
PORTUGUESE WEB ACCESSIBILITY
Portuguese Enterprises Websites Accessibility Evaluation
José Martins, José Cruz and Ramiro Gonçalves
UTAD University, Vila Real, Portugal
Keywords: Accessibility, W3C, Guidelines, Integration, Disability, Society.
Abstract: The use of the web is quickly spreading to the majority of the society. In many countries the use of the web
in government services, education and training, commerce, news, citizenship, health and entertainment is
significantly increasing. The web is extremely important for the dissemination of information and the
interaction between the various society elements. Due to this, it’s essential that the web presents itself
accessible to all, including those with any kind of disability. An accessible web may help the handicapped
citizens in their interaction with the society. With this in mind, an evaluation of the accessibility levels of
the Portuguese websites is, essential, for an assumption on the availability of these websites to all disabled
citizens.
1 INTRODUCTION
The content of this document is the result of research
and work done under a research project, whose
theme was the evaluation on the accessibility of the
Portuguese enterprises websites.
The introduction of new Technologies and
methods for, treatment and utilization of information
makes, our society, more complete and fit for
evolution. This evolution will create better life
conditions and best professional performances.
The development of the information and
communication Technologies - ICT in the last two
decades of the twentieth century and, their mass
availability within the population, lead to a profound
change in the economical and social activities. These
changes had, and still have, an impact in the citizens
quality of life, competitiveness and productivity of
enterprises (Socrates 2007b).
The information society is a society for all. The
ICT bring a clear and important influence, in the
various domains of the new way of life in society. Its
applications cover the entire spectrum of social
groups. Never the less, there are barriers to
overcome, opportunities to explore and benefits to
be collected. Therefore it’s not correct to create a
brand new group of e-excluded people, just by
abandoning the unprotected. It’s extremely
important to promote the universal access to e-
literacy and e-competence (Gurstein 2000).
The growing need of access to the online
information impels for a warranty of accessibility to
this same web content. According to the 2001
communication of the European Commission (EU
2002a), there are 37 million disabled European
citizens who need to be granted, a full access to web
content.
The ICT offer great potential to citizens with
mental and physical disabilities. Through the use of
these technologies, they can be better integrated in
their societies. It is however necessary, to increase
efforts to adapt the technology to certain groups of
people with disabilities (Wenner 2008).
2 WEB ACCESSIBILITY
CONCEPTS AND CONCERNS
The term accessibility can easily be defined has the
possibility of disabled people interact with a
product, resource, service or activity has normal
people would. In what concerns the ICT, we can
define accessibility as the creation of interfaces that
are perceived, operable and easy to understand for
people with a wide range of features. This includes
all disabilities, such as visual impairment, hearing
problems, and physical, cognitive or neurological
limitations. In this set, also should be included
conditions of temporary incapacity, such as the loss
142
Martins J., Cruz J. and Gonçalves R. (2009).
PORTUGUESE WEB ACCESSIBILITY - Portuguese Enterprises Websites Accessibility Evaluation.
In Proceedings of the 11th International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems - Human-Computer Interaction, pages 142-147
DOI: 10.5220/0002157301420147
Copyright
c
SciTePress

of glasses or the breaking of an arm. Beyond this,
accessibility also makes the products more
accessible to people who do not have any kind of
disability (W3C 2008c).
According to the European Commission, ICT are
a powerful engine for employment and growth. A
quarter of the GDP of the European Union and 40%
of the productivity growth is due to the ICT. These
facts show the importance of proactive policies to
react to the deep technological changes (EU 2002b).
Jim Thatcher and Shawn Henry claim that the
web accessibility goal consists in, providing to all
the disabled citizens, the ability to perceive,
understand, navigate and interact with the Web, even
if they have visual, hearing, physical, cognitive,
speech or neurological impairment (Thatcher,
Henry et al. 2006).
2.1 Web Accessibility – World
Perspective and Regulation
In the year 2002, the Portuguese National Institute of
Statistics - INE promoted a demographic study
named “Censos 2002 – População residente com
deficiência segundo o grau de incapacidade e sexo”.
According to this study, there were 634000
Portuguese citizens with some kind of disability.
This number represents 6% of the entire Portuguese
population (INE 2002).
The World Health Organization – WHO claims
that about 10% of the world population suffers, from
some kind of disability or incapacity. This number
clearly shows the existing need for health and
rehabilitation services. Due to this, the WHO created
an action plan called “Disability and Rehabilitation
Action-Plan 2006-2010”, whose mission goes not
only, for trying to disseminate and create awareness
of this reality throughout the world community, but
also to create initiatives that help in the process of
recovery and re-integration of disabled people back
to society (WHO 2006).
The first time web accessibility was matter of
business, in the European Union, was in September
2001, through a communication made by the
European Commission. This communication was the
result of the analysis made to the “eEurope 2002”
action-plan, that was approved in the Feira’s
European Council (EU 2002b). After 2001, and has
the web accessibility importance was growing, the
European Commission launched the “eEurope 2005”
action-plan. This plan goal was the creation of
modern public websites and the creation of a
dynamic environment for e-business. According to
the same action-plan, the referred creations would be
made with the help of an enormous amount of
broadband access offers, with competitive prices and
through a secure info structure for information (EU
2003).
Web content accessibility has been order of
business to various world entities, such as the W3C
consortium that, in the year of 1999, created the
World Accessibility Initiative – WAI. This initiative
was created aiming to be a parallel organization to
the W3C. Its mission should be developing
guidelines (that would be understood has the
international standards for web accessibility),
developing support materials for a better
understanding of the web, developing web
accessibility and developing new resources, through
international cooperation (W3C 2008a).
Since the year 1999, WAI has been aiming for
the increase of web content accessibility, by creating
several tools that allow it. An example of these tools
is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines. These
guidelines are an explicative document of how to
create web content, so that it can be accessed by just
anyone, including those who have some sort of
disability. According to these same guidelines, web
content is all the information within a web page or
web application. These accessibility guidelines are
characterized by tree main aspects, the guidelines
checkpoints, the priority levels (level 1, level 2 and
level 3) and the conformance levels (level A, level
AA and level AAA) (W3C 2008c).
The world awareness, for the web content
accessibility issue, is growing every day. This same
awareness is globally penetrating the enterprise
markets. This has been happening because, disabled
people are using ICT in a more regular basis, and
their economical influence is also growing. As a
consequence of this global “movements”, the
Portuguese enterprise market should also adapt itself
to this new reality.
2.2 The Importance of Accessible ICT
The ICT allow speeding up the pace of technical
progress, modernization and economical structural
adjustment. Since ICT stimulate, in a large extent,
the competitiveness, the European Union must take
every opportunity offered by them (EU 2005).
The ICT currently have a very high penetration
rate in the Portuguese enterprise market. The
Agency for the Society of Knowledge confirms this
statement in the analysis made to the Portuguese
National Institute of Statistics inquiry, according to
witch 95% of the enterprises, with ten or more
employees, are computer users, and 84% of these
PORTUGUESE WEB ACCESSIBILITY - Portuguese Enterprises Websites Accessibility Evaluation
143

same enterprises use e-mail and 83% have internet
access. For medium-size enterprises (50 to 249
employees) these three indicators have the value of
99%. For big enterprises (250 or more employees)
the three indicators all have a value of 100% (INE
2007).
Currently in Portugal, there are about 400000
employees in enterprises directly related to the ICT.
This value, according to the claims of the Agency
for the Society of Knowledge, will increase about
3%. Other value that, according to this same
Agency, will also increase in the future, is the
number of people working with a computer in their
place of work, that will increase from 19% (in the
year of 2004) to around 40% (UMIC 2007).
Due to this, it’s very important to have accessible
ICT so that, all of the people that work or that will
work with them, have the means to really take the
best advantage of these technologies.
The World Wide Consortium is currently present
in the World regulation of web accessibility. The
W3C 1.0 version of the accessibility guidelines is
currently, the standard used for the creation of rules
that encourage, the creation of accessible Web
content. Although the widely acceptance of the
directives of the W3C as the standard to use, this
same consortium is developing a second version of
guidelines for accessibility, in order to define a new
set of criteria and techniques, appropriately adjusted
for the current technological levels. According to the
recommendation of the W3C, the 2.0 version of the
directives for accessibility cover a large number of
recommendations to make Web content more
accessible. Following these guidelines will make
web content accessible to a larger number of people
with disabilities (including blindness or low vision,
deafness or hearing loss, learning disabilities,
cognitive limitations, restrictions of movement,
difficulties in speech, photosensitivity and
combinations of these). Following this new set of
directives, the final result will be a Web content
more accessible to all user (W3C 2008b).
3 WEB ACCESSIBILITY
EVALUATION
3.1 Web Accessibility Evaluation
Proceedings
For undertaking the evaluation of the accessibility
levels presented by the Portuguese enterprises
websites, we chosen to use the method proposed by
the W3C’s WAI.
In what the WAI concerns, the accessibility
evaluation of a website is a process made by the
following steps: definition of the evaluation scope,
definition of the evaluation tools, definition of the
proceedings for the manual evaluation and definition
of witch reports will result from the evaluation
process (W3C 2006).
For the definition of the evaluation scope, we
had to choose what criteria would the accessibility
evaluation follow and who would be part of the
target group. For the criteria to use, we decided that
the best way to achieve good results was, following
the “AAA” accessibility level announced by the
W3C (W3C 2008b).
For the definition of the target group we realised
the impossibility in evaluating all of the Portuguese
enterprises, so we decided to evaluate the 1000
biggest Portuguese enterprises during the year of
2005 (INE 2007). Even though this was our initial
target group, after a research on the websites of
these enterprises, we reached to the conclusion that
only 777 of them had online websites and 223 of
them didn’t had an available website or had one that
was “in construction” or one that was incompatible
with the evaluation tool we’ve chosen. For this
reason the “final” target group was only composed
by 777 of the initial 1000 enterprises.
For the evaluation tool to use, we’ve chosen the
TAW3 tool (CTIC 2008).
This was the chosen web accessibility evaluation
tool because its execution is done according to the
following points:
• The evaluation is based on the W3C Web
Content Accessibility Guidelines 1.0;
• It’s free to use by anyone;
• It automatically evaluates all the pages of
a website;
• It creates a report with all the accessibility
failures encountered in a website.
• It’s available in several languages,
including Portuguese and English.
For this project we decided that the manual
evaluation, of entire target group was something that
we wouldn’t be able to achieve in the period of time
that we had, for the resolution of this project. As a
result of this situation we decided not to manually
evaluate the referred websites.
In what concerns the kind of reports that would
result from the evaluation process, we decided to do
a group of simple statistical studies (average,
standard deviation, maximum and minimum), that
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
144

would represent the reality of the web accessibility
levels presented by the Portuguese enterprises.
3.2 Evaluation Results
The first analysis made was pointed to the target
group. This initial process consisted in verifying the
number of Portuguese enterprises that had an
available website. The result of this process was that
82.8% of the initial 1000 enterprises had an
available website has the figure 1 shows.
Figure 1: Relationship between the enterprises with an
available website and the ones with an unavailable
website.
After this initial process, the available websites
were tested against the W3C/WAI accessibility
guidelines with the help of the TAW3 tool. The first
element that was retrieved from this evaluation was
the fact that, 6% of the initial 82.8% couldn’t be
evaluated do to their incompatibilities with the tool
that was chosen.
Other information that was possible to retrieve
from this first analysis was, the discrepancy of the
results obtained with the accessibility evaluation.
The figure 2 shows this discrepancy.
Figure 2: Discrepancy of the accessibility evaluation
results.
Even though the objective of this evaluation was,
achieving indicators of the web accessibility levels
within, the Portuguese enterprises websites, it was
imperative that the results that supported those
indicators were correct and thrust wordy. Due to
this, a statistic treatment had to be done to the
evaluation results. The initial treatment consisted in
applying the outlier definition to the referred results
(Mendenhall and Sincich 1995; Renze 2005). The
figure 3 presents a schema of what method was
applied to the results in this statistical treatment
stage.
Figure 3: Outliers treatment schema.
After the referred statistical treatment to the
evaluation results another analysis to its values was
made. This step allowed to perceive that, although
they were already indicators of a tendency on the
accessibility levels presented by the Portuguese
enterprises websites, these values were still quite
widespread as can be viewed in table 1.
Table 1: Target group accessibility evaluation results.
Priority 1 Priority 2 Priority 3
Average
180 1375 212
Standard
deviation
215 1352 200
Median
149 1321 225
Minimum
0 0 0
Maximum
12612 35645 4831
These results indicate that almost all websites
have accessibility issues. Giving the fact that priority
1 errors are those that, according to the W3C-WAI
initiative, are those that cannot exist in a website, an
average of 180 priority 1 errors for website, is a
simple indicator of a possible lack of accessibility in
these websites. The high number of the priority 2
error average indicates that, the evaluated websites
also have priority 2 accessibility issues. This same
situation is also true for the priority 3 errors.
Even though these results can provide a
simplistic evidence for the existence of accessibility
issues in the Portuguese enterprises websites, it was
decided to an even more specialized analysis over
PORTUGUESE WEB ACCESSIBILITY - Portuguese Enterprises Websites Accessibility Evaluation
145
these same results. This analysis started with the
division of the target group according to the
enterprises activity sector. For supporting this
division was used the 3rd revision of the Portuguese
Economical Activity Classification (Socrates
2007a).
After this division was completed, the results
were grouped by the W3C Accessibility Guidelines
priority levels. This grouping can be observed in the
tables 2, 3 and 4, where the average, minimum and
maximum values are presented, along side with the
number of websites evaluated in each activity sector.
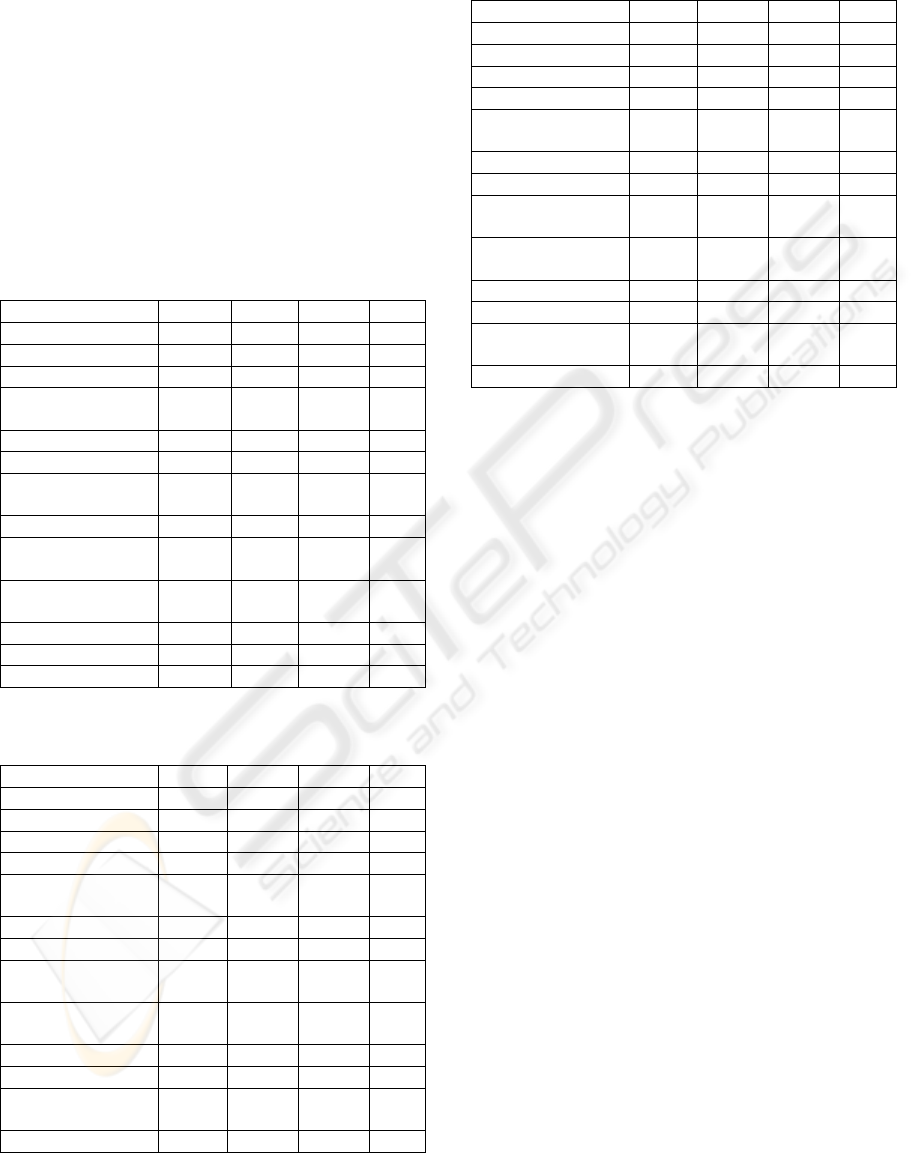
Table 2: Priority 1 accessibility evaluation results grouped
by the activity sector.
Activity Sector Avg. Min. Max. #
Agriculture
10
0
895
5
Housing
59
0
382
6
Construction
90
0
4444
74
Transformation
Industries
118
0
12612
217
Real Estate
136
32
3568
7
Transportation
137
0
4951
50
Electricity,
Water and Gas
144
13
1205
12
Auto Commerce
180
0
4780
261
Bank and
Insurance
197
4
2941
35
Administration
Activities
340
1
8817
34
Audiovisual
406
14
1900
30
Consulting
546
0
1535
16
Health
1385
46
5909
21
Table 3: Priority 2 accessibility evaluation results grouped
by the activity sector.
Activity Sector Avg. Min Max. #
Agriculture
223
5
2364 5
Housing
672 0 3490 6
Construction
812 0 16028
74
Real Estate
1031 592 9139 7
Transformation
Industries
1185 1 35645 217
Transportation
1360 5 10787 50
Auto Commerce
1370 2 18765 261
Bank and
Insurance
1815 33 18584 35
Electricity,
Water and Gas
1843 105 9541 12
Consulting
1965 11 9520 34
Audiovisual
2414 11 16058 30
Administration
Activities
3124 4 9523 16
Health
5634 92 20806 21
Table 4: Priority 3 accessibility evaluation results grouped
by the activity sector.
Activity Sector Avg. Min Max. #
Agriculture
115 0 308 5
Housing
126 0 532 6
Construction
141 0 1700 74
Real Estate
157 53 2063 7
Transformation
Industries
191 0 3542 217
Transportation
195 1 1997 50
Auto Commerce
205 0 4310 261
Bank and
Insurance
226 8 2164 35
Electricity,
Water and Gas
274 16 1306 12
Consulting
388 0 2369 30
Audiovisual
402 2 4831 34
Administration
Activities
469 5 1327 16
Health
951 39 3678 21
4 CONCLUSIONS
With this work we managed to achieve our initial
goal that was, delivering indicators on the actual
accessibility levels presented by the Portuguese
enterprises websites.
As the results that were presented show, the
accessibility evaluation that was done, leaded to the
detection of a considerable number of errors on each
of the websites that belong to the target group. This
fact indicates that the accessibility levels of the
Portuguese enterprises are very low.
Another aspect that resulted from this work was
the unveiling of the number of websites that could
be evaluated. From the initial 1000 Portuguese
enterprises with the biggest business volume, only
777 of them could be evaluated. This difference had
its origin in the fact that almost 200 of the initial
1000 enterprises didn’t have a website and in the
fact that the remaining ones didn’t have a TAW3
compatible website.
The World Wide Web is constantly evolving
and, alongside with this evolution, the citizen’s
requirements towards the services provided by the
Web (websites, web applications, etc.) are also
changing and evolving. In this way, it’s imperative
that all services available in the web are accessible.
This same situation can be applied to the Portuguese
websites, so that the Portuguese disabled citizens
can use them and be less limited in our society.
ICEIS 2009 - International Conference on Enterprise Information Systems
146

REFERENCES
CTIC. (2008). "¿Qué es TAW? ." Retrieved 19th
November 2008, from
http://www.tawdis.net/taw3/cms/es/infotaw/que.html.
EU (2002a). Delivering eAccessibility, Comission of the
European Communities.
EU (2002b) "eEurope 2002: accessibility of public
websites and their content." European Community
Official Journal. Volume, DOI:
EU (2003) "eEurope 2005 Action Plan." Europe's
Information Society Thematic Portal Volume, DOI:
EU. (2005). "Challenges for the European Information
Society beyond 2005." Retrieved 26th November
2008, from
http://europa.eu/scadplus/leg/en/lvb/l24262.htm.
Gurstein, M., Ed. (2000). Community Informatics:
Enabling Communities with Information and
Communications Technologies, IGI Global.
INE (2002). Censos 2001 – População residente com
deficiência segundo o grau de incapacidade e sexo.
INE (2007). 1000 Maiores empresas de 2005 tendo em
conta o volume de negócios. Lisbon, National Institute
of Statistics.
Mendenhall, W. and T. L. Sincich (1995). Statistics for
Engineering and the Sciences, Prentice Hall.
Renze, J. (2005) "Outliers." MathWorld - A Wolfram Web
Resource Volume, DOI:
Socrates, J. (2007a). Decreto -Lei n.º 381/2007 14 de
Novembro, Diário da República.
Socrates, J. (2007b). Portuguese Ministers Council
Resolution n.º 155/2007, Diário da Républica
Portuguesa. II.
Thatcher, J., S. Henry, et al. (2006). Web Accessibility:
Web Standards and Regulatory Compliance, friends of
ED.
UMIC (2007). UMIC - Empresas. Lisbon, Agência para a
Sociedade do Conhecimento.
W3C (2006). Conformance Evaluation of Web Sites for
Accessibility. W. A. Initiative.
W3C. (2008a). "WAI Mission and Organization."
Retrieved 18th December 2008, from
http://www.w3.org/WAI/about.html.
W3C (2008b). Web Content Accessibility Guidelines 2.0.
W. W. W. Consortium.
W3C. (2008c). "Web Content Accessibility Guidelines
(WCAG) Overview." Retrieved 1st December 2008,
from http://www.w3.org/WAI/intro/wcag.php.
Wenner, C. (2008) "ICT For Citizens and Businesses."
Volume, DOI:
WHO (2006). Disability and Rehabilitation: WHO action-
plan 2006 – 2011.
PORTUGUESE WEB ACCESSIBILITY - Portuguese Enterprises Websites Accessibility Evaluation
147
