
A CAMERA AUTO-CALIBRATION ALGORITHM FOR REALTIME
ROAD TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
Juan Carlos Tocino Diaz, Quentin Houben, Jacek Czyz, Olivier Debeir and Nadine Warz
´
ee
LISA, Universte Libre de Bruxelles, Avenue Franklin Roosevelt 50 CP165/57, Brussels, Belgium
Keywords:
Camera calibration, Road lane markings, Visual traffic analysis.
Abstract:
This paper presents a new mono-camera system for traffic surveillance. It uses an original algorithm to ob-
tain automatically a calibration pattern from road lane markings. Movement detection is done with a Σ − ∆
background estimation which is a non linear method of background substraction based on comparison and
elementary increment/decrement. Foreground and calibration data obtained allow to determine vehicles speed
in an efficient manner. Finally, a new method to estimate the height of vehicles is presented.
1 INTRODUCTION
Road traffic is increasing each year. Understanding
its characteristics is very helpful to motorway admin-
istrators to cope with this growth, and achieve regula-
tions. Among traffic characteristics, user behaviours
and classes of vehicles are the most relevant.
Until a few years ago, the main measurement tool
for traffic analysis was the magnetic inductive loop.
That kind of sensors has serious drawbacks: it is ex-
pensive to install and maintain. Indeed, it needs to be
placed inside the road, provoking traffic disruption.
Furthermore, it is unable to detect slow or stationary
vehicles, being not accurate for stop and go situations.
On the other side, video sensing is a good solu-
tion since it is inexpensive, easy to install and able
to cover a wide area. Furthemore, it has little traffic
disruption during installation or maintenance. Finally,
video analysis allows monitoring many variables such
as traffic speed, vehicle count, vehicle class and road
state.
Most of the existing video solutions are based on
mono-camera systems. A state of the art can be found
in (Kastrinaki et al., 2003). Among all the methods,
background methods are the most used since they de-
mand small computational power and are simple to
program. In such method, a residual image is ob-
tained from substracting the background from the cur-
rent image (jun Tan et al., 2007). Other solutions
use tracked features, see (Dickinson et al., 1989) and
(Hogg et al., 1984).
In this work, a new mono-camera method for traf-
fic analysis is presented. It uses an original algorithm
to obtain automatically a calibration pattern from road
lane markings. Movement detection is done with
a Σ − ∆ background estimation. It is a non linear
method of background substraction based on compar-
ison and elementary increment/decrement (Manzan-
era, 2008). Foreground and calibration data obtained
allow to determine vehicles speed in an efficient man-
ner. Finally, a new method to estimate the height of
vehicles is presented.
This paper is organized as follows: section 2
presents the auto-calibration algorithm. Methods
used to estimate vehicle characteristics are discussed
in section 3. Experiment results are depicted in sec-
tion 4 and finaly, section 5 ends this paper with the
conclusion.
2 CAMERA
AUTO-CALIBRATION
Road traffic analysis needs a calibrated camera. How-
ever, a camera calibration is performed by observing
a calibration object whose geometry in 3D-space is
known with good precision. In order to avoid the use
of special object of known geometry such as chess-
board, which implies to stop road traffic during op-
eration, the adopted solution is to form a calibration
pattern from the road lane markings. To do that, two
parameters are necessary: the lane length and width.
Based on these values, the algorithm presented in this
626
Carlos Tocino Diaz J., Houben Q., Czyz J., Debeir O. and Warzée N. (2009).
A CAMERA AUTO-CALIBRATION ALGORITHM FOR REALTIME ROAD TRAFFIC ANALYSIS.
In Proceedings of the Fourth International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications, pages 626-631
DOI: 10.5220/0001803906260631
Copyright
c
SciTePress
section determines automatically a good calibration
pattern.
2.1 Camera Model
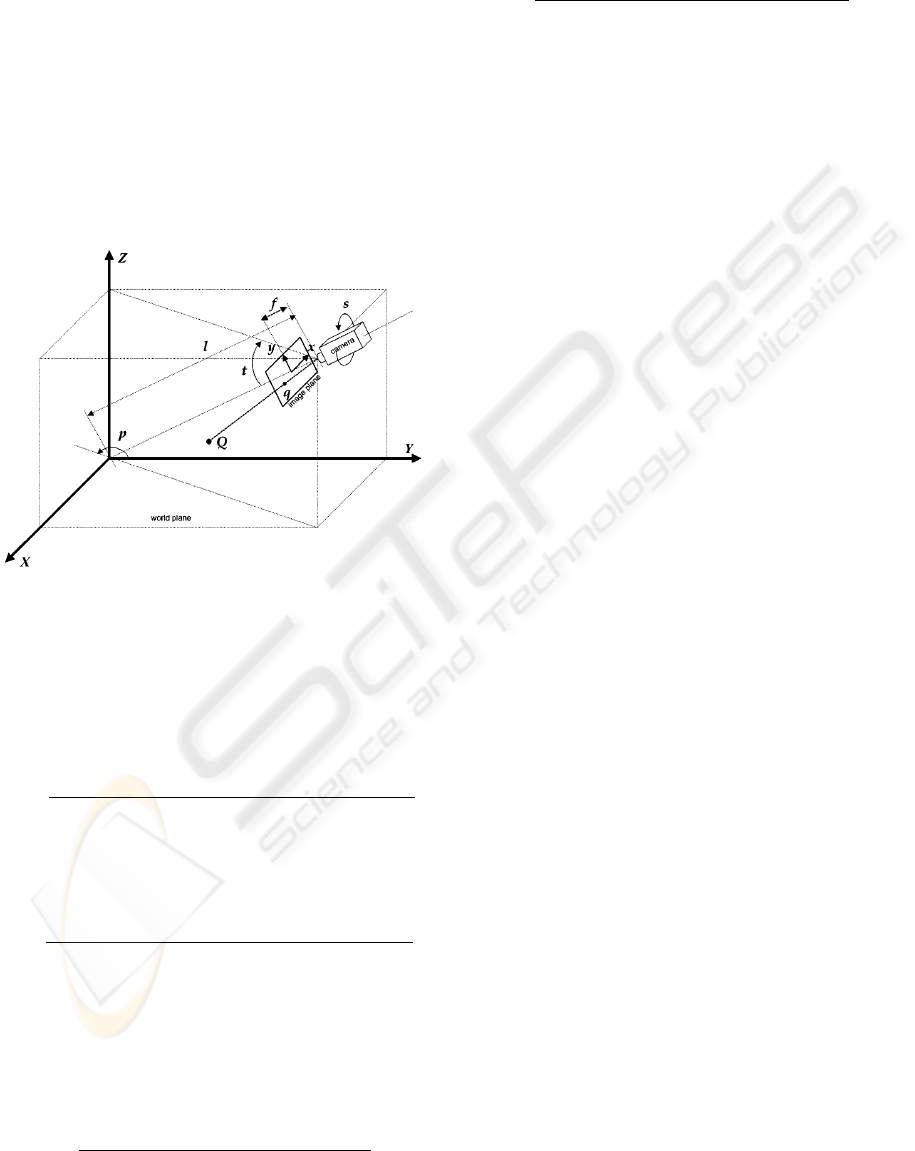
The camera model we use is the one proposed in (He
and Yung, 2007) and (Fung et al., 2003), which is de-
picted in figure 1. This model describes one intrin-
sic parameter (focal length f ) of the camera and all
its extrinsic parameters (height h, pan angle p, swing
angle s and tilt angle t), and defines the relationship
between the image coordinates and the world coordi-
nates in terms of these parameters.
Figure 1: Used camera model (He and Yung, 2007).
Let Q = (X
Q
,Y
Q
,Z
Q
) be an arbitrary point in the
3D world coordinates and q = (x
q
,y
q
) be the corre-
sponding 2D image coordinates of Q. The equations
that relate these two points are
x
q
=
f
X
Q
(cos p coss + sin p sint sins)
+Y
Q
(sin p coss − cos p sint sin s)
+Z
Q
cost sins
−X
Q
sin p cost + Y
Q
cos p cost + Z
Q
sint + h/sint
(1)
and
y
q
=
f
X
Q
(− cos p sin s + sin p sint cos s)
+Y
Q
(− sin p sin s − cos p sint cos s)
+Z
Q
cost sins
−X
Q
sin p cost + Y
Q
cos p cost + Z
Q
sint + h/sint
.
(2)
If we assume that point Q lies on the X-Y plane
then Z
Q
becomes zero and (X
Q
,Y
Q
,Z
Q
) can be calcu-
lated from (x
q
,y
q
) as:
X
Q
=
h sin p (x
q
sins + y
q
coss) / sint
+ h cos p (x
q
coss − y
q
sins)
x
q
cost sint + y
q
cost cos s + f sint
(3)
and
Y
Q
=
− h cos p (x
q
sins + y
q
coss) / sint
+ h sin p (x
q
coss − y
q
sins)
x
q
cost sint + y
q
cost cos s + f sint
. (4)
These four equations define the transformation be-
tween the world coordinates and image coordinates,
knowing the camera parameters. To estimate these
parameters, a calibration pattern of known dimen-
sions is necessary. Next section describes the proce-
dure used to get it.
2.2 Finding a Good Calibration Pattern
The desired calibration pattern is based on the road
lane markings. The first thing needed to automatically
find such a calibration pattern is a good image of the
road to work with. Typically, the background image
is a good solution.
2.2.1 Background Image
The method used is based on the Σ − ∆ filter and
belongs to the substraction technique (Manzanera,
2008). Its operating principle is to calculate a tempo-
ral and local activity map, in order to define automat-
ically the thresholds used to decide if a pixel belongs
to the background or to the foreground, these thresh-
olds being variable spatially and temporally (see fig-
ure 2a).
2.2.2 Lane Markings Detection
Parallel Lines. First of all, the assumption that lane
markings are almost parallel to each other and ap-
proximate straight lines is made.
To detect lane markings, a filter is applied many times
to the background image, but with different parame-
ter values. This filter determines pixels whose neigh-
borhood (first parameter) is brighter than itself with
a certain tolerance (second parameter). The resulting
images obtained with this filter will then be processed.
For each image, a label is assigned to each binary con-
nected components and some of their shape proper-
ties are measured (i.e. the surface, eccentricity, ori-
entation and centroid). Once this has been done, the
properties of the obtained groups in each image are
compared. The ones with more or less stable proper-
ties in all the images are kept. Finally, the groups that
do not comply with certain constraints are rejected.
The remaining groups correspond to various objects
considered as possible lane markings (see figure 2b).
After that, one virtual line is created per detected
object, each line passing through the centroid and
A CAMERA AUTO-CALIBRATION ALGORITHM FOR REALTIME ROAD TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
627

Figure 2: Calibration pattern algorithm.
having the same orientation as its corresponding ob-
ject (figure 2c). These virtual lines are called parallel
lines.
These parallel lines are filtered to retrieve the ones
corresponding to real lane markings (see figure 2d).
The filtering process has three steps. The first one
consists in merging parallel lines whose centroids and
orientation are fairly close. The second step is based
on the neighborhood of each parallel line. For each
parallel line, the neighborhood in the background im-
age is analysed to find bright objects and count them.
Any parallel lines for which too few objects were
found are deleted. Finally, the last step checks the
distance between parallel lines and rejects bad ones.
Once all of this has been done, parallel lines are ob-
tained.
Perpendicular lines. Once the parallel lines have
been detected, finding perpendicular lines can be done
easily. Pixel brightness along every parallel line is
analysed to find the beginnings and ends of lane mark-
ings along that line. Depending on the situation, two
methods can be used to find perpendicular lines. The
first one works only on roads with at least three lanes
while the second one works on roads with at least two
lanes.
For the first method, it is assumed that discontinu-
ous lane markings are more or less synchronous in the
3D space. Starting from this assumption, the parallel
lines detected before are analysed to find lane mark-
ings. Then, virtual lines passing through the corre-
sponding lane markings of each parallel line are cre-
ated, as shown in figure 2e. These virtual lines are
called perpendicular lines.
For a two lanes road, there are only two continuous
lane markings on the edge of the road and one discon-
tinuous lane marking in the middle. A perpendicular
line is obtained by taking a point (called pivot point)
on the parallel line passing through the discontinu-
ous lane marking. The traffic is then analysed to find
near perpendicular lines on vehicles with the assump-
tion that they are travelling along road axis. Each
time such a line is detected passing near a pivot point,
its orientation is used to adjust the perpendicular line
passing through that pivot point, as shown in figure 3.
Figure 3: Perpendicular lines on a two lanes road.
2.2.3 Calibration Pattern
After the lane markings detection, intersections of
parallel and perpendicular lines are calculated and the
four points farthest from each other are kept. These
points form the parallelogram used as calibration pat-
tern to calibrate the camera, as shown in figure 2f.
The reason why a calibration pattern as large as pos-
sible is desired is that it helps minimize the error due
to poor positioning points.
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
628

Figure 4: Features extraction from two consecutive frames a and b.
2.3 Camera Calibration
Once a good calibration pattern is found, the camera
parameters are estimated with the method proposed in
(He and Yung, 2007). The equations (3) and (4) are
then used to project the images on the X − Y plane of
the 3D world (Z
Q
= 0), as shown in the figure 5.
Figure 5: Image projection.
3 VEHICLE FEATURES
EXTRACTION
Extracting vehicle features implies detecting the traf-
fic. A common way to do this is to subtract the
background image (see section 2.2.1) from the current
frame to get a foreground image. In this approach, in-
stead of working with the whole image, virtual lines
called profile are used. Figure 4 shows an example
of one profile analysis. For the sake of clarity, just
one profile is shown in this example but, of course, as
many profiles as necessary can be defined. Typically,
five profiles per lane is quite sufficient.
3.1 Speed Estimation
Once features of a vehicle have been extracted from
two frames, estimating its speed by measuring the dis-
tance between the beginning of its signal in successive
frames is possible, as shown in figure 4.
3.2 Height Estimation
Based on the deformations visible on vehicle profile
(due to the perspective effect), estimating the height
of this vehicle is possible. Indeed, the equations (3)
and (4) used for the transformation from image coor-
dinates to world coordinates project the images on the
X-Y plane of the 3D world. This implies two things.
First, the more a point is high above the ground,
the more its distance from the camera will be over-
estimated. And second, the more a point above the
ground is far away from the camera, the more its dis-
tance from the camera will be over-estimated too. So,
a relation between the height of a vehicle and the de-
formation of his profile from a frame to another can
be found.
Figure 6 shows what happens when a car (repre-
sented here by a box) approaches the camera. Be-
cause the points A and B are known, distance c can be
calculated. Then, through the tilt angle of the camera,
angles
b
A and
b
B
2
are obtained, wich leads to
b
B
1
and
b
C.
Finaly, using the classical law of sines
a
sin
b
A
=
b
sin
b
B
=
c
sin
b
C
(5)
length a and height h of the vehicule are found.
4 EXPERIMENTAL RESULTS
To validate the features extraction and the speed esti-
mation method, a test was conducted on a video se-
quence. The results are presented in table 1. For your
A CAMERA AUTO-CALIBRATION ALGORITHM FOR REALTIME ROAD TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
629

Figure 6: Vehicle height estimation.
information, the last value one pass corresponds to
the estimated speed, using only the first and the last
frame (i.e. the first frame in which the vehicle is visi-
ble and the last one in which it is still visible). Un-
fortunately, these results could not be validated for
lack of radar measures. However, they ensured us that
the estimated speed was consistent compared with the
video sequence.
Table 1: Estimation speed results (in km/h).
To validate height estimation method, a chess-
board with known dimensions is used to calibrate the
camera. Then, two pictures of moving objects on the
chessboard are taken. Finally, the height of these ob-
jects is estimated. Table 2 shows that results have an
estimation error of less than 3%.
Table 2: Estimation height results (in mm).
5 CONCLUSIONS AND FUTURE
WORK
In conclusion, a mono-camera system for traffic mon-
itoring that can accurately and automatically calibrate
itself has been presented. It detects all the vehicles
and estimates their speed, and because it doesn’t need
all the image pixels to work, it is quite efficient. Addi-
tionally, a method to estimate vehicle height has been
presented which, according to first tests, should op-
erate relatively well. Furthermore, once the vehicle
height will be known, estimating its width and length
will be possible.
REFERENCES
Dickinson, K.W., and Wan, C. (1989). Road traffic moni-
toring using the trip ii system. In Second International
Conference on Road Traffic Monitoring.
Fung, G. S. K., Yung, N. H. C., and Pang, G. K. H. (2003).
Camera calibration from road lane markings. Optical
Engineering, 42(10).
He, X. C. and Yung, N. H. C. (2007). New method for
overcoming ill-conditioning in vanishing-point-based
camera calibration. Optical Engineering, 46(3).
Hogg, D. C., Sullivan, G. D., Baker, K. D., and Mott, D. H.
(1984). Recognition of vehicles in traffic scenes using
VISAPP 2009 - International Conference on Computer Vision Theory and Applications
630

geometric models. In Road Traffic Data Collection,
volume 242, pages 115–119.
jun Tan, X., Li, J., and Liu, C. (2007). A video-based
real-time vehicle detection method by classified back-
ground learning. World Transactions on Engineering
and Technology Education.
Kastrinaki, V., Zervakis, M., and Kalaitzakis, K. (2003). A
survey of video processing techniques for traffic appli-
cations. Image and Vision Computing, 21:359–381.
Manzanera, A. (2008). Progress in Pattern Recognition,
Image Analysis and Applications, volume 4756/2008
of Lecture Notes in Computer Science, chapter Σ − ∆
Background Subtraction and the Zipf Law, pages 42–
51.
A CAMERA AUTO-CALIBRATION ALGORITHM FOR REALTIME ROAD TRAFFIC ANALYSIS
631
