
APLYING COLORS BASED ON CULTURE KNOWLEDGE TO
MOTIVATE COLLABORATION ON THE WEB
Ana Luiza Dias
1
, Junia C. Anacleto
1
, Luciana M. Silveira
2
, Rosângela Ap. D. Penteado
1
and Laís A. S. Meuchi
1
1
Departamento de Computação – Universidade Federal de São Carlos (UFSCAR), São Carlos-SP, Brazil
2
Departmento de Tecnologia – Universidade Tecnológia do Paraná (UTFPR), Curitiba-PR, Brazil
Keywords: Collaborative work, Web project, Colors, Emotions, Common sense, Motivational patterns.
Abstract: Collaborative and Participatory work via Web tends to increase due to teams of professionals’ needs in
accomplishing tasks separated by distance and time, which demands more effort and stronger commitment
from each person. In this context, it must be considered cultural differences, which interfere with the
performance of each individual and either promote or deny the communication intended for the group. This
paper aims to discuss a multidisciplinary analysis about colors and stimuli in computing environment using
Common Sense knowledge, considering the cultural association people make between colors and actions,
emotions and objects, showing how it can motivate users to access and participate in collaborative tasks
through stimuli using color symbolically built in the culture.
1 INTRODUCTION
With globalization and the need for fast
communication without fixed places and time, the
use of the Internet and Web tends to become more
and more usual, creating the easiness of exchange
information and users` collaboration via Web. New
technologies have changed the ways in which people
interact and collaborate in a distance. The users can
be connected to the net and practice new ways of
collaborative work (Schümmer et al., 2007).
As a result of such situation, the tendency is that
more and more Web applications are designed to be
used by more than one user in a collaborative way.
The developers of collaborative work applications
via Web should try to understand what motivates the
users to engage and as well as to create a virtual
environment that it makes possible the individual
satisfaction to work with their applications in a
productive way.
For such satisfaction, one of the main subjects
chosen in this research is the application of colors in
the Web project, essential for visual communication,
that can reinforce or not the communicative
intention. Colors can help the developers to
highlight important points, as well as facilitate the
content reading and increase the satisfaction and the
user's engagement. It is important to study and to
understand which are the values aggregated to the
colors, once those values can be interpreted, and so
that can vary from culture to culture.
The promotion of universal access to
information comes from respect to culture,
facilitating through the colors and their meanings the
access to information and knowledge contextualized.
This article offers a multidisciplinary analysis about
colors symbolically constructed in culture to the
development of Web applications that encourage
collaborative work participatory. The significance of
color is an issue that will be explored here
considering the cultural context, represented by
knowledge of people’s common sense and what they
associate with each color, with respect to stimuli,
emotions and actions. This work considered people
with normal vision, i.e. people that see the colors.
The common sense knowledge to be used in this
work comes from the Project Open Mind Common
Sense Brazil (OMCS-Br) knowledge base
(www.sensocomum.ufscar.br).
This paper is organized as follow: section 2
points Systems that support computer-mediated-
human interaction; section 3 shows Motivation for
the engagement in activities; section 4 presents
Common sense knowledge to represent culture; the
27
Luiza Dias A., C. Anacleto J., M. Silveira L., Ap. D. Penteado R. and A. S. Meuchi L. (2009).
APLYING COLORS BASED ON CULTURE KNOWLEDGE TO MOTIVATE COLLABORATION ON THE WEB.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Human-Computer Interaction, pages 27-33
DOI: 10.5220/0001862600270033
Copyright
c
SciTePress

section 5 shows Colors classification; section 6
presents Colors and Emotions; section 7 shows
Classification of Emotion, objects and actions
according to the colors of common sense; section 8
brings some conclusions and future works.
2 SYSTEMS THAT SUPPORT
COMPUTER-MEDIATED-
HUMAN INTERACTION
There are three aspects that should be considered in
the project of applications that support human-
computer-human interaction (HCHI): (I) the core of
the definition is the group, where the computing
applications have the purpose of creating a solution
that satisfies the users' needs; (II) the interaction of
the group; (III) the process of the interaction should
be supported by the application, being like this, the
application should play an encouraging part to
stimulate the interaction among the people, even at
the distance. These are the objectives considered in
this work which aims to achieve with the colors
multidisciplinary analysis based on common sense
knowledge, the promotion of information
comprehension considering cultural aspects,
facilitating, through the colors and their meanings,
the collaborative work.
Huatong Sun (2001) quotes examples to
demonstrate the importance of cultural aspects in
interaction projects, such as: interface elements (the
Brazilian users like vibrant colors and pages with
many figures, and the Germans prefer organized
links in alphabetical order); the cultural symbols (the
Brazilians and Chinese feel comfortable when they
see figures on their cultures - Sugar Loaf and lotus
Flower); and the way of showing cultural symbols
(the Germans prefer textual components, whereas
the Brazilians and Chinese prefer colourful visual
components). Even considering the importance of
those subjects, developers still have difficulties in
obtaining support to their research regarding to the
interaction projected according to the users’ culture.
3 MOTIVATION FOR THE
ENGAGEMENT IN ACTIVITIES
In the literature, it is possible to find different
definitions for the term “motivation”, but all have a
common meaning: motivation is a personal internal
force to generate movement and it is a temporary
need, and it only exists while such force persist
(Bueno, 2007).
Motivation at the work environment has been
studied since 1900 (Salgado, 2005). One of the best
contributions for the area was the book "Motivation
and Personality" written by Maslow (1954) with
postulates that all humans have needs that lead them
to satisfaction and motivation, as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Maslow’s need hierarchy (Maslow, 1954)
According to Salgado (2005), Maslow has
structured the human necessities in a hierarchy, such
that to satisfy one level (self-actualization) it is
required to satisfy all the previous ones and the most
basics ones should be resolved first. However, in
agreement with Henry Murray apud (Novaes, 2007),
necessity factors can act in a disordered way,
according to the different personality` characteristics
of each individual, which can be achieved
simultaneously, without a rigid hierarchy.
The colors are related to people's emotions
because each person attributes certain meanings to a
certain color, what stimulates or inhibits their desire
and degrees of satisfaction. If a person gets
motivated by a color, he will possibly be able get to
accomplish Maslow`s hierarchy of needs.
An example that can be mentioned in the
Physiology level is that if a person feels good, happy
and motivated to do something in a collaborative
site, he will not fall sleep. Assisting the physiologic
needs, the body safety will be assisted, since
depends in parts on basic needs (Safety). When
people feel safe, they can have good relationships,
either with the family or friends (Love/Belonging).
From this wealthy relationship, people will feel
better, more valued, tending to respect the others and
himself/herself (self-esteem). Consequently the
person can reach the first level of the Maslow’s need
hierarchy which is personal accomplishment during
the developed activity, through creativity,
spontaneity and detachment for contribution that can
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
28
be only achieved when somebody feels good with
himself/herself.
3.1 Motivation in the Organization
With the globalization and technological progress,
competitiveness among the organizations has
increased, the need for continuous training has been
necessary and the processes of industrial automation
have been activated. Besides that, the demand for
better acting as collaborators' competence becomes
vital. So, organizations are always looking for
alternatives to motivate their collaborators, intending
to provide a better organizational environment and a
positive performance of their participant.
It is fundamental for the success of any
organization to have collaborators stimulated to
reach goals so that the expected and planned results
are reached and even overcome with good will and
satisfaction, because only after knowing the sources
of motivation of those involved is that one can
achieve additional, because the success of any
organization involves, undoubtedly, the level of their
collaborators' motivation (Novaes, 2007).
Bueno (2007) says that human motivation has
been one of the biggest challenges in organizational
administration for many psychologists, teachers and
executives. Some researches and theories have been
elaborated and have been trying to explain the
operation of this force apparently mysterious, or
even unknown that leads people to act in order to
reach their objectives. When a person follows a goal,
he is not necessarily motivated to reach this goal.
The factors that make him to follow that direction
can be intrinsic (internal) or extrinsic (external).
When they are intrinsic, there is motivation; when
they are extrinsic, there is either movement or
satisfaction (Bueno, 2007).
It is important to remind that the differences
among people make difficult the definition of
universal parameters that organizations can use to
motivate people in the same conditions. There is
always a subjective component in motivation that is
complex, related to culture and individual values.
For that reason this study will be taken into
consideration the common sense knowledge base of
OMCS-Br Project to try to soften that inequality of
conditions, as well as to provide solutions to assist
each individual's cultural values involved in the
collaborative task, considering his/her community.
4 COMMON SENSE TO
REPRESENT CULTURE
OMCS-Br Project (Anacleto et al., 2006) explores
the Web as a way for collaboratively constructing a
common sense knowledge base, counting on
contributions of Brazilian volunteers' statements.
Common Sense is defined here as a group of facts
known by most people, “including a wide part of
human experiences, knowledge on special, physical,
social, temporary and psychological aspects
involving daily experiences of humans” (Liu et al.,
2004) and that express of a certain group’s culture.
OMCS-Br Project can contribute to overcome
difficulties that many developers have to obtain
support from researches regarding the target user’s
culture designed for collaborative environment. This
project, to support this research, has been collected
information about what people think of certain
colors, what they remember when they see a certain
color, or which color people associate with certain
concepts presented. Currently, there are seven
templates used on OMCS-Br Project to collect
common sense knowledge on colors, objects and
emotions (Dias et al., 2009): Five templates (1-5) for
colors and objects, and three templates (6, 7, 8) for
colors and emotions according to table 1.
Table 1: Templates of common sense knowledge
collecting related the colors, objects and emotions.
Templates
1 (object) | makes me remind of color | (COLOR NAME)
2(color image) | makes me feel like | (OBJECT)
3(image color) | reminds me of a | (OBJECT)
4(color name) | makes me remind of a | (OBJECT)
5(color name) | makes me feel like | (OBJECT)
6 Color (image color) | makes me feel | (EMOTION)
7 When I am (emotion) | it reminds me of color | (COLOR NAME)
8 Color (image color)|makes me remind of color |(COLOR NAME)
According to templates in Table 1, it is observed
that there are three tables in the database, a table to
stores complete sentences entered by the site (Table
entries), a table for emotions (Table emotion),
another for names of the colors (Table colors) being
the images of colors generated randomly. The
outstanding words with capital letters are typed by
the users and feedback in other templates, the
underlined words are the words originated from of
other templates and the words in italic are generated
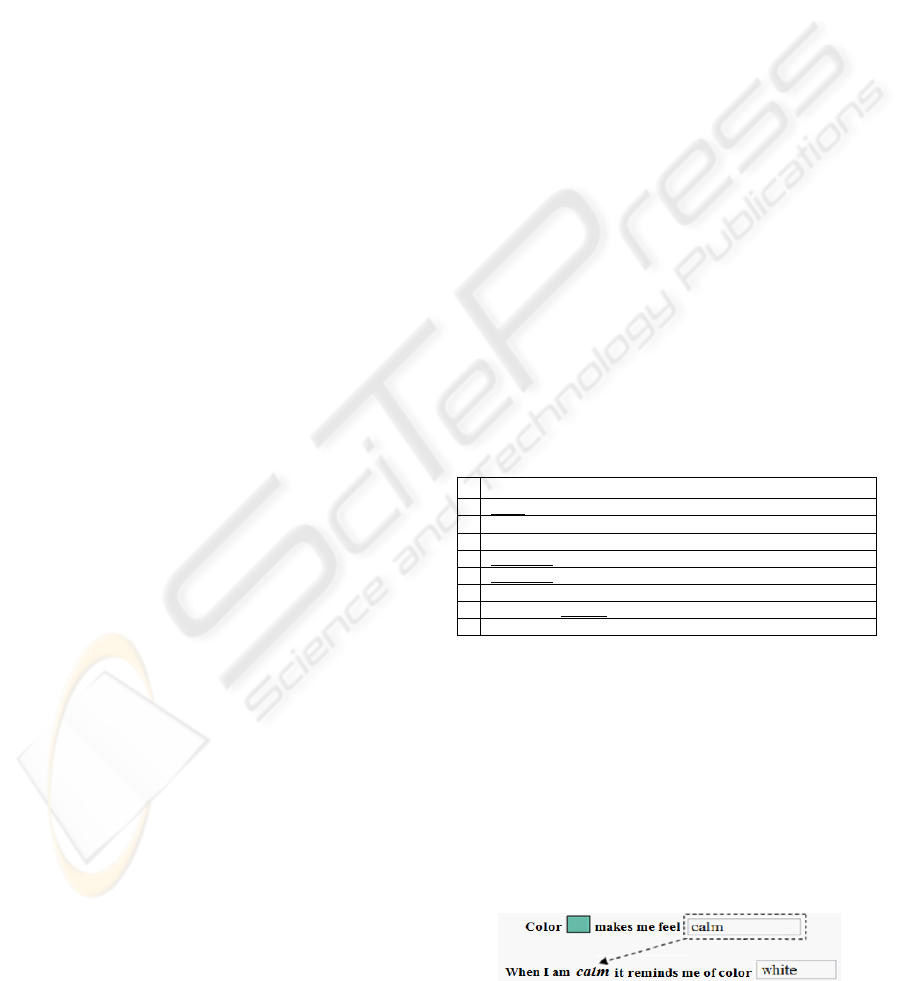
randomly. An example is presented in Figure 2.
Figure 2: Example of feedback in Templates.
No
APLYING COLORS BASED ON CULTURE KNOWLEDGE TO MOTIVATE COLLABORATION ON THE WEB
29

In this example, there are two templates. The
first is the template 6 of Table 1 that collects
emotions that serve as feedback for the second
template, which is the number 7 in Table 1. From
Figure 2, is perceived as such knowledge is collected
for Common Sense which is used in the review
process. To learn how these data are organized so
they can be used the next section deals with the
classification of colors.
5 COLOR CLASSIFICATIONS
The human eye is able to discriminate perception of
thousands of different colors, but the language
display a limited number of basic terms of color.
According to Berlin and Kay (1969), every language
that has words for colors, uses from two to eleven
basic terms, and the colors not included in these
terms, are considered variant colors.
The emergence of the basic terms for color
follows a natural logic. This logic is composed by
several evolutive trends, in particular: 1) from
general to specific, i.e., from light/dark distinction to
tone discrimination, 2) from the more evident the
less - for example, red before other tones, 3) from
the simple to the complex, i.e., from the isolated
colors for mixed ones (Sahlins, 2004). The basic
terms for color are the result of social use of color
not only to mean objective differences of nature, but
also communicate significant distinctions of culture.
This work uses the classification suggested by
Berlin and Kay (1969). The eleven colors spoken by
Brazilians are: yellow, blue, white, gray, orange,
brown, black, pink, purple, green and red. As shown
in Table 1, template 8 on common sense knowledge
collection site has been developed to confirm,
through common sense that people express
themselves using a few names of colors when they
see various shades of them. Some data already
collected by template 8 can be seen in Figure 3:
Figure 3: Example of data collected by the OMCS-Br
Project site
6 COLORS AND EMOTIONS
It is known that the light of each one of the colors,
starting from the moment that it is reflected in the
eyes and processed in the mind, can affect the center
of the emotions directly. However, each person
answers to the color in a particular way. People tend
to be attracted to some colors because of some
decisive factors, such as, personality, incidental
conditions of life or in desires and deeper more
intimate and even unconscious mental processes.
Nevertheless, Berlin and Kay (1969) report that the
personal choices are conditioned to the community
culture background what is considered in our
research. Our focus is on the culture of the
community, once it involves the individual's culture.
Colors not only evoke emotions, but also can
communicate messages or transmit concepts. It is
important to stand out that in any culture, colors can
transmit good or bad meanings. Some authors
(Pastoreau, 1997), (Silveira, 2005) mention some of
those meanings for colors in the western culture:
Yellow (color for light and heat, for sun and
summer, it is associated to prosperity and wealth);
Blue (favorite color of more than half of the western
population, color of water); Green (color of fortune
and money, nature, ecology); Red (color of danger,
prohibition, love and passion).
According to Dias et al. (2009) from that list of
meanings of the colors, then we find the need for
integration between colors and emotions to a better
light of the decisions of design of collaborative
computing environments to be developed. The
following subsections present the colors in the web
and the colors based on common sense that can be
used in the design of computational promoting the
motivation and the importance of considering the
emotions in the Web.
6.1 Colors in Web Context
According to Silveira et al. (2005), talking about
colors guarantees a debate full of controversies and a
lot of discussion, as it is a complex study and
basically interdisciplinary. For Pastoreau (1997), it
is possible to identify characteristics attributed to the
culture that the individual is inserted through the
study of symbology of colors, what helps the Web
designer take advantage of that knowledge, besides
noticing the collective meaning of colors in that
community.
For Silveira et al. (2005), to use just intuition for
color projects in the Web can work, but most of the
time it doesn't happen. For this reason, intuition
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
30
should be used added to a lot of information and
certain types or reasoning to get harmony, so that the
designer doesn't take the risk of elaborating an
unpleasant chromatic composition and driving the
project to a no-communication between user and the
system and, consequently, among people members
of the collaborative work team. To decrease the
chance of make a mistake, we propose to analyze the
common sense knowledge from a certain community
(Brazilians) and the relation among color, emotions,
actions and objects. From that analysis we are going
to formalize motivational patterns for Web design.
6.1.1 Colors based on the Common Sense
Knowledge
From the OMCS-Br Project, it can be collected
several meanings for colors related to the culture of
individuals from a certain community. An example
can be seen in Table 2 that illustrates the sentences
built by people registered in the site.
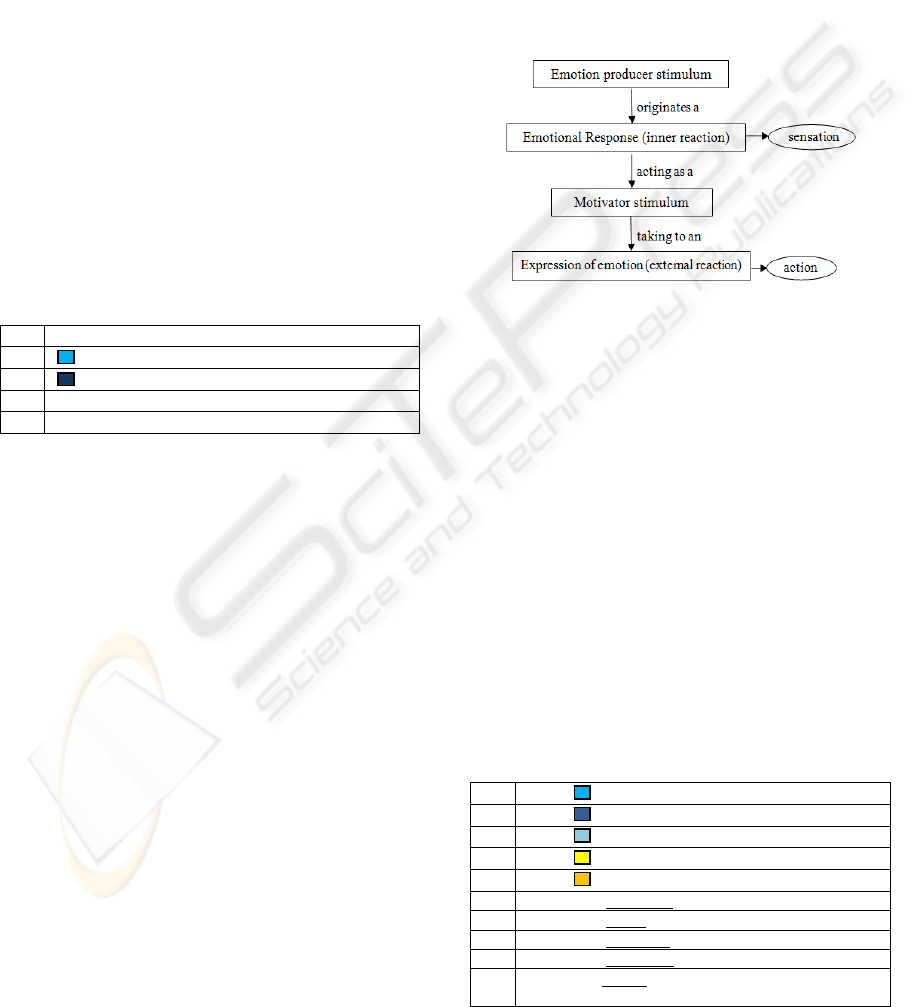
Table 2: Examples of sentences collected by OMCS-Br
Project, related to Templates 1, 2, 3, 4 and 5 in Table 1.
1
sky makes me remind of color blue
2
makes me feel like dipping in the pool
3
reminds me of a ocean
4
light blue makes remind a sky
5
blue makes me feel like swimming
According to the sample shown in Table 2, it can
be seen that blue color is related to water by most
people, which can be inferred that when a Web
designer will projects a site to a enterprise to work
collaboratively using blue color most of the team
members will tend to think in something related to
water, relaxing, and comfortable due to the blue tone
of the site, reflecting on the individual motivation
and the group productivity.
However, the emotions wakened from that
memory can hardly be inferred by people that are
not specialist in psychology, anthropology or similar
areas. The following subsection deals with the direct
association that the people make between colors and
emotions in the OMCS-Br Project.
6.2 Emotions in the Web Context
Emotion is defined as any restlessness and trouble of
the mind, or feeling or passion; any vehement or
excited mental state (Soto, 2005). An emotion-
producer stimulus originates an emotional answer
(inner reaction) that acts as a motivator stimulus that
takes to an expression of the emotion which is the
external reaction or emotional behaviour, as shown
in Figure 4.
According to Soto (2005), emotion is the
emotional behaviour or answer facing one emotional
state which turns into incentive. The function of
emotion is to provide to the organism the level of
arousal (pleasure or displeasure experience)
according to the emission of the most appropriated
answer to each specific situation. Emotion
predisposes people to a certain answer, alternatively:
(I) to get what can be useful to satisfy the needs; (II)
to avoid what can be opposed to that satisfaction.
Figure 4: Reaction chain to emotion produces stimulus.
Therefore, it is noticed that emotion is an
important issue in human behaviour and it assumes
significant role in the motivational process. Besides,
that emotion requires great level of arousal, which is
the product of subsequent physiological changes to
the activation of the nervous system.
6.2.1 Emotions based on the Common Sense
Knowledge
Some templates have been created for the OMCS-Br
Project to collect common sense knowledge related
to emotion. People tend to relate an emotion when
seeing a certain color and when speaking about a
color they remember to feel a certain emotion. Some
examples can be seen in Table 3.
Table 3: Examples of sentences collected by OMCS-Br
Project, related to Templates 6 and 7 in Table 1.
1
Color makes me feel JOY FUL
2
Color makes me feel CALM
3
Color makes me feel QUIET
4
Color makes me feel JOY FUL
5
Color makes me feel HAPPINESS
6 When I am passionate it reminds me the color RED
7 When I am happy it reminds me the color YELLOW
8 When I am depressed it reminds me the color BLUE
9 When I am aggressive it reminds me the color RED
10 When I am sleepy it reminds me the color BABY
BLUE
APLYING COLORS BASED ON CULTURE KNOWLEDGE TO MOTIVATE COLLABORATION ON THE WEB
31

In table 3 it is observed that the blue colors can
be related to several characteristics such as: to be
cheerful, calm, depressed; while the red colors are
related to passion or aggressiveness. However a
wide study on the common sense knowledge base is
being developed, to notice the cultural association of
colors and emotions, not only personal choices.
It is known that motivation is essential for
running organizations. No matter the amount of
machines, equipments or activities an organization
has, those elements cannot be used if people are
neither motivated nor engaged in their tasks
(Novaes, 2007). That is the intention here – to give
some support to motivate people to get engaged into
their Web-based tasks.
7 USING COLORS OF COMMON
SENSE TO CLASSIFICATE
EMOTIONS
To analyze the information these templates collect it
is being done a classification of emotions, actions
and objects. Figure 5 shows an example with the red
color, where the square shows the color to be
analyzed. The list of emotions that red evokes in
people is show in the left ellipse. In the back ellipse,
the actions that people are willing to perform when
they see the red color. The right ellipse brings the
objects related to the red color. See
http://www.dc.ufscar.br/~ana_dias/esquema.html for
all colors analyzed.
Figure 5: The red color associated to actions, emotions and
objects.
8 CONCLUSION
According to the hypothesis explored in this work,
individual motivation and participation in work via
Web are encouraged by the application of colors in
the computing environment design. Therefore, its
success is achieved when other variables are
considered in this application of color, exploring the
cultural meanings that evoque stimulus and action.
This application of colors can determine the
individual`s degree of engagement and participation.
We believe that information comprehension happens
when culture is respected, facilitating, through
colors and their meanings, the access to information
and contextualized knowledge. For these
considerations happen, assessments are being made
from the common sense knowledge base of potential
users to collaborative Web environments.
In the future, from the analysis of colors
collected in common sense, this work intends to
formalize Motivational Patterns, which describe
social processes (intrinsic motivation) and may
propose either changes or extensions to secondary
tech support as it is traditional in design patterns
(extrinsic motivations) (Schümmer et al., 2007).
There are some formalized Motivational Patterns
(Clear et al., 2005), (Schümmer et al., 2007). None
of these papers, however, explore the question about
the use of color in Web design for collaboration
promotion, the need to consider issues involving the
users` culture in collaborative work sites, as well as
the correlation between these two elements - color
and culture - to promote universal access to
information. Additionally, this work will extend to
people with some problems, such as: daltonism or
others disabilities.
REFERENCES
Anacleto, J. C.; Lieberman, H.; Tsutsumi, M.; Neris, V. P.
A.; Carvalho, A.F. P.; Espinosa, J.; Zem-Mascarenhas,
S.H.; Godoi, M.S., 2006. “Can common sense uncover
cultural differences in computer applications?” In:
BRAMER, M. (Org.). Artificial intelligence in theory
and practice - WCC. Springer-Verlag, v.217, p1-10.
Berlin, B; Kay, P., 1969. Basic color terms: their
universality and evolution. Berkeley: University of
California Press, 210p.
Bueno, M., 2007. “As Teorias de Motivação Humana e
sua Contribuição para a Empresa Humanizada: um
tribute a Abraham Maslow”. CESUC, anoIV, n6, 25p.
Clear, T.; Kassabova, D., 2005. "Motivational Patterns in
Virtual Team Collaboration". Australian Computing
Education Conference. Newcastle, Australia, v.2, 8p.
Dias, A.L.; Anacleto J.C.; Silveira, L.M.; Penteado,
R.A.D., 2009. Formalizing Motivational Patterns on
colors and their cultural meanings for developing Web
applications. ACM SAC2009, Honolulu.
Liu, H.; Singh, P., 2004. “ConceptNet: a practical
commonsense reasoning toolkit”. BT Technology
Journal, v.22, n.4, p.211-226.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
32

Maslow, A., 1954. Motivation and personality.NY:Harper.
Novaes, M. V., 2007. A Importância da Motivação para o
Sucesso das Equipes no Contexto Organizacional.
Revista Eletrônica de Psicologia, Ano I Num1.
Pastoreau, M., 1997. Dicionário das cores do nosso tempo.
Lisboa: Estampa, 182p.
Sahlins, M., 2004. Cores e culturas. Cultura na prática. R
Janeiro: UFRJ, 218p.
Salgado, L., 2005. Motivação no Trabalho. Qualitymark,
110p. ISBN: 857303565X.
Schummer, T.; Lukosch, S., 2007. Patterns for Computer-
Mediated Interaction. John Wiley & Sons, 600p.
ISBN: 978-0470025611.
Silveira, L. M.; Buchdid, S. B.; Silva, J. C. A., 2005.
“Metodologia de Aplicação de Cores no Projeto
WEB”. In: XI WebMedia. P. Caldas, pp.97-126.
Soto, E., 2005. Comportamento organizacional: o impacto
das emoções. São Paulo: Pioneira Thompson
Learning, 306p.
Sun, H., 2001. “Building a Culturally-Competent
Corporate Web Site: An Exploratory Study of Cultural
Markers In Multilingual Web Design”. In: ACM
SIGDOC, 8p.
APLYING COLORS BASED ON CULTURE KNOWLEDGE TO MOTIVATE COLLABORATION ON THE WEB
33
