
Skeleton-Based Shape Segmentation
Liudmila Domakhina
Moscow State University, Moscow, Russia
Abstract. Shape decomposition into meaningful parts (segmentation) problem
is considered in this paper. The shape is given either as a raster object on a ho-
mogeneous background or as a polygonal figure. A new shape decomposition
approach is called skeleton-based segmentation. The approach is based on con-
tinuous skeletons that provides an opportunity to construct visually proper seg-
mentations reflecting the shape structure. The proposed skeleton-based segmen-
tation method stands out against known methods because it is suitable to work
correctly with pairs of shapes. For a pair of shapes it is proposed to construct iso-
morphic skeleton-based segmentations which can be used on shape comparison
and morphing applications.
1 Introduction
Shape decomposition(segmentation) is a shape representation as a combination of com-
ponents (parts). The idea is to represent complex shapes in terms of simpler compo-
nents. If we have a decomposition of the shapes into parts, instead of matching the
shapes globally we could proceed by matching parts.
Shape segmentation is an important problem in many document processing applica-
tions (like organizingand querying an image database, recognition and computer-vision
problems, medical structure comparison etc.)
The goal of the present paper is to develop an effective segmentation method that
may be useful when working with pairs of shapes, especially in recognition and mor-
phing applications. Thus the segmentation should reflect the structure of the shape and
be stable to small shape fluctuations. Moreover, two similar shapes should have similar
segmentations. The segmentation method should be universal to work either with raster
objects or with polygonal figures.
The method presented in the paper is based on continuous skeletons. Continuous
skeleton reflects the shape structure but is not stable to boundary noise. The skeleton
could be considered as a graph. Skeletal graph could be transformed to become stable to
small shape variations. In case the shape is given as raster object on homogeneous back-
ground, the approximating poligonal figure and its skeleton could be constructed [1].
For a pair of shapes isomorphic skeletons and isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations
are constructed that allows solving such problems as morphing and shape comparison.
Domakhina L. (2009).
Skeleton-Based Shape Segmentation.
In Proceedings of the 2nd International Workshop on Image Mining Theory and Applications, pages 84-92
DOI: 10.5220/0001963500840092
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 SHAPE SEGMENTATION
2.1 Problem Statement
Shape decomposition (segmentation) is a representation of the shape as a combination
of components (parts). There are many ways to decompose a shape (pic. 1). Not all of
them give a correct decomposition, choose the meaningful decomposition parts. Seg-
mentation quality could be estimated based on different criteria, for example:
Fig.1. Different shape decompositions.
1. Successful segmentation applications.
2. Correspondence to visual intuition.
3. Optimal number of segments in a final decomposition.
4. Computational speed of the segmentation algorithm.
5. Boundary noise stability.
The criteria 1-4 are subjective(2) or heuristic (1,3) or external a segmentation model
(4). Thus such criteria can’t be used to construct a correct segmentation. Noise stability
requires to be correctly defined, though not sufficient to choose the best segmentation.
Heuristic methods hardly fit the real applications.
In this work the segmentation problem is stated to find the best and correct de-
composition for a pair of shapes. Therefore the needed segmentation should satisfy the
following requirements:
requirement
1
: shape structure reflection;
requirement
2
: small shape fluctuations stability, including boundary noises;
requirement
3
: similarity for a pair of similar shapes;
2.2 Previous Work in Shape Segmentation
Existing segmentation methods can be classified into two groups:
1. Those that are boundary-based,using only contour information for extracting parts.
2. Those that are region based, using information about the interior of the shape.
First are not suitable to the problems where structure analysis is required. Second
often use skeletons [4,6, 3,5]. Most of existing approaches do not contain the correct
criterion of choosing the segmentation method. The methods are hardly suitable when
pairs of shapes ought to be considered. For example [4] proposes one the method that
decomposes the figure into its ”significant parts” based on linear skeleton. It’s not al-
ways true for two similar figures that their decomposition gives same ”significant parts”
which is not correct.
85

2.3 Skeleton-Based Shape Segmentation
Medial axis (skeleton) of the shape [1] is a set of all maximal circles inscribed in the
shape.
Let’s consider the continuous skeleton of a raster object given on a homogeneous
background as a medial axis of object’s approximating figure (the figure that separates
object from the background). The latter could be effectively constructed using known
methods [1]. An example of the object’s approximating figure is the polygonal figure of
minimal perimeter [1] (fig. 2).
Fig.2. Polygonal figure of minimal perimeter for a raster object.
Skeleton reflects the shape structure. Therefore using of the skeleton the first re-
quirement of the stated problem is satisfied automaticallys.
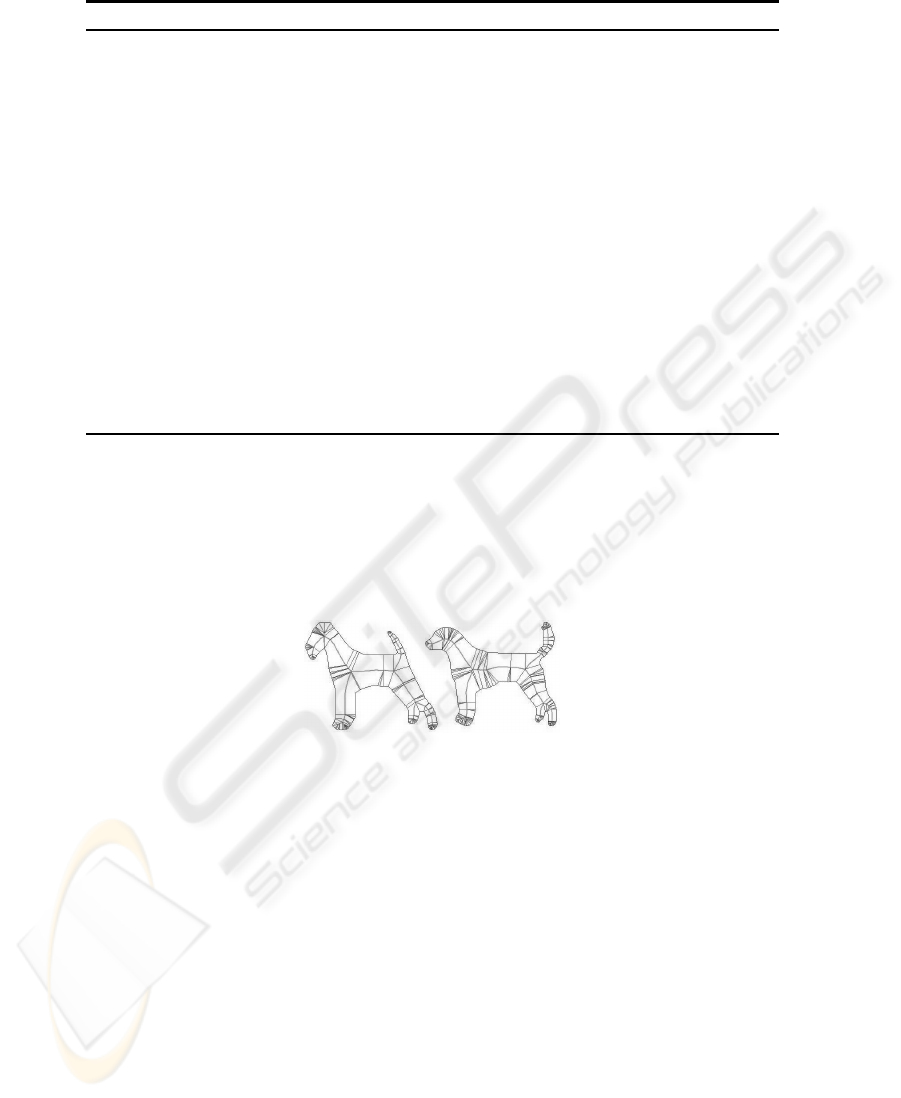
The skeleton-based segmentation is considered as a special decomposition (fig. 3)
on a finite number of skeleton edges areas (segment areas). The skeleton-based segmen-
tation of a shape can be constructed by definition as described in algorithm 1.
To simplify the algorithm several remarks should be made. By definition the seg-
ment area SubArea(v
i
v
i+1
) of an edge v
i
v
i+1
is the set of all perpendiculars each point
of an edge v
i
v
i+1
to B(R). However there is no need ro find the continuum number of
perpendiculars. The segment area SubArea(v
i
v
i+1
) is bounded by two (for a terminal
edge) or four (for an in internal edge) as well as the boundary B(R).
The skeleton-based segmentation shown on a figure 3 has the follwong elements:
(a) a polygonal approximating border (or a polygon itself in case the shape is given as
a polygon);
(b) continuous skeleton;
(c) perpendiculars from skeletons vertices;
(d) segment areas (skeleton edges areas).
Fig.3. Shape skeleton-based segmentation.
86
Algorithm 1: Skeleton-based segmentation construction: M : Shape → Seg(Shape).
Require: Shape ∈ {R, P }, Shape is a raster object or a polygonal figure P ;
Ensure: Skeleton-based segmentation Seg(Shape);
1: if figure is raster object (Shape = R) then
2: construction of a polygonal boundary approximation Appr(R) of a raster object R;
3: let the boundary of a shape is a constructed boundary approximation Border(Shape) :=
Appr(R);
4: else
5: let the boundary of a shape is a given polygon Border(Shape) := P ;
6: construction of the shape’s skeleton sk = M A(Shape);
7: n — the number of skeleton sk edges;
8: v
1
, ..., v
m
— all skeletal graph sk vertices;
9: for all vertices v
k
: k = 1, ..., m; deg(v
k
) ≥ 3 do
10: construction of perpendiculars from v
k
to Border(Shape);
11: the number of perpendiculars from v
k
equals to v
k
: deg(v
k
);
12: for i = 0, . . . , n do
13: fix the edge e
i
= v
i
v
i+1
;
14: find an edge area SubArea(e
i
);
15: Seg(Shape) =
S
n−1
i=0
SubArea(v
i
v
i+1
) — needed skeleton-based segmentation.
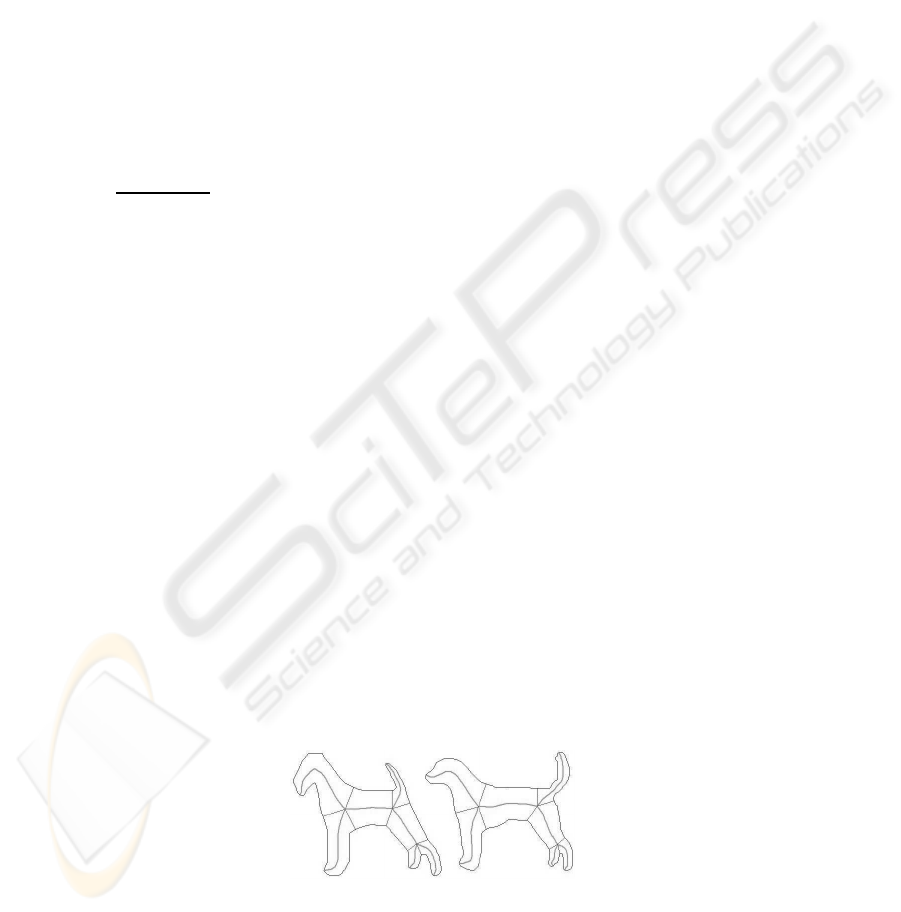
The medial axis is not stable to small shape changes. Therefore segmentations
based on such skeleton are not stable either. Therefore applications with pairs of ob-
jects involved can’t use such segmentations (fig. 4). The segmentation method should
be adapted to be more stable and to satisfy the 3rd problem statement requirement.
Fig.4. Skeleton-based segmentations for a pair of shapes.
3 Skeleton-based Segmentation for a Pair of Shapes
The proposed segmentation method may use a modified continuous skeleton (step 6).
A subgraph of the medial axis could be taken, for example. When choosing the best
skeleton we have to eliminate several problems.
– A skeleton may often have noise branches that have nothing in common with gen-
eral shape’s structure (odd noisy branches affect odd not meaningful segments ap-
pear).
– A skeleton may have serious structure changes (branches reversing) affected by
small boundary variations (therefore segments may be reversed in similar figures
as well).
87

The first problem could be solved as an example by noisy branching cutting with
a fixed accuracy [8]. Thus skeletons and skeleton-based segmentation become more
stable (fig. 5). However the second problem remains unsolved. Moreover as per stated
problem a pair of similar shapes should have similar segmentations (the third require-
ment of 2.1). This requirement should be mathematically reformulated. Therefore the
definition of ”segmentation isomorphism” should be given.
Fig.5. Segmentations based on a skeleton with a fixed accuracy.
3.1 Segmentation Isomorphism
Two graphs are isomorphic G
∼
=
H if a mapping between their vertices keeps their
edges adjacency.
Segmentation dual graph is a plain graph that has
– vertices corresponding to segments and two vertices;
– two vertices make an edge if corresponding segments are adjacent in segmentation
(i.e. has the common border).
Two segmentations are isomorphic if their dual graphs are isomorphic.
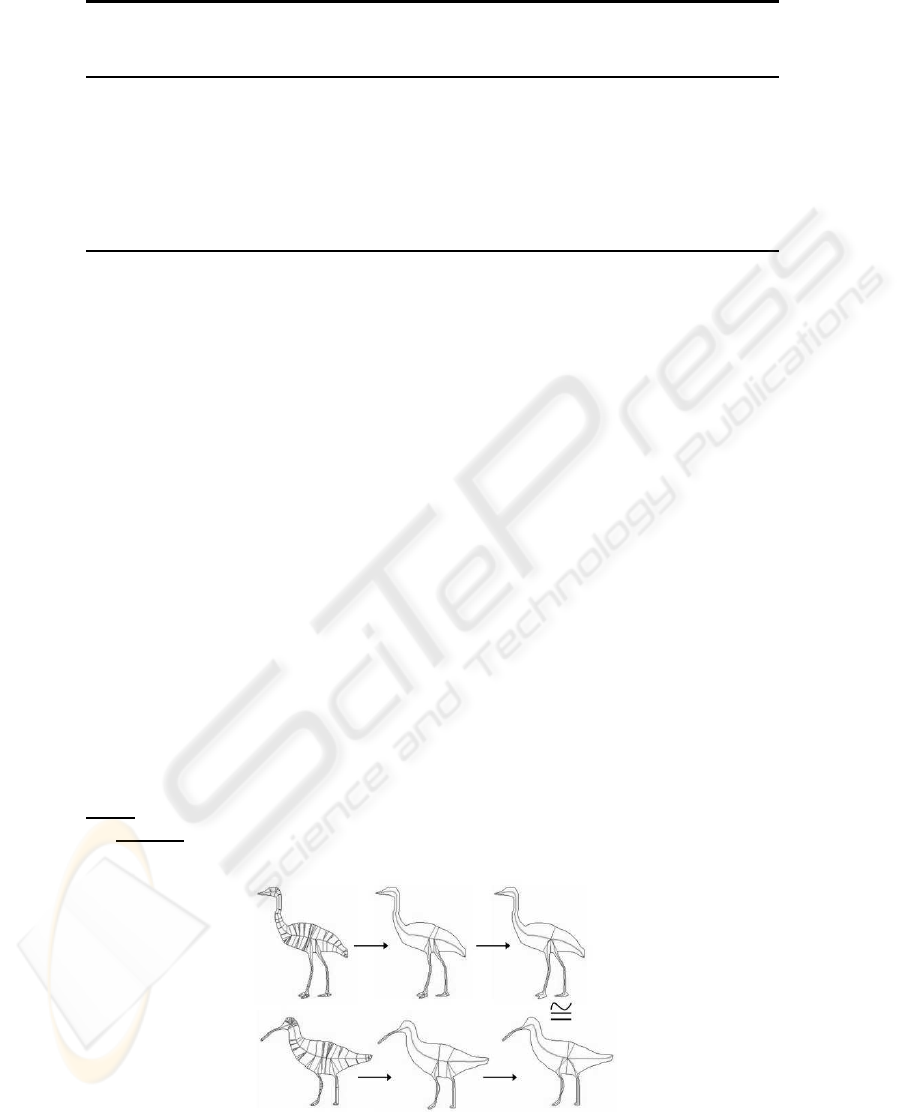
Skeleton-based segmentationsseem to reflect the visual meaningfulnessof the shape
(fig. 3,5). However they are hardly isomorphic for two similar shapes (an example on
fig. 3). It means that two similar figures have different meaningful parts which is incor-
rect. When we work with pairs of shapes it is useful to find their isomorphic segmenta-
tions for several reasons:
1. If shapes are similar, their corresponding parts (by isomorphism) are often those
”significant parts” reflecting general shape structure. Therefore it is easy to
(a) make shape analysis;
(b) compare shapes;
(c) solve a morphing problem by map corresponding parts.
2. When shapes are not really similar we still may use their isomorphic segmentations
as follows:
(a) estimate the difficulty (or impossibility) of isomorphic segmentations construc-
tion, therefore compare shapes;
(b) solve the morphing problem even for not similar shapes.
88
3.2 Skeletal Graphs
Medial axis can be represented as a planar graph [2], i.e. a skeletal graph. Vertices of
the skeletal graph are the centers of maximal inscribed circles that touch the shape’s
boundary ∂Ω in three or more points. Edges of the skeletal graph touch the shape’s
boundary ∂Ω in two or more points. A skeleton vertex that has only one incident edge
is called a terminal vertex, more than one edge — a knot. An edge that is incident to a
terminal vertex is called a terminal edge.
Skeletal graphs provide a good opportunity to work effectively with shape structure.
3.3 Skeleton Isomorphism
Two skeletons are isomorphic if their skeletal graphs are isomorphic and the traversal
order of terminal vertices is the same in both graphs.
Theorem 1: Segmentations based on isomorphic skeletons are isomorphic as well.
Basing on the theorem 1 obtaining isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations could
be reduced to obtaining isomorphic skeletons for a pair of shapes. Here is the problem:
how could we obtain isomorphic skeletons of two shapes if medial axis is so unstable
to small shape fluctuations and noise? The solution is given in [7]. In that work the
followong problem has been solved: For two given raster objects I
1
and I
2
construct
their approximating shapes F
′
1
∈ Φ
εI
and F
′
2
∈ Φ
εI
that have isomorphic skeletons
ma(F
1
)
∼
=
ma(F
2
). Φ
εI
denotes the class of shape approximations with an ε accuracy,
i.e. all shapes f that has not more than ε distance to the fixed shape I are in class Φ
εI
,
i.e. Φ
εI
= {f : µ(f, I) < ε}. The distance between raster shape and its approximating
shape µ(f, I) is defined as a maximum of two Hausdorff distances: between black pix-
els and the approximating shape and between white pixels and the approximating shape
supplement.
As a stated problem solution an algorithm is given in [7]. In the algorithm the skele-
ton and the figure are changed simultaneously at each step. Two types of operations are
handled: terminal branches cutting and internal knots merging (branch deletion). Shape
is changed a bit at each step. The algorithm stops when two isomorphic skeletons are
obtained. Therefore as an output of an algorithm two changed (not more than for a fixed
accuracy ε) shapes are obtained. Let’s denote an algorithm described in [7] as follows:
L(Shape
1
, Shape
2
) → {Shape
1
′, Shape
2
′}, where M A(Sh a pe
1
′)
∼
=
MA(Shape
2
′).
Therefore, skeleton-based segmentation construction for a pair of shapes is based
on the theorem 1 and could be done using the algorithm 2. An example of isomorphic
segmentations obtained by this algorithm is shown on figure 6.
Fig.6. Isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations.
89
Algorithm 2: Skeleton-Based Segmentation Construction for a Pair of Shapes:
A(Shape
1
, Shape
2
) → {Seg(Shape
1
), Seg(Shape
2
)} : Seg(Shape
1
)
∼
=
Seg(Shape
1
)
Require: Shape
1
∈ {R, P },Shape
2
∈ {R, P }. Shapes are raster objects or polygonal figures;
Ensure: Seg(Shape
1
), Seg(Shape
2
) — isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations;
1: construction of the close shapes having isomorphic skeletons using the algorithm
L(Shape
1
, Shape
2
) → {Shape
1
′, Shape
2
′};
2: 1st skeleton-based segmentation construction: M(Shape
1
′)) → Seg(Shape
1
).
3: 2nd skeleton-based segmentation construction: M(Shape
2
′)) → Seg(Shape
2
).
4 Shape Comparison Using Skeleton-based Segmentation
Shape comparison is the problem of definition the similarity measure for two given
shapes. Skeleton-based segmentation can be used to solve this problem in the following
ways:
1. Let two shapes are fixed and two isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations are con-
structed for them. The cost should be defined that means how difficult is to obtain
the isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations (fig. 7). This cost is considered to be
a similarity measure for two shapes.
2. The process of isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations is not taken into account.
Let’s consider the final isomorphic skeleton-based segmentations. Corresponding
significant parts could be matched and thus a very good and correctmetrics between
two segmentations could be defined.
5 Shape Morphing Using Skeleton-Based Segmentation
Shape morphing problems can be stated as follows:
5.1 Problem 1: Moving Object Painting
Given
: two shapes D
1
and D
2
. The first shape D
1
has the color function f(x), x ∈ D
1
The task: paint the second shape D
2
accordingto the colourationof the first one D
1
.
(fig. 6)
Fig.7. Shape Comparison Basing on Cost.
90

Fig.8. Morphing problem statement.
5.2 Problem 2: Shapes Mapping
Given: two shapes D
1
and D
2
.
The task: find the homeomorphic mapping of the first shape D
1
into the second
one D
2
.
5.3 The Stated Problems Solution Using Skeleton-Based Segmentation
The second problem could be solved by construction of two isomorphic skeleton-based
segmentations of shapes D
1
and D
2
. If two skeleton-based segmentations are isomor-
phic then each pair of segments can be mapped, i.e. a homeomorphism ϕ : D
1
→ D
2
could be constructed.
Fig.9. Morphing Problem Solution.
The first problem may use the solution of the second problem, i.e. the homeomor-
phism ϕ : D
1
→ D
2
. Once the homeomorphism is constructed the second shape D
2
could be painted as follows: ∀x ∈ D
2
the color is f(ϕ
−1
(x)).
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper a new approach to shape decomposition is presented. An approach in-
volves skeleton-based segmentation construction. The proposed decomposition reflects
the shape structure, stable to small shape fluctuations and to boundary noise. The cen-
tral idea lays in using continuous skeletons. An effective algorithm to construct such
segmentations is presented for a shape given either as a raster object on homogeneous
background or as a polygon.
For a pair of shapes it is proposed to construct isomorphic skeleton-based segmenta-
tions. Isomorphic decompositions are easily applied to shape comparison and morphing
problems. Further development and implementation of methods are in progress.
91

Acknowledgements
Work is supported by the RFBR project 08 − 01 − 00670.
References
1. L. Mestetski: Continuous Skeleton of Raster Images.8th Int. Conference Graphicon-1998
2. Hyeong In Choi and Sung Woo Choi and Hwan Pyo Moon: Mathematical theory of medial
axis transform. Pacific.J. of Math,1997, volume 181, number 1, pages 57-88.
3. Maryann Simmons and Carlo H.Sequin: 2D Shape Decomposition and the Automatic Gener-
ation of Hierarchial Representations. International Journal of Shape Modelling,1998.
4. Mirela Tanase: Shape Decomposition and Retrieval.PhD thesis, 2005,Utrecht University.
5. Jyh-Ming Lien and Nancy M. Amatoy: Simultaneous Shape Decomposition and Skeletoniza-
tion.Technical Report TR05-015, ”2005,Parasol Lab. Department of Computer Science Texas
AM University.
6. Davi Geiger, Tyng-Luh Liu, and Robert V.Kohn: Representation and Self-Similarity of Shape.
IEEE Transactions on Pattern Recognition Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2008, volume
25, number 1, pages 86-89,
7. L. Domakhina and A.Okhlopkov: Isomorphic Skeletons of Raster Images. 18th International
Conference Graphicon-2008, Moscow.
8. L. Mestetski, I. Reyer: Continuos skeletal image representation with a fixed accuracy. 13th
International Conference Graphicon-2003, Moscow. . 246–249.
92
