
A RULE-BASED APPROACH AND FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING
BEST PRACTICES
An XML-based Management using Pure Database System Utilities
Essam Mansour and Hagen H¨opfner
School of Information Technology, International University in Germany, Campus 3, D-76646 Bruchsal, Germany
Keywords:
Best practice, Rule-based information, ECA rule paradigm, Active database, XML, Replay information scene.
Abstract:
Best practice refers to the best way to perform specified activities. In this paper we present our SIM approach
that incorporates best practices as skeletal plans from which several entity-specific (ES) plans are generated.
The skeletal and ES plans represent the complex information incorporating the best practices into organization
activities. The paper also presents the SIM framework for managing complex information through three
phases: specifying the skeletal plans, instantiating ES plans, maintaining these ES plans during their lifespan.
The paper outlines an implementation, a case study and the evaluation of the SIM approach and framework.
1 INTRODUCTION
Best practice refers to the best way to perform speci-
fied activities (O’Leary, 2007), and is utilized in sev-
eral domains, such as in: 1) Health-care, Clinical
Guidelines (Field and Lohr, 1992) are used in disease
management activities; 2) Agriculture, Good Agri-
cultural Practices (Neely et al., 2003) are utilized in
activities, such as animal production management;
and 3) Stock Exchange, Best Execution Guidelines
(EAMA, 2002) are harnessed to manage customer se-
curities orders.
In these domains, the best practices are instanti-
ated for a particular domain entity, which is involved
in a specific activity. In the health-care domain, e.g.,
the Clinical Guidelines are instantiated to a specific
patient to generate a patient plan used in the activity
of disease management (Shahar, 2002).
Implementing best practices into systems, such
as workflow or expert systems, forces organizations,
who have less formally defined procedures, to con-
form to a single standard. Deviation from this stan-
dard requires a change to these systems (Rinderle and
Reichert, 2007).
The major challenge addressed in this paper is
to flexibly incorporate best practices into the day-to-
day organization’s activities, and managing the in-
stantiated plans, such as patient plans, at the domain
entity level. The problem of this research is three-
fold: first, providing an empirical approach for mod-
eling the best practices in order to provide flexibil-
ity in customizing the modeled best practices to suit
an organization standard or domain entity situations;
second, providing a management framework for the
modeled best practices while covering the organiza-
tion’s needs; third, realizing the approach and frame-
work as a unified and high-level method using the
available technologies.
This paper presents a generic approach and a
multi-dimensional framework, called SIM (Mansour,
2008), for incorporating best practices and managing
of complex information through modeling this infor-
mation as one distinct entity. SIM is supported us-
ing an advancedlanguage called AIM (Mansour et al.,
2006; Mansour et al., 2007a; Mansour and H¨opfner,
2009) and utilized by AIMS (Mansour et al., 2007b),
a system for managing the complex information.
The remainder of the paper is organized as fol-
lows: Section 2 outlines the related work. Section 3
highlights a working scenario. Section 4 presents the
SIM modeling approach. Section 5 presents the SIM
framework for the three management planes (speci-
fication, instantiation, and maintenance). Section 6
highlights our prototype system AIMS using a clin-
ical case study. Section 7 discusses the concluding
remarks of SIM. Section 8 summarizes the paper.
2 RELATED WORK
Several approaches exist for incorporating best prac-
tices into organization’s activities. Active database
approaches, such as (Caironi et al., 1997; Bry et al.,
109
Mansour E. and Höpfner H. (2009).
A RULE-BASED APPROACH AND FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING BEST PRACTICES - An XML-based Management using Pure Database System
Utilities.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Information Systems Analysis and Specification, pages
109-115
DOI: 10.5220/0001976801090115
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2006), provide support for representing and executing
best practices as event-condition-action (ECA) rules
(Paton, 1999). These approaches are easy to be in-
tegrated with the organizations’ information systems
by utilizing the DBMSs to manage the ECA rules
and organization’s data. However, active database
approaches suffer from 1) the low-level representa-
tion that is not easy to be reviewed or modified by
the non-technical users; 2) a lack of support for real-
world situations that require time-based rules at a do-
main level (e.g. 2 hours after patient admission or-
der a blood test); and 3) little or no support for ma-
nipulating and querying these rules. Our work over-
comes these problems by providing a high-level man-
agement supported via a declarative language.
Workflow approaches, such as (van Dongen et al.,
2007; Rosemann and van der Aalst, 2007), provide
formalization and validation models that specify the
best practices as processes with focus on the control
flow and order of processes. These models provide lit-
tle or now support for the information produced by in-
corporating the best practices, such as the medical in-
formation related to the patient plan. Different work-
flow approaches, such as (Lee et al., 2007; Rinderle
and Reichert, 2007), have addressed the problem of
adapting the formalized processes to a specific orga-
nization‘s need. Workflow approaches provide little
or no support to the deviation between the domain en-
tities, to which the process is applied. Our work sup-
ports this deviation by generating an entity-specific
version of the best practice for each entity.
Furthermore, our approach differs from decision
making approaches, such as (Ruland and Bakken,
2002), in assisting the decision making process by
issuing notifications, reminders, and/or observations
regarding the situation of interest to domain users.
We provide a generic approach and framework for
managing the best practices incorporation platform-
independently and high level under an unified man-
agement environment.
3 WORKING SCENARIO
This section presents a working scenario for manag-
ing best practices that could be formalized as ECA
rules. The scenario is based on a clinical protocol for
the diagnosis and treatment of microalbuminuria in
diabetes patient. Microalbuminuria is diagnosed ei-
ther on 24 hour urine collections (20 to 200 g/min)
or more commonly if elevated concentrations (30 to
300 mg/L) on at least two occasions.
To compensate for the variable possible urine con-
centration on spot check samples, it is more typical
in the UK to compare the amount of albumin in the
sample against its concentration of creatinine. This
is termed the Albumin/creatinine ratio (ACR) and
microalbuminuria is defined as ACR 2.5 mg/mmol
(male) or 3.5 mg/mmol (female).
The microalbuminuria protocol (MAP), best prac-
tice, is to be formalized at a generic form to be used
with several patients. In hospital, there is a MAP-
based medical patient plan for each particular patient.
In the execution process of the plan, it is required to
react to the changes of the patient’s state according to
MAP. Doctors manipulate the plan over time accord-
ing the patient progress. This manipulation might be
by adding or removing part of the plan or incorpo-
rating a new version of MAP. Doctors are interested
to review the execution history of the plans. Conse-
quently, the execution history is logged.
4 THE SIM APPROACH
SIM is an acronymfor specification, instantiation, and
maintenance. The SIM approach aims at incorporat-
ing best practices through an electronic and adaptive
template (skeletal plan), from which several entity-
specific (ES) plans are generated. A skeletal plan
changes when necessary in order to be suitable for a
particular organization and/or environment. It is static
in the sense that it is almost fixed before, during, and
after the execution. However, the ES plan is dynamic
as it may undergo significant changes during the ex-
ecution and it does have state transitions, such as ac-
tive state or inactive state. For simplicity, an ES plan
should belong to only one skeletal plan. However,
the skeletal plan might belong to several ES plans.
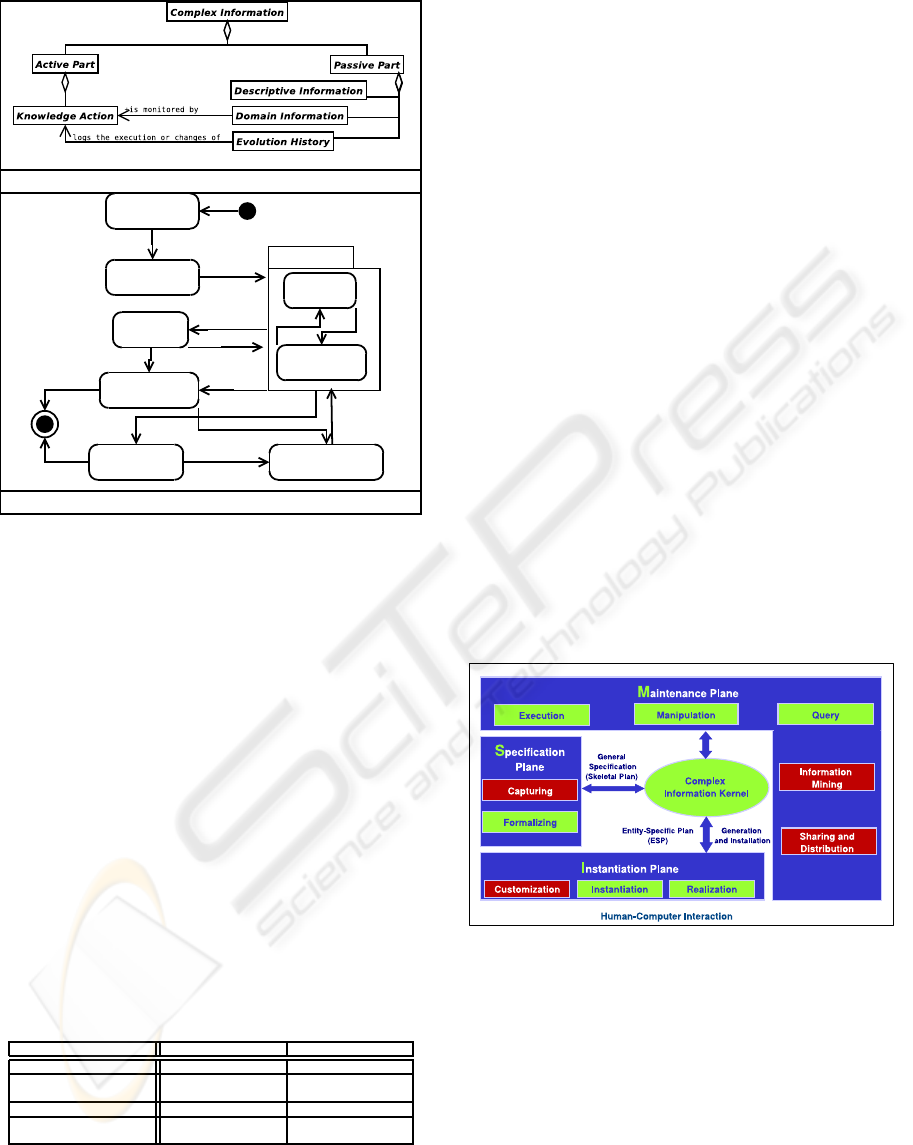
An ES plan has a limited lifespan, during which it is
created and eventually completed, terminated and/or
suspended, as shown in Figure 1(B).
The conceptual model of complex information in
SIM is a theoretical construct: a set of information
components and a set of logical relationships between
these components. As depicted in Figure 1(A), com-
plex information has an active and a passive part.
The active part represents the way in which an ac-
tivity should behave and react in a particular situation.
The information component under this part is express-
ing actions rather than states of being. The passive
part is a subject to changes without taking any action.
As shown in Figure 1(A), the active part is repre-
sented by the knowledge action component that spec-
ifies the reaction that should be taken as a response
to a specific situation. The initial steps for incorpo-
rating best practices into organization activities are to
describe the primitive decision logic of the best prac-
tice for a specific situation. In our approach this is
supported by using the ECA rule paradigm.
The passive part consists of domain information,
evolution history, and descriptive information com-
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
110
(A)
active
waiting
executing
generated
registered
inactive
terminated
completed re-registered
(B)
Figure 1: (A) the complex information conceptual model
and (B) the life-cycle of the ES plan.
ponents. The domain information component mod-
els the situations, to which the knowledge action re-
acts. Situations are represented through terms, whose
values are monitored by the knowledge action com-
ponent. The evolution history tracks changes to the
initial complex information, dependencies, and goals.
Moreover, the execution of the primitive decision
logic is logged by the evolution history. The descrip-
tive information component provides 1) didactic in-
formation, such as purpose and explanation, and 2)
release information, such as version, and specialist.
The four components of the complex information,
knowledge action, domain information, evolution his-
tory, and descriptive information, exist in both the
skeletal plan and the ES plan, but at different abstrac-
tion levels. Table 1 summarizes the differences.
Table 1: Comparison between the complex information
components.
Components Skeletal Plan ES Plan
Knowledge Action platform-independent platform-specific
Domain Information
domain-specific and platform-specific and
entity-independent entity-dependent
Descriptive Information specification-oriented execution-oriented
Evolution History logs modification logs modification
and execution
The knowledge action component in the skele-
tal plan is a platform-independent, which means the
decision logic should be formalized as platform-
independent statements that could be directly mapped
into executable statements attached to the ES plan.
The domain information component in the skeletal
plan is domain-specific. Hence, the terms represent-
ing specific situations are defined using the domain
terminologies. In the ES plan, these terms should
be mapped into computer interpretable terms, such as
data items of a database schema.
The descriptive information component in the
skeletal plan is specification-oriented to provide de-
scriptive information regarding the specification and
formalization process, such as information about the
author. However, in the ES plan, it provides a descrip-
tive information related to the execution, such as per-
son in charge of the ES plan, and a specific entity, to
which the ES plan is generated. The evolution history
component in the skeletal plan logs the modification
made to the skeletal plan. In the ES plan, this compo-
nent logs the modification and the execution history.
5 THE SIM FRAMEWORK
The SIM framework consists of three planes: spec-
ification, instantiation, and maintenance, with the
human-computer interaction (HCI) support as a base
(see in Figure 2). The functionalities for capturing,
customization, information mining, sharing and dis-
tribution are work in progress. The HCI basis is part
of our future work.
Figure 2: The SIM framework.
5.1 The Specification Plane
The specification plane provides support to capture
the best practices and to formalize them as skeletal
plans. It is common that best practice is provided in
non-computer-interpretable form. That is a major ob-
stacle to exchange best practices among organizations
and/or individuals. In the formalization process, the
specification plane provides a computer-interpretable
model for expressing the skeletal plans. We adopted
an event-driven method to formalize the best prac-
tices. The specification plane formally specifies the
A RULE-BASED APPROACH AND FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING BEST PRACTICES - An XML-based
Management using Pure Database System Utilities
111

skeletal plan according to the conceptual model of the
complex information as discussed in Section 4.
5.2 The Instantiation Plane
This plane aims at refining the skeletal plan to suit an
organization and at generating ES plans. In the SIM
framework, the customization is a process of adapting
the skeletal plan to meet the customer’s and/or organi-
zation’s needs. Professional service firms generate an
enormous amount of high-value best practices. How-
ever, customizing them to meet the client specific sit-
uation adds the greatest value to the process of incor-
porating best practices into organization activities.
The instantiation is the process of generating an
ES plan from the skeletal plan. The instantiation pro-
cess in our working scenario is supported by a model,
called DRDOC, for implementing the ES plan. DR-
DOC (Mansour and H¨opfner, 2009) takes into account
the features distinguishing the ES plan from the skele-
tal plan, such as platform- and entity-specific. This
process considers the information of a specific entity
and maps the components of a skeletal plan into the
corresponding component in the ES plan.
The realization is the process of giving the appear-
ance of reality. After reviewing the ES plan clearly
and distinctly, it is authorized to be in the condition of
being in full force or operation. This process deploys
the best practices in the system.
5.3 The Maintenance Plane
The maintenance plane provides support to the life-
cycle of the ES plan and keep the complex informa-
tion in a functional state. The functions of this plane
are execution, manipulation, query, information min-
ing, and distribution management.
The ES plans are executed as soon as a change
of interest happens. In the instantiation process,
the knowledge action component of the skeletal plan
is mapped into a platform-specific statement that is
amenable to execution by using a specific execution
environment, such as an active DBMS due to the use
of the ECA rule paradigm to represent primitives of
the best practices. Part of the execution process is to
log all the execution history in the evolution history
component of the complex information.
The manipulation is a process that provides the
operations against the complex information, which is
subject to the same manipulation operations, as other
kind of information. However, these operations are
performed at a high-level of abstraction that deals
with the complex information in terms of its compo-
nents, as a first-class object, plus special operations,
such as activate, deactivate, and terminate.
The query process provides the ability to retrieve
complex information. Queries may be issued in or-
der to obtain information about a skeletal plan deal-
ing with specific situations and/or about a ES plan
belonging to a specific entity. These queries handle
complex information as first-class object. The ES
plan is subject to special queries for recovering and/or
reviewing the plan at a specific time point or period.
The information mining targets the automatic dis-
covery of information from an evolution history com-
ponent of the entity-specific plan that represents a real
case study. The discovered information can be used to
deploy new best practices or as a feedback tool that
helps in auditing, analyzing and improving already
enacted best practices.
The sharing and distribution provide interoper-
ability support for managing complex information in
highly heterogeneous, widely distributed, and frag-
mented context. This context brings together a geo-
graphically dispersed stockholders, who are partici-
pating in the management process of complex infor-
mation. It is also needed to exchange this information
among and deliver it to other people.
5.4 Other Components
An HCI support is required to be provided for all
planes of the framework. The nature of the best prac-
tice and its complex information as a huge amount of
information must be considered as an essential factor
for the user interface. Complex Information Kernel is
the core of the SIM framework. It is the integrating
factor among the three planes and provides storage
and retrieval support for the complex information.
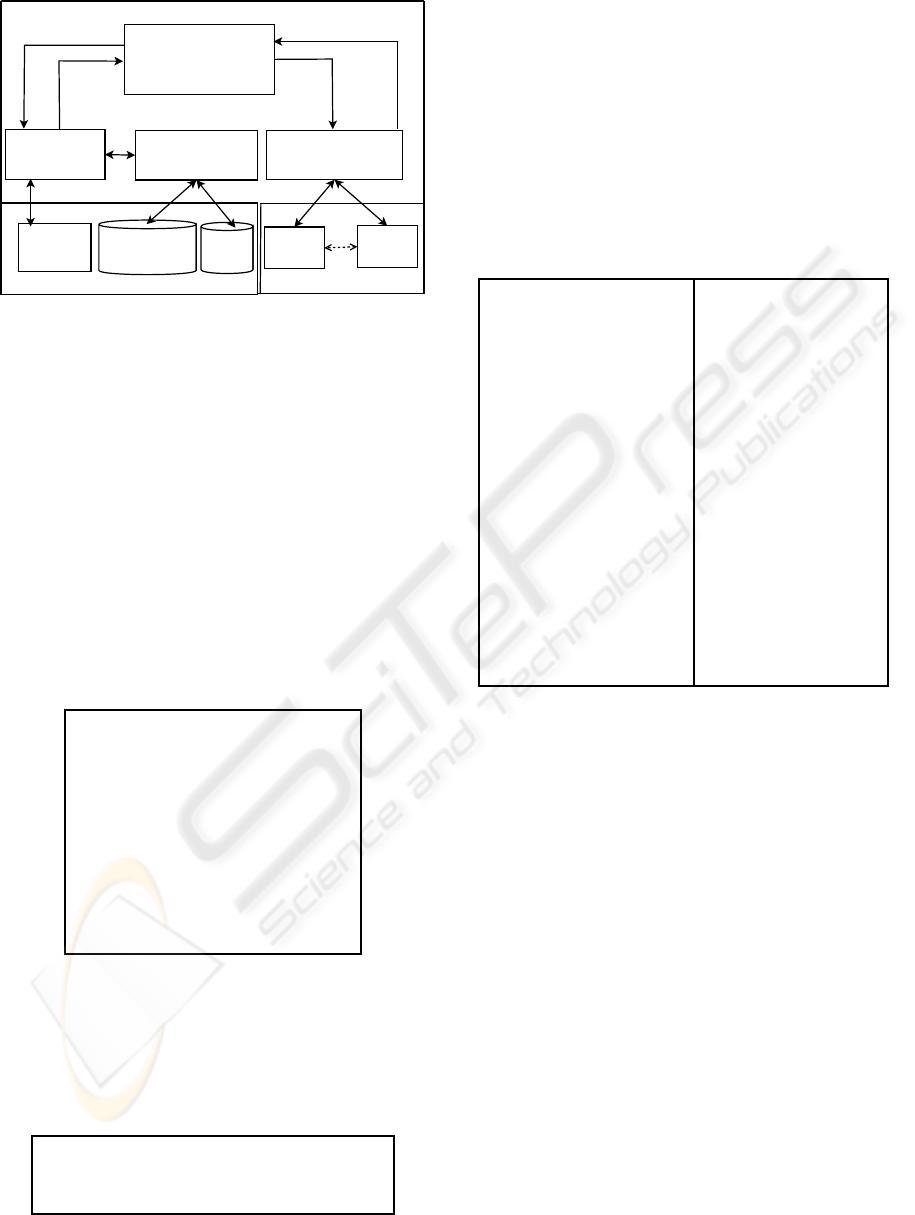
6 A PROTOTYPE SYSTEM
The AIMS system utilizes the available DBMS
as a base for managing the complex information
and implementing the AIM language consisting of
three main components; specification component
(AIMSL), instantiation model (DRDOC) and query
component (AIMQL). AIMS has been implemented
using DB2 and Java. The conceptual architecture of
AIMS is illustrated in Figure 3. The Complex In-
formation Manager supports the best practices incor-
poration and the complex information management
at a high level. The domain users and information
providers, such as patient information system or stock
items system, deal with Complex Information Man-
ager through the Communication Manager.
The Rule Manager maps the platform-
independent and domain-based rules specified
by AIMSL into triggers managed by the DBMS.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
112
XML
Schemas
XML Repository
- Domain Information
- AIMSL Specification
- AIM ESPDoc
Complex Information
Manager
- Specification
- Instantiation
- Execution
Rule Manager
- Temporal Execution
- Rule Manipulation
Communication Manager
- Dissemination method
- Distribution method
DBMS Trigger
Mechanism
Registration and
Manipulation
Modifications
Information Manager
- Validation method
- Temporal storage method
- Temporal query method
- Queries and Manipulations
- Skeletal Plan Doc
- Entity-Specific Plan Doc
AIM Language Statement
Result and Acknowledgement
Information
Provider
User/Client
Messages
AIMS: A Complex Information Management System
External Entities
Modern DBMS
- Manipulation
- Query and Replay
Figure 3: the AIMS conceptual architecture.
The Information Manager extends the XML support
provided by DBMSs to provide temporal support and
utilizes the DBMS to validate and store the AIMSL
specification document and the DRDOC document
using their XML Schema.
6.1 The Specification
In the specification plane, the formal specification of
the utilized MAP protocol is made using AIMSL. The
outcome of the formal specification process is a well-
formed XML document validated against the AIMSL
Schema. Figure 4 illustrates an overview of the MAP
protocol specification, which has the ID PRO124, and
belongs to the category, whose ID is CID124.
-<protocol id=”PRO124”>
<name>microalbuminuria protocol (MAP) </name>
<categoryID>CID124</categoryID>
+<header>
-<Schedules>
-<schedule id=”SIDMAP”>
<name>Basic MAS</name>
+<header>
-<scheduleRules>
+<rule id=”rul1”>
...
+<rule id=”rulN”>
</scheduleRules>
</schedule>
+<schedule id=”FIDMAP”>
+<schedule id=”MIDMAP”>
</Schedules>
</protocol>
Figure 4: AIMSL specification for MAP.
Rule 5 shown below is a comprehensive rule that
covers several features of the AIMSL rule element. Its
specification is illustrated in Figure 5. The rule body
consists of the elements Terms, event, condition, and
action.
Rule 5 (static Rule, repetitive 10 times):
event : every 12 hours after patient admission
condition: the test result > 55
action : send a message ordering an ACR test for the patient.
There are two terms in rule 5. The first one is value of
the ACR test result, which is a term of type element.
Its ID is TO1234 and its value is of integer data type.
The second term is patient admission, which is a term
of type event. Its ID is DEPA11. The event element is
a repetitive relative time event that happens every 12
(time length) hours (granularity) after the term, whose
ID is DEPA11 that is the patient admission term, and
the event is repeated 10 times. The condition element
is a simple predicate checking that the value of the
term, whose ID is TO1234, is grater than the integer
value 55. The action is to send the doctor an email to
order an ACR test for the patient.
-<rule id=”rul5”>
<name>Rule 5 of MAP</name>
+<properties>
+ <header>
- <body>
-<Terms >
<term id=”TO1234”>
<title>The value of the
ACR test Result</ title >
<type>element</type>
<dataType>integer</dataType>
+<mappingToDB>
</term>
<term id=”DEPA11”>
<title>patient admission</ title >
<type>event</type>
+<mappingToDB>
</term>
</Terms >
-<event id=”E1R5”>
<on>
<relativeTime>
<every>
<granularity>hours</granularity>
<timeLength >12</timeLength>
<beforeORafter>
<BAValue>after</BAValue>
<term id=”DEPA11”>
patient admission</term>
</beforeORafter>
<for >10</for>
</every> </relativeTime>
</on> </event>
-<condition id=”ID36”>
+<description>
<logic>
<simplePredicate>
<operand1>
<termID>TO1234</termID>
</operand1>
<operator>gt</operator>
<operand2>
<value>
<amount>55</amount>
<datatype>integer</datatype>
</value>
</operand2>
</simplePredicate>
</logic>
</condition>
- <action id=”AID36”>
- <do>
-<proceduralAction>
+<sendEMAIL>
</proceduralAction>
</do>
</action>
</body>
</rule>
Figure 5: AIMSL specification for the rule 5.
6.2 The Instantiation and Execution
In the instantiation plane, patient plans are instanti-
ated for a specific patient using the AIMSL specifica-
tion by 1) generating an instance of the MAP protocol
and 2) mapping its knowledge action component into
SQL triggers, which are to be created in the AIMS
system. Thus, the patient plans are continuously and
automatically adjusted to the changes in the patient
state. DRDOC provides an implementation for ES
plans. Figure 6 illustrates part of a patient plan gen-
erated using DRDOC. This part is at four hours af-
ter the patient admission. The rule MAP
1
and MAP
2
were generated at time point zero and registered at
time point 1.
The generated status is a system-defined status
that happens at the generation time of an ES plan. The
rule MAP
1
was fired two hours after patient admis-
sion. Therefore, the status registered of rule MAP
1
was valid from 1 to 2. The status executed was added
with validity period 2 to 2. The actual evaluation of
the event and action of MAP
1
were recorded. The
A RULE-BASED APPROACH AND FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING BEST PRACTICES - An XML-based
Management using Pure Database System Utilities
113

Figure 6: A part of a patient plan.
rule MAP
2
was fired three hours after patient admis-
sion. Therefore, the status registered of rule MAP
2
was valid from 1 to 3. The status executed was added
with validity period 3 to 3. The evaluation of the
event, condition, and action of MAP
2
were recorded.
The rule MAP
3
was added at time point 3 and it is
recorded that MAP
2
caused such modification, actor.
6.3 Query and Manipulation
There is a need to move the complexity of manipu-
lating and querying the complex information (skele-
tal and entity-specific plans) from user/application
code to a high level declarative language. AIMQL
is a high level XQuery-based language providing fa-
cilities to perform manipulation operations, and ad-
vanced queries, such as replaying dynamic execution
scenarios of the complex information. For more de-
tails about AIMQL, the reader is referred to (Mansour
et al., 2007b; Mansour and H¨opfner, 2009).
AIMQL introduces seven manipulation opera-
tions (expressions). These expressions includes
add
,
remove
,
modify
,
activate
,
deactivate
,
terminate
and
fire
. They are distinguished in the
sense that they do not only potentially modify the
AIMSL specification or ES plan, but also propagate
the modification to the corresponding ES plan docu-
ments and modify the corresponding triggers created
in the system. Furthermore, the manipulation expres-
sions log the changes of DRDOC documents.
The AIMQL replay language provides an essen-
tial role for retrieving and reviewing the complex in-
formation. The user does not need to know the details
of the complex information schemata as the AIMQL
language is a declarativelanguage. The replay queries
are applied only to the plan, schedule and rule ele-
ments, which are called re-playable elements. Two
or more re-playable elements might be joined (com-
bined) in order to produce the query result. By map-
ping the replay query into XQuery script, the uti-
lized XQuery engine is to be in charge of managing
AIMQL queries.
Figure 7 shows examples for AIMQL queries. Re-
play query 1 replays the history of plan no (X
1
, PID
1
)
after the validity period of the state ST of the plan
no (X
2
, PID
2
). In this query the variables X
1
, PID
1
,
ST, X
2
, and PID
2
are to be replaced with appropri-
replay query 1
REPLAY PLAN p1,p2
SHOW When, How, Why OF p1
WHERE p1[@DEID = X1 and @SPID = PID1] and
p2[@DEID = X2 and @SPID = PID2] and
NOT(p1.precedes(valid(p2.state[value=ST])))
replay query 2
REPLAY RULE plan[@DEID = X and @SPID = PID]
//schedule[@IDREF=S]/rule[@IDREF=A] R
SHOW How, Why OF
count(R.state[value/status=’executed’]
WHERE R.meet(
valid(R.state[value/status=’executed’]))
Figure 7: AIMQL replay queries.
ate values. This replay query returns the versions of
the plan no (X
1
, PID
1
), whose validity period does not
precede the validity period of the state ST of the plan
no (X
2
, PID
2
). This query helps in comparing the
progress of two different patients, to who the same
generic plan is applied.
In replay query 2, it is required to retrieve how
many times was rule R of schedule S of the plan
(X, PID) executed, and why. The OF element spec-
ifies the re-playable information using the function
count, which counts the states, whose value is exe-
cuted, of the rule R. This query shows the how and
why parts of the re-playable information. So, the ac-
tual evaluation of the event and condition elements
are to be shown for each execution of R. The replayed
period is the period, at which R was executed, as spec-
ified using the function meet.
7 CONCLUDING REMARKS
The clinicians do not need to continuously monitor
the patient state changes in order to react to the clin-
ical events of interest and adjust the patient plan.
The clinicians participating in the disease manage-
ment will be able to remotely access, manipulate or
query, patient plans. By the replay support, the clin-
icians can review the evolution of a specific patient
plan in a particular time period.
Furthermore, we can state out the following:
Maintainability: The SIM approach uses a declara-
tive language, AIM, to allow a unified management to
best practices. The AIM language formalizes the best
practices as a skeletal plans at a domain and declar-
ative level, thus making it easy to incorporate and
maintain best practices by the domain users; Extensi-
bility. Extending the best practices or specific skele-
tal plans can be made easily using the AIM manipu-
lation operations. Hence, new skeletal plans can be
easily added to the AIMS repository; Re-usability.
best practices are specified in an interpretable for-
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
114

mat using AIMSL. A similar application could reuse
this AIMSL specification; Flexibility and Adaptabil-
ity. The SIM framework manages best practices in-
corporation at several levels of abstractions. To adapt
to any changes at the organization level or domain en-
tity level, the user has to modify the skeletal plans be-
fore re-instantiating the ES plans that are deployed in
the AIMS system transparently by the Rule Manager.
8 SUMMARY AND OUTLOOK
We presented the SIM approach that models best
practices as an electronic and adaptive template
(skeletal plan), which is to be instantiated to several
ES plans. Both the skeletal and ES plan are referred
to as complex information. We presented also the
SIM framework for managing complex information
through three planes, specification, instantiation and
maintenance. SIM has been implemented based on
the ECA rule paradigm, XML and DB2; and applied
to manage clinical test ordering activities.
Currently we are doing additional experiments
with different workloads and query sets. Besides this,
more advanced visualization mechanism to review the
replayed information and a method for automatically
discovering information from the execution history of
the complex information need to be developed. This
discovered information can assist in auditing, analyz-
ing and improving already enacted best practices.
REFERENCES
Bry, F., Eckert, M., P˘atrˆanjan, P.-L., and Romanenko,
I. (2006). Realizing Business Processes with ECA
Rules: Benefits, Challenges, Limits. In Principles and
Practice of Semantic Web Reasoning, volume 4187 of
LNCS, pages 48–62. Springer.
Caironi, P. V., Portoni, L., Combi, C., Pinciroli, F., and
Ceri, S. (1997). HyperCare: a Prototype of an Active
Database for Compliance with Essential Hypertension
Therapy Guidelines. In AMIA Annual Fall Sympo-
sium, pages 288–292. Hanley & Belfus, Inc.
EAMA (2002). Best Execution: Executing Transactions in
Securities Markets on behalf of Investors. European
Asset Management Association.
Field, M. J. and Lohr, K. N. (1992). Guidelines for Clin-
ical Practice: From Development to Use. National
Academy Press, Washington, DC.
Lee, K., Sakellariou, R., Paton, N. W., and Fernandes, A.
A. A. (2007). Workflow adaptation as an autonomic
computing problem. In WORKS ’07 Proceedings,
pages 29–34. ACM.
Mansour, E. (2008). A Generic Approach and Frame-
work for Managing Complex Information. PhD the-
sis, Dublin Institute of Technology (DIT). available
online
http://arrow.dit.ie/sciendoc/51/
.
Mansour, E., Dube, K., and Wu, B. (2007a). AIM: An
XML-Based ECA Rule Language for Supporting a
Framework for Managing Complex Information. In
RuleML 2007 Proceedings, volume 4824 of LNCS,
pages 232–241. Springer.
Mansour, E., Dube, K., and Wu, B. (2007b). Managing
complex information in reactive applications using an
active temporal XML database approach. In ICEIS
2007 Proceedings, pages 520–523. INSTICC Press.
Mansour, E. and H¨opfner, H. (2009). Replay the execution
history of rule-based information. In the First Interna-
tional Conference on Advances in Databases, Knowl-
edge, and Data Applications (DBKDA 09). IEEE.
forthcoming.
Mansour, E., Wu, B., Dube, K., and Li, J. X. (2006).
An Event-Driven Approach to Computerizing Clinical
Guidelines Using XML. In Proceedings of the IEEE
Services Computing Workshops, pages 13–20, Wash-
ington, DC, USA. IEEE Computer Society.
Neely, C., Haight, B., Dixon, J., and Poisot, A.-S. (2003).
Report of the FAO Expert Consultation on a Good
Agricultural Practice approach. Technical report,
Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Na-
tion (FAO).
O’Leary, D. E. (2007). Empirical analysis of the evolution
of a taxonomy for best practices. Decision Support
Systems, 43(4):1650–1663.
Paton, N. W., editor (1999). Active Rules in Database Sys-
tems. Springer.
Rinderle, S. and Reichert, M. (2007). A formal frame-
work for adaptive access control models. Journal on
Data Semantics IX, 4601/2007:82–112. LNCS 4601,
Springer.
Rosemann, M. and van der Aalst, W. (2007). A configurable
reference modelling language. Information Systems,
32(1):1–23.
Ruland, C. M. and Bakken, S. (2002). Developing, imple-
menting, and evaluating decision support systems for
shared decision making in patient care: a conceptual
model and case illustration. J. of Biomedical Infor-
matics, 35(5/6):313–321.
Shahar, Y. (2002). Automated support to clinical guidelines
and care plans: the intention-oriented view. Techni-
cal report, Ben Gurion University, Beer Sheva, Israel.
Commissioned by OpenClinical, 2002.
van Dongen, B. F., Jansen-Vullers, M. H., Verbeek, H.
M. W., and van der Aalst, W. M. P. (2007). Verifica-
tion of the sap reference models using epc reduction,
state-space analysis, and invariants. Computers in In-
dustry, 58(6):578–601.
A RULE-BASED APPROACH AND FRAMEWORK FOR MANAGING BEST PRACTICES - An XML-based
Management using Pure Database System Utilities
115
