
How to Adapt the KAOS Method to the
Requirements Engineering of Cycab Vehicle
Farida Semmak
1
, Christophe Gnaho
1,2
, Joêl Brunet
1
and Régine Laleau
1
1
University Paris –Est, Val de Marne, LACL, France
2
University Paris Descartes, France
Abstract. The Cycab is a new public vehicle with fully automated driving ca-
pabilities which aims at offering other alternatives to the private car. This work
is done as part of the Tacos project. The objective of this project is to define a
component-based approach to specify trustworthy systems from the require-
ments phase to the specification phase in the Cycab domain. Due to the long
time required to experiment the Cycab vehicle prototype, it becomes very im-
portant to deal with this kind of system from the requirements phase to the test
phase. In this paper, we propose an approach that provides a process specifying
in a flexible way a Cycab requirement model. This process is based on two
models: a generic model and a variant model. The former captures in integrated
view the large variety of the systems-to-be and the latter identifies and explicit-
ly expresses the features having an interest for the Cycab domain.
1 Introduction
The Tacos
1
Project [18] aims at defining a component-based approach to specify
trustworthy systems from the requirements phase to the specification phase in the
land transportation domain. It is well accepted that a gap still remains between the
initial specification of the requirements of a system and its software specification.
Thus, it becomes imperative to consider this first step in order to increase the global
control of the development of those systems and to ensure their reliability and safety.
The paper focuses on this phase of requirement engineering. These systems which
are both distributed and embedded require a rigorous requirement engineering ap-
proach integrating adaptation and tailoring. In the Cycab domain, very few studies
have focused on expressing the requirement at a high level. Moreover, the Cycab
system building is subject to requirements' change according to the effective tests on
the Cycab prototype. Therefore, the issue is how to take into account those changes
and integrate them in the current specification.
Our approach consists in defining a process for the application engineer allowing
him to create the Cycab requirement model and to adapt it when the requirements
1
1
The TACOS project (Ref. ANR-06-SETI-017) is partially supported by the French National
Research Agency.
Semmak F., Gnaho C., Brunet J. and Laleau R. (2009).
How to Adapt the KAOS Method to the Requirements Engineering of Cycab Vehicle.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Evaluation of Novel Approaches to Software Engineering - Evaluation of Novel Approaches to
Software Engineering, pages 87-94
DOI: 10.5220/0001952900870094
Copyright
c
SciTePress

change. This process is based on two models: a generic model describing the Cycab
domain and a variant model to help the application engineer to define situations ac-
cording to the future Cycab features.
The paper is organized as follows. Section 2 presents the domain context and the
proposed approach. Section 3 respectively describes the variant model and the gener-
ic model. Section 4 focuses on the Cycab model building process. Related work is
given in section 5. Section 6 concludes with some remarks about the results and fu-
ture works.
2 Overview of the Research Project
2.1 Domain Context
Land transportation and particularly Cycab has been chosen as the application domain
of the project. The Cycab concept is an experimental platform already used in several
research projects [2]. Cycab, are small self-service electric vehicles designed for
restricted access zones: historic city centers, airports, train stations or university cam-
puses. They have fully automated driving capabilities controlled by embedded soft-
ware. Two years of work have been necessary to design and implement the first two
prototypes [13]. Prototype development takes time and requires frequent testing and
thus needs constant evolution. In order to handle these changes, it is necessary to
define a requirement engineering process giving a requirement model capable of
evolution and adaptation.
2.2 Our Approach
These issues related to Cycab requirement model induce to consider a generic Cycab
model from which one can obtain specific models; for instance, "a Cycab with the
GPS localisation mode" or "a Cycab with the Wifi and GPS localization" or "a Cycab
with an automatic driving without doors" and so on.
We believe that Goal-Oriented Requirement Engineering (GORE) methods like
KAOS [3], I* [20], CREWS [15], GBRAM [1] are suitable to specify the generic
Cycab model. We have adopted the first one to which we have integrated the variabil-
ity concept. The KAOS approach allows to express "goals and their operationaliza-
tion into specifications of services and constraints (WHAT issues), and the assign-
ment of responsibilities to agents such as humans, devices and software pieces avail-
able or to be developed (WHO issues)" [9].
The purpose of variability is to be able to consider and express the discriminatory
elements between the applications of a given domain. Several approaches study va-
riability at an early requirement engineering step [7], [10]. Our approach of variabili-
ty is in continuation to our previous works [16] except that we now use the KAOS
method.
The objective of the approach is threefold: Firstly, it takes into account the re-
quirements at the highest level of abstraction with a goal orientation. Secondly, all
88
options and alternatives of the Cycab domain should be represented made possible
thanks to the variability paradigm. And thirdly, a building Cycab process must be
defined and thus that it will provide the possibility of creating, adapting and evolving
the requirement model in a flexible way.
To achieve this, we apply a two-step approach. In the first step, the domain engi-
neer with the domain experts elaborates a generic domain model and a variant model
named product models. In the second step, the application engineer builds a Cycab
model according to the situation it should satisfy.
In the sequel, we focus on the product models used as input of the Cycab model
building process.
3 The Product Models
3.1 The Variant Model
The variant model aims at capturing the variable aspects in the Cycab domain. It is
used as input point of the Cycab model building process.
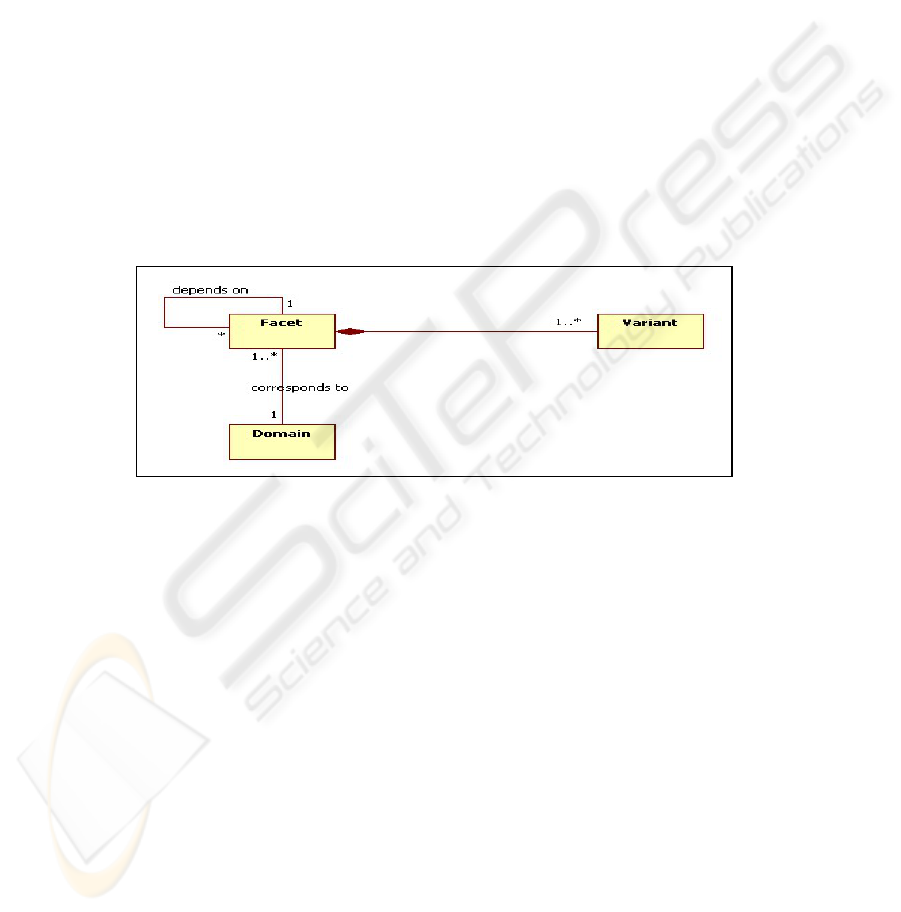
Fig. 1. The variant meta-model.
The variant model is defined as an instance of the variant meta-model. Figure 1
presents this meta-model as an UML class diagram. In this model, a facet represents a
feature having an interest for a given domain. For instance, the Cycab transportation
domain has several facets like: the localization mode which deals with the Cycab
localization from external sensors, the Road type to precise the kind of route the Cy-
cab takes and so on.
To a "facet" is attached one or more possible variants. A "variant" defines a va-
lued characteristic. For example, the localization mode may be attached to the follow-
ing set of variants: {GPS, Bluetooth, Wifi}; and the road type facet may also have the
set: {the pedestrian route, the dedicated route, normal route}. Finally, a given facet
may depend on other ones; this is captured in the "Depends on" relationship. The
latter can be refined to a number of more specific relations like requires, restricts,
enables, excludes or ensures. For example, a manual driving mode may restrict the
localization mode to only GPS.
89
3.2 The Generic Model
The generic model aims at capturing in integrated view, the common and variable
elements of the system-to-be, describing thus the large diversity of options the system
may take. It is based on an extension of the KAOS goal-driven methodology [9]. In
order to respect space constraint, we mainly focus on goal model.
The goal model allows to capture and to express all the possible options of the Cy-
cab system at the requirements level. It then represents all possible ways by which
stakeholders may achieve their goal.
Goal
Requisite
Requirement Expectat io n
Agent
1..*
*
High lev el goal
*
*
Reduces
+face tName
+va riantName
Responsability
+face tName
+va riantName
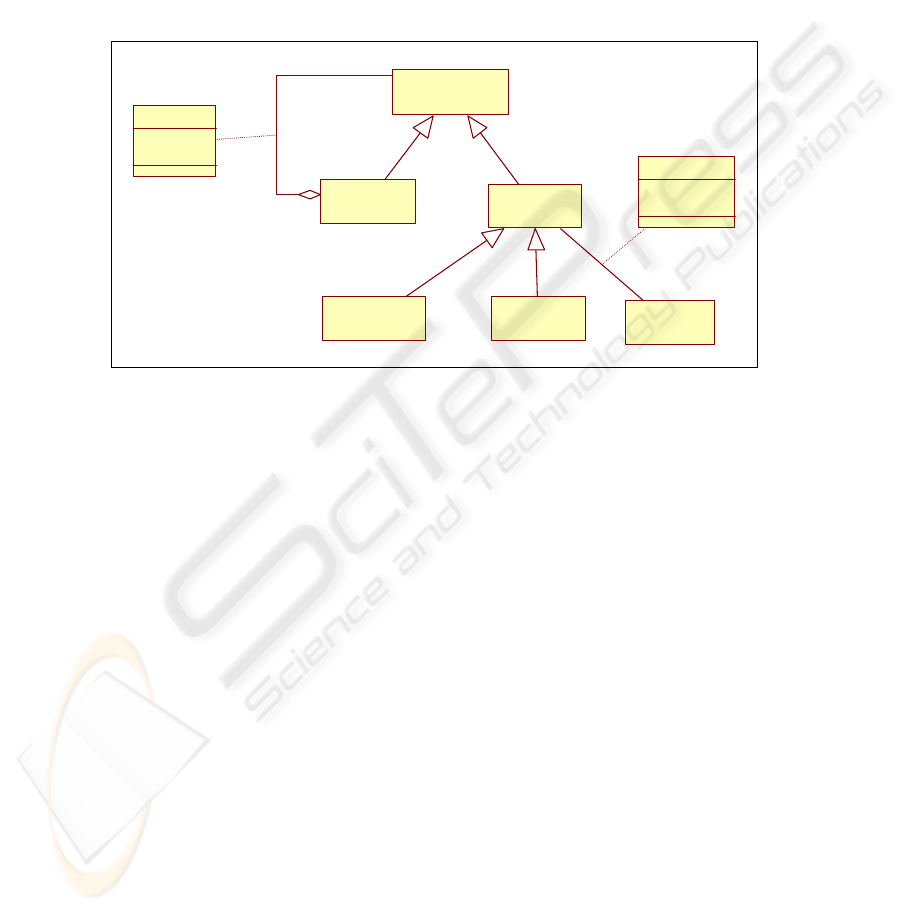
Fig. 2. A portion of the generic meta-model.
The goal model is constructed as an instance of the meta-model of which a portion
is illustrated in Figure 2. The central concept of this model is the concept of goal; a
goal is defined as an objective to be achieved by the system-to-be. For example, an
objective for the Cycab would be to have any passenger transportation request even-
tually satisfied. For more details about the KAOS meta-model, see [3], [9], [12].
The KAOS approach has not been found to address a class of systems of a domain
but a specific system. The concept of alternative in KAOS is a mechanism
representing a kind of variability that is local to a goal. But, variability may have an
impact on different part of the goal model. Consequently, we think that the concept of
<Facet-Variant> as we propose, related to a reduction link, allows in addition to take
into account different situations which could be considered by the Cycab designer.
Let us consider the high-level goal "Cycab transportation requests satisfied. There
are many ways to fulfill this goal according to the situations considered by the appli-
cation engineer. The concept of facet makes it possible to represent variability which
consists in indicating, according to the context to be reached, if the goal is reduced or
not in a sub-goal. It is thus defined as a property attached to the "reduces" relation-
ship, and then is represented in the model as an UML association class.
In order to illustrate this, let us consider the facet named "Cycab calling mode"
with the following two associated variants : automatic (a Cycab stopping at each
station) and on demand (it stops at a station only if there is an external or internal
demand).
90

Figure 3 shows the refinement of the above goal taking account these variants,
some reduction links are annotated with a couple <facet variant> representing the
variants that it addresses.
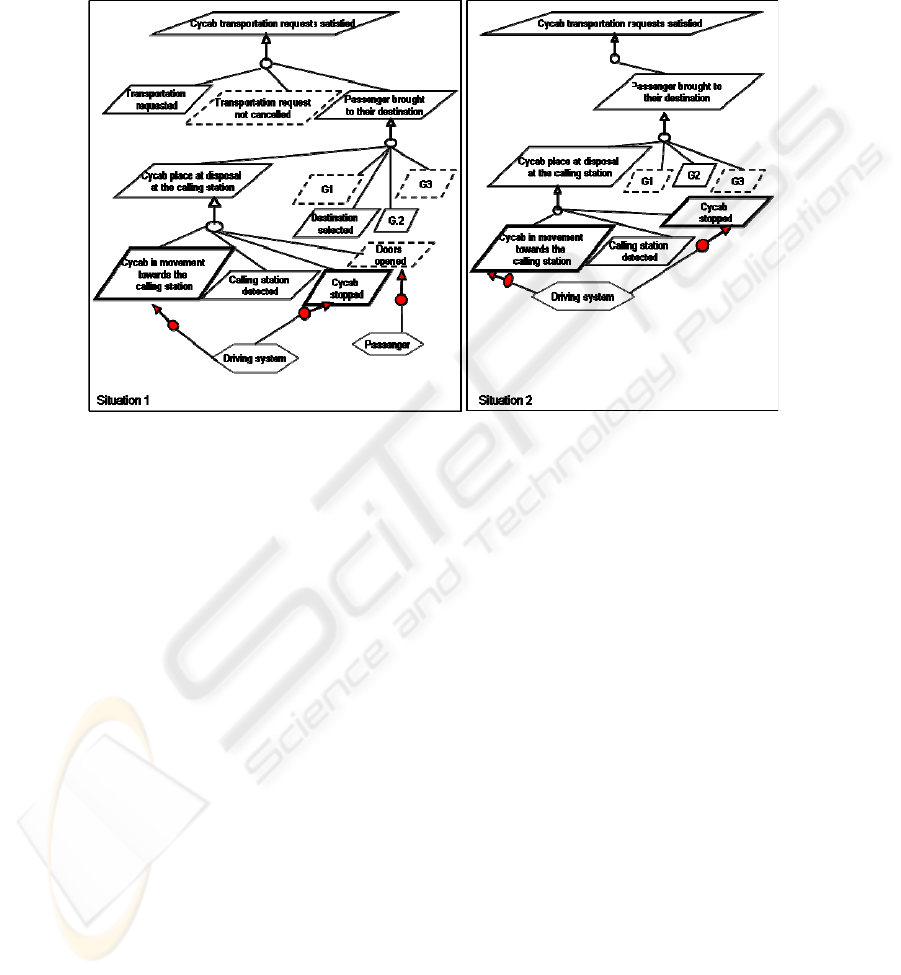
Fig. 3. Partial Goal Model of the simplified Cycab Case Study.
Consequently, Figure 3 presents two possible options that the Cycab system may
take when achieving the goal "Cycab transportation requests satisfied". So, accord-
ing to the "on demand calling" variant, for the Cycab transportation requests to be
satisfied, the transportation must be requested and transportation request not can-
celled and then, passengers brought to their destination. With "automatic calling"
variant, this goal is just reduced to the Passengers brought to their destination sub-
goal.
4 Cycab Model Building Process
In a traditional process, requirements are identified from documentation and domain
experts' interviews. In the proposed process, requirements are selected and adapted
thanks to both generic model and variant model. The process consists in four main
steps:
- Step 1: the application engineer selects a facet from the variant model. For in-
stance, let us consider the choice of the facet 1 related to Cycab calling mode.
- Step 2: he (she) selects the variant of the chosen facet. For instance, with the facet
1, the variant V2 is selected so we obtain the couple <F1: Cycab calling mode,
V2: Automatic>. If all couples (facet-variant) are selected, continue to step 3.
Otherwise, do again step 1 and 2.
- Step 3: The choice of a set of couples (Facet-Variant) leads to one situation. In-
deed, choosing several facets defines one situation to implement. The step 3 con-
91
sists in matching the selected features with the generic goal model. This step per-
formance leads to the requirement model of a Cycab system.
- Step 4: This step consists in validating the model obtained in step 3.
Figure 4 shows the results corresponding to the selected features.
Fig. 4. Two specific Cycab Goal Models.
The matching performed in the step 3 gives two specific Cycab models: the situa-
tion 1 on the left and the situation 2 on the right. Thus, the situation 1 leads to the
specific Cycab model with manual calling mode, manual doors opening mode and
automatic driving mode whereas the situation 2 defines another specific Cycab model
with automatic calling mode, automatic doors opening mode and automatic driving
mode.
5 Related Works
Variability is considered as the key challenge in building reusable infrastructure.
There are several approaches to express variability [4]. Intensive works have notably
been done in the domain of software product lines [19], [6] where 'variability' is ex-
pressed by the variation points and variants concepts: a variation point defines a point
in the model where variation occurs, while a variant is a manner of reaching variabili-
ty. Variability has also been studied in domain analysis. Among domain analysis
methods, the FODA method [7], [8] has been the first one to propose the concept of
feature, defined as a prominent or distinctive user-visible aspect, quality or characte-
ristic of a software system or systems. The feature model highlights, in the form of
hierarchy sets, the characteristics that discriminate systems in a domain.
92

In our project, we are interested in applying this concept of variability at goal-
based requirement level [17]. The approaches as Foda or SPL do not deal with varia-
bility at goal-oriented requirement level. However, some approaches have studied
variability at an early requirement engineering stage [10], [11].
We use the KAOS alternative link (OR-decomposition) that states that the sub-
goals represent alternative ways to achieve the parent goal. Nevertheless, we think
that it is not sufficient to acquire the variability effectiveness with only the OR-
reduction Link and we propose the couple <facet-variant> concepts. The concept of
facet represents a viewpoint or dimension of domain; it allows classifying and orga-
nizing domain knowledge. The notion of facet has been pointed out in library science
to classify library domain [14]. In our work, it makes it easier to understand and or-
ganize domain knowledge. Finally, the couple <facet-variant> enables first to
represent a richer variability while reducing combinatory explosion, and second be-
comes an effective support to designers in building a domain application.
6 Conclusions
In this paper, we have proposed a process whose objective is to offer a means to spe-
cify a Cycab requirements model. This process is based on two models: generic mod-
el describing possible needs of the Cycab domain and variant model expressing the
features of the same domain. The latter is useful to define situations to meet
The benefit of such approach is to be able to specify a Cycab model in a flexible
way and to adapt it according to the constant requirements' change.
We are currently validating the approach through a software prototype [5]. This
work is still at an early stage. Many further investigations have to be done. The first
one will concern the completeness of the variant model. The second one will be to
formally express requirement model which will help the mapping from requirements
model to software design.
References
1. Anton A. I., Goal based requirements Analysis, The 2
nd
Int. Conf. on RE 1996
2. Baille G. et al. The INRIA Rhônes-Alpes Cycab, Technical Report N°0229, Avril 1999,
ISSN 0249-0803
3. Dardenne A., Lamsweerde A. van and Fickas S., Goal-oriented Requirements Acquisition,
Science of Computer, April 1993
4. Frakes W., Pole T., An empirical study of representational methods for reusable software
component, In IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering, Vol. 20, N°8, August 1994
5. Gnaho C. & Al, "A Tool for Modeling Variability at Goal Level", Third Int. Workshop on
Variability Modelling of Software-intensive Systems (VaMoS), 2009
6. Halmans G., Pohl K., Communicating the variability of a software product family to cus-
tomers, Software and System Modeling, Springer-Verlag 2003
7. Kang K., Cohen S., Hess J., Novak W. and Peterson S., Feature-oriented domain analysis
(FODA) feasibility study CMU/SEI-90-TR-21, Univ. Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania, 1990
93

8. Kang K., Kim S., Lee J. et al., FORM: A Feature-Oriented Reuse Method with Domain-
Specific Reference Architectures, Annals of Software Engineering, 5, 143-168, 1998
9. Lamsweerde A., From Systems Goals to Software Architecture, Formal Methods for Soft-
ware Architectures, vol. 2804 of LNCS, Springer, 2003
10. Liaskos S., Lapouchnian A., Yu Y., Yu E. and Mylopoulos J., On Goal-based Variability
Acquisition and Analysis, 14th IEEE Int. Conf. on Requirements Engineering, 2006
11. Liaskos S., Jiang L., Lapouchnian A., Wang Y., Yu Y., Sampaio do Prado Leite J. C. and
Mylopoulos J., Exploring the Dimensions of Variability: a Requirements Engineering
Perspective, First International Workshop on Variability Modelling of Software-intensive
Systems (VaMoS), 2007
12. Objectiver Requirement Engineering tool, http://www.objectiver.com/
13. Parent M., Automated public vehicle: a first step towards the automatic highway, in the
Proc. Of the World Congress on Intelligent transport systems, Oct. 1997
14. Prieto-Diaz R., Implementing Faceted Classification for software reuse, Communications
of the ACM, Vol. 34, N°5, May 1991
15. Rolland C., Souveyet C., and Ben Achour C., Guiding Goal Modelling Using Scenarios,
IEEE Transactions on Software Engineering (TSE), 1998
16. Semmak F., J Brunet., Variability in Goal-oriented Domain Requirements, 9th Internation-
al. Conference on Software Reuse (ICSR), vol. 4039 of LNCS, Springer Verlag, 2006
17. Semmak, F. & Al, "Extended Kaos to support Variability for Goal oriented Requirements
reuse", Int. Workshop Model Driven Information Systems Engineering with Caise'2008
18. TACOS project, ANR-06-SETIN-017, programme SETIN'06, http://tacos.loria.fr
19. Van Gurp J., Bosch J., Svahnberg M., On the notion of variability in Software Product
Lines, Proceedings of the Working IEEE/IFIP Conference on Software Architecture, 2001
20. Yu E., Towards Modeling and Reasoning Support for Early-Phase Requirements Engineer-
ing, ACM Press, 3
rd
IEEE International Symposium on Requirements Engineering, pages
226-235, 1997
94
