
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING
SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS
An Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous Business Services
Thomas Moser, Richard Mordinyi, Stefan Biffl
Institute of Software Technology and Interactive Systems
Vienna University of Technology, Favoritenstrasse 9-11/188, Vienna, Austria
Alexander Mikula
Frequentis AG, Vienna, Austria
Keywords: System Integration, Integration of Heterogeneous Data Sources.
Abstract: Business system designers want to integrate heterogeneous legacy systems to provide flexible business ser-
vices cheaper and faster. Unfortunately, modern integration technologies represent important integration
knowledge only implicitly making solutions harder to understand, verify, and maintain. In this paper we
propose a data-driven approach, “Semantically-Enabled Externalization of Knowledge” (SEEK), that expli-
citly models the semantics of integration requirements & capabilities, and data transformations between he-
terogeneous legacy systems. Goal of SEEK is to make the systems integration process more efficient by
providing tool support for quality assurance (QA) steps and generation of system configurations. Based on
use cases from industry partners, we compare the SEEK approach with UML-based modeling. In the evalua-
tion context SEEK was found to be more effective to make expert knowledge on system requirements and
capabilities available for more efficient tool support and reuse.
1 INTRODUCTION
Designers of modern distributed business systems
need to integrate heterogeneous legacy systems and
their associated data interfaces to provide a platform
for more flexible business services. Major chal-
lenges are to provide this integration with little extra
effort, short time to market, and keeping the integra-
tion knowledge explicit and easy-to-understand in
order to simplify the overall system evolution
process. Modern integration technologies like web
services or the enterprise service bus (ESB) contri-
bute advanced interface technologies for legacy sys-
tems, but need a semantically consistent data model
agreed by the cooperating business services. Unfor-
tunately, such a kind of common data model is often
costly and hard to provide. Communication require-
ments that are not explicitly modeled make the solu-
tion hard to verify externally and configurations are
defined on a rather low level make the solution un-
necessarily hard to verify.
In this paper we propose a data-driven approach
“Semantically Enabled Externalization of Know-
ledge” (SEEK) that explicitly models a) the seman-
tics of integration requirements and capabilities
(Moser et al., 2009a); and b) the connectors and data
transformations between heterogeneous legacy sys-
tems (Mordinyi et al., 2008), to simplify systems
integration. We describe the overall SEEK systems
integration process. Major steps of the SEEK process
are the creation of the semantic model representing
the integration knowledge, the generation of trans-
formation instructions, and the semi-automated deri-
vation of technical system configurations.
The SEEK approach aims at improving the effi-
ciency of the systems integration process by a) more
effective support for concurrent modeling of stake-
holder requirements and system capabilities to lower
the risk of missing or wrong requirements; and b)
reducing effort with semi-automated consistency
checks of the derived system configuration as quali-
ty assurance (QA) approach. Based on use cases
from a research project with two industry partners,
56
Moser T., Mordinyi R., Biffl S. and Mikula A. (2009).
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS - An Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous
Business Services.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Databases and Information Systems Integration, pages 56-63
DOI: 10.5220/0001941600560063
Copyright
c
SciTePress

we evaluate SEEK with a UML-based integration
approach regarding the effort for modeling in the
context of the evaluation scenarios.
Major results of the evaluation are that SEEK
took considerably shorter for the modeling phase
and lowered the risk of errors in the system configu-
ration. While the integration analysis with explicit
knowledge modeling takes slightly more effort than
with the UML approach, the more efficient QA and
configuration generation activities can be expected
to return this investment after two iterations of sys-
tems integration (assuming conservative estimates).
The remainder of this paper is structured as fol-
lows: Section 2 summarizes related work on systems
integration, semantic integration, and service mat-
chmaking. Section 3 explains the research issues in
more detail, introduces the industry case study, and
derives the research method. Section 4 describes the
process for transforming the knowledge on the sys-
tem integration requirements and capabilities into
valid system configurations. Section 5 describes the
evaluation of the proposed concepts with a UML
approach to show similarities and discuss differenc-
es and open issues. Section 6 concludes the paper
and suggests further work.
2 RELATED WORK
This section summarizes related work on systems
integration, semantic integration, and service mat-
chmaking.
2.1 Systems Integration
System integration is the task to combine a range of
different systems to appear as one big system. There
are several levels at which system integration can be
performed (Balasubramanian et al., 2006), but there
is so far no standardized integration process that
explains how to integrate systems in general.
System integration can require changes (Hohpe
and Woolf, 2004) in the actual business policy of a
company not only due to the emerging communica-
tion needs between multiple computer systems but
also due to the communication requirements which
have to be established between business units.
Therefore, integration can have strong implications
on the company as improper integration solutions
can lead to considerable inefficiencies. Another in-
tegration challenge is to keep sufficient control over
the involved applications as in most cases integra-
tion developers have only limited control over these
applications, e.g., legacy systems. The classification
of system integration approaches (Trowbridge et al.,
2004) distinguishes between the design of an inte-
gration layer (process integration, portal integration
and entity aggregation) and ways to connect the sys-
tems (data integration, functional integration, and
presentation integration).
2.2 Semantic Integration
Semantic integration of heterogeneous information
systems has recently become an intensive area of
research. Semantic integration aims at resolving se-
mantic heterogeneities that can occur between lega-
cy information systems. Goh identified three main
categories of semantic conflicts in the context of
data integration that can appear: confounding con-
flicts, scaling conflicts, and naming conflicts (Goh,
1996). The use of ontologies as a solution option to
semantic integration and interoperability problems
has been studied over the last 10 years. Wache re-
viewed a set of ontology-based approaches and ar-
chitectures that have been proposed in the context of
data integration and interoperability (Wache et al.,
2001). Good examples for architectures or systems
in the context of semantically enhanced data integra-
tion can be found in the projects reports COIN (Goh,
1996), OBSERVER (Mena et al., 2000), BUSTER
(Stuckenschmidt et al., 2000), COG (Lara and de
Bruijn, 2004), and CLIO (Miller et al., 2001).
2.3 Service Matchmaking
Software components discovery and Web Service
discovery can be classified into two categories: sig-
nature matching and semantic matching.
Purtilo and Atlee (1991) propose a signature-
matching approach by specifying the invocation
parameters. Zaremski and Wing (1995) describe
exact and relaxed signature matching as a means for
retrieving functions and modules from a software
library. Wang and Stroulia (2003) provide a struc-
ture-matching-based signature matching for Web
Service discovery. Signature matching is an efficient
means for software components retrieval, but two
software components with similar signatures may
have completely different behaviors.
Semantic matching addresses this problem by
comparing software components based on formal
descriptions of the semantics of their behaviors. Za-
remski and Wing (1997) extend their signature-
matching work with a specification-matching
scheme. Cho et al. (1998) use a protocol to specify
interoperability of objects. Semantic matching iden-
tifies suitable services more precisely than signature-
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS - An
Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous Business Services
57

matching methods, but the cost of formally defining
provided and required services is considerable.
Paolucci et al. (2002) propose a DAML-S
(OWL-S) based approach for a declarative descrip-
tion of web services outside the representation capa-
bilities of UDDI and WSDL. They provide an upper-
level ontology of service profiles consisting of ser-
vice actors, functional service attributes, and func-
tion service descriptions.
3 RESEARCH MOTIVATION
Recent projects with industry partners from safety-
critical domains raised concerns about the chal-
lenges of verification in modern technology-driven
integration environments. From a certification point
of view a major goal was to improve the capability
to verify the correctness of an integration solution
while facilitating team work and tool support.
Consequently, we propose a data-driven ap-
proach that explicitly models the semantics of the
problem space, i.e., integration requirements and
capabilities (Moser et al., 2009a); the solution space,
i.e., the connectors, and data transformations be-
tween heterogeneous legacy systems (Mordinyi et
al., 2008); and finally provide a process to bridge
problem and solution spaces, i.e., find out whether
there are feasible solutions and minimize the cost of
integration. From this general approach we focus in
this paper on the overall description and evaluation
of the proposed integration approach compared to a
UML-based integration approach.
Research Method. For investigating these research
issues we gathered requirements from a set of use
cases from an industry case study. Based on these
use cases we designed a process for data-based sys-
tems integration based on the semantic description
of the integration knowledge. This process uses this
knowledge to support design, quality assurance
(QA), and finally configuration with semantic tools.
For empirical evaluation we determine the integra-
tion effort needed for each process step to compare
the steps in the new SEEK approach with traditional
methods and measure the effectiveness and efficien-
cy of the available methods and tools.
Air Traffic Management Use Case. Business ser-
vices in the Air Traffic Management (ATM) domain
are based on providing timely and correct data ana-
lyses from a network of heterogeneous legacy appli-
cations. With the strategic need to dramatically im-
prove the flexibility of traditional point-to-point in-
tegration to provide new ways of systems integration
while keeping the usual high level of safety, this
domain seems very well suited for the SEEK ap-
proach. The use case represents information that is
typically extracted from customers and domain ex-
perts during workshops for requirements elicitation
for information systems in the aviation domain. The
business system Air Traffic Management Informa-
tion Service (ATMIS) has to provide information
services about flights to business partners via a Pub-
lic Flight Information Portal (PFIP). ATMIS needs
to collect and refine information from at least 2 other
systems: the Central Flight Controller (CFC) and
the Single Flight Data Processors (SFDPs).
4 TRADITIONAL AND
SEMANTICALLY ENABLED
INTEGRATION PROCESSES
This section describes a traditional UML-based inte-
gration process approach, and a semantically
enabled integration approaches that make expert
knowledge explicit to facilitate tool support. Both
process variants are based on a generic integration
process described in section 4.1.
4.1 Generic System Integration Process
The generic systems integration process (see Figure
1) consists of 3 major steps: 1. modeling system
requirements and capabilities, 2. derivation and op-
timization of an integration system configuration;
and 3. lab/field testing and performance measure-
ment. Between these major steps, QA steps are
needed for assuring both a correct working system
model and a valid integration system configuration.
Modeling of Systems Requirements & Capabili-
ties. Subject Matter Experts (SMEs) provide systems
knowledge to describe the data exchange require-
ments and capabilities of the participating legacy
systems. This includes the descriptions of the inter-
faces to be shared, a detailed description of the ex-
changed messages types and a description of the
global and/or local additional (non-functional) re-
quirements of the systems (e.g., the maximal time
allowed for message delivery). Output of this
process step is a model representing the require-
ments and capabilities of the systems to be inte-
grated. Typical requirement and capability models
include a) communication contracts for defining the
communication capabilities and requirements of
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
58

business systems; b) policies for reflecting interests
of the organizations contributing to systems; and c)
infrastructure capabilities for describing the topolo-
gy and characteristics of the underlying network.
Figure 1: Steps in the Generic System Integration Process.
Requirements QA. QA personnel validate and
check the model created in the previous step for de-
fects and issues by comparing the knowledge cap-
tured in the model with the knowledge given as in-
put to the modeling process step. In case of issues
raised, these issues are reported back to the model-
ing step for resolution.
Systems Configuration Design & Optimization.
The Integration Expert (IE) uses the validated and
checked model created in the first process step to
derive as output a technical system configuration
representing the integration solution for the partici-
pating legacy information systems.
Configuration QA. QA personnel validate and
check the system configuration created in the pre-
vious process step for defects and issues (e.g., un-
suitable integration partners). This is achieved by
comparing the knowledge captured in the systems
configuration with both the knowledge captured in
the system requirements and capabilities model as
well as the knowledge given as input to the model-
ing process step. In case of issues raised, these issues
are reported back to either the systems configuration
creation step or the modeling process step for resolu-
tion.
Lab/Field Test and Performance Measurement.
The integration tester tests the validated and checked
technical system integration configuration in lab and
field tests to measure system performance characte-
ristics. This process step is beyond the scope of this
work and mentioned for completeness.
4.2 Traditional Systems Integration
Approach
This section describes a traditional (i.e., UML-
based) integration approach (see top process in
Figure 2).
System Description. For each legacy information
system to be integrated, the Subject Matter Expert
(SME) responsible for the particular system de-
scribes the requirements and capabilities of the sys-
tem using human-readable language. The outcome
of this process step is a set of legacy systems inter-
face description documents.
Integration Partner Derivation. In order to identi-
fy possible and select suitable integration partner
legacy systems, the SMEs of all participating sys-
tems, a domain expert (DE) who is capable of man-
aging the knowledge involved in the problem do-
main and an integration expert (IE) who is responsi-
ble for the actual integration need to cooperate. The
integration partner candidates are identified by the
SMEs by comparing the legacy systems interface
description documents created in the previous step
and by the DE by identifying similar knowledge
represented in the participating systems. The IE then
selects the best fitting integration partners from the
pool of possible integration partners. The outcome
of this process step is a set of accepted integration
partners.
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS - An
Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous Business Services
59
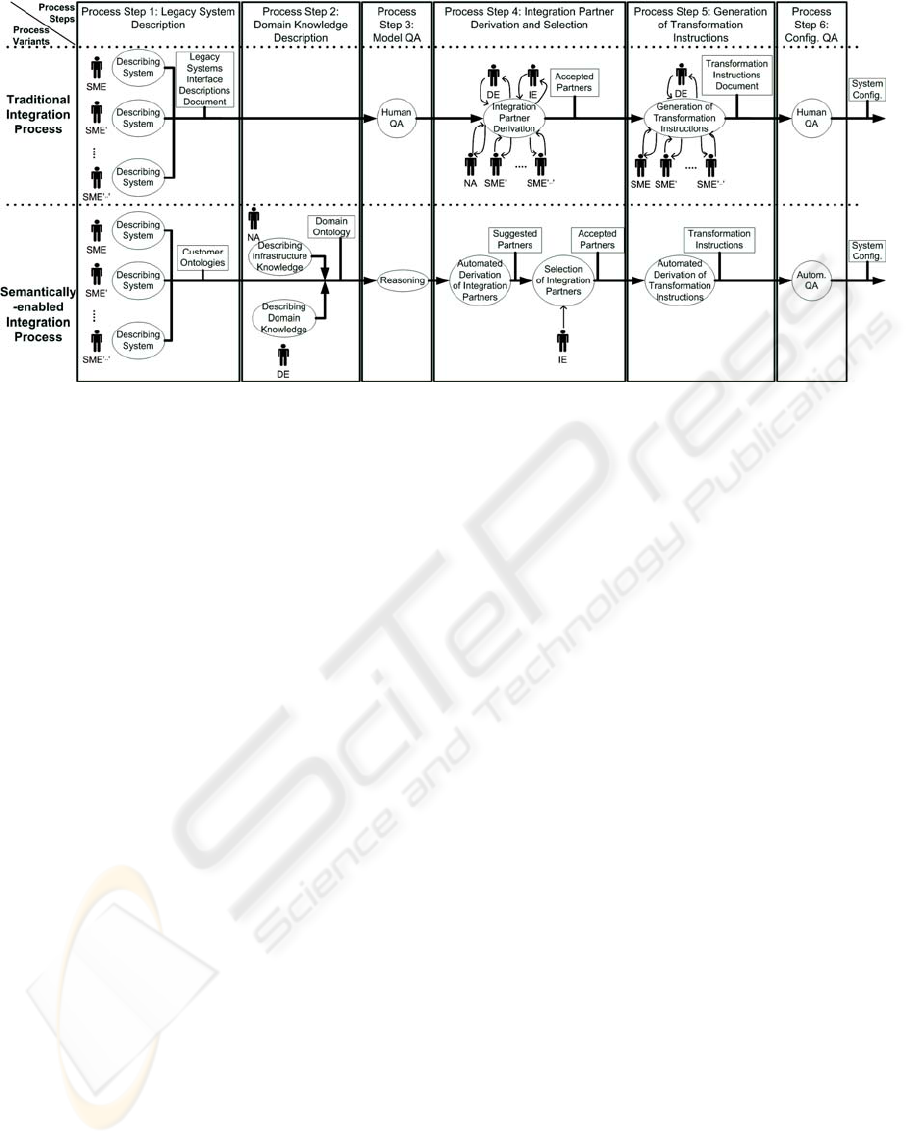
Figure 2: Comparison of a traditional UML-based approach and the semantically-enabled SEEK approach.
Transformation Instruction Generation. In order
to allow the interoperability between proprietary and
heterogeneous legacy information systems, semantic
transformation is needed at run time. Instructions are
needed to perform these transformations.
In this process step, the DE and the SMEs of the
particular affected system cooperate in order to de-
rive these transformation instructions. The outcome
of this process step is a document representing the
transformation instructions needed for the integra-
tion solution.
QA Steps. In the traditional integration process, the
2 QA steps are performed manually a) by comparing
the knowledge represented in the legacy systems
interface description documents with the knowledge
captured implicitly by the SMEs; and b) by compar-
ing the accepted set of integration partners and the
needed transformation instructions with the know-
ledge represented in the legacy systems interface
description documents and again with the know-
ledge captured implicitly by the SMEs. As key parts
of the knowledge are not available in machine-
understandable form, tool support for QA is very
limited and takes much effort from scarce human
experts.
4.3 Semantically Enabled Systems
Integration Approach (SEEK)
This section describes the SEEK system integration
approach (see bottom process in Figure 2). The fol-
lowing paragraphs summarize the process steps of
SEEK, with special regard to a continuous example
from the ATM domain presented in Figure 3.
Legacy System Description. For each legacy in-
formation system to be integrated, the SME respon-
sible for the particular system describes the require-
ments and capabilities of the system using machine-
understandable notations. In comparison to the tradi-
tional integration process, the outcome of this
process step is a set of ontologies describing the re-
quirements and capabilities of the legacy informa-
tion system to be integrated, as well as the mapping
of this information to general domain knowledge.
In the continuous example, there are 4 business
systems on the left hand side which provide a total
of 5 services that send messages, and 2 business
systems on the right hand side which provide a total
of 3 services that receive messages. The content of
these messages is represented using a tuple-based
notation. Additionally, services can define extra re-
quirements, like secure transmission.
Domain Knowledge Description. In addition to the
description of the requirements and capabilities of
the participating systems, the DE describes the
common knowledge of the problem domain used in
the integration scenario. This externalized domain
knowledge is used by the SMEs while describing the
particular legacy systems, who map proprietary sys-
tem information to more general knowledge
represented in the domain ontology in order to over-
come semantic gaps between legacy systems. On
infrastructure level the network administrator (NA)
describes the architecture and capabilities of the un-
derlying network. The outcome of this process step
is an ontology describing the shared problem domain
knowledge as well as the integration network infra-
structure. This domain ontology can be reused for
several integration scenarios in this domain.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
60
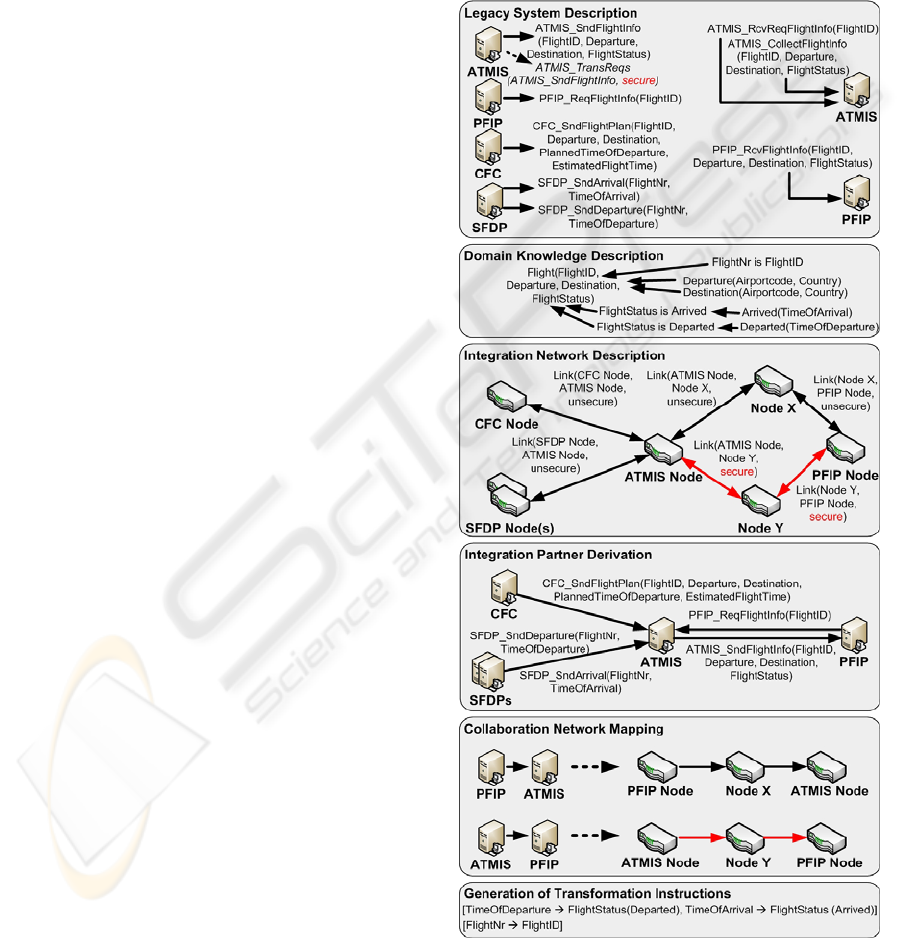
The first part of the continuous example shows
the description of the domain knowledge. The do-
main knowledge is exemplarily represented using a
tuple-based notation plus a set of arrows to indicate
relationships between domain knowledge elements,
e.g., the element “FlightStatus” could either be de-
fined using the element “Arrived” or the element
“Departed”, or the elements “FlightNr” and “Fligh-
tID” can be treated equally. The second part shows
the description of the integration network infrastruc-
ture. On the one hand, the architecture of the net-
work is represented by a set of nodes and links
which connect these nodes, on the other hands addi-
tional capabilities of nodes (e.g., secure transmis-
sion) are described.
Automated Integration Partners (IP) Derivation
and Selection. The externalized knowledge of the
SMEs, the DE, and the NA which was captured in
the ontologies in the previous steps is used to auto-
matically derive the set of possible Integration Part-
ner (IP) candidates with ontology-based reasoning,
allowing an easier and less error-prone identification
of possible IPs compared to the traditional integra-
tion process. The IE is responsible for choosing suit-
able IPs from the set of possible IPs derived in the
previous step. The outcome of this process step is a
set of accepted IPs.
The first part of the continuous example shows
the derivation of the possible IPs. Based on the lega-
cy system descriptions, the description and mapping
of the domain knowledge and the description of the
architecture and capabilities of the integration net-
work, the possible sending and receiving service
partners are derived using heuristics and ontology-
based reasoning (Moser et al., 2009b). In the exam-
ple, this is represented as a graph consisting of the
possible collaborations (i.e., the services which are
able to communicate) and the exchanged messages.
The second part shows the mapping of these derived
collaborations to the underlying network infrastruc-
ture. The example focuses on the collaboration be-
tween “PFIP” and “ATMIS”, showing that the re-
quest collaboration initiated by “PFIP” used the un-
secure route via “Node X”, while the reply collabo-
ration initiated by “ATMIS” used the secure (“red”)
route via “Node Y”, as defined in the additional ser-
vice requirements of the “ATMIS” business system.
Automated Derivation of Transformation In-
structions. In this process step, instructions for the
transformations between the participating heteroge-
neous legacy systems selected in the previous step
are automatically derived from the ontologies
created in the first 2 process steps. The outcome of
this process step is a set of transformation instruc-
tions needed for the integration solution.
In the continuous example, 3 exemplary trans-
formation instructions are generated, e.g., the trans-
formation of the element “FlightNr” to the element
“FlightID”, or the transformation of the element
“TimeOfDeparture” to the element “FlightSta-
tus(Departed)”.
Figure 3: Continuous example of the SEEK process.
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS - An
Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous Business Services
61

QA Steps. There are 2 QA steps in the SEEK inte-
gration process, which can be very well supported
with tools based on ontology-based reasoning. This
allows a much faster and more reliable QA com-
pared to the traditional integration process and re-
lieves scarce experts from tedious work.
5 EVALUATION
As part of a research project with two industry part-
ners, the approach has been evaluated in several sce-
narios from the ATM domain. We determined the
effort for both process step variants and compared
the overall outcome. The following paragraphs
summarize the effort needed to perform the particu-
lar process steps. The effort estimates are based on
the expertises of the integration experts from both
companies.
Step 1: Legacy System Description. The externali-
zation of legacy system knowledge using ontologies
needs slightly more effort than the traditional ap-
proach using only human-readable artifacts like
documents because the knowledge needs to be trans-
formed from implicit expert or system knowledge
into machine-understandable ontology models.
Step 2: Domain Knowledge Description. In the
traditional integration process the domain know-
ledge is not made explicit but implicitly captured by
domain experts and documents in a non-machine-
understandable way requiring no additional effort.
Additionally, the integration network knowledge
(i.e., the architecture and capabilities of the underly-
ing network infrastructure) are described, which
again represents additional effort compared to the
implicit knowledge of the traditional integration
process. Using SEEK the domain and integration
network knowledge has to be incrementally externa-
lized by the domain expert and the network adminis-
trator resulting in medium effort in the first instance.
This effort is reduced due to reuse within similar
integration scenarios or additional process iterations
triggered by reconfiguration issues.
Step 3: Model QA. The traditional approach re-
quires high effort to check the consistency and com-
pleteness of the documents since it is a manual ap-
proach. SEEK uses automated ontology-based rea-
soning techniques to assure consistent models lead-
ing to comparatively low model QA effort.
Step 4: Derivation and Selection of Integration
Partners. This traditional integration process step
demands exhaustive communication between the
involved roles (SME, DE, IE, NA) in order to derive
possible integration partners and clarify considerable
dependencies between legacy systems. This results
in very high integration effort for the traditional in-
tegration process while the SEEK approach provides
automated derivation of suitable integration partners
with ontology-based reasoning. The step involves
the IE only who is responsible for selecting the most
suitable set of integration partners from the provided
suggestions; the mapping of the selected integrations
partners to the underlying integration network is
fully automated using the externalized integration
network knowledge provided from step 2.
Step 5: Generation of Transformation Instruc-
tions. In case of the traditional approach the effort
for generating transformation instructions is higher
than with SEEK because the derivation of those in-
structions has to be done manually, but still lower
than in the previous step because the number of in-
volved roles is lower. The SEEK process step is per-
formed automatically using ontology-based reason-
ing for deriving transformation instructions based on
the explicitly captured knowledge.
Step 6: System Configuration QA. Consistency
and completeness checks in the traditional approach
are time-consuming and error-prone, leading to a
high level of manual human effort. On the other
hand, SEEK again uses automated ontology-based
reasoning techniques to quickly locate invalid sys-
tem configurations, resulting in much lower effort
for this process step.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper we proposed and evaluated the “Se-
mantically-Enabled Externalization of Knowledge”
(SEEK) approach to integrate heterogeneous legacy
systems to provide integration services with little
extra integration effort, short time to market, and
explicit and easy-to-understand integration know-
ledge to simplify the overall system evolution. In
contrast to integration technologies like web services
or the enterprise service bus, the SEEK approach
externalizes explicit integration requirements and
capabilities in machine-understandable formats,
making them easier to change and maintain.
Based on use cases from a research project with
two industry partners, we evaluated SEEK in com-
parison to an UML-based modeling approach. Major
results of the evaluation are: a) the semantically
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
62

enabled approach was found to be more efficient to
retain expert knowledge and make this knowledge
available to experts from different domains; b)
SEEK took considerably shorter for the modeling
phase and lowered the risk of errors in the system
configuration. While the integration analysis with
explicit knowledge modeling takes slightly more
effort than the traditional approach, the more effi-
cient QA and configuration generation can be ex-
pected to return this investment after two iterations
of systems integration (based on conservative esti-
mates). In many projects experiences have been that
a high modeling effort which has to be invested be-
fore any benefit can be shown is not accepted.
Therefore an approach such as the presented can
only succeed if convincing ways exist to minimize
modelling efforts. As the approach also introduced
new sources of complexity by more fully modeling
the integration knowledge, empirical evaluation of
larger cases are necessary to validate the benefits
and limitations of the approach.
Further work aims at a large-scale evaluation of
SEEK using scenarios and traditional integration
effort measurements of a real-world integration
project.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge all project
members of the SWIS (System-Wide Information
Sharing) project performed from 2006-2008 at
Vienna University of Technology together with Fre-
quentis AG and Austro Control GmbH.
REFERENCES
Balasubramanian, K., Gokhale, A., Karsai, G., Sztipano-
vits, J. & Neema, S. (2006) Developing Applications
Using Model-Driven Design Environments.
COMPUTER, 33-40.
Cho, I.-H., Mcgregor, J. D. & Krause, L. (1998) A proto-
col based approach to specifying interoperability be-
tween objects. In Proc. of the 26th Intl. Conf. on Tech-
nology of Object-Oriented Languages, 84-96.
Goh, C. H. (1996) Representing and Reasoning about
Semantic Conflicts in Heterogeneous Information Sys-
tems. MIT.
Hohpe, G. & Woolf, B. (2004) Enterprise Integration
Patterns: Designing, Building, and Deploying Mes-
saging Solutions, Addison-Wesley Professional.
Lara, R. & De Bruijn, J. (2004) Ontology-based Trans-
formations for the Automotive Industry. In Proc. of
the 1st Europ. Semantic Web Symp., Heraklion, Crete.
Mena, E., Illarramendi, A., Kashyap, V. & Sheth, A. P.
(2000) OBSERVER: An Approach for Query
Processing in Global Information Systems Based on
Interoperation Across Pre-Existing Ontologies. Jour-
nal on Distributed and Parallel Databases, 8, 223-
271.
Miller, R. J., Hernández, M. A., Haas, L. M., Yan, L., Ho,
C. T. H., Fagin, R. & Popa, L. (2001) The Clio
project: managing heterogeneity. ACM SIGMOD
Record, 30, 78-83.
Mordinyi, R., Moser, T., Mikula, A. & Biffl, S. (2008)
Foundations for a Model-Driven Integration of Busi-
ness Services in a Safety-critical Application Domain.
Technical Report (online version available at:
http://www.complang.tuwien.ac.at/richard/techrep/MD
IBSSAD.pdf).
Moser, T., Mordinyi, R., Mikula, A. & Biffl, S. (2009a)
Making Expert Knowledge Explicit to Facilitate Tool
Support for Integrating Complex Information Systems
in the ATM Domain. In Proc. of the Intl. Conf. on
Complex, Intelligent and Software Intensive Systems
(CISIS 2009), Fukuoka, Japan, accepted for publication.
Moser, T., Schimper, K., Mordinyi, R. & Anjomshoaa, A.
(2009b) SAMOA - A Semi-automated Ontology
Alignment Method for Systems Integration in Safety-
critical Environments. In Proc. of the 2nd IEEE Intl.
Wsh. on Ontology Alignment and Visualization, Fuku-
oka, Japan, accepted for publication.
Paolucci, M., Kawamura, T., Payne, T. R. & Sycara, K. P.
2002. Semantic Matching of Web Services Capabili-
ties. In Proc. of the 1st international Semantic Web
Conference on the Semantic Web, Lecture Notes In
Comp. Science, vol. 2342. Springer, 333-347.
Purtilo, J. M. & Atlee, J. M. (1991) Module Reuse by
Interface Adaptation. Software - Practice and Expe-
rience, 21, 539-556.
Stuckenschmidt, H., Wache, H., Vogele, T. & Visser, U.
(2000) Enabling technologies for interoperability. In
Proc. of the Wsh. on the 14th Intl. Symp. of Computer
Science for Environmental Protection (ISCSEP), Ger-
many, 35–46.
Trowbridge, D., Roxburgh, U., Hohpe, G., Manolescu, D.
& Nadhan, E. (2004) Integration Patterns. Patterns &
Practices, Microsoft Press.
Wache, H., Vögele, T., Visser, U., Stuckenschmidt, H.,
Schuster, G., Neumann, H. & Hübner, S. (2001) On-
tology-based integration of information-a survey of
existing approaches. In Proc. of the Wsh. on Ontolo-
gies and Information Sharing (IJCAI-01), Seattle,
USA, 108-117.
Wang, Y. & Stroulia, E. (2003) Flexible interface match-
ing for Web-service discovery. In Proc. of the Fourth
Intl. Conf. on Web Information Systems Engineering,
(WISE 2003), 147-156.
Zaremski, A. M. & Wing, J. M. (1995) Signature Match-
ing: A Tool for Using Software Libraries. ACM Trans.
on Softw. Eng. and Methodology, 146-170.
Zaremski, A. M. & Wing, J. M. (1997) Specification
matching of software components. ACM Trans. Softw.
Eng. and Methodology, 6, 333-369.
EFFICIENT SYSTEM INTEGRATION USING SEMANTIC REQUIREMENTS AND CAPABILITY MODELS - An
Approach for Integrating Heterogeneous Business Services
63
