
TOWARDS COMPUTERIZED DIGITAL PRESERVATION BASED ON
INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND WEB SERVICES
Xiaolong Jin, Jianmin Jiang and Geyong Min
School of Informatics, University of Bradford, Bradford, BD7 1DP, U.K.
Keywords:
Intelligent agents, Web services, Multi-agent systems, Digital preservation.
Abstract:
The explosively growing volume of digital information results in pressing demands to transfer digital objects
from active IT systems to digital repositories, libraries, and archives for long-term preservation. However,
existing strategies of digital preservation are labour intensive and often require specialist skills. In order to
meet the preservation demands of immense digital information, it is necessary to find new levels of automation
and self-reliance in preservation strategies. On the other hand, intelligent agent technology is widely viewed
as a promising approach to developing large-scale complex software systems. It has already been successfully
applied in some industrial and commercial areas. Meanwhile, Web services have evolved into a key paradigm
for distributed computing. They provide an efficient way to realize loosely-coupled architecture and interop-
erable solutions across heterogeneous platforms and systems. Therefore, Web services have received great
attention from both industry and academia. However, to the best of our knowledge, there are no initiatives that
employ the technologies of intelligent agents and Web services as the general methodology to study long-term
digital preservation in the open literature. In this paper, we describe an intelligent agent and Web service
based architecture of the PROTAGE system, which is funded by the European FP7 Research Programme and
aims to computerize long-term digital preservation. We discuss the fundamental agents involved in the PRO-
TAGE system as well as their interactions. We further present a general framework of automated decision
making based on intelligent agents and Web services, which are crucial for the automation of long-term digital
preservation. Finally, we discuss several key issues related to the implementation of the PROTAGE system.
1 INTRODUCTION
Agent oriented computing has been regarded as a
promising computing paradigm for developing and
implementing complex, distributed software systems,
as this paradigm based on intelligent agents enables
software engineers to model applications in a natural
way that resembles how humans perceive the prob-
lem domains (Chmiel et al., 2005; Jennings, 2001).
Intelligent agent technology has been successfully ap-
plied in many industrial and commercial areas, such
as, information retrieval and filtering, electronic com-
merce, and process control. It has also gained great
success in studying complex physical and social prob-
lems. For example, multi-agent systems have been
adopted to investigate the impact of climate change
on biological populations.
Recently, Web services have evolved into a key
paradigm for distributed computing (Bartoletti et al.,
2008; Xiong et al., 2008). Briefly speaking, a Web
service is an Internet URL providing a series of use-
ful functions to implement the desired service. The
functions as well as its data structures are described in
Web Services Description Language (WSDL). WSDL
allows Web applications to treat Web services the
same as other functions within the application pro-
grams. Web service providers publish their Web
services and the corresponding invocation interfaces.
Next, Web applications discover the needed Web ser-
vices and send requests via invocation interfaces.
After receiving the response from a Web service
provider, they invoke those services using the Simple
Object Access Protocol (SOAP). Web services offer a
cost-effective way to realize loosely-coupled architec-
ture and interoperable solutions across heterogeneous
platforms and systems. Therefore, Web services have
received great attention and adoption from both in-
dustrial and academic bodies (Chou et al., 2008).
From the last decades on, more and more infor-
mation exists in digital form and some information
276
Jin X., Jiang J. and Min G.
TOWARDS COMPUTERIZED DIGITAL PRESERVATION BASED ON INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND WEB SERVICES.
DOI: 10.5220/0001826802760281
In Proceedings of the Fifth International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies (WEBIST 2009), page
ISBN: 978-989-8111-81-4
Copyright
c
2009 by SCITEPRESS – Science and Technology Publications, Lda. All rights reserved

is even born-digital. Digital objects have already
emerged as the primary means in which we create,
disseminate, and exchange information (Farquhar and
Hockx-Yu, 2007). As the volume of digital infor-
mation is growing with an explosive speed, there are
pressing demands to transfer digital objects from ac-
tive IT systems to digital repositories, libraries, and
archives for long-term preservation. However, due to
rapid changes and ongoing development in hardware
and software as well as the IT infrastructure, long-
term archiving of digital objects is a highly compli-
cated task. Moreover, the diversity in the size and
complexity of digital objects implies that modern dig-
ital preservation systems must be highly scalable and
adaptable to various types of digital objects. How-
ever, existing strategies of digital preservation are la-
bor intensive and often require specialist skills. To
meet the preservation demands of immense digital in-
formation, it is necessary to find new levels of au-
tomation and self-reliance in preservation solutions.
For this reason, long-term digital preservation has
been attracting more and more research and develop-
ment efforts (Farquhar and Hockx-Yu, 2007; Watry,
2007).
However, to the best of our knowledge, there are
no initiatives that employ both intelligent agent and
Web service technologies as the general methodology
to study long-term digital preservation in the open lit-
erature. To bridge this gap, the PROTAGE (PReser-
vation Organization using Tools in AGent Environ-
ments) project, funded by the European FP7 Research
Programme, aims to investigate the application of
intelligent agents and Web services to computerize
long-term digital preservation. It intends to make dig-
ital preservation automated and easy enough such that
users can readily preserve their own digital objects,
while reducing the preservation cost and increasing
the preservation capacity. PROTAGE will also de-
velop flexible and extensible software agent and Web
service tools for long-term digital preservation and
access, which can cooperate with and be integrated
in existing or new preservation systems.
In this paper, we elaborate how long-term digi-
tal preservation can be computerized by adopting in-
telligent agent and Web service technologies. More
specifically, we present an intelligent agent and Web
service based architecture of the PROTAGE system
and discuss several key issues related to its imple-
mentation. The rest of this paper is organized as fol-
lows. Section 2 describes the multi-agent system in
the PROTAGE system. We present the four types of
fundamental intelligent agents in Section 3. Section 4
offers a general framework of decision making based
on software agents and Web services. In Section 5
some key issues related to the implementation of the
PROTAGE system are discussed. Finally, Section 6
concludes the paper.
2 PROTAGE METHODOLOGY TO
DIGITAL PRESERVATION
The PROTAGE project employs and will further ad-
vance intelligent agent and Web service technologies,
which not only facilitates the production, transfer, and
ingest of digital contents, but also assist archival mon-
itoring and user access to digital information. The
digital preservation solutions of the PROTAGE sys-
tem imply a shift of focus in digital preservation from
information systems to preservation-friendly digital
objects.
2.1 Multi-Agent System in PROTAGE
In order to deal with the increasing complexity of
digital preservation in distributed and open environ-
ments, the PROTAGE system has resorted to cross-
disciplinary fields, such as, distributed artificial intel-
ligence and biology, for inspiration that can be uti-
lized to develop new ways for designing hybrid ap-
proaches. The resulting concept is a resilient ap-
proach that assures the persistence, dynamic stabil-
ity, and flexibility of a bio-inspired multi-agent sys-
tem for digital preservation objects. From the PRO-
TAGE point of view, the challenges in digital preser-
vation should be considered using the concept of
agent ecosystem.
In the agent ecosystem involved in the PROTAGE
system, intelligent agents are structured into two lev-
els. At the high level, four types of agents are defined,
namely, monitoring agents, pre-ingest agents, trans-
fer agents, and ingest agents. These agents can be
regarded as the functional components of the PRO-
TAGE system. They are responsible for different
preservation tasks. At the low level, there are mainly
two types of agents, i.e., decision making agents and
Web services agents. Decision making agents are
responsible for various decision making tasks raised
during the process of digital preservation, while the
tasks of accessing various databases, repositories,
Electronic Records Management Systems (ERMSs),
and digital archives are assigned to Web services.
2.2 Intelligent Agent and Web Service
based Architecture
The PROTAGE system will be primarily applied to
the following three aspects.
TOWARDS COMPUTERIZED DIGITAL PRESERVATION BASED ON INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND WEB
SERVICES
277
Transfer
Agents
Monitoring Agents
Pre-Ingest
Agents
Ingest
Agents
ERMS
SIPs
Repository
AIPsSIPs
Digital
Records
Content
Producers
Content
Curators
Internet
Transfer
Agents
Monitoring Agents
Content Creation Content Preservation
Content
Consumer
Web
Services
Web
Services
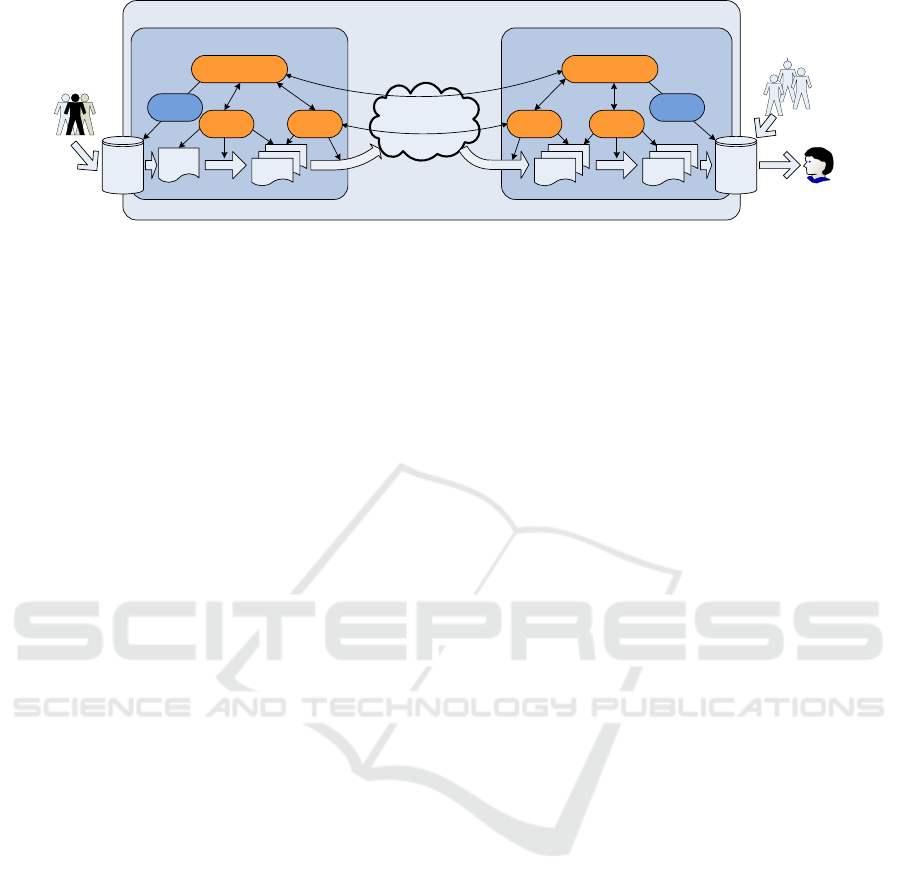
Figure 1: The schematic diagram of the agent ecosystem involved in the PROTAGE system.
• Monitoring Preservation: Monitoring the preser-
vation system with the help of intelligent agents
will reduce its complexity and make preservation
activities easier, and will also support dynamic
and flexible organization of personal and institu-
tional information repositories, distributed on the
Web. These in turn enable the sharing of infor-
mation between users at the knowledge-level, and
automate the discovery of new relevant informa-
tion through collaborative information exchange
between software agents.
• Pre-Ingest and Ingest of Digital Objects: Digital
objects to be submitted to a repository are usu-
ally checked for consistency in terms of file for-
mats and metadata. This task incurs substantial
workload of the personnel who are responsible for
handling the pre-ingest and ingest tasks of digital
objects, either at the submitting side or at the re-
ceiving side. Our intelligent agent and Web ser-
vice based digital preservation solution will sig-
nificantly lighten this burden, as both pre-ingest
and ingest tasks can be greatly automated in meta-
data collection and in the quality assurance of the
delivered materials.
• Transfer of Digital Objects between Repositories:
Instead of having to manually schedule for large
deliveries of digital objects at both the transfer-
ring and receiving repositories, intelligent soft-
ware agents can negotiate between themselves
when the delivery should be made in order to min-
imize the impact on both network traffic as well as
on the systems and storage solutions in respective
repositories.
In order to fulfill the above tasks, four types of in-
telligent agents are engineered in the PROTAGE sys-
tem. Figure 1 shows the intelligent agent and Web
service based architecture of the PROTAGE system.
It can be noted that the digital preservation environ-
ment is distributed on the Internet and can be naturally
divided into two sides, namely, the content creation
side and the content preservation side. Figure 1 also
demonstrates the work flow of digital preservation as
well as the interactions between intelligent agents.
We can note that pre-ingest agents are responsible for
packing the digital records, which are extracted from
the ERMS and will be transferred to a digital repos-
itory, into Submission Information Packages (SIPs).
Next, transfer agents deliver the SIPs from the con-
tent creation side to the content preservation side. In-
gest agents generate Archival Information Packages
(AIPs) based on the received SIPs and finally store
AIPs into the digital repository for permanent preser-
vation. Monitoring agents are responsible for moni-
toring the operation of other three types of agents and
the whole work flow of digital preservation. They are
also in charge of the operation and management of
ERMSs and repositories via Web services.
3 FUNDAMENTAL
INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND
THEIR INTERACTIONS
In this section, we will describe the functionality of
the four types of fundamental agents in the PRO-
TAGE system. Meanwhile, we present the interac-
tions among different types of intelligent agents.
3.1 Monitoring Agents
The purpose of monitoring agents is to monitor the
overall work flow of digital preservation so as to en-
sure that digital objects can be correctly dealt with
and subsequently either be transferred to the repos-
itory at the content preservation side for long-term
preservation or be destroyed. Monitoring agents are
distributed at both the content creation and content
preservation sides. In order to fulfill their tasks, mon-
itoring agents have to closely interact with pre-ingest
agents, transfer agents, and ingest agents. For exam-
ple, the monitoring agents at the content preservation
side are usually requested by pre-ingest agents to de-
termine the archival value and retention period of dig-
ital records.
WEBIST 2009 - 5th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
278
3.2 Pre-Ingest Agents
In general, the task of pre-ingest agents is to create
SIPs of the records that havearchival valueand should
thus be transferred to the content preservation side for
long-term preservation. For this purpose, pre-ingest
agents should first automatically check the records
whose retention deadlines are approaching or have al-
ready expired so as to make sure that they have been
assigned archival value or allowed to be destroyed af-
ter their retention period. After that, pre-ingest agents
will further interact with the monitoring agents to ob-
tain the detailed requirements on SIPs. Finally, they
create and validate SIPs according to the requirements
on the size and structure of SIPs.
3.3 Transfer Agents
Transfer agents are mainly responsible for transfer-
ring all SIPs from the content creation side to the con-
tent preservation side. To this end, the transfer agents
at both sides need first to negotiate a test transfer in or-
der to ensure that SIPs to be transferred fully comply
with the SIP requirements, and their metadata meets
the metadata standards. After that, the transfer agents
at both sides will further negotiate an appropriate time
and a method for final transfer. Eventually, the trans-
fer agents at the content creation side transfer SIPs
one by one to its counterpart at the content preser-
vation side at the appointed time and in the allowed
method.
3.4 Ingest Agents
There are three primary tasks for ingest agents,
namely, (1) validate SIPs received, (2) extract meta-
data, and (3) create AIPs. To fulfill these tasks, ingest
agents should first check viruses and malware possi-
bly contained in digital files of the SIPs. Next, ingest
agents check the quality of SIPs. If there are errors
found, ingest agents will interact with the monitoring
agents so as to inform the pre-ingest agents or trans-
fer agents to re-prepare or retransfer the vicious SIPs.
The last task of ingest agents is to create AIPs, which
follow the AIP configurations defined by the content
preservation side. These AIPs will be stored and man-
aged in the digital repository for a long term.
4 AUTOMATED DECISION
MAKING BASED ON
INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND
WEB SERVICES
During the process of long-term digital preservation,
there are lots of decisions to be made, which are of
different types and different importance. For instance,
monitoring agents at the content preservation side of-
ten need to determine whether or not assign archival
value to a group of records so that they will be perma-
nently preserved after their retention period expires.
At present, all of these decisions are made by human
beings, which results in the low efficiency of the cur-
rent digital preservation. As the PROTAGE system
aims at computerizing long-term digital preservation,
one of the key issues is to automate decision making
involved in the PROTAGE system.
Decision Making
Learning and
Updating
Decision
Making
Rules
User Final Decision
Detection
Decision
Making
History
Task
Classification
Task-
Specific DB
Web Services
Invocation
Web Service
(Rule Management)
Web Service
(DB Management)
Web Service
(History Management)
UDDI
Decision
Refinement
Web Service
(UDDI
Management)
Decision Making Agent
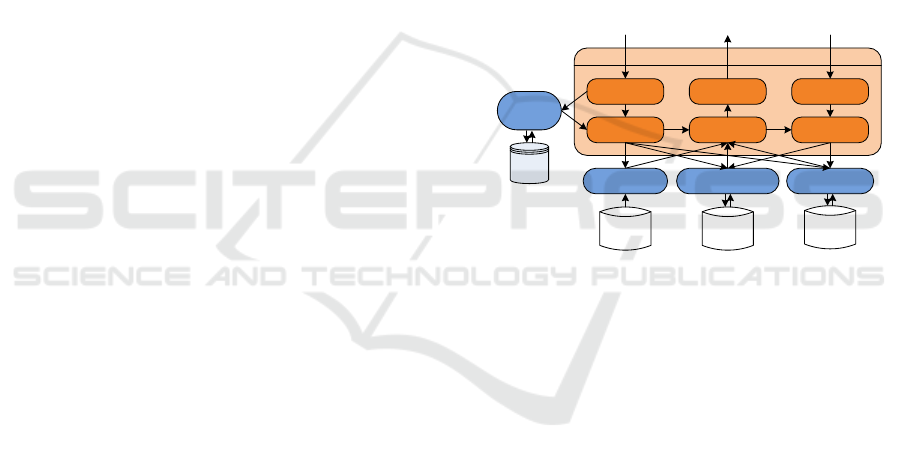
Figure 2: A general framework of automated decision mak-
ing.
Figure 2 presents a general framework of deci-
sion making agents in the PROTAGE system. In what
follows, we will briefly introduce its primary compo-
nents as well as the corresponding work flow.
Task Classification. When a decision making agent
receives a task, it first needs to identify the type of
the task. Next, the agent checks the Universal De-
scription, Discovery, and Integration (UDDI) registry
to discover the Web services which correspond to the
type of the task in hand. Note that all Web services
have been registered at the UDDI registry before the
task is submitted. The UDDI management is a special
Web service responsible for managing and maintain-
ing the UDDI registry.
Web Services Invocation. The UDDI manager
identifies the Web services related to the present task
and then invokes them to support the decision mak-
ing. Usually, three Web services will be invoked,
namely, database management, history management,
and strategy management.
TOWARDS COMPUTERIZED DIGITAL PRESERVATION BASED ON INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND WEB
SERVICES
279

Decision Making. With the support of the man-
agers of task-specific databases, decision making his-
tory, and decision making strategies, the decision
making agent selects the strategy suitable for the task
in hand to make the decision. For example, in order
to determine the retention period of the digital records
that will be organized under a new function, case-
based reasoning is usually adopted at present digital
preservation environments. Here, a significant issue
is to determine what decision making strategy is to be
used in the decision making process.
Decision Refinement. This component is responsi-
ble for refine the decisions that have been made. In
some cases, more than one choice will be generated
in order to avoid the inaccuracy inherent in the deci-
sion making agent.
User Final Decision Detection. In order to advance
the efficiency and accuracy of the decision making
agent, this component is used to detect the final de-
cision that users make or collect the feedback from
other agents.
Learning and Updating. Based on its decision
making results and the final decision that users adopt,
the agent updates the decision making history and par-
ticularly the decision making strategies, which will be
used in later decision making of the same task type.
5 IMPLEMENTATION ISSUES
The potential application of the PROTAGE system
inevitably involves distributed IT systems with dis-
tinct operating platforms. For this reason, one of the
most important properties of the PROTAGE system is
cross-platform, which is one of the key advantages of
the Java programming language. Therefore, the PRO-
TAGE system will mainly be implemented in Java. In
what follows, we will describe several crucial issues
relevant to the implementation of the PROTAGE sys-
tem.
5.1 Agent Platform
As the PROTAGE system intends to build an agent
ecosystem for automatic digital preservation, one of
the key issues in its implementation is to choose
a suitable agent platform, which is crucial for the
success of the PROTAGE system. So far, there
are quite a few generic agent platforms/frameworks
that have been produced and employed to develop
various multi-agent based applications (Laukkanen
et al., 2001; Chmiel et al., 2005). Among these
platforms/frameworks, to the best of our knowledge,
JADE is the most widely adopted one. Therefore, we
choose to employ JADE platform to build our PRO-
TAGE agent ecosystem.
JADE is essentially a free middle-ware for de-
veloping agent applications, which fully complies
with the FIPA (Foundation for Intelligent Physical
Agents)
1
specifications for inter-operable agent sys-
tems. JADE is implemented completely in the Java
programming language. This feature ensures that it
can be distributed across different machines even with
heterogeneous operating systems. Particularly, since
JADE adopts a Java-implemented agent model, which
is more primitive than those models offered in other
agent frameworks/platforms, JADE can offer good
runtime efficiency and software reuse. For relatively
complex agent models, they can be readily imple-
mented on the top of the primitive JADE agent model
(Chmiel et al., 2005).
In the PROTAGEsystem, we will developour own
intelligent software agents by extending the primi-
tive agent model provided in JADE. Since JADE is
FIPA-compliant, our developed intelligent agents will
also be FIPA-compliant and hence can be readily in-
tegrated into other platforms.
5.2 Web Service Platform
In the PROTAGE system, we adopt AXIS (Apache
eXtensible Interaction System) as the platform for de-
veloping our Web services. In what follows, we will
make a brief introduction to the AXIS platform and
clarifies why we employ it for the PROTAGE system.
Actually, AXIS is an implementation of the SOAP
submission to the W3C
2
. It is an open-source product
from the Apache Software Foundation
3
and available
for use under the Apache Software License (Callahan,
2002). AXIS is a two-in-one application in that it of-
fers not only tools for writing client Java programs
that use Web services, but also tools for deploying
Java programs as Web services (Callahan, 2002). It
should be particularly mentioned that because AXIS
deals with the encoding and decoding details of the
low-level SOAP protocol, the access to Web services
provided by AXIS is transparent. As a result, it can
significantly improve the development efficiency of
Web service based applications. Also in this sense,
we can say that AXIS is a cost-effective solution to
the development and deployment of Web services.
1
http://www.fipa.org/.
2
http://www.w3.org/.
3
http://www.apache.org.
WEBIST 2009 - 5th International Conference on Web Information Systems and Technologies
280

5.3 Integration of Agent and Web
Service Platforms
As we will resort to both intelligent agents and
Web services for computerizing the long-term dig-
ital preservation, the key issue is the integration of
the JADE and AXIS platforms. Actually, there have
been some studies on the integration of Web services
and agents so as to provide access to Web services
from agent platforms or vice versa (Greenwood et al.,
2007). In the integration, the main obstacles are the
description mismatch and communication mismatch
between Web services and intelligent agents. In the
JADE platform, agents communicate in ACL, while
in the AXIS platform Web services are described us-
ing WSDL and the communication between Web ser-
vices are carried out by SOAP.
In our integration schema of the JADE and AXIS
platforms, three modules are designed to overcome
the problems caused by the description and communi-
cation mismatch between FIPA compliant agents and
W3C compliant Web services. The functionality of
the modules can be described as follows:
• Communication Protocol Converter. This con-
verter is used to translate agent function invoca-
tion requests in ACL into Web service invocation
requests in SOAP, or vice versa.
• Service Description Converter. It is responsible
for translating the description of Web services
in WSDL into the description of agent functions
such that the Web services can be registered and
published in the Directory Facilitator (DF) of the
JADE agent platform.
• Search Query Converter. It is used to translate
an agent function query into that of Web services.
This converter enables Web services packed into
an agent to be discovered by other JADE agents
or Web services.
6 CONCLUSIONS
The PROTAGE project intends to integrate intelli-
gent agent and Web service technologies into long-
term digital preservation. Specifically, it aims to au-
tomate long-term digital preservation based on the au-
tonomy of multi-agent systems and the interoperabil-
ity of Web services, and consequently make digital
preservation easy enough such that organizations and
individuals can readily preserve their digital objects.
In this paper, besides a brief introduce to the PRO-
TAGE project, we have presented the intelligent agent
and Web service based architecture of the PROTAGE
system in details. Four types of intelligent software
agents, namely, monitoring agents, pre-ingest agents,
transfer agents, and ingest agents, have been designed
to deal with the long-term digital preservation task.
We have presented their key functional components
and discussed the interactions among them. We have
further provided a general framework of automated
decision making based on intelligent agents and Web
services. Finally, the key issues related to the imple-
mentation of the PROTAGE system, namely, the plat-
forms for implementing agents and Web services and
their integration were discussed.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by the Seventh Framework
Programme of the European Union under grant (FP7-
ICT-216746).
REFERENCES
Bartoletti, M., Degano, P., Ferrari, G. L., and Zunino, R.
(2008). Semantics-based design for secure Web ser-
vices. IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering,
34(1):33–49.
Callahan, J. (2002). AXIS: Jave Web services.
http://www.cmswatch.com/Feature/68-AXIS.
Chmiel, K., Gawinecki, M., Kaczmarek, P., Szymczak, M.,
and Paprzycki, M. (2005). Efficiency of JADE agent
platform. Scientific Programming, 13(2):159–172.
Chou, W., Li, L., and Liu, F. (2008). Web services for
communication over IP. IEEE Communications Mag-
azine, 46(3):136–143.
Farquhar, A. and Hockx-Yu, H. (2007). Planets: Integrated
services for digital preservation. International Journal
of Digital Curation, 2(2):88–99.
Greenwood, D., Lyell, M., Mallya, A., and Suguri, H.
(2007). The IEEE FIPA approach to integrating soft-
ware agents and Web services. In Proceedings of the
Sixth International Joint Conference on Autonomous
Agents and Multiagent Systems (AAMAS’07), pages
1407–1413.
Jennings, N. R. (2001). An agent-based approach for build-
ing complex software systems. Communications of
the ACM, 44(4):35–41.
Laukkanen, M., Tarkoma, S., and Leinonen, J. (2001).
FIPA-OS agent platform for small-footprint devices.
Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pages 447–460.
Watry, P. (2007). Digital preservation theory and appli-
cation: Transcontinental persistent archives testbed
activity. International Journal of Digital Curation,
2(2):41–68.
Xiong, P., Fan, Y., and Zhou, M. (2008). QoS-aware Web
service configuration. IEEE Transactions on Systems,
Man and Cybernetics, Part A, 38(4):888–895.
TOWARDS COMPUTERIZED DIGITAL PRESERVATION BASED ON INTELLIGENT AGENTS AND WEB
SERVICES
281
