
DISCOVERY AND ANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY PATTERN
CO-OCCURRENCES IN BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS
Jean Michel Lau, Cirano Iochpe
Informatics Institute, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, 9500 Bento Gonçalves Av., Porto Alegre, Brazil
Lucinéia Heloisa Thom, Manfred Reichert
Institute of Databases and Information Systems, University of Ulm, Germany
Keywords: Business process modeling, Workflow activity patterns, Knowledge discovery, Data mining, Reuse.
Abstract: Research on workflow activity patterns recently emerged in order to increase the reuse of recurring business
functions (e.g., notification, approval, and decision). One important aspect is to identify pattern co-
occurrences and to utilize respective information for creating modeling recommendations regarding the
most suited activity patterns to be combined with an already used one. Activity patterns as well as their co-
occurrences can be identified through the analysis of process models rather than event logs. Related to this
problem, this paper proposes a method for discovering and analyzing activity pattern co-occurrences in
business process models. Our results are used for developing a BPM tool which fosters the modeling of
business processes based on the reuse of activity patterns. Our tool includes an inference engine which
considers the patterns co-occurrences to give design time recommendations for pattern usage.
1 INTRODUCTION
Process-aware information systems (PAIS) prove to
be efficient tools for the design and automation of
business processes. Business process is a set of
(structured) activities which jointly perform a
particular business goal. Such activities are related
to specific business functions or process fragments
(e.g., notification, approval) having a well defined
semantics (Thom, 2006a, Thom, 2006b). In
particular, a certain process fragment or business
function (e.g., enabling document approval) may
occur several times within one or different process
models. That means multiple logical copies of the
same process fragment may be used with same or
different parameterization (e.g. approval by a single
actor or by multiple actors). In (Thom, 2009) such
fragments are represented as workflow activity
patterns: Request for Activity Execution without
Answer, Request for Activity Execution with Answer,
Approval, Notification, Decision-making and
Information Request.
An example of activity pattern is the
unidirectional performative pattern. This pattern
represents a unidirectional message as described in
(zur Muehlen, 2002). A sender uses unidirectional
performative messages to request the execution of a
particular activity from a receiver (e.g., human or
software agent) involved in the process. The sender
continues execution of his part of the process
immediately after having sent the request. The
complete set of activity patterns on which this work
is based is described in (Thom, 2006b, Thom, 2009).
Generally, multiple activity patterns can be
composed to a process model using workflow
patterns (e.g., Sequence, AND-Split, AND-Join,
XOR-Split). Through an empirical study, in which
214 real-world process models were analyzed, the
existence of seven activity patterns has been
confirmed (cf. Thom 2008a, Thom, 2008b, Thom,
2009). In that approach it was shown that the
analyzed process models can be completely
designed based on the aforementioned patterns; i.e.,
the set of identified activity patterns has been
necessary as well as sufficient to design the 214
process models, at least at a certain level of
granularity. This pattern set is closer to the
vocabulary abstraction level which business
processes are usually described by domain experts.
Though it is known that pattern utilization
83
Lau J., Iochpe C., Thom L. and Reichert M. (2009).
DISCOVERY AND ANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY PATTERN CO-OCCURRENCES IN BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages 83-88
DOI: 10.5220/0001958800830088
Copyright
c
SciTePress

improves the quality and performance of process
modeling, contemporary BPM tools like Intalio,
ARIS Toolset and WBI Modeler do not support
process designers in defining, querying and reusing
activity patterns as building blocks for business
process modelling (OASIS, 2006).
In this paper we present preliminary results
concerning the discovery and analyses of the co-
occurrences of the activity patterns in real-world
process models. Our goal is to use the results of this
analysis for developing a BPM tool, which fosters
the modeling of business processes based on the
reuse of activity patterns. The results of our analysis
can be further used by this tool to suggest a ranking
of the activity patterns best suited to succeed the last
applied pattern in a process design, facilitating the
modeling phase and leading to more standardized
and less error prone process models.
In order to perform the analysis we apply a
knowledge discovery on databases (KDD) process.
It is a process which involves theories and tools to
help humans to extract knowledge from large,
growing digital datasets. Its main purpose is to
identify valid patterns, potentially useful and
understandable from a set of data. In this context,
data constitute a set of facts; and patterns are
expressions in some language describing a subset of
the data or a model applicable to them. It can be split
into 5 main phases: 1) data selection; 2) data pre-
processing; 3) data transformation; 4) data mining,
and 5) result validation (Fayyad, 1996).
In particular, we implement a process model
mining tool (BPM mining tool for short) to be used
for identifying activity patterns co-occurrences. Our
miner allows analysing process models instead of
event logs as proposed in literature (Günther, 2008),
(Aalst, 2003). This can be considered as a very
important functionality to automatically identify
activity patterns co-occurrences in real-world
process models.
The remainder of this paper is organized as
follows: In section 2 we discuss related work.
Section 3 presents the data mining technique as well
as the algorithm used to perform the mining of the
activity patterns co-occurrences in real process
models. Section 4 applies the KDD process for
mining the process models. In this section we also
introduce the BPM mining tool we are developing
and some results generated by this tool when being
applied to real process models. Finally, Section 5
concludes the paper with a summary outlook.
2 RELATED WORK
Recently, a variety of workflow patterns was
suggested for capturing different aspects in PAISs
including control and data flow, resources, process
change, and exception handling (Aalst, 2003),
(Weber, 2007). However, there has not yet been a
mapping of activity patterns onto process (meta)
models and process modeling tools respectively.
Concerning workflow patterns, tool support is
provided by YAWL (Aalst, 2005), which uses
extended workflow nets as building blocks for
workflow specifications. Multiple extended
workflow nets involved in a workflow specification
can be connected to each other by composite tasks.
The PICTURE approach proposes a set of 37
domain specific process building blocks (Becker,
2007). More precisely, these building blocks are
used by end users in Public Administrations to
capture the process landscape and are also specific
to this domain). Finally, ProCycle presents an
approach implementing process change patterns in
ADEPT2 (Weber, 2009).
3 SELECTING A DATA MINING
METHOD AND ALGORITHM
If the goal of a KDD process is to predict the
behaviour of some variables, utilization of models,
which only describe or group the data, will not be
useful. Besides that the kind of learning, the task to
be done, the type of repository to be mined, and
knowledge representation must be considered during
the selection of the data mining technique (Brand,
1998), (Goebel, 1999), (Han, 2001). Table 1
presents these aspects and respective values which
were considered in the selection of the data mining
algorithms used in our approach.
Table 1: Aspects which were considered in the selection of
the data mining method.
Data mining aspect Value
Model Type Predictive
Learning Type Unsupervised/Batch
Task to be done Association Analysis
Repository to be mined Process models database
Knowledge Representation White box
Based on Table 1 we have studied the algorithms
for association rules discovery. This technique is
best suited for association analysis and is a
predictive one. This choice was made, because what
we are looking for is a future prediction based on
already occurred facts. In our case, the occurred
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
84
facts are represented by process models partially
designed, while the goal is to discover (or to predict)
the next activity pattern to be used in the modeling
of these process models.
The technique is also based on
unsupervised/batch learning, i.e., it allows to prepare
a set of processes in a file and send this file to the
data mining algorithm in a batch mode.
Besides that, the white box concept guarantees
that the results when applying this technique are
easily understandable by humans so that we can
make some manual inferences with the mined
information (Agrawal, 1993).
Given a set of transactions, where each
transaction is a set of items, an association rule is an
expression A (antecedent) => C (consequent), where
A and C are sets of items. The intuitive meaning of
such a rule is that transactions in the database, which
contain the items in A, tend to contain the items in C
as well. (Agrawal, 1993).
The main advantages of association rules that
motivate their use in our approach are as follows: (a)
they are easily understood by humans; (b) they are
used to represent empirical associations; (c) through
special measures (support and confidence) it
becomes possible to evidence how useful mining
results are (Han, 2001).
A workflow process model can be understood as
a graph with a predefined semantics. In this context,
patterns are identified in recurrent subgraphs within
a set of graphs (e.g., a set of processes models).
Given a set of graphs, a graph mining algorithm
searches for substructures which satisfy some
criteria (e.g., minimum frequency of patterns and
minimum confidence). Based on recurrent
substructures, association rules can be derived. In
this context, we have selected the Frequent
SubGraph (FSG) algorithm to be used in our
approach (Kuramochi, 2004). We choose FSG due
to its good performance results, scalability, good
documentation and simple and well defined I/O.
4 APPLYING KDD FOR MINING
PROCESS MODELS
In the data selection step of our KDD process we
analyzed 190 process models. Most analyzed models
had been created with the Oracle tool or an UML
based process modeling tool. Altogether, the
considered process models stem from 12 different
organizations and are related to different application
domains. Note that the mining is performed
considering the process models and not their
execution logs as done in other approaches (see
(Tristão, 2008), (Aalst, 2003)).
UP
NP
N
P
BP
BP – Bi-directional
NP – Notification
UP – Unidirectional
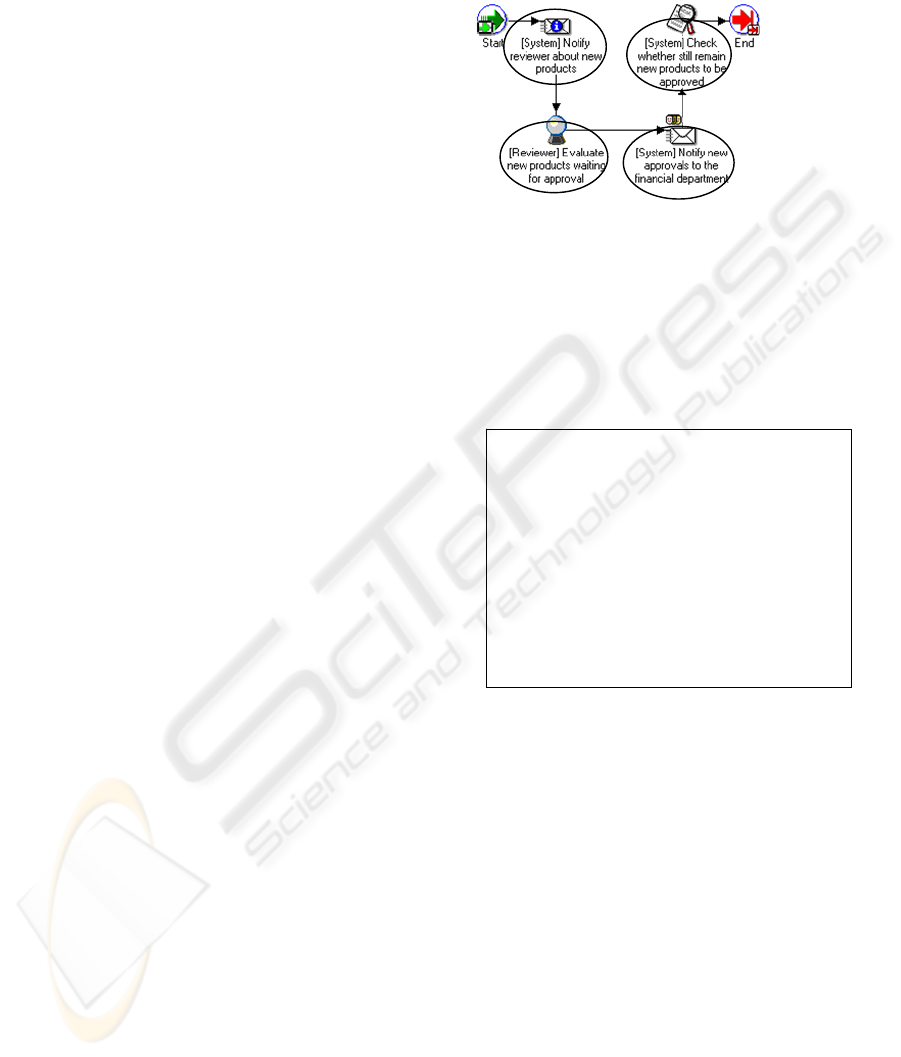
Figure 1: Example of activity patterns identification.
To mine process models, first of all we need to
transform the model such that the mining algorithm
can extract the needed information. In this pre-
processing phase the 190 process models were
analyzed and the activity patterns they use were
identified. Each activity or partial order of activities
was labelled as activity pattern.
t # Example – 1 – Approval process for a marketing
campaign of a new product
v 0 S
v 1 N
v 2 B
v 3 N
v 4 U
v 5 E0
u 0 1 N
u 1 2 N
u 2 3 N
u 3 4 N
u 4 5 N
t –transaction
v – graph node (activity pattern)
u –edge
S – start node
N – notification
B – bi-direcional pattern
U – unidirectional pattern
E0 – end node
# - comment sign
t # Example – 1 – Approval process for a marketing
campaign of a new product
v 0 S
v 1 N
v 2 B
v 3 N
v 4 U
v 5 E0
u 0 1 N
u 1 2 N
u 2 3 N
u 3 4 N
u 4 5 N
t –transaction
v – graph node (activity pattern)
u –edge
S – start node
N – notification
B – bi-direcional pattern
U – unidirectional pattern
E0 – end node
# - comment sign
Figure 2: Example of process transformation.
In the data transformation phase we mapped
each process model together with the identified
activity patterns, to the format required by the FSG
algorithm (cf. Section 3). For example, the process
model shown in Fig. 1 was transformed to the
format depicted in Fig. 2. Each node has an
incremental index and a label which indicates the
activity pattern this node represents. Edges refer to
the nodes they connect and have a label. All edges
have the N (Normal) label since we are not making
any differentiation between them.
In the mining phase the FSG algorithm is
executed. As a result of the mining, the frequent sub-
graphs in the analyzed process models are identified
as well as the support value of each sub-graph within
the set of process models and their parent-child
relation. This information is stored in a file similar
to the input file, since the frequent patterns are
DISCOVERY AND ANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY PATTERN CO-OCCURRENCES IN BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS
85

graphs as the input process models are.
4.1 On a Process Model Mining Tool
In order to analyze the results from the mining phase
we developed a BPM mining tool which allows to
automatically execute specific parts of the data
mining and the evaluation steps of the KDD process.
The tool receives a set of normalized activity
patterns as input and then simulates their
construction with the use of the mined co-
occurrences patterns. In this context co-occurrence is
a recurrent construction of activity patterns within
process models (e.g., the pattern pair D
ECISION Æ
NOTIFICATION).
To evaluate the usefulness of the activity patterns
co-occurrence, the tool simulates a user modeling
the input processes. In this modeling all processes
are re-constructed activity by activity. For each
activity insertion, the tool generates a
recommendation list. This list is composed by rules
describing how the process can evolve according to
the partial model designed so far and the co-
occurrences found on the data mining phase. These
rules have on their antecedent and consequent parts
of process models. Fig. 3 shows two examples of
rules (see item b).
As the tool receives as input the complete
process, it knows all intermediary stages of the
modeling phase as well as how process elements
must be added to completely design it. The order in
which elements are added to the process is obtained
from the order they appear in the input file.
Therefore, the tool knows what would be the user’s
choice on the recommendation list if he was
modeling the process with the help of it since the
order of elements insertion is specified. For instance,
the process shown in Fig. 2 could be part of an input
for the BPM mining tool. With that description the
tool simulates a user which models that process by
first adding an edge between the start node and the
notification pattern. Then, it adds an edge
connecting this notification pattern to a bi-
directional performative one. After that, the bi-
directional pattern is connected to other notification
pattern, which is then connected to a unidirectional
performative pattern, which is finally connected to
an end node.
The output of the BPM mining tool is a summary
containing calculations regarding the simulation of
the input models designed. It can be used to analyze
how useful the information on the co-occurrence of
activity patterns can be to predict and thus to foster
the design of process models. Sample outputs are:
the total number of co-occurrence rules found
in the data mining phase;
the number of steps of user’s rule selection
simulated, i.e., number of times that a
recommendation list was created and the
appropriate rule was searched on it;
a ranking with the total number of steps where
the rule on position n th of the recommendation
list would be chosen by the user, i.e., the total
times that the rule on first (and second, …, n th)
position of the recommendation list would be
selected by a user when modeling the process;
the total number of rules of size i that were
chosen in the simulation (in this analysis the size
of a rule is the number of edges that its
antecedent model has).
4.2 Implementation of a Process Model
Mining Tool
Based on the recurrent activity patterns found in the
mining phase, our BPM mining tool creates all rules
of interest with their respective support and
confidence. In future, we intend to implement some
filters within this class, or in a new class called by,
in order to filter the created rules according to
specific criteria. This filtering contributes to avoid
the creation of too many rules and improves the
performance of the algorithm. Currently, the used
filtering creates only one step rules. Item b of Fig. 3
shows two rules of this type. These rules have a
partial process model as antecedent and have on the
consequent the same process model with one more
edge and eventually a node. It is assumed that each
process model may evolve only by adding new edge
in each design step. When adding a new edge we
have two situations: a) the new edge closes a cycle
on the process, so that no new nodes are added; or b)
the new edge connects a node of the partial model
designed to a new activity pattern (node). In case of
b a new node is added to the model as well. By
doing so, we assure that all created rules represent
an evolution of the model of one step. Note that this
approach is easier for a user to understand when
comparing to rules which may present greater
modifications of the partial model designed so far. If
we allow to create rules which introduce greater
changes of the process they will hardly match all
user intentions. Besides that, this is not our purpose,
i.e., we do not want to present an almost complete
process to the user. Instead, we want to interactively
help on each pattern insertion to the process model,
so the rules are kept simple and easily readable.
Our tool also simulates the design of the input
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
86

process models. It has an inference engine which
receives a partially modelled process as input and
then tries to match the complete process, or part of
it, with the antecedent of the rules as created in the
data mining phase. All matching rules are returned
in the ranking list of activity pattern co-occurrences,
so they represent a possible evolution for the design
of the partial model. Currently, the rules are ordered
by their size and confidence. Thus, rules which
match the largest part of the partial model are
presented first. If the rules have same size, the one
presenting the greatest confidence will be shown
first.
Fig. 3 shows a fragment of the process model we
introduced in Fig. 1, (see a). Fig. 3 also presents a
recommendation list with two rules to continue the
modeling of the process from the model fragment
designed so far (see b). The partial process model is
considered to construct this recommendation list. It
contains all rules that match entirely or partially the
model presented in a.
Figure 3: Modeling evolution.
Based on the complete process model (cf. Fig.
1), our tool knows that, in this case, if the user is
assisted by the recommendation list when designing
the process, he will choose rule number two, since it
represents an evolution of the partial model by
adding a new bi-directional performative pattern
connected to the already existing notification
pattern.
4.3 Evaluating the Discovered Patterns
To evaluate the patterns discovered with the KDD
process we have done a randomly stratified
partitioning of the available processes. We reserved
1/3 to pass to the Tester class once the co-
occurrences patterns are mined over the other 2/3 of
the processes. It was considered a minimum support
of 3, i.e., if three process models contain the same
co-occurrence of activity patterns it will be, then,
considered a pattern in our data mining step. Doing
so we assure that the co-occurrences found during
data mining step are not obtained from processes we
use to verify our approach. Thus, we can check
whether they are predictive enough for ‘never seen’
process models.
In our experiment we had observed that the 470
steps of rule selection were simulated, i.e., 470 times
a co-occurrence ranking of activity pattern was
generated and the appropriate rule which describes
the model evolution was searched. This ranking has
an average size of 26 rules. We can observe that on
almost 20% of the simulated steps, the rule which
correctly predicts the evolution of the model is on
the first three positions of the ranking. Accumulating
the values until the 10
th
position we have a correct
prediction in more than 35% of the simulated steps.
Considering that we have 6 activity patterns, the
probability of correctly predict the next activity
pattern, without additional information, is around
16.67%. Further, we need to predict where this new
activity pattern will be inserted. For instance, in a
model with 2 nodes, this probability decreases to the
half. In a model with 10 nodes, this probability is ten
times lower.
We can also see that the majority of the rules that
correctly predicts the model evolution are rules of
size 1, 2 or 3. This conclusion can further be used to
filter the generated rules to return rules of only these
sizes and reduce the amount of rules on the ranking.
We expect that this filter will improve the prediction
rate of the inference engine.
After evaluating the mined patterns we have re-
executed the process using all the available process
models. At this time, we used the complete set of
models to execute the data mining step and then
simulated their construction. 1425 simulation steps
were executed. On the first three positions of the
ranking we had a correct prediction rate of more
than 30% while on the 10
th
first positions this rate
goes to more than 50%. The percentage of
unmatched rules has decreased from 41% on before
execution to 20.5%. Considering the average size of
11 nodes in the processes models analysed, we have
around 1.52% of chances to correctly predict the
next pattern to be inserted in a model and where to
insert it if no prior information is used. With three
chances, i.e., creating a list of three possible next
patterns, we have 4.55% of chances to get a match.
Increasing from 4.55% to 30% is a great gain and
this illustrates the power of using mined information
to predict the future on our experiments.
Notification
Pattern (NP)
NP
NP NP
NP
P
(a)
NP
Bi-directional
1.
2.
DISCOVERY AND ANALYSIS OF ACTIVITY PATTERN CO-OCCURRENCES IN BUSINESS PROCESS MODELS
87

5 SUMMARY
This paper reports on the use of KDD in the
development of a BPM mining tool, which allows
mining process models based on activity patterns as
highly relevant. The functionalities of this tool can
be considered very important: a) after having
identified the activity patterns in the process models
the tool can count the recurrences of each pattern as
well as their co-occurrences; b) the inference engine
of our BPM mining tool can give design time
recommendations for any new processes being
modelled, which ease process modelling based on
already mined information; c) we can use our tool
for conducting a series of experiments in which we
compare process modeling with and without activity
pattern support as well as investigate different
process classes and their most recurrent co-
occurrences and; d) finally, the basic concepts
behind this tool (e.g., the inference engine) can be
added as extensions to existing BPM tools.
As future work, we aim at extending our tool
with a module to update the frequency of activity
patterns co-occurrences and corresponding raking of
recommendations based on the user modeling. This
update will be done on-the-fly as new models are
developed aided by the inference engine. Thus, we
aim at increasing the accuracy of the
recommendations for each pattern co-occurrence.
In addition we intend to investigate methods
which allow the automatic identification of activity
patterns in real process models.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to acknowledge the
Coordination for the Improvement of Graduated
students (CAPES), the DBIS of the Ulm University.
(Germany), and the Informatics Institute of the
UFRGS (Brazil).
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R., Imielinski, T., Swami, A., (1993). Mining
association rules between sets of items in large
databases. In: Proc. of the ACM SIGMOD, p.207-216.
Becker, J., Pfeiffer, D., Räckers, M. (2007). Domain
Specific Process Modelling in Public Administrations
- The PICTURE Approach. Proc. EGOV’07, pp. 68-79
Brand, E., Gerritsen, R., (1998). Data Mining and
Knowledge Discovery, Oct. 1998.
Fayyad, U., Shapiro-Piatetsky, G., Smyth, P., (1996).
From Data Mining to Knowledge Discovery in
Databases, AI Magazine, v.17, n.3, p. 37-54, [s.l.].
Goebel, M., Gruenwald L., (1999). A survey of data
mining and knowledge discovery software tools. In:
SIGKDD Explorations, v. 1, p. 20-33.
Günther, C.W., Rinderle-Ma, S., Reichert, M., van der
Aalst, W.M.P., Recker, J., (2008). Using Process
Mining to Learn from Process Changes in
Evolutionary Systems. In: Int. Journal of Business
Process Integration and Management, 3(1):61-78.
Han, J., Kamber, M., (2001). Data Mining: Concepts and
Techniques, Morgan Kaufmann, 550 p., San Diego.
Kuramochi, M., Karypis, G., (2004). An Efficient
Algorithm for Discovering Frequent Subgraphs, In:
IEEE Transaction on Knowledge and Data Eng.,
Minneapolis, v.16, n.9, p. 1038-1051.
Li, C. Reichert, M., Wombacher, A., (2008). Discovering
Reference Process Models by Mining Process
Variants. proc. In: Proc. of ICWS, Beijing. pp. 45-53.
OASIS. (2006). Web Services Business Process Execution
Language. Version 2.0.
Thom, L. H., Iochpe, C., Amaral, V., Viero, D., (2006a).
Towards Workflow Block Activity Patterns for Reuse
in Workflow Design. In: WfMC Workflow Handbook.
pp. 249-260.
Thom, L.H., (2006a). A Patterns –based Approach for
Business Process Modeling. PhD Thesis. UFRGS:
Porto Alegre, Brasil.
Thom, L.H., Reichert, M., Chiao, C., Iochpe, C., Hess, G.,
(2008b). Inventing Less, Reusing More and Adding
Intelligence to Business Process Modeling. In: Proc.
of DEXA, Turin, LNCS 5181, pp. 837-850.
Thom, L. H., Iochpe, C., Reichert, M., Weber, B., Droop,
M., Nascimento, G., Chiao, C. M., (2008c). On the
Support of Activity Patterns in ProWAP: Case
Studies, Formal Semantics, Tool Support. In: iSys.
Vol 1, No 1, pp. 27-53.
Thom, L. H., Reichert, M., Iochpe, C., (2009). Activity
Patterns in Process-aware Information systems: Basic
Concepts and Empirical Evidence. In: IJPIM.
Tristão, C., Ruiz, D. D., Becker, K., (2008). FlowSpy:
exploring Activity-Execution Patterns from Business
Processes. In: Proc. of Simp. Brasileiro de Sistemas de
Informação, Rio de Janeiro, 2008. v. 1. p. 152-163.
van der Aalst, W.M.P., ter Hofstede, A.H.M.,
Kiepuszewski, B., Barros, A., (2003). Workflow
Patterns. In: Distributed. and Parallel. Database,
14(3): 5-51.
van der Aalst, W.M.P., (2005). YAWL: Yet Another
Workflow Language. Information Syst., 30(4):245-
275.
Weber, B., Rinderle, S., Reichert, M., (2007). Change
Patterns and Change Support Features in Process-
Aware Information Systems. In: Proc. of CAiSE'07,
LNCS 4495, pp. 574-588.
Weber, B., Reichert, M., Wild, W., Rinderle-Ma, S.,
(2009). Providing Integrated Life Cycle Support in
Process-Aware Information. In: Int'l Journal of
Cooperative Information Systems, 18 (1).
zur Muehlen, M. (2002). Workflow-based process
controlling: foundations, design, and application of
workflow-driven process information systems. Logos.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
88
