
A DOMAIN SPECIFIC LANGUAGE FOR THE I* FRAMEWORK
Carlos Nunes
1
, João Araújo
1
, Vasco Amaral
1
and Carla Silva
2
1
CITI/ Faculdade de Ciências e Tecnologia, Universidade Nova de Lisboa, Portugal
2
Centro de Informática, Universidade Federal de Pernambuco, Brazil
Keywords: Organizational Modeling, i* Framework, Metamodeling, Domain Specific Languages, CASE Tools.
Abstract: The i* framework proposes a goal-oriented analysis method for requirements engineering. It is a
systematic approach to discover and structure requirements at organizational level where functional,
non-functional requirements and their relations are specified. A Domain Specific Language (DSL) has
the purpose to specify and model concepts in some domain, having several advantages in relation to
general purpose languages, such as it allows expressing a solution in the desired language and at the
desired abstraction level. In order to create such a DSL, normally it is necessary to start by specifying
its syntax by means of a metamodel to be given as input to the language workbenches that generate the
corresponding editors for it. With a proper editor for the language we can specify models with the
proposed notation. This paper presents a DSL for the i* framework, with the purpose to handle
complexity and scalability of its concrete models by introducing some innovations in the i* framework
metamodel like mechanisms that will help to manage the models scalability.
1 INTRODUCTION
The i* framework (Yu, 1995; Yu, 1997) main
objective is to discover and structure requirements
at an organizational level. Systems and their
environments are specified in terms of intentional
relationships among strategic actors. Actors are
intentional as they have desires and needs, and are
strategic since they are concerned about
opportunities and vulnerabilities. To achive that
purpose the i* framework proposes two models,
Strategic Dependency Model (SD) and Strategic
Rationale Model (SR). The SD model describes a
group of dependency relations between the
organizational actors. The SR model describes
relations between the internal components that With
these two models, we expect that the i* framework
gives us some answers at modeling level to
questions about the system behaviour.
Although using the i* framework helps in
discovering requirements from stakeholders needs,
the produced i* models get visual complexity very
easily, preventing them from being accepted in
industry. The current tools (Matulevicius et al.,
2006; The i* wiki, 2008) propose editors to i*, but
they do not provide enough mechanisms to deal with
the complexity problem, and when they do, that is
not reflected in the metamodel. This means that the
language syntax is not correctly specified, leading to
editors that allow to build sintatically incorrect and
inconsistent models.
In order to build a tool that is able to implement
the i* framework and handle the complexity of its
models, we use a properly defined i* based Domain
Specific Language (DSL). The purpose of a DSL is
to specify and model concepts of some domain
(Kelly and Tolvanen, 2008; The DSL wiki, 2008), in
this case the domain is the i* framework. Therefore,
the purpose of this tool is to create a graphical editor
for i* based models and contribute with some new
features, such as mechanisms to tackle the model
visual complexity.
In order to create the i* based DSL with success
it is necessary to specify a metamodel that can
represent correctly the framework and its rules, so
we can specify correctly the desired DSL. In this
paper we create a metamodel for the i* framework
having as base some existing i* framework
metamodels (Alencar et al., 2008; Ayala et al., 2006;
Lucena et al., 2008). The proposed metamodel is an
extended version of these metamodels so that it
could incorporate new properties to help managing
and reducing the scalability of i* models.
This article is organised as follows. Section 2
shows in detail the two models that constitute the
158
Nunes C., Araújo J., Amaral V. and Silva C. (2009).
A DOMAIN SPECIFIC LANGUAGE FOR THE I* FRAMEWORK.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Databases and Information Systems Integration, pages
158-163
DOI: 10.5220/0001995301580163
Copyright
c
SciTePress

framework in study. Section 3 shows the metamodel
used to build the i* based DSL in order to
implement the new constructors, the i* based DSL
itself and its new constructors. Section 4 shows an
evaluation of the i* based DSL editor. Section 5
presents the conclusions and some future work.
2 BACKGROUND
In the i* framework (Yu, 1995; Yu, 1997) the
Strategic Dependency Model (SD Model) describes
a configuration of dependent relations among
several organizational actors.
The Strategic Rationale Model (SR Model)
describes the internal relations between the several
internal elements of an actor.
Using the SD and SR models offered by this
framework we can make questions relatively to
actors and respective relations and give some
answers to the questions made. The stakeholders’
needs can be resolved through alternative solutions.
To illustrate the i* framework as well as our
proposal, the Health Watcher system case study is
used. This system allows citizens to make several
kinds of complaints about questions that may put in
risk public health and security, and also get
information about diseases and vaccines. Those
complaints will then be analysed by professionals
designated for that task.
2.1 SD Model
The SD Model purpose is centered in making a
modeling using several actors interacting with each
other. With this approach, the SD Model offers an
analysis method that allows to study in more detail a
process when compared with other conventional
analysis methods, which do not support an
intentional modelling. So this model helps to
identify the stakeholders, helps to discover
vulnerabilities and oportunities in relation to the
analysed system. It also recognizes relations
between the participant actors, helping to find
solutions for the detected vulnerabilities during the
system analysis.
A SD Model (Figure 1) consists of a group of
actors (e.g., User and Health Watcher), goals (e.g.,
Consult Complaint and Make Complaint), tasks
(e.g., Get Info and Give Info), resources (e.g.,
Complaint Info and HW Info), softgoals (e.g.,
Performance and Usability) and dependencies
between those elements (see relationships between
User and Health Watcher actors).
In this model it is not mandatory that all of these
elements exist and it is possible to have more than
one element of the same kind.
2.2 SR Model
The SR Model (also depicted in Figure 1) contains
all the features that have been seen in SD Model,
plus the possibility to expand actors and model its
internal behavior. When an actor is expanded there
is the possibility to have a group of goals, tasks,
resources, softgoals and links between those
elements. These links can be of three different kinds:
• Task-Decomposition Links determine that an
element can be decomposed in several sub-
elements (e.g., Record Compliant task is
decomposed into Verify Complaint task and Fill
Complaint goal).
• Means-End Links allow explaining how a certain
goal is achieved by using a alternative solutions
(e.g., Fill Complaint goal can be achieved by
either Fill Food Complaint, Fill Animal
Complaint or Fill Special Complaint alternative
tasks).
• Contribution Links determine how certain
elements contribute positively or negatively to a
attain softgoals (e.g., Verify Complaint task
contributes positively to attain Security softgoal.
An expanded actor can have an undetermined
number of elements. It is not mandatory all the
elements to be present. It may even happen that the
actor has no elements at all. An actor can also have a
non-determined number of links between elements.
3 DSL SPECIFICATION
Domain Specific Languages are used to specify the
solution model for some specific problem at a
particular domain. The recent technologies for
implementing DSLs by means of language
workbenches can be quite an advantage if the DSLs
are at the right abstraction level and use proper
notations. Meaning that, is they are able to express
some problem in a more concrete way when
compared to other existing general purpose
languages.
A domain is a viewpoint of a specific area like a
family of products or a subject area. For instance, we
can have a domain to simulate combats or a domain
to resolve a company billing problems.
A DOMAIN SPECIFIC LANGUAGE FOR THE I* FRAMEWORK
159
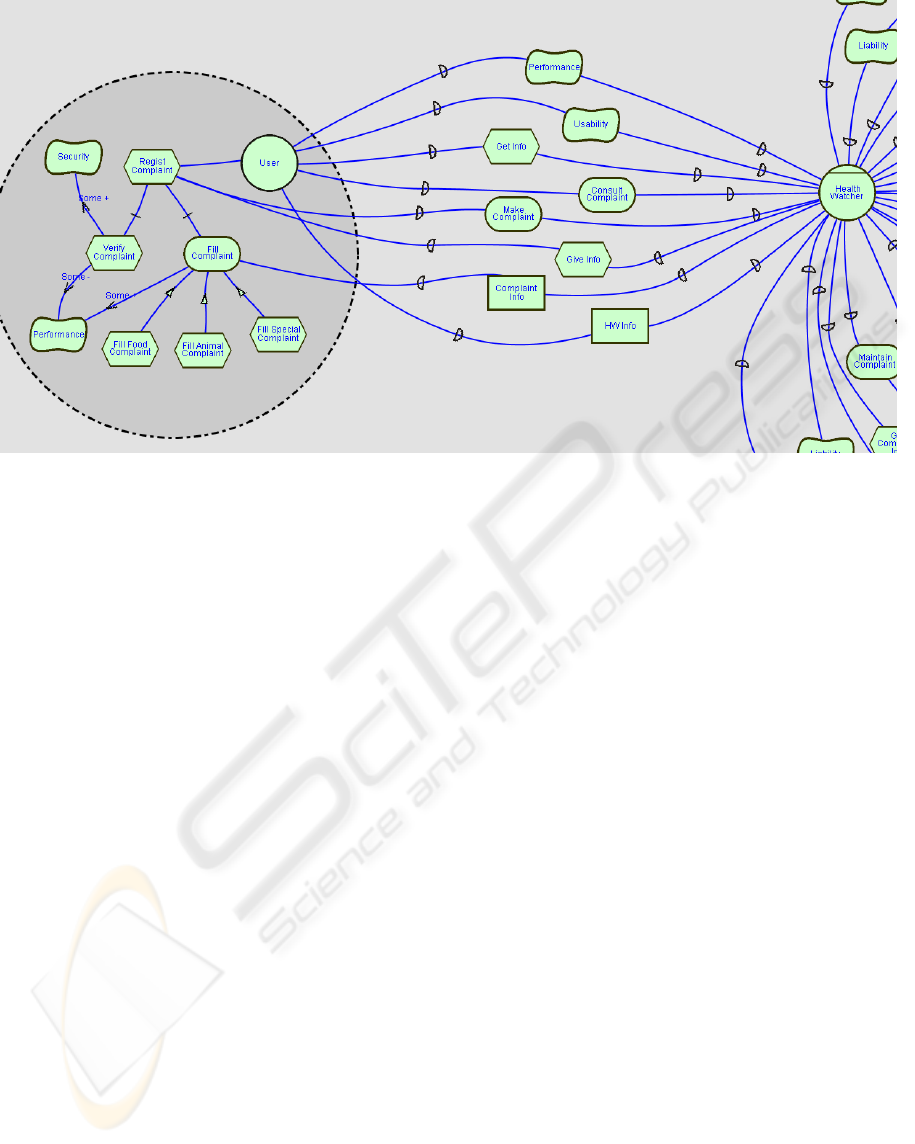
Figure 1: SR Model for Health Watcher Case Study using OME.
The DSLs can be used at any abstraction level,
e.g. requirements, design or implementation level.
They can be either a diagrammatic language or a
textual language (Kelly and Tolvanen, 2008; The
DSL wiki, 2008).
The advantages of DSLs consist of having the
possibility to express a solution in the desired
language and at the desired abstraction level passing
by the domain problem that has to be solved. Thus
the domain specialists can understand, validate and
even modify the DSL.
DSLs allow code generation to the specified
domain. Thus it is possible at the domain level to
validate the DSL, so it may be considered that if the
DSL is problem free, then any problem that is
resolved using that DSL can be considered problem
free as well. Due to this characteristics DSLs
increase productivity, dependability, portability and
reusability when apllied to a certain specific domain
(Kelly, 2008, The DSL wiki).
3.1 The i* Metamodel
In order to create the i* based DSL, we use Ecore
(The DSL wiki 2008; The Eclipse/GMF page, 2008)
to specify the language that will be built. We use
Ecore model as it is a graphical way to specify the
language, thus being easier to specify the i*
framework Metamodel.
An Ecore model consists of a specific metamodel
for a determined DSL. Using that Ecore model all
the rules necessary to create the DSL could be built.
To build the Ecore metamodel that specifies the
i* framework, several specific i* metamodels were
used as reference (Alencar et al., 2008; Ayala et al.,
2006; Lucena et al., 2008) and only the essential
components present in those metamodels were used.
Thus, it was posssible to create a valid Ecore Model
to represent a DSL for the i* framework.
However, in order to introduce new features to
the i* language, it has been necessary to create new
elements in the Ecore model. Those elements were
not present in the original i* framework metamodel
and will be explained next.
In order to resolve the complexity problem that
had always afected this framework, two new
elements were created: the “ElementContainer” and
the “SoftGoalContainer”. These two new elements
added to the framework are containers for the
intentional elements that compose a dependency, so
it is possible to group several elements (e.g., goals,
tasks, resources and softgoals) inside these new
elements, thus diminishing the number of
dependencies between actors. These new classes still
have the possibility to be expanded or retracted, thus
allowing focused analysis to elements that constitute
a dependency between two actors, something that is
not possible using the original i* framework. Figure
2 shows parts of the created metamodel that refer to
the SD model and it is possible to see these two new
elements and the way they relate with other
elements.
Another improvement we have made is the
possibility to use actors as compartments so that
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
160

Figure 2: Part of Metamodel used to specifiy the i* framework.
they can be expanded and retracted individually,
maintaining the organization structure of its
internal elements. This is a feature that other tools,
such as (The i* wiki, 2008), have not implemented
with great success. Thus, it is possible to analyse
individually the internal elements and links
concerning each actor, as it is possible to go from a
SD Model to a SR Model and vice-versa without
the need to create another model.
3.2 i* based DSL
After the metamodel that represents the i*
framework is built, it is possible to generate the
DSL that will implement that metamodel.
Once the code was generated for the
metamodel, the graphical editor for the i* based
DSL could be defined, as well as all the mappings
responsible for the interactions between elements
and their connections. Finally, after this process
was concluded, the i* based DSL editor could be
generated. Figure 3 shows a picture referencing the
i* based DSL editor, where at the right hand side
there is the palette responsible for having all the
elements and links that can be used in this tool, and
the rest of the canvas is for the editing area.
The model presented in Figure 3 is a SR Model
created suing the i* based DSL for the Health
Watcher case study. Besides the features included
in other tools that this DSL implements as well,
this DSL addresses the scalability problems
presented in this framework. This solution used the
containers referred earlier. Using these containers
will decrease the number of dependencies between
actors.
There are two kinds of compartments, one just
for softgoals that exist between two actors and
another compartment for the other elements
(Goals, Tasks and Resources). In this way, it is
possible to separate efficiently non-functional
requirements (softgoals) from functional
requirements and the scalability and complexity of
models is reduced.
With the compartments, it is also possible to
make an individual analysis by compartment,
showing the elements contained in a dependency
between actors. This helps to better understand the
models that are being analysed, reducing their
complexity.
Figure 3 also shows an example where
compartments are highlighted for analysis
purposes. It is still possible to build models without
compartments, using only the original i*
framework.
3.3 Comparison with other Tools
To model the Health Watcher case study, both the
OME tool (The i* wiki, 2008), in Figure 1, and the
i* based DSL tool, in Figure 3, were used. Next, all
the evaluation results will be shown and also all the
differences and advantages in both tools. In both
tools (the i* based DSL editor and the recent
version of OME tool), it is possible to expand and
A DOMAIN SPECIFIC LANGUAGE FOR THE I* FRAMEWORK
161
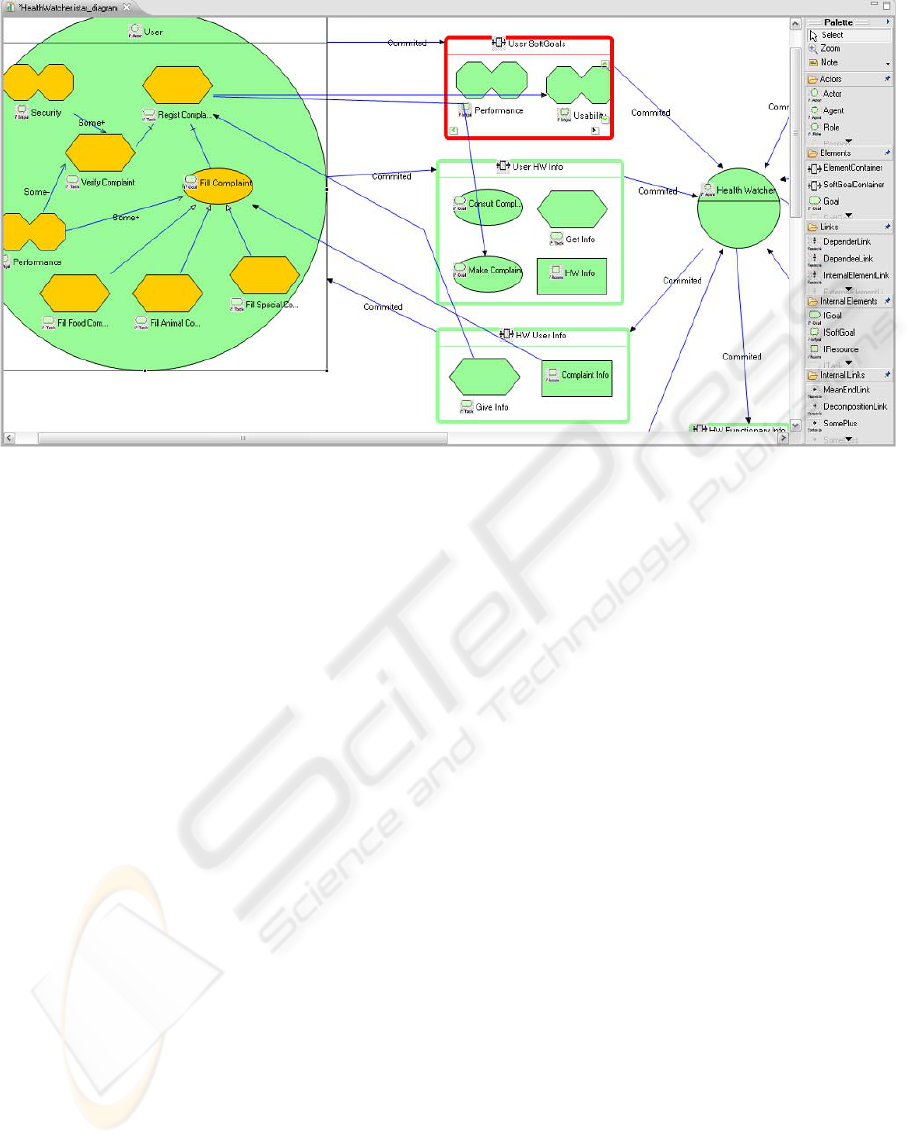
Figure 3: DSL editor for the i* Framework.
retract actors, so it is possible to migrate from a SD
Model to a SR Model and the other way
round.With this feature it is possible to analyse
individually each actor’s content.
Figure 1 shows the Health Watcher system SR
Model created in OME. In this picture, we can see
that there are several dependencies between actors,
making it difficult to read and comprehend
medium and large scale models.
4 EVALUATION
In order to perform a valid evaluation, it is
necessary to define the evaluation scope. With that
line of knowledge the evaluation method used in
(Murray et al., 2000) has been chosen to perform
this evaluation.
The purpose of this evaluation is to gather
qualitative data and to use that data to compare and
demonstrate that the i* based DSL and its editor
bring innovation and a better method to manage
scalability when compared with other tools that
implement the i* framework.
Ten Master’s students from the Computing
Department of the New University of Lisbon,
Portugal, with previous knowledges about the i*
framework were chosen to perform this evaluation.
It was necessary to choose individuals with those
capacities so that valid results and a valid analysis
between tools could be obtained. Next, the results
of this test will be presented and analysed.
To the question “Q1: How easy did you peform
the given tasks?”, all of the testers said it was easy
or very easy.
To the question “Q2: Compared to other tools
did you find this one easier to use or harder?”, all
of the testers said it was easier to use this tool.
To the question “Q3: Compared to other tools
did you think the methodology used in this tool is
similar to the methodology used in other tools?”,
all of the testers said that there were some
similarities and some diferences. This answer is
expected because of the new features that were
introduced in the i* framework as, for example, the
element containers and softgoal containers. Thus,
these new features change some aspects of the
standard i* framework.
To the question “Q4: Do you think this tool
brings innovation to the i* framework?”, all of the
test subjects said that it brought some innovation or
a lot of innovation when compared to other tools.
To the question “Q5: Do you think this tool
helps to manage the scalability in the i* models?”,
all of the test subjects said that this tool helps or
helps a lot to reduce and manage the models
scalability.
These answers are justified because of the new
features introduced in this tool, which helps to
simplify the use of this framework and helps to
reduce the models scalability.
Figure 4 shows the results of this evaluation.
The “x” axis represents the question number and
the “y” axis represents the satisfaction level of the
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
162

test subjects towards each question. The
satisfaction level values go from 1, which
represents a low degree of satisfaction to 5, which
represents a high degree of satisfaction. It can be
seen that to all the questions made the satisfaction
level is always above 3.5 thus showing that the test
subjects were pleased with the new tool.
Figure 4: Graphic for i* based DSL evaluation results.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper focused on the definition and
implementation of a DSL for the i* framework,
with the purpose to formalize its models and tame
their complexity. A tool was designed and
developed to implement the i* based DSL, in
which the notion of compartments was introduced
to control the visualization of dependencies
between actors.
It has been done a comparative study between
the i* based DSL editor and the OME tool. It was
shown what are the common aspects of both tools
and it was possible to show the innovations
implemented by the i* based DSL. The tool was
assessed by ten Master’s students, so that we could
have quantitative measurements. After the
evaluation phase and having analysed the resulting
data, we have concluded that the i* based DSL has
corresponded to the expectations. Thus, after the
data analysis and the test subjects oppinions, we
can conclude that the i* based DSL really brings
innovative features, helps to reduce models
complexity and is more user friendly than other
tools.
Relatively to future work, we have as an
objective to study other goal-oriented approaches
such as KAOS, so that we can identify common
aspects between it and the i* frameworks and
which aspects would be necessary to introduce in
order to build a more efficient framework for goal-
oriented methodologies.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
Partially financed by the Portuguese Foundation
FCT/MCTES – Project PTDC/EIA/65798/2006
and CAPES research grants
REFERENCES
Alencar, F., Silva, C. Lucena, M., Castro, J., Santos, E.,
Ramos, R., Improving the understandability of i*
models, In 10th International Conference on
Enterprise Information Systems (ICEIS’08),
Barcelona, Spain, 12 - 16, June 2008.
Ayala, C., Cares, C., Carvallo, J., Grau, G., Haya, M.,
Salazar, G., Franch, X., Mayol, E., Quer, C., A
Comparative Analysis of i*-Based Agent-Oriented
Modeling Languages. In SEKE’06, San Francisco,
USA, 5 - 7 July 2006.
Lucena, M., Santos, E., Silva, C., Alencar, F., Silva, M.,
Castro, J., Towards a Unified Metamodel for i*. In
Research Challenges in Information Science..
Marrakech, Morocco, 3 – 6 June, 2008.
Matulevicius, R., Heymans, P., Sindre G., Comparing
Goal-Modelling Tools With The RE-TOOL
Evaluation Approach, In Information Technology
And Control, Kaunas, Technologija, 2006, Vol. 35A,
No. 3, 276 - 284.
Yu, E., Modelling Strategic Relationships for Process
Reengineering. Ph.D thesis. Department of
Computer Science. University of Toronto, 1995.
Yu, E., Towards Modelling and Reasoning Support for
Early-Phase Requirements Engineering. In: Third
IEEE International Symposium on Requirements
Engineering, 1997.
Kelly, S., Tolvanen, J., Domain Specific Modeling
Enabling Full Code Generation,In IEEE Computer
Society Press, 2008.
Murray, N., Paton, N., Goble, C., Bryce, J.,
Kaleidoquery--a flow-based visual language and its
evaluation, In Conference on Advanced visual
interfaces, 2000.
The i* wiki, last access, December 2008:
http://istar.rwth-aachen.de/tiki-index.php
The DSL wiki, last access, December 2008i:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Domain_Specific_Lang
uage
The Eclipse/GMF page, last access, December 2008:
http://wiki.eclipse.org/GMF_Documentation
Massoni, T., Soares, S., Borba, P., Requirements Health-
Watcher version 2.0, In: Early Aspects at ICSE,
USA, 2007.
i* based DSL Evaluation
0
0,5
1
1,5
2
2,5
3
3,5
4
4,5
5
1
2
3
45
Questions
i* based DSL
OME Tool
A DOMAIN SPECIFIC LANGUAGE FOR THE I* FRAMEWORK
163
