heritage: where hi-tech touches
the past: risks and challenges for the 21st century,
Short papers from the joint event CIPA/VAST/EG/Eu-
roMed, Budapest, Hungary. Archaeolingua.
Besl, P. and McKay, N. (1992). A Method for Registration
of 3-D Shapes. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis and
Machine Intelligence, 14(2).
Carcavallo, S. (1980). Oplontis: The Villa Poppea. Weald
Publishing Agency.
Chen, Y. and Medioni, G. (1992). Object Modelling by
Registration of Multiple Range Images. Image and
Vision Computing, 10:145–155.
Clarke, J. R. (1991). The Houses of Roman Italy, 100 B.C.-
A.D. 250: Ritual, Space, and Decoration. Berkeley,
University of California Press.
Cosmas, J., Itagaki, T., Green, D., Grabczewski, E., Gool,
L. V., Zalesny, A., Vanrintel, D., Leberl, F., Grabner,
M., Schindler, K., Karner, K., Gervautz, M., Hynst, S.,
Waelkens, M., Pollefeys, M., DeGeest, R., Sablatnig,
R., and Kampel, M. (2001). 3D MURALE: A Multi-
media System for Archaeology. In Proceedings of the
International Conference on Virtual Reality, Archae-
ology and Cultural Heritage, pages 297–305, Athens,
Greece.
Hoppe, H., DeRose, T., Duchampy, T., McDonaldz, J., and
Stuetzlez, W. (1992). Surface reconstruction from un-
organized points. In Proc. of 19st Annual Conference
on Computer Graphics and Interactive Techniques,
SIGGRAPH, pages 71–78.
Kalasek, R., Mara, H., and Taeuber, H. (2008). Reading
weathered ancient laws in 3rd dimension. In Proc. of
the 13. Int. Tagung: Kulturelles Erbe und Neue Tech-
nologien, page to appear.
Kampel, M. and Sablatnig, R. (2003). An Automated Pot-
tery Archival and Reconstruction System. Journal of
Visualization and Computer Animation, Vol. 14:111–
120.
Lettner, M., Mara, H., Mueller, A., Sablatnig, R., Singer,
M., and Krenn, M. (2006). Pat: Profile analysis tool
for the documentation of archaeological finds. In Sab-
latnig, R., Hemsley, J., Kammerer, P., Zolda, E., and
Stockinger, J., editors, Digital Cultural Heritage - Es-
sential for Tourism, Proc. of 1st. EVA 2006 Vienna
Conference, volume 211 of Schriftenreihe der OCG,
pages 83–90, Vienna, Austria.
Lettner, M., Mara, H., M¨uller, A., Sablatnig, R., Singer, M.,
and Krenn, M. (2006). Pat: Profile analysis tool for
the documentation of archaeological finds. In Proc. of
Electronic Imaging & the Visual Art Digital Cultural
Heritage Essential for Tourism (EVA Wien), pages
83–90.
Leute, U. (1987). Archaeometry: An Introduction to Phys-
ical Methods in Archaeology and the History of Art.
John Wiley & Sons.
Mara, H., Trinkl, E., Kammerer, P., and Zolda, E. (2007).
3d-acquisition and multi-spectral readings for docu-
mentation of polychrome ceramics of the antiquities
collection of the kunsthistorisches museum vienna. In
Proc. of the International Cultural Heritage Informat-
ics Meeting (ICHIM), pages CD–ROM.
Ogleby, C. (2007). The ”truthlikeness” of virtual re-
ality reconstructions of architectural heritage: con-
cepts and metadata. In Proc. of the 2nd ISPRS In-
ternational Workshop 3D-ARCH 2007: ”3D Virtual
Reconstruction and Visualization of Complex Archi-
tectures”, International Archives of Photogrammetry,
Remote Sensing and Spatial Information Sciences Vol-
ume XXXVI-5/W47.
Sablatnig, R. and Menard, C. (1997). 3d reconstruction of
archaeological pottery using profile primitives. In Sar-
ris, N. and Strintzis, M., editors, Proc. of Intl. Work-
shop on Synthetic-Natural Hybrid Coding and Three-
Dimensional Imaging, pages 93–96, Rhodes, Greece.
Sablatnig, R., Menard, C., and Dintsis, P. (1991). A Pre-
liminary Study on Methods for a Pictorial Acquisi-
tion of Archaeological Finds. Technical Report PRIP-
TR-010, Vienna University of Technology, Institute
of Computer Aided Automation, Pattern Recognition
and Image Processing Group.
Shannon, C. (1948). A Mathematical Theory of Commu-
nication. Bell System Technical Journal, 27:379–423
and 623–656.
V´egv´ari, Z. and Breuckmann, B. (2008). High definition
3d-surface scanning and applications in arts and cul-
tural heritage. In Proc. of the 36. Computer Applica-
tions in Archaeology ”On the Road to Reconstructing
the Past” (CAA), page in press.
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
620
