
COLLIMATION OF X-RAY DIAGNOSTIC BUNDLE BY MEANS OF
STEERING FERROFLUID
Andrzej Dyszkiewicz
1,2,3
, Paweł Połe´c
1,3
, Jakub Zajdel
1,3
, Bartłomiej Pawlus
3
Damian Chachulski
1,3
and Paweł Kpi´nski
1,3
1
Laboratory of Biotechnology Cieszyn ul.Go´zdzik´ow, 2, Poland
2
Technical University of Opole, Faculty of Physical Education and Physiotherapy, Poland
3
Specialist Rehabilitation Department ”VIS” Cieszyn ul. Bielska 3A, Poland
Keywords:
Incoherence x-ray beam, Collimation of x-ray beam, Ferrofluids, Computer steering.
Abstract:
The study addressed the problem of the incoherence of an X-ray tube generated bundle. In spite of the large
progress made in the area of the durability and efficiency of these devices, the problem of the inherent diver-
gence of the bundle hasnt yet been resolved in a satisfying way. In the face of difficulties with concentrating
X-rays, the only practical way of eliminating non-axial rays is by applying lead collimators of a suitable length
and diameter as well as mechanical systems of movable distracting grids. An entirely new approach has been
the use of electro-magnetorheological fluids as filters, which are capable of modifying their physical and quan-
tum properties contingently based on the parameters of the applied external electric current, centrifugal force
and magnetic field. The experiments carried out showed, that the described changes also concern the absorb-
tion, distraction or change in the direction of the X-ray beam. In the constructed prototype device, interesting
and recurrent results in the modification or eleimination of non-axial rays were obtained, which resulted in the
improvement of the quality of bone images. The following research questions were posed: (1) are changes
in the photodensitometric parameters of joint (PIP) X-ray images containing soft and osseous tissues proof
of alterations of the physical parameters of a diagnostic X-ray beam? (2) is there a relationship between the
volume of ferrofluid in a lens and its capability to alter the parameters of a permeating X-ray beam? (3) is there
a relationship between the r.p.m. of the collimator and its capability to alter the parameters of a permeating
X-ray beam, and does it have a linear character? Based on the conducted research a non-linear dependancy
was observed between the volume of ferrofluid in the lens as well as its rotational speed and the capability of
the system to alter the parameters of the permeating X-ray beam.
1 INTRODUCTION
William Roentgens pioneer works began a completely
new chapter in the history of medical diagnostics, en-
abling small invasive investigationsof internal organs,
especially the osseous tissue. Progress in the field
of electronics resulted in X-ray tubes becoming in-
creasingly more efficient, reliable and the repeatabil-
ity of emission in relation to a given electric param-
eter was largely improved (Bankier et al., Carlson,
Dyszkiewics, 2001, Dyszkiewics, Folster, Grampp et
al., 1997b, Ławniczak and Milecki, 1999). From
the dawn of the development of radio-photographic
technology, beginning with tubes with a motionless,
and later rotating and multi-focal anode, constructors
struggled with the problem of the originally divergent
diagnostic bundle, the geometry of which results from
the way an X-ray beam is formed as a consequence
of breaking the stream of accelerated electrons on the
anode. A divergent bundle produces geometrical dis-
tortions and leads to a considerable worsening of the
acutance of the photo. A large quantity of non-axial
rays is the reason for this phenomenon. Constructors
of X-ray tubes have been trying to achieve a larger co-
herence of the bundle for many years. As a result, the
use of collimators began, that is, thick-walled tunnels,
made of materials of a large thickness, able to absorb
non-axial rays. Applying tubes with a multi-focal
anode was another solution, which enabled a better
adaptation of the bundle geometry to the distance of
a photographed object. Still another solution was the
use of stable filters or oscillating metal grates placed
above the film, distracting non-axial rays (Czerny et
al., 1997, Grampp et al., 1997a, Kainberger, et al.,
1997, Kollmann, et al., 1997, Kramer et al., 1997). In
spite of the results achieved in improving the quality
of X-ray images, it can be clearly observed that these
activities lead exclusively to the removal of part of the
441
Dyszkiewicz A., Połe
´
c P., Zajdel J., Pawlus B., Chachulski D. and Kpi
´
nski P. (2009).
COLLIMATION OF X-RAY DIAGNOSTIC BUNDLE BY MEANS OF STEERING FERROFLUID.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices, pages 441-447
DOI: 10.5220/0001817704410447
Copyright
c
SciTePress

rays from the bundle by using materials of large den-
sity, which only increase the difference between the
real and effective power of the tube and have a mea-
surable influence on the weight and durability of the
device (Dyszkiewicz, 1999, Dyszkiewicz, 2001, Ma-
jumdar et al., 1997, Phule, Rand et al., 1997, Sasaki).
One new innovative solution used by scientists in
Geneva has been the application of ferrofluids with
variable physical and chemical parameters, which, af-
ter being introduced into capillary tubes placed in an
X-ray beam axis allow the parameters of the beam to
be changed contingently.
1.1 Ferrofluids
Ferrofluids display the characteristics of both fluids
and magnetic substances at a very wide temperature
range. With the absence of an external magnetic
field they behave like normal newtonian fluids, where
the shear stress is in direct proportion to the shear
velocity without displaying any signs of magnetisa-
tion. The viscosity of controlled ferrofluids can be
adapted within a range of 5 - 25 000 cP. Analogi-
cally to electrorheological fluids they are built of two
basic components: carrier fluid (<85% ) and ferro-
magnetic particles covered with a surface layer (from
2% to 15% , for ferrofluids, up to 80% for MRF).
The carrier fluid is a non-magnetic substance; how-
ever the components of the particles of the suspen-
sion are solid soft magnetic materials which form mi-
cromagnets [27]. Removing the action of Van der
Waals forces and magnetic attraction forces (group-
ing) makes it possible to cover the particles with a
surface active agent (e.g. oleic acid). Depending on
the size of the particles two types of ferrofluids can
be distinguished: (1) nanomagnetorheological also
called ferromagnetic; (2) magnetorheological fluids
MRF. In ferromagnetic fluids the diameter of the par-
ticles (most commonly Fe
3
O
4
) ranges from 3 15nm.
At smaller sizes they do not display any magnetic
properties. Normally, synthetic oil is used as a car-
rier, or (not so often) light mineral oil, esters, glycer-
ine, poliphenyl or water. The maximum magnetisa-
tion of 0,6T domains limits the magnetic absorption
of the fluids (0,005 0,13 T) and the maximum shear
stress is less than 5 kPa. They can operate at tem-
peratures from -65 to 200 C, as it is within this range
that magnetisation is independent from temperature.
Their durability depends on the evaporative power of
the carrier fluid, which should be as low as possible
whilst the conductivity of the entire system should
be the highest. As the particles are of small dimen-
sions they do not accumulate at the bottom of the
container even if the fluid remains still for long pe-
riods of time (they are raised as a result of thermic
motions). In magnetorheological fluids the size of the
particles ranges from 0,5 to 8 mm. Mineral or sil-
icon oil with a low evaporative power is used most
often as the carrier fluid. In industrial applications the
magnetic induction can total 1,2T (max.2,15T).These
properties do not change within the temperature range
of -50 ÷ 150C. The maximum shear stress at a mag-
netic field strength of 150 ÷ 250 kA/m is 50 to 250
kPa. A characteristic feature of magnetorheological
fluids is their capability of rapidly (<10ms) changing
their viscosity after a relatively weak magnetic force
is applied. Leaving the magnetorheological fluid still
leads to the accumulation of particles at the bottom of
the container, which is their drawback. However, their
production is much easier, making them significantly
cheaper compared to ferromagnetic liquids. In the sit-
uation when an external magnetic field is not present,
the magnetic moments linked to the particles are dis-
tributed at random, which leads to a complete dissipa-
tion of their forces. After applying an external force,
the magnetic moments of the particular particles line
up along the flux created by the force field and thus
are no longer subject to thermal currents. This mech-
anism is similar to the mechanism of chain creation
in electrorheological fluids. Magnetorhelogical fluids
display considerably stronger magnetisation than fer-
rorheological fluids. By controlling the strength of
the magnetic field we can influence the viscosity of
the fluid, e.g. with a field of ca. 200 kA/m it can
reach a value of 700 P for magnetorheological fluids
and 50 P for ferromagnetic fluids, which allows for
the application of shear stress of 100 kPa and 5 kPa
respectively.
1.2 New Methodology
The prototype device has been shown in fig. 1a. It
consists of a ring with grooves adapted to the dimen-
sions of the electromagnets or solid magnets active
elements, which are synchronised geometrically and
parametrically to work at a desired angle within the
ring, where a suitable container with ferrofluid has
been placed.
1.3 Collimator Function
A collimator (fig. 1a) is composed of a cylinder filled
with ferrofluid which serves as a diffraction crystal.
The ferrofluid, being situated inside a ring contain-
ing several or more powerful magnets with alternate
or compatible polarities becomes spatially organised,
forming the shape of a convex lens with a relatively
large curvature and containing additional smaller lo-
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
442

Figure 1: Collimator for modifying the geometry and en-
ergy of the diagnostic X-ray radiation: (a) example arrange-
ment of fixed magnets or electromagnets in induction ring;
(b) concept showing the relation between the induction of
the magnetic field (increasing the thickness of the lens) and
centrifugal force in a rotating motion, the action of which
flattens the curvature of the ferrofluid lense.
Figure 2: Collimation system: (a) view of ferrofluid inside
the inducting ring of the collimator at one magnet config-
uration; (b) laboratory unit on a adjustable stand equipped
with a dental X-ray tube.
cal convexes. After putting the entire arrangement
into motion by an electric motor, the action of cen-
trifugal forces which act in an opposite direction to
the magnetic inductance vector decrease the size of
the lens curvature proportionally to the speed with
which the magnetic ring turns and in inverted propor-
tion with the value of the magnetic inductance (fig.
1b).
The X-rays emitted from the tube, when passing
through a collimator are curved to the axis, concen-
trated in the focal point or are diverged away from the
axis (dispersed) depending on the type of ferrofluid
used, the shape of the field (depending on the num-
ber and induction of the used magnets or additional
electrodes) as well as on the rotational speed of the
collimator.This allows the rays which are outside the
axis to be aligned towards it or focused. Using a col-
limator also enables energetic filtration to take place
which eliminates image distortions resulting from an
uneven distribution of radiation on the images plane
(initially divergent beam) (fig. 2a).
The operation of the new generation collimator
Patent P366266 is based on Lawrence Braggs law,
which explains the mechanism of how the path of
hard radiation is distributed in a crystal. Ray 1 falls
Figure 3: The central element of the collimator is its rotat-
ing ferrofluid lens, the curvature of which is determined by
the relation between the centrifugal force and the magnetic
induction of the rings magnets. (a) the initially divergent X-
ray bundle is modified especially within the range of non-
axial beams (b) Braggs law describes this process.
onto the surface of the crystal at angle V and affects
the electron layer of atom C, whilst the second beam
which is parallel to beam 1 affects the layer of atom
M. The electron layers of the atoms scatter the X rays.
The symmetry straight AC which is perpendicular to
the incident rays constitutes the face of the incident
wave. Such is also line BC a wave scattered at an-
gle V. As a result the difference between the paths of
rays 1 and 2 is AM + MB. Triangle AMC produces
the following formula:
AM = dsinV(1)
where d is the distance between neighbouring planes
in the crystal. AM = MB, thus the difference between
the paths of beams 1 and 2 is:
2dsinV(2)
Amplification takes place when the difference be-
tween the paths of two rays equals an integral mul-
tiple of the the length of wave 1. Thus the condition
for amplification can be expressed by:
2dsinV = nl(n = 1, 2, ...)(3)
If this condition known as Braggs formula - is ful-
filled, then the scattered beams 1 and 2 become am-
plified and a reflection will occur. It can be noticed
that the reflection is a result of scattering and interfer-
ence (Bankier, et al.). Experiments have shown that
the computer controlled prototype collimator allows
a sharp focus of the divergent beam to be obtained in
a precisely determined point of a structure (fig. 4a, b),
and the focus to be precisely moved within the tested
structure (scanning). Such a system creates the foun-
dations for gradient tomographywithout a need to use
the expensive gantry system and multislice scanners.
2 AIM OF WORK
The subject of the clinical tests was the RTG UDR1
prototype collimator. The tests were conducted
COLLIMATION OF X-RAY DIAGNOSTIC BUNDLE BY MEANS OF STEERING FERROFLUID
443

Figure 4: One of the first images taken- the authors hand
showing two extreme parametrical compositions: (a) image
taken by axial beams at 770 r.p.m., displaying a sharp bone
trabeculae structure with an almost complete elimination of
soft tissue; (b) image taken with a non-axial beam com-
ponent at 650 r.p.m. displaying soft tissue with an almost
completely faded bone trabeculae structure.
among a group of healthy volunteers employed as re-
searchers at the Laboratory of Biotechnology. The
aim of the research was to answer the following ques-
tions:
(1) Does a ferrofluid which is spatially organised in
a magnetic field and put into a spinning motion
change the properties of a permeating diagnostic
X-ray bundle produced by a dental X-ray unit?
(2) Are changes in the photodensitometric parame-
ters of joint (PIP) X-ray images containing soft
and osseous tissues proof of alterations of the
physical parameters of a diagnostic X-ray beam?
(3) Is there a relationship between the volume of fer-
rofluid in a lens and its capability to alter the pa-
rameters of a permeating X-ray beam?
(4) Is there a relationship between the r.p.m. of the
collimator and its capability to alter the parame-
ters of a permeating X-ray beam, and does it have
a linear character?
2.1 Subjects Tested and Method
Male white-collar volunteers aged 356, 7 , in good
health were qualified for the research.
Excluding Criteria. History of hand injury (bruises,
dislocation, fracture) treated by immobilisation, in-
flammation of the joints, osteoporosis, diabetes,
heavy physical work or extreme sports, contact with
vibration, ionising radiation.
Testing Apparatus. The tests were carried out in a
standard room of the Laboratory of Biotechnology in
Cieszyn under the supervision of a Radiology Protec-
tion Inspector (of the Central Laboratory for Radio-
logical Protection), on a prototype UDR1 collimator
linked to a small-size Siemens X-ray unit for standard
dental diagnostics. All photos were made with a 0.5
second exposure time using 50kV to power the tube.
The registration of the bone structure radiograms and
their conversion to digital form was carried out on a
DIGORA dental 30 x 50mm matrix.
Test Method. The aim of the experiments was to test
the possibilities of controlling an X-ray beam by us-
ing different rotational speeds of a ferromagnetic lens
composed of different volumes of ferrofluid and also
to determine the applicability of the obtained photos,
which were modified in terms of quality, in diagnostic
medicine. The experiment schedule included:
1. Performing a series of shots of the PIP 3 (R) joint
with a lens containing 0.5 ml of ferrofluid at 11
ascending and repeatable rotational speeds of the
collimator.
2. Performing a series of shots of the PIP 3 (R) joint
with a lens containing 1.5 ml of ferrofluid at 11
ascending and repeatable rotational speeds of the
collimator.
3. Performing a selective densitometric analysis of
bone trabeculae groups in standard measurement
area locations (fig. 5) by means of the Structure
1.0 software.
4. Performing an analysis in measurement areas lo-
cated diagonally to the length axis of the long
bone with visible soft tissue on one side of the
bone P(1) and on the other P(2) by means of
the authors trademark ”Density 1.0” software (fig.
6,7).
Following a 5 minute acclimatisation in the labora-
tory, the tested persons were seated in a comfortable
position at station UDR1, placing their hands loosely
on the positioning pad. The trunk and legs of the pa-
tient were screened by a standard protective lead rub-
ber apron. The geometric axis of the lamp was di-
rected at the center of the picture converting matrix
size 20 x 30 mm, and the hand position pad forced
the third finger of the right hand to be situated so that
the axis also passed through the center of the PIP III
(R) gap. The distance between the bottom opening of
the X-ray tube collimator and the surface of the ma-
trix was 100mm. In the first series the shot was taken
through a still lens containing 0.5 ml of ferrofluid.
Then the collimator was put into a spinning motion
for the 10 subsequent rotational speeds and shots were
taken at approx. 30-40 second intervals following the
stabilisation of the successively set speed. In the sec-
ond series the lens was replaced with one containing
1.5 ml of ferrofluid and all of the above procedures
were repeated for the 10 rotational speeds. A standard
system of DIGORA converting matrices was used to
register the images and enabled the X-ray shadow to
be saved directly and repeatably in the computers op-
erational memory in BMP format which, as a result,
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
444
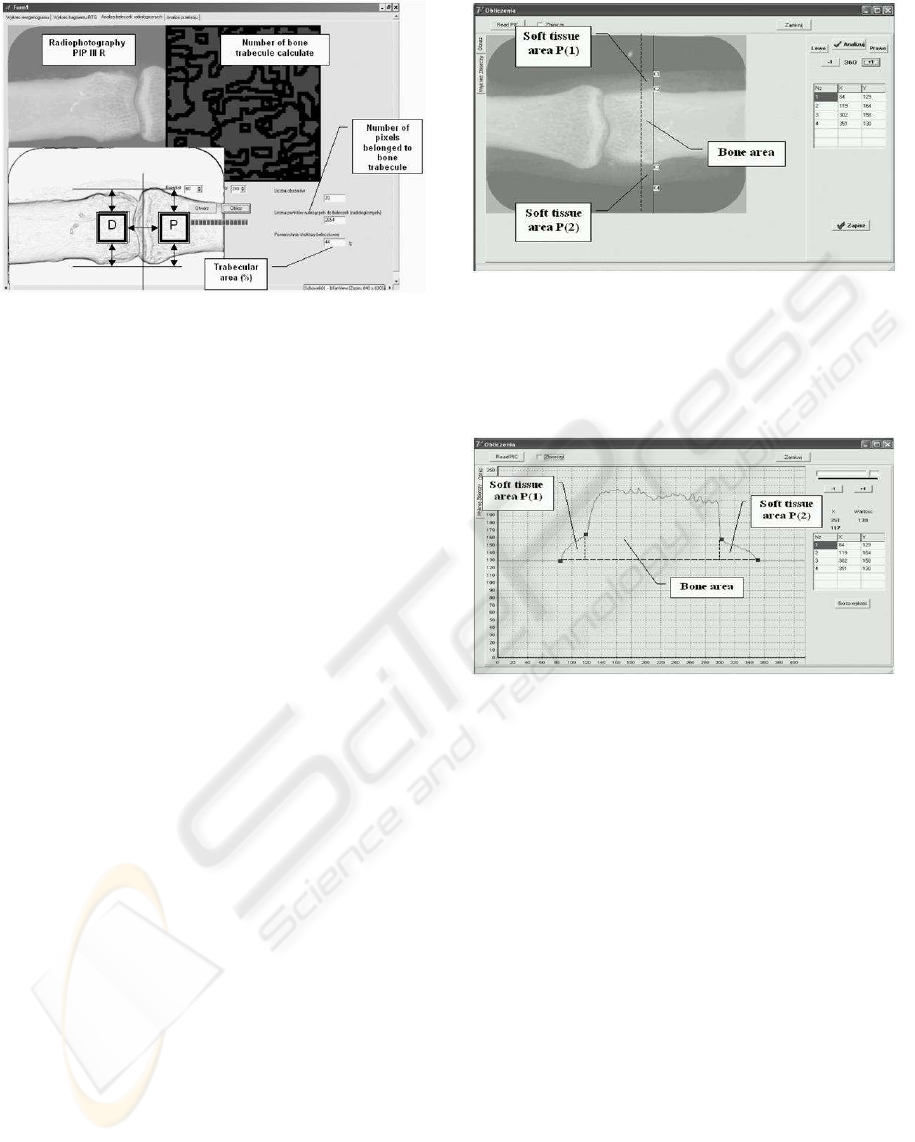
Figure 5: ”Structure 1.0” graphical interface allowing for
the determination of the surface area of pixels belonging to
the visible bone trabeculae groups in measurement fields P
and D.
allowed for the complete elimination of errors which
could occur if the images were processed photochem-
ically.
X-ray Image Analysis
(1) Analysis of the visible bone trabeculae groups
surface area compared to the surface of the en-
tire image performed via the authors trademark
Structure 1.0 software implemented in the C++
environment. The standard area around the proxi-
mal phalangeal II (P) epiphysis and the distal pha-
langeal I (D) epiphysis, proximal interphalangeal
joint of the right hands third digit.
(2) Analysis of the X-ray shadows photdensitomet-
ric cross-section - was performed by the authors
trademark ”ensity 1.0” software implemented in
the ”Delphi 7.0 Professional” environment. The
program enables a photodensitometric evaluation
to be made of the image in the measurement field
situated crosswise to the long bone axis with con-
sideration given to the soft tissue background on
one side of the bone (P1), the bone area (P3) and
the soft tissues (P2) on the other side of the bone
area (fig. 5,6).
2.2 Results
Next pictures shows the results of photodensitometric
tests of bone trabeculae groups visible macroscopi-
cally in X-ray shadows of the PIP III joints, made in
a stand which positioned the axis of the bone against
the X-ray beam, and processed by the ”Structure 1.0”
software. The averaging results for the relative den-
sity in measurement field P (proximal epiphysis) and
D (distal epiphysis) were based on the 11 tested col-
limator rotational speeds. The picture fig. 8 presents
Figure 6: ”Density 1.0” graphical interface enabling the
preparation of a histogram displaying the optical density in
the measurement field situated typically around the distal
phalangeal epiphysis of the right hand’s third digit. The
program performs a measurement in the soft tissue areas
P(1), P(2) and in the bone area.
Figure 7: Example histogram displaying the optical density
in area P(1), P(2), B(bone area).
differences between the average values in measure-
ment areas P and D.
Measurement data displayed in diagrams 8-10
show the non-linear dependency between the degree
of the modification of the X-ray beam and the rota-
tional speed.
3 CONCLUSIONS
(1) The ferrofluid which has been spatially arranged
in a magnetic field and put into a rotational motion
changes the properties of the permeating diagnos-
tic X-ray (with constant and repeatable parame-
ters), inducing changes in the clarity and optical
density of the soft tissue and bones.
(2) Changes in the optical clarity and translucency of
the analysed fragments of X-ray images of soft
tissues and bones obtained from a repeatable lamp
exposition at different collimator parameter set-
tings prove that changes in the physical properties
COLLIMATION OF X-RAY DIAGNOSTIC BUNDLE BY MEANS OF STEERING FERROFLUID
445
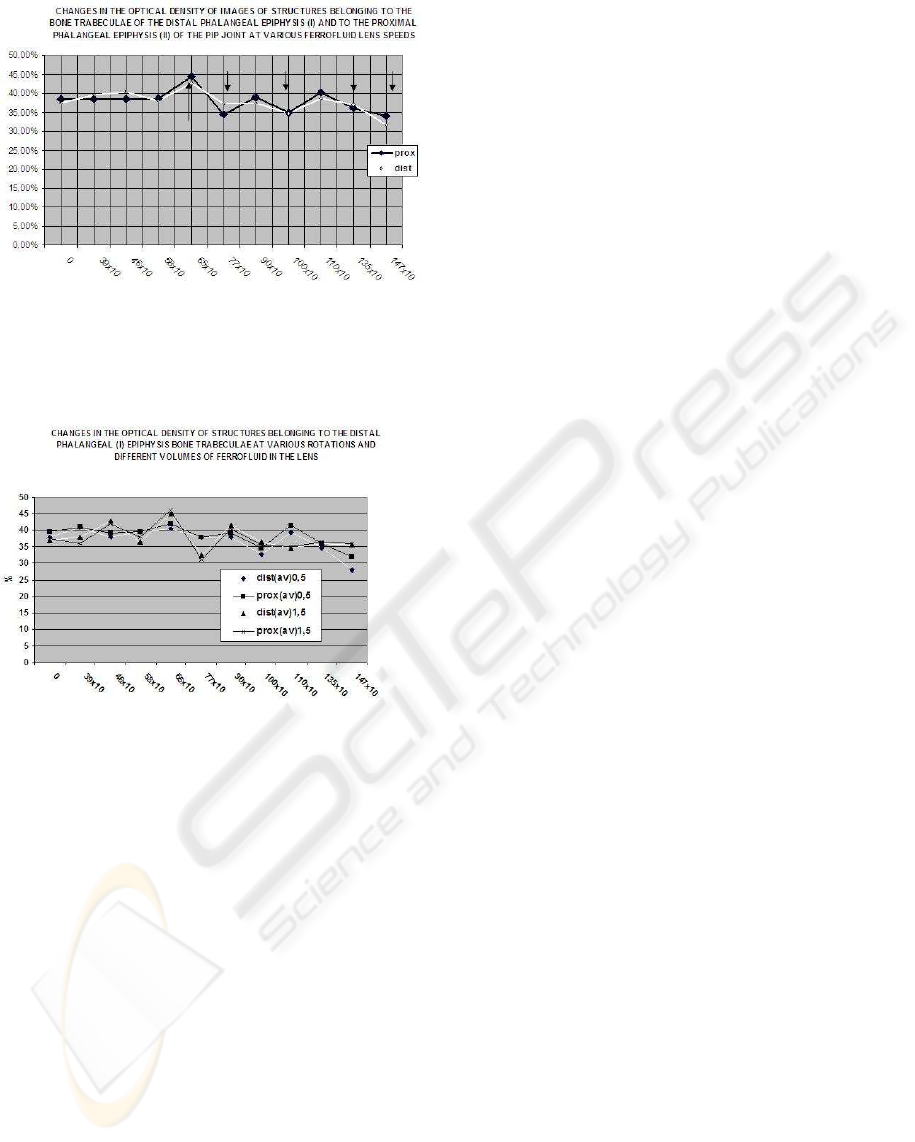
Figure 8: Averaging photodensitometric values of bone tra-
beculae groups in measurement areas P and D in X-ray
shadows made by the collimator at 11 rotational speeds of
the lens with ferrofluid (significant changes occurred at 650,
770, 1000, 1350, 1450 r.p.m).
Figure 9: ”Structure 1.0” diagram presenting the averaging
optical density values of structures belonging to macroscop-
ically visible bone trabeculae in areas (P1) and (P2), (D1)
and (D2) for images made by lenses containing 0.5 and 1.5
ml of ferrofluid respectively.
of X-ray beams have occured
(3) A dependency has been noted between the vol-
ume of ferrofluid in the lens and its capability of
changing the permeating X-ray beam
(4) A non-linear dependency has been noted between
the rotational speed of the collimator and its capa-
bility of changing the permeating X-ray beam
4 DISCUSSION
The original divergence of a diagnostic X-ray bundle
resulting from the design of the X-ray tube is an is-
sue which has been accompanying radiological diag-
nostics ever since the emergence of the method. The
heterogeneity of the beam leads to significant geomet-
rical changes of the image and causes an uneven dis-
tribution of radiation on the surface of the registering
matrix. Attempts at a compensating this issue focus
on two main areas:
(1) computer image processing
(2) technical elimination of non-axial beams
The collimation of non-axial diagnostic X-ray beams
has for long been performed by means of moving fil-
ters (grids) or by lead collimators with thick walls
and a narrow pass which allowed only axial beams
to pass through. One drawback of using this type of
collimator is facing a significant loss of the tube’s ef-
fective power as the axial beams constitute a small
share of the entire emission. Correcting an X-ray im-
age by homogenising the optical density and restoring
the geometric relations to a 1:1 status entail a com-
plete remodelling of the image matrix which results in
breaching the principle of filing patients’ test results
in lossless formats (Dyszkiewicz, Wrbel; ICXOM
Vienna 2001). An interesting approach to solving
this issue were attempts at modifying the direction
of non-axial beams (Atkinson K, Folkard M et all;
ICXOM Chammonix 2003) based on magnetorheo-
logical fluids which made it possible to make imme-
diate changes to the parameters of the beam by using
filters of varying densities (Remesh, N; Malagodi D at
all; ICXOM Chammonix 2003). A completely differ-
ent approach, on the other hand, was the idea of con-
structing a collimator which would be able to mod-
ify the propagation angle of non-axial beams towards
the axis and even to focus them (Dyszkiewicz, Wrbel
ICXOM Chammonix 2003), which would result in an
insignificant loss of energy from the initially diver-
gent beam while maintaining relatively good control
over the parameters of the produced image (e.g. expo-
sition of soft tissue (fig. 4b) or hard tissue (fig. 4a)).
The conducted laboratory experiments have proved
that the ferrofluid which has been spatially arranged
and put into motion by a magnetic field changes the
properties of the permeating diagnostic X-ray beam
generated in a parametrically repeatable manner by
the tube (permanently coupled with the collimator),
located at a fixed distance away from the tested dig-
its on the hand (positioned against the tubes axis by
means of a special stand), inducing changes in the
optical clarity and density of the contours of soft tis-
sue and bones. Changes in the contrast and thick-
ness of the edge contour of the bone tissue’s struc-
ture are accompanied by a change in the proportions
between the axial and non-axial rays in the diagnos-
tic beam, enabling or disabling the development of a
sharp and narrow border line in the presence of an
excess numer of rays. Changes in the optical clarity
and translucency of the analysed fragments of X-ray
images of soft tissues and bones obtained from a re-
BIODEVICES 2009 - International Conference on Biomedical Electronics and Devices
446

peatable exposition at a fixed distance from the object
and different collimator parameter settings prove that
changes in the physical properties of X-ray beams oc-
cur. Proof of the existence of a dependency between
the volume of ferrofluid in the lens and the lens’ capa-
bility for modifying the parameters of the permeating
X-ray beam was of significant importance in confirm-
ing the influence of ferrofluid on the physical proper-
ties of an X-ray bundle. This may in the future lead
to the creation of lenses for various practical applica-
tions. A non-linear dependency has also been found
between the collimator’s rotational speed and its abil-
ity to modify the parameters of the permeating X-ray
beam. This feature seems to be best evidence that
interference occurs at closely quantized electron or-
bits of atoms belonging to the rotating quasi-crystal
of the ferrofluid as it should be remembered that if
the crystal was understood to operate as a simple stop,
the characteristics would most probably have a linear
character. Therefore the clear dependency between
the modifying properties of the collimator and the ro-
tational speed, exluding changes in the volume of fer-
rofluid, seems to be of significant value for the fu-
ture perspective of creating easily-controllable units,
serially produced devices broadening the diagnostic
capabilities of standard X-ray tubes or enhancing the
further development of work on gradeint tomography.
Although the research results have been quite interest-
ing, it is important to bear in mind that the presented
scientific evidence concerning the modification of an
X-ray bundle has an intermediate character, this due
to the fact that it deals with a secondary evaluation
of effects induced in the tested object following a
conversion of the ray’s energy into the visible light
range. The main reason why such an approach for
conducting this research was chosen is that the med-
ical community has become used to utilising X-ray
diagnostics in such a manner, as well as for its con-
siderably lower costs. Currently work is underway in
the Laboratory of Biotechnology on the next stage of
research which involves making direct measurements
of difraction and interference in the output X-ray bun-
dle after being modified by the collimator.
REFERENCES
Bankier A, Fleichmann D, Aram L, Heimberger K,
Schindler E, Herold C. Bildgebung in der In-
tensivmedizin Techniken, Indikationen, diagnos-
tische Zeichen. In: Bardenheuer H, Hilfiker O,
Larsen R, Radke J. Weiterbildung fr Ansthesisten.
Springer,Berlin, 15-48
Carlson J. D., Electrorheological Fluids, US Patent 4,772,
407
Czerny C. Steiner E., Gstttner W., Baumgartner WD.,
Imhof H. Postoperative radiographic assessment
of the Combi 40 cochlear implant. Am. Journ.of
Roentgenology 1997:169(6):1689
Dyszkiewicz A, Sapota G, Wrbel Z. Standaryzowana
fotometria zdj radiologicznych ukadu kostnego w
tworzeniu komputerowych algorytmw densytome-
trycznych. Konf. TIM 99, Jaszowiec 1999
Dyszkiewicz A, Wrbel Z. The procedure of supervising
treatment of thyroid gland with isotope j 131 and using
2d and 3d analysis of scintigraphical image. ICXOM
Vienna 2001
Dyszkiewicz A. Procedure for monitoring the evolution of
inflammatory and degeneration changes in sacroiliac-
lumbar joints and correcting the rtg-picture density di-
vergence. ICXOM Vienna 2001
Dyszkiewicz A., Kolumna chromatograficzna do sczenia
lub filtracji, patent PL 175577
Folster R. T., Magnetoorheological Fluids, US Patent
5,667,715
Grampp S. Steiner E. Imhof H. Radiological diagnosis of
osteoporosis. Eur J Radiol 1997a:7:2:S11-9
Grampp H. Genant A. Mathur Ph. Lang M. Jergas M.
Takada C. Gler Y. Lu, M. Chavez Comparison of
noninvasive bone mineral measurements in assessing
age-related loss, fracture discrimination, and diagnos-
tic classification. J Bone Miner Res 12 (5) (1997b):
697
Kainberger F. Mittermaier F. Seidl G. Parth E. Weinstabl
R. Imaging of tendons–adaptation’ degeneration’ rup-
ture. Eur J Radiol 1997:25(3):209
Kollmann, K. Turetschek, W. Backfrieder, G. Most-
beck Quantitative analysis with an amplitude-coded
color Doppler imaging system (in-vitro study). World
Congress on Medical Physics and Biomedical Engi-
neering. Nice, France Sept 14-19, 1997
Kramer J. Hofmann S. Plenk H. Schneider W. Engel A.
Imaging of avascular necrosis of bone. Eur Radiol
1997: 7:2:180
Ławniczak A., Milecki A., Ciecze elektro- i mag-
netoreologiczne oraz ich zastosowania w technice,
Wydawnictwo Politechniki Poznaskiej 1999
Majumdar, H. Genant, S. Grampp, D.C. Newitt, V. Truong,
J.C. Lin, A. Mathur Correlation of trabecular bone
structure with age, bone mineral density, and osteo-
porotic status: in vivo studies in the distal radius using
high resolution magnetic resonance imaging. J Bone
Miner Res 12 (1) (1997): 111
Phule P. P. Magnetoorheological Fluid, US Patent
5,985,168
Rand T. Seidl G. Kainberger F. Resch A. Hittmair K.
Schneider B. Gler CC. Imhof H. Impact of spinal de-
generative changes on the evaluation of bone mineral
density with dual x-ray absorptiometry (DXA). Calc.
Tissue 1997: 60:430
Sasaki M., Ishii T., Haji K, Electrorheological Fluid com-
prising lyotropic liquid crystalline polymer, US Patent
5,746,934
COLLIMATION OF X-RAY DIAGNOSTIC BUNDLE BY MEANS OF STEERING FERROFLUID
447
