
DEMO PROGRAMS FOR NORMAL AND UNIFORM
RANDOM VARIABLES TRANSFORMATION
Gordana Jovanovic Dolecek and Fred Harris
Department of Electronics, Institute INAOE, Puebla, Mexico
Department of Electrical Eng., SDSU San Diego, U.S.A.
Keywords: Demo program, MATLAB, Linear transform, Nonlinear transform, Normal variables, Uniform variables.
Abstract: This paper presents MATLAB-based demo programs for transformation of normal and uniform random
variables. Linear as well as nonlinear transforms are considered. It is demonstrated how the transform
changes the corresponding probability density function. It is also shown how to use the transformation of
given random variable to generate a new desired random variable. The programs can be used as a
complement to theoretical classes or alone as a self-study tool.
1 INTRODUCTION
Computer-aided learning has become an important
educational research activity in various engineering
disciplines and there has been a growing interest in
the development of educational software in all areas
of study (Fernandez and Sanchez, 2004). As a result
many computer packages have been developed to
assist learning (Yann and Teng, 2003; Li and Lie,
2004).
It is known that random variable (r.v.) is generally
considered as one of the most abstract and
conceptually difficult areas in the engineering
education and teaching of random variables is one of
the subjects that requires more time for its
understanding. Our experience shows that the use of
demo programs gives students the visual and
intuitive representation of the random variables
which had traditionally been stated in terms of
abstract mathematical description (Jovanovic, 1997;
Jovanovic and Champac, 2000). Such software tools
must have characteristics like repeatability, capacity
to motivate students, interactivity, versatility, easy to
use etc.
Presented in this paper are demo programs to
teach the transform of uniform and normal random
variables. The programs can be used as a
complement to theoretical classes or alone as a self-
study tool. The programs are interactive, i.e., the
user chooses the parameters of the input variables
and the corresponding transform.
Each program presents input and output variables
and the desired transform as well as the estimated
probability densities. The exact densities are also
presented.
The rest of the paper is as follows. Next section is
devoted to the linear and nonlinear transformations
of uniform random variables, while Section 3
demonstrates the linear and nonlinear transforms of
normal random variables.
2 UNIFORM VARIABLE
2.1 Demo for Linear Transform
In this program the linear transform (LT) Y=aX+b of
the uniform random variable X is discussed. The
user chooses the range (R
1
, R
2
) of the uniform r.v.
and the parameters of the linear transform a and b.
The program shows the output variable and the
estimation of the input and output probability
densities (PDS), thus demonstrating that the linear
transform of the uniform r.v. results in an uniform
r.v. As an illustration Fig.1 shows the result for R
1
=
-1, R
2
= 4, a = 2, and b = 3. The estimation of the
corresponding PDFs is given in Fig.2.
Figure 3 presents the corresponding uniform
PDFs.
It is also demonstrated how this result is useful to
generate the desired uniform r.v. from the given
uniform r.v. For example, in MATLAB the file rand
363
Dolecek G. and Harris F. (2009).
DEMO PROGRAMS FOR NORMAL AND UNIFORM RANDOM VARIABLES TRANSFORMATION.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 363-366
DOI: 10.5220/0001835003630366
Copyright
c
SciTePress
generates the uniform r.v. in the interval (0, 1). To
obtain uniform r.v. in the interval (R
21
, R
22
), we have
to apply the linear transform with a=R
22
-R
21
, where
a=R
22
-R
21
; b=R
21
, to the uniform random variable
generated by rand. Figure 4 illustrates the generation
of the uniform r.v. in the interval (-3, 5).
Figure 1: Linear transform of uniform r.v.
Figure 2: Estimated Input and Output Densities.
Figure 3: Input and Output Densities.
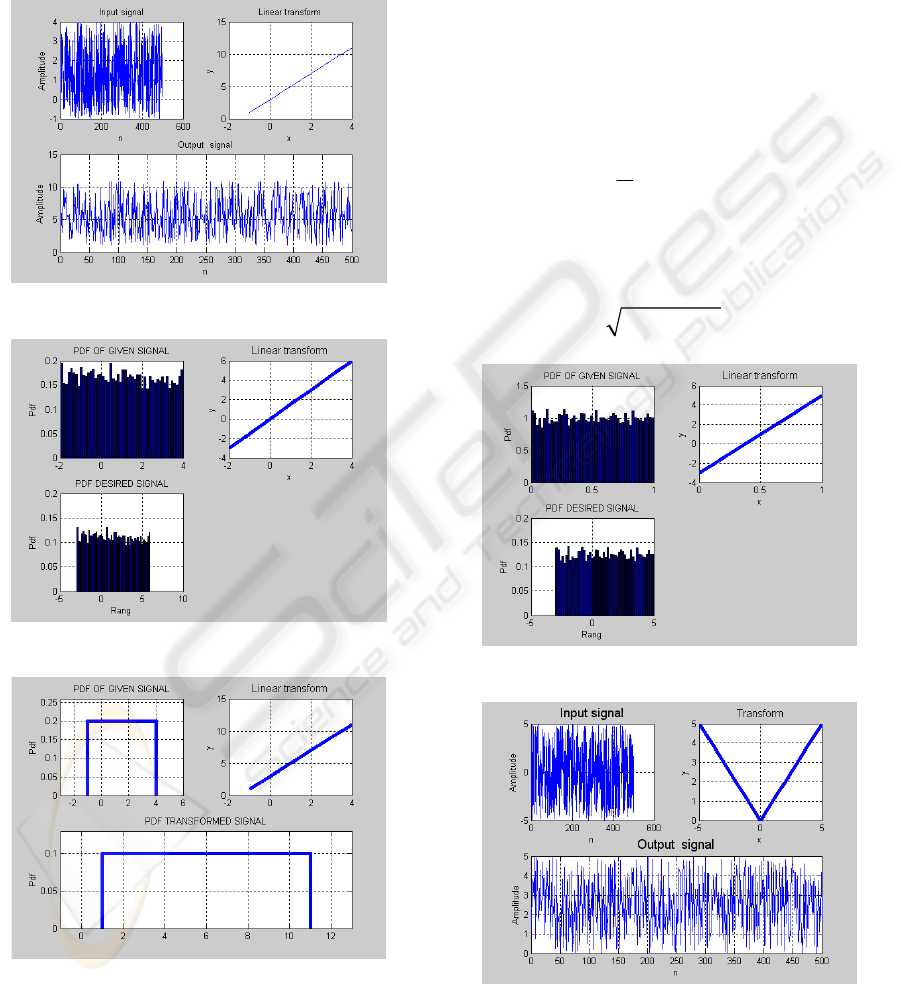
2.2 Demo for Nonlinear Transform
The Demo program for the absolute value of
uniform r.v. illustrates that the transform does not
change the type of the uniform r.v., as shown in
example in Fig.5, where the input r.v. is uniform in
the interval (-5, 5). The estimation of the input and
output PDFs are given in Fig.6.
The following demo shows the transformations
of the uniform r.v. X in the range (0, 1).
The demo illustrated in Figs 7 and 8 shows how
to generate an exponential random variable by
applying transform
1
log(1 )YX
λ
=− −
,
(1)
to a uniform variable X.
Figure 9 illustrates the demo for the
transformation of the uniform random variable X,
2
2lnYX
σ
=− .
(2)
Figure 4: Generation of the desired uniform r.v.
Figure 5: Absolute value of uniform r.v.
The resulting random variable is Rayleigh as
shown in Fig.9.
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
364

3 NORMAL VARIABLE
3.1 Demo for Linear Transform
This program demonstrates that the linear transform
of the normal r.v. gives again the normal r.v. User
chooses the mean value and variance of the normal
variable, as well as the parameters of the linear
transform a and b. Figure 10 illustrates the demo for
the mean value 2, variance 4, and a=3, b=4. The
figure shows the estimation of the output PDF
demonstrating that the output random variable is
also the normal variable. The same is confirmed in
Fig.11.
MATLAB file randn generates the normal r.v.
with the zero mean value and the variance 1. The
normal random variable with mean m and the
variance
2
σ
is obtained by applying the following
transform
YXm
σ
=+.
(3)
Figure 6: Estimation of the corresponding densities.
Figure 7: The generation of exponentional r.v.
Figure 8: Estimation of the corresponding densities.
Figure 9: Estimation of the Rayleigh density.
Figure 10: Estimation of the output density.
3.2 Demo for Nonlinear Transform
Figure 12 illustrates the absolute value of the normal
r.v. with zero mean and the variance 4. The resulting
random variable is the one-sided normal variable.
The exponential transform
X
Ye
=
(4)
of the normal variable is illustrated in Figs.13 and
14.
DEMO PROGRAMS FOR NORMAL AND UNIFORM RANDOM VARIABLES TRANSFORMATION
365

4 CONCLUSIONS
This paper describes the educational software for
transformations of the uniform and normal random
variables. The linear as well as nonlinear transforms
are considered. It is also described how to use the
transformations to generate different random
variables.
Figure 11: Input and output densities.
Figure 12: Absolute value of normal r.v.
Figure 13: Exponential transform.
Figure 14: Estimation of the densities.
The programs are written in MATLAB, although
any previous knowledge of MATLAB is not
required. The programs can be used as a
complement to theoretical classes or alone as a self-
study tool for teaching basic course on random
signals.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
This work is supported by CONACYT grant No.
91013.
REFERENCES
Garcia, A. L., 2008. Probability and Random Processes
for Elecreical Engineering. Prentice Hall, 3
th
edition.
Gubner, J., 2006. Probability and Random Processes for
Electrical and Computer Engineers, Cambridge
University Press.
Fernandez, A. J., Sanchez J. M, 2004. Educational
Software for Learning the Foundations of
Programming. In Computer Applications in
Engineering Education. 11(4), 167-179.
Jovanovic-Dolecek G., 1997. RANDEMO: Educational
Software for Random Signal Analysis. In Computer
Applications in Engineering Education, 1997 5(2), 93-
99.
Jovanovic-Dolecek G., Champac, V., 2000. CGTDEMO-
Educational Software for the Central Limit Theorem.
In ACM Press, SIGCSE Bulletin, 32(2), 46-48.
Li, S. G. , Lie, Q., 2004. Interactive Groundwater (IGW):
An Innovative Digital Laboratory for Groundwater
Education and Research. In Computer Applications in
Engineering Education, 11, (4), 179-203.
Yann, X. F., Teng, J. G., 2003. Interactive Web-Based
Package for Computer-Aided Learning of Structuarl
Behavior. In Computer Applications in Engineering
Education, 10, (3), 121-137.
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
366
