
DYONIPOS
Redesigned Knowledge Management
Josef Makolm, Silke Weiß
Federal Ministry of Finace, Hintere Zollamtsstraße 2b, 1030 Wien, Austria
Doris Ipsmiller
m2n consulting and development gmbh, Marienstraße 10, 4020 Linz, Austria
Keywords: Knowledge Management, Knowledge Work Support, Semantic Technologies, Research Project
DYONIPOS, Use-Case Project DYONIPOS, Public Administration.
Abstract: Traditional knowledge management is often combined with extra work to collect the information again
which is already electronically available. Another obstacle to be overcome is to make the content of the
collected information easy accessible but. At present conventional searching tools provide only documents
and not the meaning of the content. They are often based on the search after character strings, deliver many
unnecessary hits and no or less context information. DYONIPOS offers a new way. The research project
DYONIPOS focuses on detecting the knowledge needs of knowledge workers and automatically providing
the required knowledge just in time, while avoiding additional work and violations of the knowledge
worker’s privacy. This knowledge is made available through semantic linkage of the relevant information
out of existing artifacts.
1 INTRODUCTION
Current Knowledge Management approach: a
knowledge worker shortly wants to prepare an
important topic but he neither knows where the
according information is stored nor what colleagues
he can ask for expertise. To get an overview about
the topic, he normally proceeds in the following
way: he successively searches in the available
sources (server drive, own hard disk, internet, e-mail
archive, specific applications, etc.) for important
information with different “search tools”. Therefore
he has to run each query individually. In addition he
must know the various functionalities of the
different “search tools”. Finally he has to screen the
delivered search results if they adequately describe
the relevant topic.
Knowledge Management with support of the
DYONIPOS prototype: after activation of
DYONIPOS, all keyboard entries and mouse moves
are recorded as well as the reactions of the computer
system. For instance, if the knowledge worker
begins to create a power point presentation
DYONIPOS is looking the knowledge worker over
his shoulder. DYONIPOS calculates information
needs to the entered words. The knowledge worker
edits for example the title page for his presentation
and writes “DYONIPOS (DYnamic ONtologybased
Integrated Process OptimiSation): Effective and
Efficient Knowledge Management science and
research hand in hand”. DYONIPOS detects the
knowledge needs, e.g. “DYONIPOS“, „Knowledge
Management“ etc. In addition, DYONIPOS
calculates so called “resources”. These are
corresponding documents, PDF-files, links to
websites, electronic record management data
(ELAK) which cover the information needs. The
knowledge worker gets these resources indicated
only by request. In fact, constantly local and global
search results are delivered only if the button for this
function is pressed. Apart from this associated
concepts of the topic and the detected information
need are indicated. These are for example
individuals or organizations which deal with this
topic. Besides the proactive support, DYONIPOS
also offers active search for information.
This is done similar to conventional search tools
via entering of a search item in a search window.
507
Makolm J., Weiç S. and Ipsmiller D.
DYONIPOS - Redesigned Knowledge Management.
DOI: 10.5220/0001822205070512
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2009), page
ISBN: 978-989-8111-81-4
Copyright
c
2009 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

Moreover DYONIPOS enriches the further handling
and analysis of the indicated search results. For
example important key words can be displayed
which represent the content of the knowledge
resource as well as association graphs that visualizes
the relations of the associated concepts. DYONIPOS
also classifies the detected resources and visualize
them in topic landscapes. In these topic landscapes,
thematically similar resources are mapped closer
together. Trough the use of DYONIPOS knowledge
workers get an impression of the content of search
results without having ever read them. Furthermore,
existing knowledge in an organization becomes
available, transparent and semantically enriched.
2 KNOWLEDGE MANAGEMENT
”Knowledge is relevant information in context”; this
is the underlying definition of the DYONIPOS
project. In public administration knowledge has
always played a central role because the production
of public services would not be possible without
knowledge. As a matter of fact knowledge workers
need more and more knowledge for processing their
daily knowledge intensive work. Furthermore the ad
hoc part of the processes increases steadily.
Knowledge acquisition also becomes more complex
because the amount of information increases
continually and heterogeneous systems are used to
obtain the needed knowledge. In addition the
multitude of found information complicates the
selection of the really needed knowledge. This leads
to the fact that already existing knowledge gaps
grow, respectively available information is not used.
It is often not recognized that knowledge gaps exist
or that information is available – even in the own
organization – which could be used for streamlined
processing or better results. Implementing e-
Government is intended to solve these problems not
just by using information and communication
technologies to exchange information with and to
provide services for citizens and businesses. What is
more, e-Government should also provide better and
more efficient working conditions for civil servants
in order to boost agility of public administration and
quality of public services. DYONIPOS aim is to
provide personal, agile and proactive support for the
knowledge worker by means of proactive, context
sensitive knowledge delivery. The DYONIPOS
vision of knowledge management is that knowledge
management works for people, not that people work
for knowledge management. Additionally the system
should adapt to the wishes of the peoples and not the
other way round. The main idea is to release
knowledge workers from additional work for
knowledge management. For reaching the project
visions, a completely new approach with
technologies „on the leading edge“ was used to
develop the prototype DYONIPOS. Conventional
search applications currently deliver only documents
– DYONIPOS also delivers the knowledge stored in
these documents.
3 KNOWLEDGE DISCOVERY
TECHNOLOGIES
The identification of knowledge gaps, the just in
time delivery of relevant information, the supply of
associated concepts related to the corresponding
topic and further analysis through filtering and
evaluation of the delivered information are the major
functions of DYONIPOS. To provide these
functions DYONIPOS captures the user’s
knowledge work, discovers inherent tasks, and
supports the knowledge worker with information.
The first challenge is the observation of the
knowledge worker’s interactions with and reactions
to the system and existing application data. This data
is the so called low-level sensor data on the
application and operating system level (Maier, 2005,
p. 443). The second challenge is to develop adequate
techniques to discover work patterns and to
automatically support users with appropriate
information. The third challenge is to detect how
knowledge workers can be effectively supported
(Tochtermann, 2006).
In order to capture the worker’s patterns a java
tool called DYONIPOS Task Recognizer has been
implemented (Rath, 2007). At first DYONIPOS
records all interactions between the users and their
computers; these are so called "events", e.g. mouse
clicks or key strokes. Different sensors of the
context observer module observe all interactions of
the user with the desktop environment. DYONIPOS
uses a key logger program to record and log all
recognized events (Kröll et al., 2006; Rath et al.,
2007). The observed events are stored in the so
called event log. This monitored data is the basis for
determining the work patterns. The next step is to
reduce the immense quantity of data and to assign
events to event blocks by filtering and relation
analysis. This allows the elimination of irrelevant
data, e.g. mouse movements. Owing to relation
analysis a set of events can be bundled into an event
block. At present, generic rules, application based
WEBIST 2009 - 5th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
508

rules and web browser based rules are applied for
bundling events into event blocks (Rath, 2007).
Generic rules are based on the title of the window
currently opened by the user. A reason for the
assignment of events to an existing event block is
e.g. the title of the window currently opened. The
implementation of further rules for assigning events
to event blocks can easily be accomplished. The
methods used for learning task assignments are k-
nearest neighbor classification, Support Vector
Machines based on graph kernels (Rath et al., 2007).
Additionally there is the possibility to train the
classifier, i.e. the above mentioned bundling agent,
by means of task assignments is done by the user. A
method for detecting tasks, which is the next level of
semantic enrichment, is clustering based on
similarity between content and structural features
and the scatter/gather approach. During the first test
phase the assignment was initially performed by the
key-user but in the second test phase the
classification of features and tasks worked
automatically and had only to be controlled by the
key-user.
4 SEMANTIC TECHNOLOGIES
DYONIPOS is a modern information system which
supports users by proactive delivery of contextual
information (resources) while knowledge workers
are doing their daily work. The use of ontologies is
useful in such a system, because they ensure
interoperability and the development of "new"
knowledge. Furthermore, ontologies are used for the
learning process of the user context. Not only the
structure but also the recognition of context is based
on ontologies. The knowledge base and also the
internal program flow are based on ontologies. In
addition ontologies can be used for the unambiguous
description of information resources. As a
consequence, Resource Description Framework
(RDF) is a key technology of DYONIPOS. RDF is
an ontology and a formal language used to encode
ontologies. All events, event blocks and tasks
described in section 3 are represented and stored by
RDF-Triples (Kröll et al, 2006).
5 THE USE-CASE PROJECT
DYONIPOS
Parallel to the research project DYONIPOS the use-
case project DYONIPOS is implemented in the
Directorate General for Information Technology
(DG-IT) of the Federal Ministry of Finance, Austria.
In order to handle their daily work, knowledge
workers in public administration need the following
additional knowledge:
• Where is the relevant information stored?
• How can this information be found?
• How relevant is the delivered information?
The challenge is to provide administrative
employees automatically with information they
need. Consequently the above mentioned additional
know-how is made available by DYONIPOS. Other
objectives are to support the employees of the DG-
IT without creation of additional work by means of
knowledge management and to ensure privacy of the
knowledge workers. DYONIPOS contribute to the
resolution of these challenges by an efficiently and
an effectively support of the daily work of the
individual employees in the DG-IT. The
DYONIPOS Task Recognizer provides employees
with the necessary knowledge produced by semantic
cross-linking of the relevant information from the
existing repositories and processes. Additionally,
DYONIPOS independently develops new relations
between sources of knowledge. This explains why
the DYONIPOS Task Recognizer at the one hand
supports the user by visualization of existing
documents, files or websites etc. and on the other
hand displays the new generated information such as
the name of the person who has the specific know-
how. The ministry or rather fifteen employees
support the research consortium. Together they work
on the realization of the research results and they
ensure the transformation of current scientific results
into an easily useable software solution. The staff of
the ministry shares its domain specific know-how
with the research consortium, by supporting the
development of DYONIPOS base technologies.
Initial interviews with employees were carried
out to get both, an impression of the kind of work
and how this work is done. The results of these
interviews provided information which sensors
should be developed and which events the sensors
should observe. The researchers found out that
employees work mainly with standard applications
such as Microsoft Office tools, Internet Explorer and
the e-mail system Novell GroupWise. That is why a
first research step was to develop sensors to observe
events of these applications. In addition to the
observation of these standard applications the final
DYONIPOS prototype records all electronic artifacts
from the electronic record management system
(ELAK), the file-system on the servers, the Livelink-
system (a system to store office documents in a
DYONIPOS - Redesigned Knowledge Management
509

specific server environment) as well as the specific
application KOMPASS, a system to administrate
persons, resources and authorizations.
6 THE RESULTS OF THE FIRST
AND SECOND TEST PHASE
Through evaluation of the log files, questionnaires
and the analysis of the first and the second test the
following information and operating figures about
the key-user and the DYONIPOS Task Recognizer
were derived. A basic result of the evaluation of the
first test was that key-users always worked on
several tasks at the same time. This information
represented a challenge for DYONIPOS, because it
is an objective of DYONIPOS to provide just in time
information based on the context. Furthermore we
found out that a key-user used different searching
tools and searched in very heterogeneous sources.
Another objective of DYONIPOS is to support the
work of the user by proactive and context sensitive
information delivery. DYONIPOS therefore
searches for information in different repositories and
implements the function of a searching tool.
Moreover it creates cross-links between the context
of different repositories in order to deliver existing
and new generated information. By using
DYONIPOS knowledge workers receive
transparency over the existing sources of
information.
DYONIPOS gives additional references about
the relevance of the found search results which
include all currently available information. The
parallel implementation of the funded research
project and the use-case project made it possible to
exchange ideas between research and practice
constantly; this was useful for both projects.
Furthermore the inclusion of all stakeholders
(Makolm & Orthofer, 2007, p.391) such as
researchers, users, IT experts and also the staff
council – in the development process assures that the
results of the research project DYONIPOS can and
will be transformed optimally and in real time into a
practical application.
The second test phase was started in January
2008 and took approximately two months. A
fundamentally improved version of the prototype
DYONIPOS was released. It established an
organizational knowledge base with new
functionalities and also included artifacts stored on
the server.
The third prototype enables the classification of
detected resources and the visualisation of topic
landscapes (see Figure 1). In the topic landscape,
thematically similar resources are mapped to close
regions. Moreover, the selection of different
resources and the display “how similar they are” is
possible. In addition, DYONIPOS allows the
selection of artifacts according to sources e.g. file
system, KOMPASS, ELAK and Web.
Figure 1: DYONIPOS enables the display of information
in topic landscapes.
Figure 2: The graphical user interface of DYONIPOS.
Figure 2 shows the DYONIPOS user interface.
When the task recognizer is started, all mouse clicks
and tasks are registered. Information needs for a
certain topic are recognized. On demand the user is
provided with information that he searches for or
that is related to the content of his work. If the user
works for example on a power point presentation
concerning the topic DYONIPOS, the task
recognizer shows all web resources, presentation,
word documents etc. related connected to this topic
in the “global search results”. To every newly
entered word or sentence, DYONIPOS searches for
information or concepts in the personal and
organizational database which could be useful for
the knowledge worker. While the user is working on
WEBIST 2009 - 5th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
510
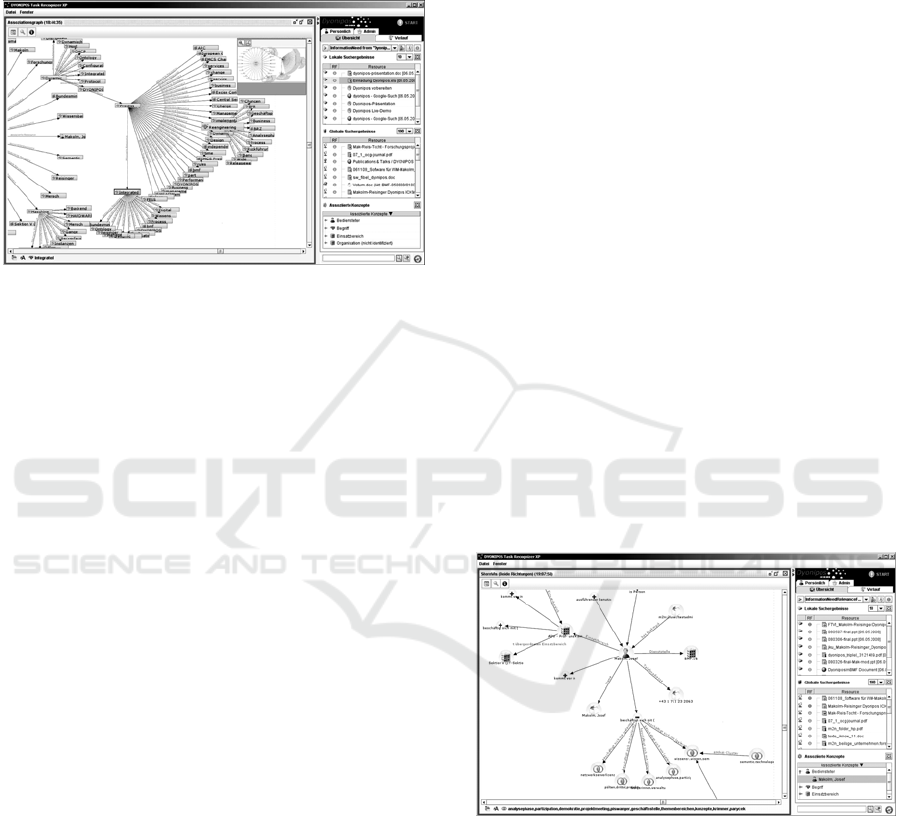
a particular topic, the DYONIPOS task recognizer is
always shown in the right front of the desktop. As a
consequence, information found by the application
appears permanently. If this is not wished the task
recognizer can be minimized.
Figure 3: Screenshot of the DYONIPOS Task Recognizer.
Figure 3 shows the graphical user interface of the
DYONIPOS Task Recognizer window for the third
test phase. Like in the second test phase, different
tabs allow the navigation between the various
delivered supplied resources and functionalities. On
the screenshot the tab “Übersicht” (overview) is
opened. On this tab the so called “Information
needs” are mapped at the top. The deduction of
“Information needs” occurs automatically, but for
performance reasons the related resources are
measured only after clicking on the activating
button. Afterwards the detection of the individual
and global resources related to the “Information
Need” gets started. With the help of filter criteria
e.g. filtering on associated persons or organization,
the located search results can be improved once
again. In addition also the associated concepts such
as the name of experts, terms, application areas and
organizations corresponding to the particular topic
are offered. “Information needs” will be stored and
may be calculated again at a later date. All located
resources are opened directly in its operational
application. For example, a located e-mail can be
opened in the associated e-mail application with a
double click . A key-user has also the possibility to
search actively for information in the iteratively
generated resource repository by using the search
field. This search field is displayed on the screenshot
at the bottom next to the magnifying glass. On the
left side of the screenshot an association graph is
opened. This graph shows different associated
concepts regarding a selected resource. On the tab
“Persönlich” (individual) the adjustment of personal
DYONIPOS functionalities can be carried out, e.g.
the deletion of knowledge, which is stored at the
organizational knowledge base. On the tab “Verlauf”
(progress) all finally opened resources is displayed.
Furthermore the release of these resources to the
organizational data base is possible on this tab. The
tab “Admin” with the corresponding authorizations
is only available for administrators. This tab
contains diverse control functions for assembling of
the index, the internal system procedures, the
KOMPASS-mappings etc.
Figure 4 shows the star-shaped graph of the
associated concepts. Because of the identified
information needs, the DYONIPOS task recognizer
also indicates associated persons with certain
concepts. The graph which shows these concepts is
mapped star-shaped here and has the name of the
person in the centre. In the association graph, those
persons, organizations etc. are identified that are
connected with several topics linked to information
need. Furthermore it is displayed for which company
respectively which department the person works and
contact details are given. In the same way the graph
points out, for which other projects the person works
or rather with which concepts he or she is identified.
Consequently links to further information are
available by clicking on a symbol. For example if
the person is responsible for semantic technologies,
information about “semantic technologies” can be
received.
Figure 4: Screenshot of the DYONIPOS star shaped
association graph.
Finally the third test phase starts in November
2008. Starting in February 2009 the whole DG-IT or
rather all 180 employees will take part in a final test
of the prototype DYONIPOS. The final evaluation
will be done after one year of practical experience.
The documentation and evaluation of this final test
provides the basis for the decision whether
DYONIPOS will be used in the DG-IT further on. In
the same way the decision will be made whether
DYONIPOS - Redesigned Knowledge Management
511

DYONIPOS should be proceeded as a commercial
tool or not.
7 FUTURE TRENDS
In the DYONIPOS project, the Directorate General
of Information Technology of the Federal Ministry
of Finance is innovation driver and solution provider
at the same time. Altogether 15 key-user from
different areas and selected experts support the
research consortium directly with the
implementation of the pilot software. Through the
joint venture of science, economy and public
administration good results could be generated.
DYONIPOS supports above all organizations which
collect knowledge in a written form, which do a high
part of knowledge intensive activities, which are
active in a very dynamic environment and
implement ad-hoc processes. DYONIPOS is a very
flexible system. For the implementation of
DYONIPOS open standards such as RDF, OWL and
Jena are used. The DYONIPOS system is model-
based and can be individually configured. The
connector principle enables the integration in
different IT-landscapes. The scale and the
performance allocation can also be individually
adapted.
8 CONCLUSIONS
The use of DYONIPOS leads to an increase of the
effectiveness of the knowledge organization. This is
because not only the own individual knowledge is
available for the handling of the daily work but also
the global organizational knowledge is supplied
proactively. Likewise, more knowledge can increase
the quality of products since important information
can be considered for the creation of products.
DYONIPOS can also contribute to a reduction of
double work because similar work that is already
done is automatically indicated to the present topic.
Due to the fact that work can (partly) be used again
valuable work time can be saved and consistency
can be assured which ends up in a more efficient
work method. Furthermore DYONIPOS improves
the individual work situation of single knowledge
workers. Workers of a knowledge organization can
concentrate on their core responsibilities as
bureaucratic activities are reduced. In addition,
DYONIPOS links individual employees through the
indication of potential conversational partners and
therefore encourages the cooperation and the
exchange of information in a company. Newest
leading edge technologies are tested in the
DYONIPOS research and use-case project. It can be
concluded that the joint venture between research,
economy and administration was successful.
REFERENCES
Kröll, M., Rath, A., Granitzer, M., Lindstaedt, S. and
Tochtermann, K., 2006. Contextual Retrieval in
Knowledge Intensive Business Environments. Paper
presented at Workshop Information Retrieval 2006,
Hildesheim, Germany.
Maier, R., 2005. Modelling Knowledge Work for the
Design of Knowledge Infrastructures. Journal of
Universal Computer Science, 4, 11, 429-451.
Makolm, J. and Orthofer, G., 2007. Holistic Approach,
Stakeholder Integration and Transorganizational
Processes: Success Factors of FinanzOnline. In
Makolm, J. and Orthofer, G. (Eds.), E-Taxation: State
& Perspectives, E-Government in the Field of
Taxation: Scientific Basis, Implementation Strategies,
Good Practice Examples, pp. 389-402, Linz, Trauner
Verlag.
Rath, A., Kröll, M., Andrews, K., Lindstaedt, S.,
Granitzer, M. and Tochtermann, K, 2006. Synergizing
Standard and Ad-Hoc Processes. Proceedings of the
6th International Conference on Practical Aspects of
Knowledge Management (pp. 267-278). Heidelberg:
Springer Berlin.
Rath, A., Kröll M., Lindstaedt, S. and Granitzer, M., 2007.
Low-Level Event Relationship Discovery for
Knowledge Work Support. In Gronau N. (Ed.), Proc.
of the 4th Conference on Professional Knowledge
Management (pp. 227-234), Potsdam: GITO-Verlag.
Rath, A., 2007. A Low-Level Based Task And Process
Support Approach for Knowledge-Intensive Business
Environments. Proceedings of the 5th International
Conference on Enterprise Information System
Doctoral Consortium DCEIS 2007 (pp. 35-42),
Madeira, Portugal.
Tochtermann, K., Reisinger, D., Granitzer, M. and
Lindstaedt, S., 2006. Integrating Ad Hoc Processes
and Standard Processes in Public Administrations.
Knowledge transfer across Europe, 4th Eastern
European eGov Days and 5th eGov Days, Volume
203, OCG Serie. Vienna.
WEBIST 2009 - 5th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
512
