
COMMON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COURSE
Experiences from Different Countries
Zoran Budimac, Zoran Putnik
Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Science, University of Novi Sad, Serbia
Mirjana Ivanović
Department of Mathematics and Informatics, Faculty of Science, University of Novi Sad, Serbia
Klaus Bothe
Institute of Informatics, Humboldt University Berlin, Germany
Keywords: Joint Course, Software Engineering, Team assignments.
Abstract: A joint common course has been created as a result of a project of the “Stability Pact of South-Eastern
Europe” and DAAD. It has been conducted in Novi Sad, Serbia, with graduate students, and in Tirana, Al-
bania, with master students by teachers from Berlin and Novi Sad. In this paper, similar methods used in
each of these courses, and outcomes reached by students are presented and compared with the achievements
within the “original” course, conducted at the Humboldt University in Berlin.
1 PRELIMINARIES
With support of DAAD and the “Stability Pact of
South-Eastern Europe”, a joint project was estab-
lished in 1999. Idea was to build and evolve com-
mon courses in several fields of computer science,
starting with “Software Engineering”.
The project consists of participants from 15 uni-
versities, from 9 countries: Germany, Serbia, FYR
Macedonia, Bulgaria, as core members, and Croatia,
Bosnia and Herzegovina, Romania, Albania, and
Montenegro as associate members (Bothe, 2003;
Bothe, 2005; Budimac, 2008; Zdravkova, 2003).
The main goals of the project were:
– “Software Engineering” is included into univer-
sities’ curricula of all participating countries;
– Agreement on a joint course was performed,
with creation of teaching, examination, and as-
sessment material;
– Founding of e-Learning facilities was completed;
Goals are performed through cooperation in de-
velopment of teaching materials, and production of a
distributed, Internet-based, multilingual university
course. Joint course originated from one conducted
at the Humboldt University in Berlin. It covers more
than 85% of the elementary lessons suggested in
“Curricular guidelines for undergraduate programs
in computing” (ACM 2001, SWEBOK 2001).
2 STRUCTURE OF THE COURSE
The course is conducted at several participating uni-
versities as a whole, or in part:
– At Humboldt University in Berlin, it’s been con-
ducted for a decade, for undergraduate students;
– At the University of Novi Sad, Faculty of Sci-
ence, course has been conducted:
– for postgraduate CS students, for 2 years,
– for undergraduate CS students, for 4 years.
– At the University of Beograd, Serbia, Timisoara,
Romania, Plovdiv, Bulgaria, and Skopje, FYR
Macedonia, course has been conducted in differ-
ent ways and durations in the last several years;
– At the Polytechnics University of Tirana, a 7-day
crash-course has been conducted for 2 years.
The course consists of 28 topics covering intro-
ductory notions of software engineering.
375
Budimac Z., Putnik Z., Ivanovi
´
c M. and Bothe K. (2009).
COMMON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COURSE - Experiences from Different Countries.
In Proceedings of the First International Conference on Computer Supported Education, pages 375-378
Copyright
c
SciTePress

The second essential component of the course is
usage two of complex case-studies.
The third component of the course is team as-
signments. An assignment pool was created, and
lecturers are free to choose from it. From 5 to 20
teams was created per year, sizing from 3 to 5 stu-
dents. During the school year, assignments are given
to teams, with a deadline of 2-3 weeks to solve it. A
minimum number of points required to qualify for
the final exam is 50%, yet how those influence the
final grade is not the same. In Germany, number of
points does not influence the final grade. In Serbia,
and Albania, points gained for the assignments di-
rectly influence the final grade.
3 ASSIGNMENTS AND
ACHIEVEMENTS
For the first time during the school year 2004/05 an
identical complete course, with the same case stud-
ies, and the same assignments for students was held
in Berlin and in Novi Sad. Later on, the same course
was conducted in a different style in Tirana, but with
the same general structure.
A pool of nine assignments has been created.
– Assignment 1: Review of “(preliminary) re-
quirements specification”.
– Assignment 2: Application of a function-point
method on a given requirements specification.
– Assignment 3: Review of a product model re-
sulted after structured analysis.
– Assignment 4: Development of a use-case dia-
gram and class diagram for a given problem.
– Assignment 5: Definition of a formal specifica-
tion for several given operations.
– Assignment 6: Review of a solution of the fourth
assignment of a different team.
– Assignment 7: Measuring a quality of software.
– Assignment 8: Specification of a regression test.
– Assignment 9: Creation of a classification tree.
The following procedure for assignments is ap-
plied: Teams are given specific tasks and have to
produce results in a given time. Later, one exercise
class is organized where the most provoking solution
is presented by the members of the team submitting
it.
For solving of the assignments, students are di-
vided into teams, according to their own choice.
This approach has several advantages (Bielikova
2004). The first is simplicity from the managerial
point of view. Second is the fact that the opportunity
to sign up for a team of their choice creates an addi-
tional personal relationship within team.
There are at least two disadvantages to this ap-
proach. First, the team quality can (and usually does)
vary significantly. The second drawback is that oc-
casionally, members of the groups have complaints
on the other members. While students are informed
that they are allowed to “fire” their colleague from
the team, this is much more difficult when team
members are mutual friends.
Not all of the assignments are performed each
year. Especially, the length of the course influences
the choice of assignments for the course in Tirana.
Another important point is the fact that the “correct
solution” which is presented to students is created in
cooperation, based on the combined experience of
lecturers from Berlin and Novi Sad.
4 RESULTS FOR ASSIGNMENTS
Results gained at different universities, for the as-
signments are presented here. Number of students
grows every year, yet percentage of gained points
for assignments shows regular behaviour. For stu-
dents from Novi Sad results are given in Table 1.
– Percentage of gained points for the first year is
significantly different than during the following
years. Reason for this probably is connected to
the non-experience of lecturers.
– The worst results are usually gained for the as-
signment number 2 (the function-point method).
The assignment is quite straightforward, yet it
seems that it has some hidden difficulties.
Table 1: Assignment points for Novi Sad students of Computer Science.
Novi Sad
Nr of
Students
Average
Points
Assgn 1
Average
Points
Assgn 2
Average
Points
Assgn 3
Average
Points
Assgn 4
Average
Points
Assgn 5
Average
Points
Assgn 6
Average
Points
Assgn 7
Total
Points
Assgn
2004 45 81,11% 66,67% 63,78% 73,11% 75,78% 88,61% 68,52% 74,05%
2005 54 73,89% 74,53% 80,38% 79,90% 80,68% 94,32% 95,45% 81,75%
2006 60 81,67% 75,42% 88,00% 75,56% 80,67% 95,00% 81,85%
2007
66 77,73% 75,99% 85,76% 77,42% 78,30% 94,38% 91,67% 82,18%
Average
78,60% 73,15% 79,48% 76,50% 78,86% 92,43% 87,66% 79,96%
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
376
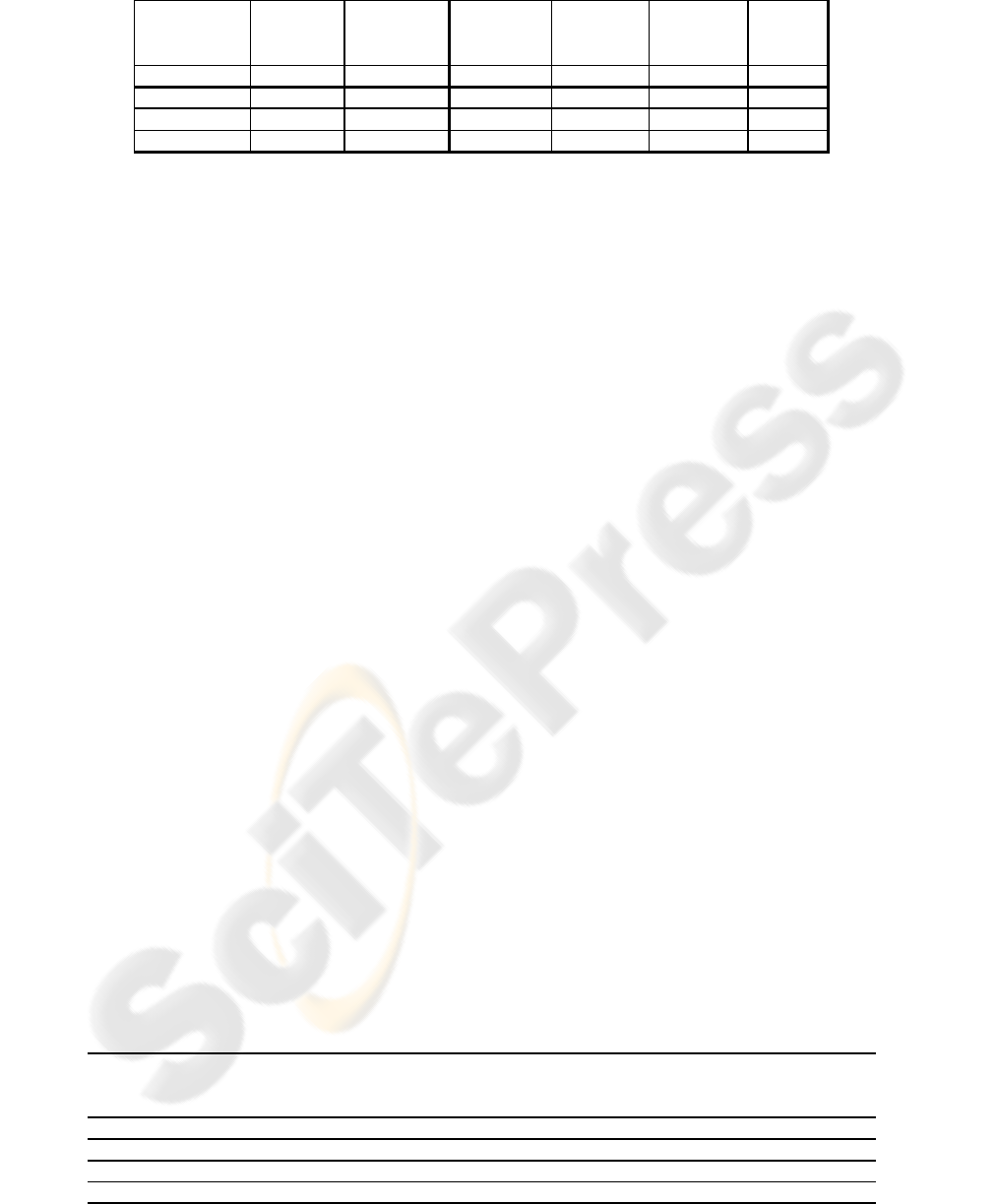
Table 2: Assignment points for Tirana master students.
Nr of
Students
Average
Points
Assgn 1
Average
Points
Assgn 2
Average
Points
Assgn 5
Average
Points
Assgn 7
Total
Points
Assgn
Tirana 2007 17 78,24% 80,59% 80,00% 98,24% 84,26%
Tirana 2008 15 69,30% 74,00% 76,70% 95,30% 78,83%
Tirana 2008 II 15 66,00% 78,70% 80,70% 92,70% 79,53%
Average 71,18% 77,76% 79,13% 95,41% 80,87%
– Assignment number 6 (review of a solution of
another teams’ assignment) has the highest aver-
age percentage of points, which is expected,
since it represents mostly the ability of a team to
defend their own opinion.
– The best results and the highest number of points
are gained for the assignment 7 (measuring of
the quality of software). First, it is straightfor-
ward and relatively simple task. Second, this is
the last assignment, when students are experi-
enced of what they have to do to solve their task.
– The assignment 4 (creation of use-case and class
diagrams), asking for the highest level of “crea-
tive” work, has the second worst results. The
main point here is the lack of experience with the
real-life work, no practical abilities and skills.
– Average total points achieved by students are
sufficient for them to approach the rest of the
exam. Even more, it is close to 80% of points.
At the Polytechnic University of Tirana, in
spring of 2007, a 7-day crash-course for the students
of master studies was conducted by professor from
Berlin and assistant from Novi Sad. Again in 2008,
course was conducted again, this time with 15 stu-
dents from the first year, and 15 students from the
final year of master studies.
These students had to solve 4 assignments: 1
(review of requirements specifications), 2 (function-
point method), 5 (definition of formal specification),
and 7 (measuring of the quality of software). The
first one they solved before the course started, to be
introduced to the requirements specification. Other
three had to be solved after the course, 2 weeks per
each assignment. Results are presented in Table 2.
Results are quite comparable to the results of
Novi Sad students. If we disregard the first year,
percentages for the same assignments in Novi Sad
are 77.76%, 75.31%, 79.88% and 94.04%. The dif-
ference is not high, since students from Tirana were
studying in non-mother tongue, preventing them to
achieve better results as master students.
How does all this compare to Berlin students?
For Berlin, statistics is given in Table 3. One thing
that influenced those results is the fact that during
2007, assistant was changed in Berlin. Notice that in
Novi Sad, Tirana, and Berlin (during the first two
years) average percentage of points is around 80-
82%, yet, inexperienced assistants had different re-
sults: 74% in Novi Sad, or 87% in Berlin.
5 THEORETICAL TESTS
The second part of the exam was tests with theory.
The particular structure is different, but general form
is the same. A repository of around 400 questions is
created. There were 2 tests in Albania, or 3-4 in Ser-
bia, yet in total they sum up to 60 points for tests,
added to 40 points for assignments. For students
from Germany, the second part of the exam is per-
formed orally. Table 4. presents Serbian students’
results achieved in tests.
Students from Tirana had only two tests, both
were performed “on the distance” by a local profes-
sor, and at the same time. This is different than in
Novi Sad, where tests are scheduled throughout the
school year. Test results are presented in Table 5.
Number of points is much lower than for Novi Sad
students. The only reasonable explanation is a usage
of English, non-mother language. Additional prob-
lem was the fact that the test was performed on the
distance. So, problems with questions, even the lin-
gual ones, could not be solved.
Table 3: Assignment points for Berlin students.
Berlin
Nr of
Students
Average
Points
Assgn 1
Average
Points
Assgn 2
Average
Points
Assgn 3
Average
Points
Assgn 4
Average
Points
Assgn 5
Average
Points
Assgn 7
Total
Points
Assgn
2003 52
88,57% 78,41% 75,00% 72,27% 65,00% 86,73% 77,14%
2005 85
86,88% 80,63% 86,25% 74,67% 75,63% 78,00% 80,34%
2007 64
87,14% 87,62% 87,62% 87,62% 81,00% 91,90% 87,15%
Average
87,53% 82,22% 82,96% 78,19% 73,88% 85,54% 81,54%
COMMON SOFTWARE ENGINEERING COURSE - Experiences from Different Countries
377
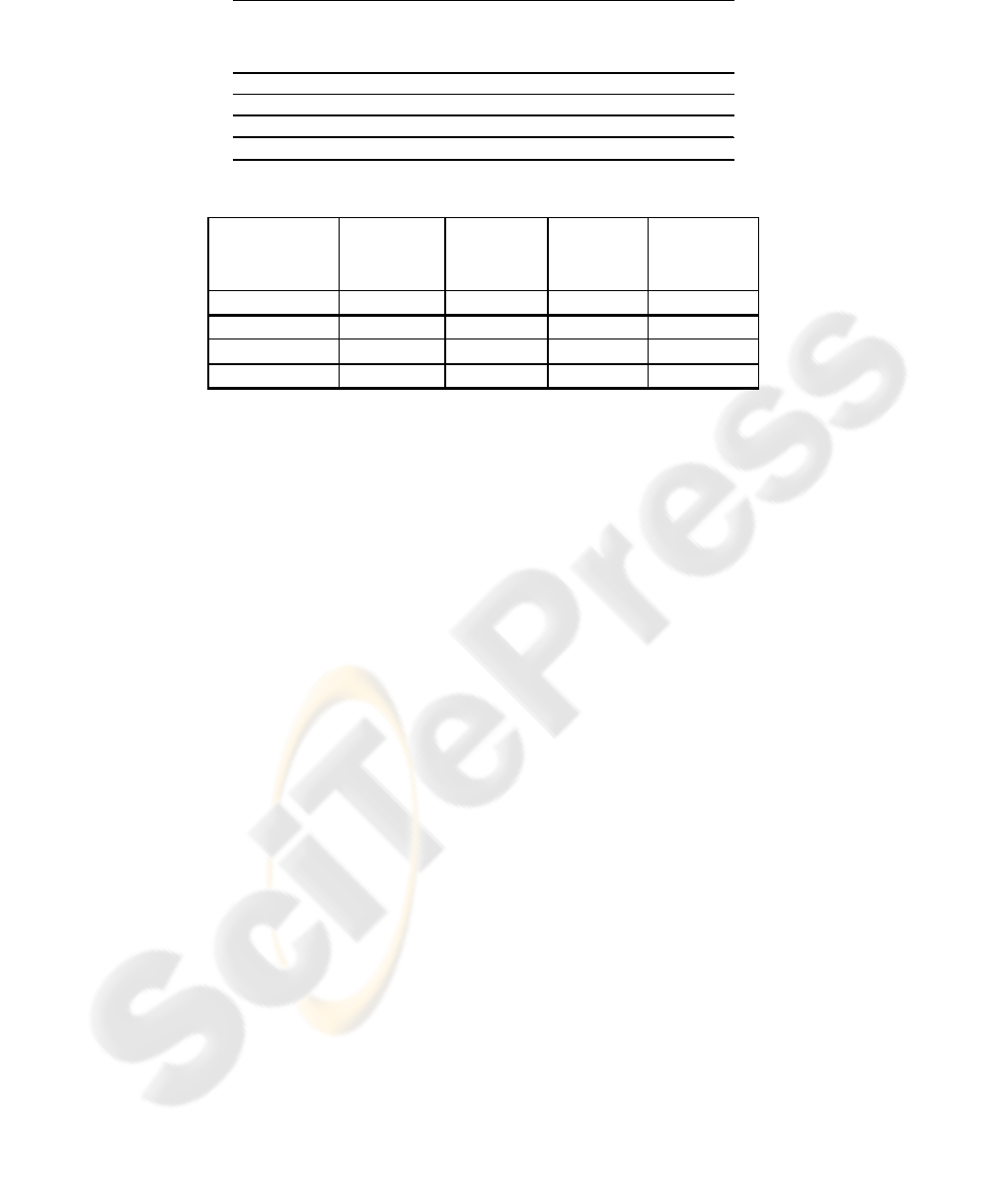
Table 4: Test points for Novi Sad students of Computer Science.
Novi Sad
Average
Points
Test 1
Average
Points
Test 2
Average
Points
Test 3
Average
Points
Test 4
Total
Points
Tests
2005
68,07% 66,09% 66,92% 63,95% 66,25%
2006
70,41% 71,35% 67,54% 70,89% 70,05%
2007
68,63% 70,00% 54,01% 53,33% 61,49%
Average
69,03% 69,14% 62,82% 62,72% 65,93%
Table 5: Test points for Tirana master students.
Nr of
Students
Average
Points
Test 1
Average
Points
Test 2
Total Points
Tests
Tirana 2007 17 58,33% 50,33% 54,33%
Tirana 2008 15 64,23% 56,43% 60,33%
Tirana 2008 II 15 67,33% 52,00% 59,67%
Average 63,30% 52,92% 58,11%
6 CONCLUSIONS
Results of the project were very successful, first of
all for students:
– Students are enabled to learn according to con-
temporary contents, principles and standards;
– Course compatibility, both general and particu-
lar, is achieved;
– Experiences, methods, and learning activities
and styles of lecturers from several different
countries are adopted;
There are a lot of similarities with the results
gained for the assignments. The final grade for each
of conducted courses is on the average between 8,20
and 8,29 for all countries.
Considering the method of passing the exam and
results for assignments and tests general conclusions
are drawn out:
– Students belonging to higher years are: (slightly)
more serious; get (slightly) higher number of
points for the assignments and for tests; pass the
exam in (slightly) larger percentage.
– Comparable groups of students from different
countries have similar results: they use the com-
mon material; are confronted with the same
methodology and didactics; meet the similar
style, techniques of presentation and exam
– Good results with the application of common
course material and techniques are a conse-
quence of exchange of experiences and opinions
of Project participants.
REFERENCES
Bielikova, M., Navrat, P., 2004. Experiences with Design-
ing a Team Project Module for Teaching Teamwork to
Students, Journal of Computing and Information
Technology, Vol 13, Nr 1, (pp.1 – 10).
Bothe, K., Schuetzler, K., Budimac, Z., Zdravkova, K.,
Bojic, D., Stoyanov, S., 2003. Technical and Manage-
rial Principles of a Distributed Cooperative Develop-
ment of a Multi-Lingual Educational Course, 1st Bal-
kan Conference in Informatics, Thessaloniki, Greece,
(pp.112-120).
Bothe, K., Schützler, K., Budimac, Z., Zdravkova, K.,
2005. Collaborative Development of a Multi-Lingual
Software Engineering Course across Countries, 35th
ASEE/IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference, Indi-
anapolis, USA, (pp. T1A-1 – T1A-5.Z.).
Budimac, Z., Putnik, Z., Ivanović, M., Bothe, K., Schu-
etzler, K., 2008 Conducting a Joint Course on Soft-
ware Engineering Based on Teamwork of Students, In-
formatics in Education, An International Journal, In-
stitute of Mathematics and Informatics, Lithuanian
Academy of Sciences, Vol 7., Issue 1., (pp. 17-30).
ACM, 2001. Computing Curricula 2001, ACM and the
Computer Society of the IEEE, http://www.acm.org
SWEBOK, 2001. Guide to the Software Engineering Body
of Knowledge SWEBOK, Bourque, P. and Dupuis, R.
(Ed.), IEEE Computer Science Press.
SE course homepage, http://www2.informatik.hu-
berlin.de/swt/intkoop/daad/
Zdravkova, K., Bothe, K., Budimac, Z., 2003. SETT-Net:
A Network for Software Engineering Training and
Teaching, ITI-Information Technology Interfaces,
Cavtat, Croatia, (pp.281-286).
CSEDU 2009 - International Conference on Computer Supported Education
378
