
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE WORD-OF-MOUSE
Sales of New Products at Amazon.Com
Geng Cui
Department of Marketing and International Business, Lingnan University, Tuen Mun, Hong Kong
Xiaoning Guo
Department of Marketing, University of Cincinnati, 2600 Clifton Ave., Cincinnati, Ohio 45221 U.S.A.
Keywords: Word-of-Mouth, Product Reviews, New Products, e-Marketing, Panel Data Analysis.
Abstract: Online word-of-mouth (WOM) has become a major information source for consumers planning to purchase
new products. This study examines the effect of online consumer reviews on the sales of new products.
Using the data collected from Amazon.com over a period of nine months, we find that while the effect of
valence of online reviews is greater than that of volume, negative consumer reviews affect new product
sales more than positive reviews, but not in a negative way. Volume and valence of online reviews have
greater impact on experience products than on search products. Moreover, the volume of consumer reviews
has a greater effect on new product sales in the later stage of product life cycle (PLC). Thus, online WOM
gains momentum over time and significantly affects the sales of new products beyond the initial period.
Marketers need to pay greater attention to online WOM and promote consumer reviews when launching
new products.
1 INTRODUCTION
Word-of-mouth (WOM) refers to oral, person-to-
person communication between a receiver and
communicator with respect to a topic. In recent
years, online WOM communication in the form of
online consumer reviews has become a major
information source and decision aid for consumers
when they plan their purchases. With the help of
online consumer reviews, consumers can benefit
from the diverse opinions of different people who
have bought or used the new products so that they
can make informed decisions. A recent survey of
DoubleClick (2004) finds that WOM plays a very
important role in consumers’ purchasing processes
for many types of products and that for some goods,
such as electronics and home appliances, product
review websites outrank all other media in
influencing consumer decisions. As more consumers
search for information on new products from online
forums and exchange their opinions on the Internet,
marketers also see online forums as a good platform
to promote their new products. Both researchers and
practitioners view online WOM as an important
driver of consumer behavior when they plan their
purchases of new products.
Compared with offline WOM, online WOM has
unprecedented speed and reach. Compared with paid
advertising, consumers trust online reviews more,
because they are based on the experiences of others
and are perceived as more relevant and easier to
understand (Herr et al., 1991). Several researchers
have found a positive relationship between online
consumer ratings and sales of books and movies and
viewership of TV shows (Chevalier and Mayzlin,
2006; Godes and Mayzlin, 2004). While it is
plausible that online WOM affects the sales of new
products, we need more in-depth investigations of
the effects of online WOM on new product sales
with respect to the following research questions.
First, what attributes of online consumer reviews,
volume or valence, affect new product sales?
Second, do positive and negative reviews affect new
product sales differently? Third, does the effect of
online reviews vary for different types of products?
Fourth, does the effect of online reviews differ over
stages of product life cycle? Unlike previous
research focusing on entertainment or information
products over a short time, this study examines the
143
Cui G. and Guo X. (2009).
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE WORD-OF-MOUSE - Sales of New Products at Amazon.Com.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 143-150
DOI: 10.5220/0002178101430150
Copyright
c
SciTePress

effects of online WOM on the sales of new products
over an extended period and explores such effects
across two product categories: experience vs. search
products.
Using data from Amazon.com, we conduct a
longitudinal study of the effects of online customer
reviews on the sales of new products. The results
suggest that while the valence of online reviews has
a greater impact than the mere volume of reviews,
negative consumer reviews affect new product sales
more than positive reviews, but not in a negative
way. The volume and valence of online reviews
affect experience products more than search
products. Moreover, the volume of online consumer
reviews has a greater effect on new product sales in
the later stage of product life cycle (PLC). Thus,
online WOM gains momentum over time and
significantly affects the sales of new products
beyond the initial period. These findings have
meaningful theoretical and managerial implications
for understanding the role of online WOM in
affecting new products sales.
2 LITERATURE REVIEW
2.1 Word of Mouth
In the marketing context, WOM represents the type
of interpersonal communication that significantly
influences product evaluations and purchase
decisions and has been shown to be more powerful
than printed information because WOM is
considered more credible. Moreover, negative WOM
is believed to spread more quickly than positive
WOM, making it a fearful phenomenon to
practitioners. WOM has been seen as a double-
edged sword as informal discussions among
consumers can make or break a product. Despite its
omnipresent and prevalent impact, WOM remains
one of the most effective, yet least understood form
of marketing communication, because it is largely
beyond the control of marketers.
The advent of the Internet has brought new ways
for marketers and consumers to disseminate and
receive messages regarding products and provided a
new platform for WOM communication. Online
WOM is an extension of offline WOM on the
Internet. It can be any positive or negative statement
made by potential, actual or former customers about
a product or company, which is available to a
multitude of people and institutions via the Internet.
Online communities allow the opinions of a single
individual to reach thousands or even millions of
other people, and can significantly affect other
consumers’ decision about products.
Compared with offline WOM, online WOM has
several distinctive features. First, offline WOM and
online WOM are different in terms of the quality and
mode of transmission (Rogers, 2003; Bass 1969).
Offline WOM communication consists of spoken
words exchanged with a friend or relative, usually in
a face-to-face situation. By contrast, online WOM
involves the exchange of personal experiences and
opinions through written words transmitted over the
Internet, often among strangers in a non face-to-face
situation. Written messages often transmit the
information in an intact manner and make the
content more thoughtful as people spend more time
writing their thoughts down. Thus, written
communication is usually more logical and maybe
more impactful than oral communication.
Second, compared with offline WOM, online
WOM has unprecedented scalability and speed of
diffusion. Online WOM is more influential due to its
speed, convenience, one-to-many reach, and its
absence of face-to-face human pressure. By using
the Internet, one can seek out the opinion of
strangers. This seldom happens in the conventional
interpersonal context where opinion providers are
embedded in social networks and known to people
as credible sources. The escalation in the size of
audience and reach is also changing the dynamics of
many industries in which WOM has traditionally
played an important role. For example, the
entertainment industry has found that the rapid
spread of WOM is shrinking the life cycles of its
products and prompting firms to rethink its pre- and
post-launch marketing strategies. In fact, movies are
seeing much more rapid changes in revenues
between the opening weekend and the following
weekends, suggesting that public opinion is
spreading faster.
Third, by comparison, online WOM also has
greater persistence and measurability than its offline
parallel. In offline settings, WOM without a
dedicated recorder disappears into the thin air. In
online settings, WOM can be recorded and displayed
in many public Internet forums, such as review sites,
discussion groups, chat rooms, and web blogs. With
written comments posted on the Internet, people can
seek out the information at their own pace, even
long after its initial posting. Since most online
reviews of products are kept on the forum for a
prolonged period, marketers can accurately measure
WOM and its effect by mining information available
on these Internet forums (Dellarocas, 2003).
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
144
2.2 WOM and New Product Sales
From a theoretical perspective, there exists a strong
rationale for the effect of WOM on new product
sales. Roger’s (2003) theory of diffusion of
innovation puts great emphasis on the effect of
WOM as a channel of communication among certain
groups, particularly among the early majority and
late majority, who tend to follow the innovators and
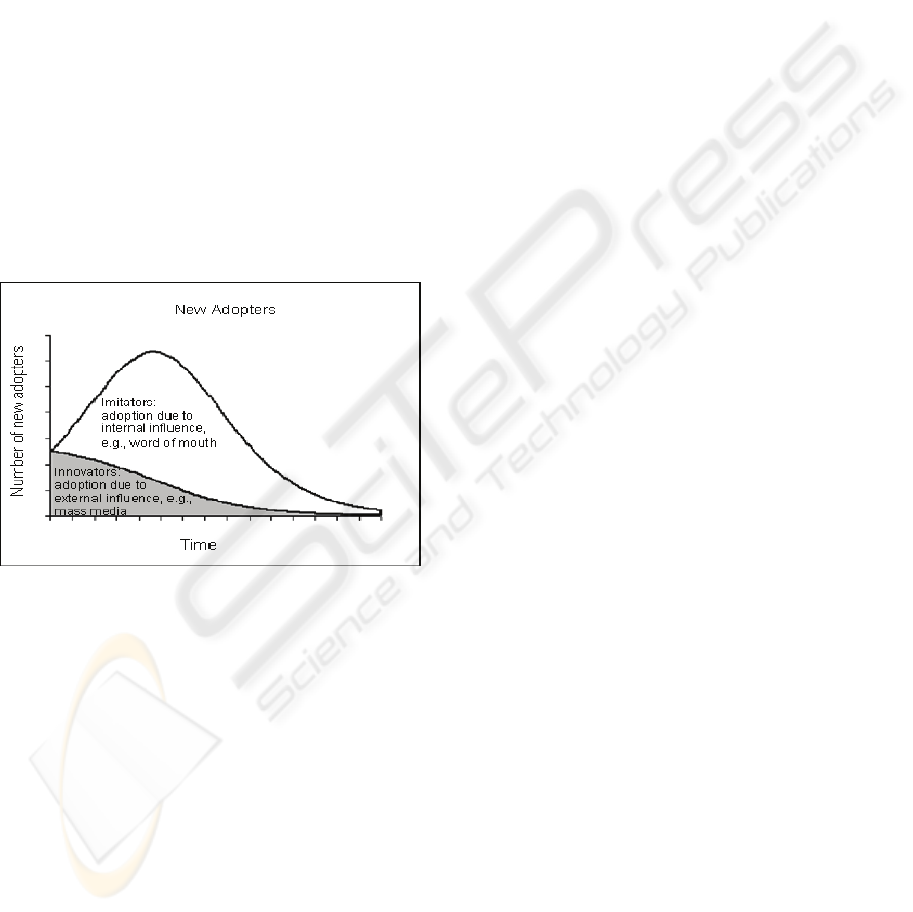
early adopters. According to the Bass (1969) Model
of Diffusion, in the early stage of a product's life
cycle (PLC), innovators are mainly affected by mass
media and; after using the new products, they pass
their opinions on to others. Later, the others seek out
the opinions from innovators and make their own
purchase decisions. The coefficient of external
influence (mass media) for innovators and that of
internal influence (WOM) for imitators can be
estimated using the density function of time. Thus,
the Bass model suggests that WOM plays a greater
role in consumers’ purchase of new products beyond
the early stage of PLC (Figure 1).
Figure 1: The Bass Model.
As shown in Figure 1, the Bass model assumes
that the impact of WOM communication on
adoption increases with time early in a product’s life
cycle and then decreases later on. This model has
been shown to have some success in predicting the
growth of a wide range of new products based on
just a small number of data points. Similar effect of
WOM on the diffusion of innovations has been
observed in other settings (Reingen et al., 1984).
However, Van Den Bulte and Lilien (2001) show
that despite the evidence of social contagion,
marketing effort, and not interpersonal
communication, plays a dominant role in people’s
adoption decisions. Thus, the findings about the
impact of offline WOM on new product sales have
been mixed.
2.3 The Effect of Online WOM
In the online environment, consumers can share their
experiences, opinions, and knowledge with others
via chat rooms, newsgroups, and electronic forums.
Three metrics of online WOM have received
attention: volume, valence, and dispersion. The
rationale behind measuring volume is that the more
consumers exchange their views on a product, more
consumers will become aware of it. The valence,
i.e., the average ratings or the fraction of positive
and negative opinions, carries important information
about consumers' evaluation of a product and
captures the nature of WOM messages. In an online
forum, WOM is commonly articulated in the forms
of consumer reviews and ratings of products. The
majority of past research on online WOM has
focused on the use of customer ratings as a revenue-
forecasting tool for "new products" such as TV
shows, movies, and books (e.g., Dellarocas, 2003).
The dispersion or spread of communication
measures how fast WOM spreads within and across
communities.
Armed with these new measurement tools,
researchers have conducted an increasing number of
studies using data from online forums and
championed the online WOM as the driver of new
product sales in the e-marketplace. Online WOM is
believed to exert a greater influence on consumer
purchases than in the offline environment. For
instance, the volume of messages on newly released
movies has been found to be a good predictor of
their box office success (Liu, 2006). The valence of
online ratings posted during a movie’s opening
weekend has proven to be the most important
predictor of its revenue in subsequent weeks
(Dellarocas et al., 2007). The dispersion of
discussion about weekly TV shows across Internet
communities was found to have a positive
correlation with the viewership of these shows
(Godes and Mayzlin, 2004).
Since researchers have used different measures
of online WOM in forecasting new product sales,
their findings have not been always consistent. Some
scholars find that the volume of reviews has a
significant impact on new product sales, but not the
ratings (Dellarocas, 2003; Duan et al., 2008; Liu,
2006). On the other hand, a number of studies
support the effect of valence or ratings on new
product sales (Chevalier and Mayzlin, 2006;
Dellarocas et al., 2007). Others consider the
dispersion of online discussion having significant
explanatory power (Godes and Mayzlin, 2004).
Thus, it is not clear which aspect of online WOM,
volume, valence and dispersion, exerts a greater
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE WORD-OF-MOUSE - Sales of New Products at Amazon.Com
145

influence on new product sales. Overall, the findings
on the effect of different measures of online WOM
on new product sales have been inconclusive.
2.4 Theoretical Framework
First, the individual effects of WOM, volume,
valence and dispersion need to be estimated more
accurately. Second, researchers have so far focused
on information and entertainment products, such as
books, movies and TV shows, which traditionally
attract customer reviews within a short period of
their releases. Researchers have not examined the
role of online WOM in other consumer products
(such as search products) or compared the effect of
online WOM across product categories. Third,
although the effect of valence of online WOM has
been examined, few researchers have investigated
the difference between the effect of positive reviews
and that of negative WOM on new product sales.
Fourth, most studies followed the online WOM and
new product sales only for a short period, from
weeks to a few months. The short time span does not
lend an opportunity to examine the effect of online
WOM beyond the initial period. Lastly, but more
importantly, researchers have not expended much
effort to explain theoretically how online WOM
among members of a virtual community affect the
sales of new products
With these issues in mind, we draw from the
Social Networks Theory and treat the online forums
as a social network. The existing research suggests
that the weak ties among the members of an
informal social network facilitate the flow of
information among them (Brown and Reingen,
1987). Online forums with many members, who are
perfect strangers to one another, have unprecedented
wide reach and frequency of interactions (Brown et
al., 2007). Furthermore, consumer reviews are
generally perceived as more trustworthy than paid
advertising. Thus, online customer reviews should
exert a significant effect on new product sales. In
this study, we propose an integrative theoretical
framework on the role of online WOM in affecting
the sales of new products.
First, innovation diffusion studies often examine
WOM by the number of adopters and their
interactions with the non-adopters. Such interactions
(i.e., the volume of WOM) help to create consumer
awareness (Bass, 1969; King and Balasubramanian,
1994). Following the same rationale, online WOM
(i.e., reviewers by adopters) can also influence the
opinions of other consumers and albeit new product
sales. Second, the rationale for the effect of valence
is straightforward: positive WOM promotes the
perceived quality and/or value of a new product
whereas negative WOM dampens a product's
reputation (Liu, 2006). Third, the valence of online
consumer reviews (i.e., the ratings of the products)
has a higher level of diagnosticity and is a more
influential factor than the volume of online
consumer reviews on new product sales. Fourth,
negative cues tend to attract more attention and are
weighed more heavily than positive cues (Kanouse
and Hanson, 1972). Negative online customer
reviews are perceived as more diagnostic albeit more
influential in consumer decision making and have a
greater impact on new product sales than positive
information.
Fifth, based on their nature, products can be
classified as search or experience goods. Search
products such as consumer electronics are usually
evaluated by instrumental evaluative cues (i.e., the
technical or performance aspects of a product).
Experience goods, such as recreational services, are
difficult to describe using specific attributes, and
consumers need to directly experience the products
to evaluate their quality based on their personal
contacts with the products and their idiosyncratic
experiences (Weathers et al., 2007). The attributes of
search products are often standardized and available
at online stores as well as the e-commerce sites and
frequently discussed in the product advertisements
and reviews. The attributes of experience products
are, however, not as accessible in the online
environment, thus making the opinions and
recommendations of other consumers more valuable
to the potential buyers. Therefore, online product
reviews in terms of both volume and valence have
greater effect on consumer purchases for experience
products than for search products.
According to the Bass Diffusion Model,
consumers that adopt a new product in the early
stage (the introduction stage) of PLC are mostly the
innovators who are affected by external influence
such as mass media. The model also suggests that in
the later stages of PLC, the adoption of new
products speeds up as an increasing number of
imitators begin to adopt the new product, and that
the imitators or followers are mostly affected by
internal influence such as WOM. Therefore, WOM
plays a more important role in new product adoption
beyond the initial introduction stage (Bass, 1969). In
the online environment, WOM travels even faster
and spreads more widely, making it even a stronger
driving force for new product sales. Therefore, due
to the accelerated dissemination of WOM across the
online forums, the effect of WOM on the new
products sales is expected to be stronger beyond the
introduction stage.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
146

3 METHOD
The WOM data were collected from Amazon.com,
which sells a variety of consumer products from its
online store and has been used in a number of
studies on B2C e-commerce (e.g., Liu, 2006).
Amazon.com serves as a good setting for studying
the effect of online WOM on new product sales.
First, it is one of the most popular online shopping
websites with millions of registered members and
frequented by non-members. It requires no fee for
joining and helps reduce any possible bias in the
demographic composition of the Web site’s visitors.
Second, Amazon has been well-known for its
extensive customer review system. Anybody
including non-members can post, browse, and
comment on a product review and rating. Third, the
structure of the Web site is well designed with all
the relevant information (prices, sales ranks,
customer reviews and ratings of products)
conveniently displayed so that finding and collecting
information is straightforward, thus reducing
possible errors during data collection. Most
importantly, the release dates for new products are
displayed prominently by the calendar dates. WOM
messages (i.e., reviews and replies) and ratings are
archived and indexed by the dates of their original
postings. All the information including the sales
ranks of products and the number of reviews are
updated frequently. Thus, it is possible to collect the
data on customer reviews and other information and
track the changes in the product data on a continuous
basis.
Existing studies of online WOM have largely
focused on information or entertainment products
such as books, movies and TV programs. Although
these products can be classified as experience
products, their life cycle varies from a short period
of concentrated sales since the release dates (e.g.,
movies) to a long time (TV series). While most
previous studies of online WOM focus on one
product category (movie or book), this study
incorporates product category and includes two
different types of products: search vs. experience
products. It is important that the data from both
product categories be from the same source. This is
another important reason for collecting the data from
Amazon.com. In this study, we use video games, an
entertainment product, as the category for
experience products. For search products, we choose
consumer electronics. These two types of products
have been used to represent experience and search
products in previous studies (Weathers et al. 2007).
Mostly importantly, these two product types are
stand-alone categories on Amazon.com, which posts
the sales rank data of products based on these
categories. In other words, the sales rank and the
other relevant data are category-adjusted.
We tracked the online consumer reviews in
terms of volume and valence, sales ranks and related
information of the new products from these two
product categories on a weekly basis from August
2007 to April 2008 for 9 months, which are
sufficient to examine the relevant data beyond the
introductory stage of product life cycle. Starting on
August 1st, 2007, we identified each new product
from these two categories released on Amazon.com,
where the product release dates largely coincided
with the offline release dates. For this and each of
the following weeks, we downloaded all the relevant
information for these products and saved them in a
data archive for data input and verification. Then,
the data including sales ranks, number of reviews,
average and frequencies of ratings, etc., were
extracted from these saved webpages and input into
a database. Thus, we have altogether a maximum of
36 weeks of data from the new products in these two
categories.
The dependent variable in this study is a new
product's sales. Amazon.com does not disclose the
actual sales volumes for its products. Instead, we use
the sales ranks of the products posted by
Amazon.com as a proxy of actual sales. The sales
ranks are category-adjusted and inversely related to
sales. That means that the top-selling product has a
sales rank of one, and relatively slow-moving
products are assigned higher sequential ranks.
According to Chevalier and Mayzlin (2006), the
relationship between the sales rank and the actual
volume of book sales on Amazon can be
approximately describe by: ln [Sales] =β0-β1*ln
[SalesRank], β is measured in two time intervals.
The relationship between ln (sales) and ln (ranks) is
approximately linear. Thus, in lieu of sales data, the
log of sales rank can be the appropriate dependent
variable. Because sales rank is a log linear function
of sales with a negative slope, we use –log
[SalesRank] as the dependent variable.
Independent variables include the volume and
valence of online consumer reviews. Based on
Chevalier and Mayzlin (2006), we use the number of
reviews to measure the volume of online consumer
reviews. Following Dellarocas et al. (2007), we use
the average ratings, i.e., average number of stars that
the reviewers assigned (on a scale of one to five
stars, with five stars being the best) to capture the
valence of online consumer reviews. Moreover, the
frequencies of numeric ratings are also recorded to
generate the percentage of positive and negative
ratings. Moderating factors include product type
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE WORD-OF-MOUSE - Sales of New Products at Amazon.Com
147

(search vs. experience products) and the stage of
PLC. A product's stage of life cycle is defined by a
product's week age (the number of weeks since its
release).
Control variables include product category,
product subcategory, list price, price promotion
(discount), other stores that provide such products
(but still sold through Amazon.com), and
availability of free shipping. We include the product
subcategories to control for the subcategory
variations to minimize any confounding effect.
Search products have nine subcategories including
electronic accessories, cameras, televisions, MP3
players, computers, office electronics, GPS,
equalizer and optics. Experience products have the
following subcategories: Playstation 3, Xbox360,
Nintendo Will, Playstation 2, Xbox, GameCube,
Mac Games, Sony PSP, Nintendo DS, and Game
Boy Advance.
4 RESULTS
During the nine month period, we collected the data
for 417 new products: 165 search products
(consumer electronics) and 252 experience products
(video games). We excluded those products that had
no sales data or too much missing data. The final
sample contains 332 new products, 131 search
products and 201 experience products. Within their
own category, the sales ranks for video games range
from 12 to131,316, while those for consumer
electronics range from 2 to 378,314. The maximum
volume of reviews includes 274 positive reviews and
38 negative reviews for videogames, compared with
543 positive reviews and 63 negative reviews for
consumer electronics. Standard deviation of the
volume of reviews for video games is 34.49
compared with 32.46 for consumer electronics. The
average rating for video games is 3.15, much higher
than that for consumer electronics (1.85).
Since cross-sectional analysis may suffer from the
cohort bias, we conduct panel data analysis for all
the hypotheses. Hierarchical regressions are used to
test the effects of the predictor variables.
First, we regress the dependent variable (sales) on all
the covariates (shipping, price, promotion, other
stores and product type). In step two, we
add the predictor variables including volume of
online reviews and valence (ratings). Table 1 shows
that this regression model has a good fit of the data
(adjusted R-squared=0.596, F =1576.83, p≤ .001).
The beta coefficient of volume of consumer reviews
is 0.199 (p≤.001) while the coefficient of the valence
of consumer reviews is 0.367 (p≤.001).
Table 1: The Effects of Volume and Valence.
Model Fitness/Variables Results/Coefficients
R-Square 0.597
Adjusted R-Square 0.596
F Value 1576.83
Sig. (p≤) 0.001
Shipping 0.226***
Price 0.071***
Promotion 0.092***
Other Store(OS) –0.039***
Product: Experience 0.179***
Volume 0.199***
Valence 0.367***
Note: ***: Sig.≤0.001
Thus, both volume and valence of online
reviewers have a significant positive effect on new
product sales, but valence has a stronger impact than
volume.
Regarding the effect of negative reviews versus
that of positive reviews on new product sales, we
enter the percentage of positive reviews and that of
negative reviews. Table 2 shows that this regression
model is significant (adjusted R-squared=0.525, F
=1179.06, p≤ .001). The coefficient of the
percentage of negative reviews is 0.347 (p≤.001),
while the coefficient of the percentage of positive
reviews is 0.158 (p≤.001). Thus, the effect of
negative reviews on new product sales is greater
than that of positive reviews. But the coefficient of
negative reviews is positive rather than negative,
similar to the finding of a previous study (Liu,
2006).
Table 2: The Effects of Positive and Negative Reviews.
Model Fitness/Variables Results/Coefficients
R-Square 0.525
Adjusted R-Square 0.525
F Value 1179.06
Sig. (p≤) 0.001
Shipping 0.291***
Price 0.102***
Promotion 0.122***
Other Store(OS) –0.054***
Product Type: Experience 0.151***
% of Negative Reviews 0.347***
% of Positive Reviews 0.158***
Note: ***: Sig.≤0.001
Then, we run separate regressions for search
products and experience products. The parameter
estimates of volume and valence for experience
products (0.379 and 0.376) are much higher that
those for search products (0.282 and 0.147). Then
we used Chow’s test to compare the regression
models of these two types of products. The F-value
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
148

for the Chow's test is 316.81 (p≤.001), suggesting
that the two regression models are significantly
different from each other. The t-tests for the
parameter coefficients of the two models are also
significant, suggesting that both volume and valence
have significantly greater effects on new products
sales for experience products than for search
products. Meanwhile, it is interesting to note that
while volume and valence have similar effects
(0.379 and 0.376) for experience products, volume
has a much stronger impact on search products than
valence (0.282 vs. 0.147).
Table 3: The Fixed Effect Models for the Effect of
Volume of Reviews.
Model
Fitness/Variables
Search
Products
Experience
Products
R-Square 0.104 0.163
F Value 24.1 129.7
Sig. (p≤) 0.0001 0.0001
Shipping –0.764 0.048
Price 0.001 0.006*
Promotion 0.347*** 0.052**
Other Store (OS) –0.303
Subcategories omitted omitted
Volume 0.043*** –0.023***
Valence 0.044*** 0.0175***
Week age 0.006*** –0.013***
Volume*valence –0.009*** 0.004***
Week age*volume –0.002*** 0.00003***
Note: *: Sig.≤0.05, **: Sig.≤0.01, and ***: Sig.≤0.001
Regarding the effect of online WOM over time,
we use a separate fixed effect model for experience
products and search products. We enter all the
control variables, predictor variables, and their
interactions. Table 3 shows that week age (the
number of weeks since the release date) has a
positive effect on the sales of search products
(β=
0.006), while its effect on experience products is
significantly negative (β=
–0.013), perhaps reflecting
the shorter product lifecycle of video games. As for the
effects of the volume of online reviews over time,
the interaction between week age and volume of
consumer reviews is significantly negative (β=–
0.002) for search products, suggesting the effect of
online WOM decreases over time. This finding is
contradictory to our expectation. However, for
experience products, the interaction between week
age and volume of online reviews (β =0.00003) is
very small yet significantly positive, which means
the effect of online WOM on new experience
product sales increases with time. However, the
coefficient of volume turns out to be negative (–
0.023). Since the variance inflation factors (VIF) of
all variables for the collinearity diagnostic tests are
below 10, we cannot attribute these findings to the
presence of multicollinearity in this model.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The findings provide strong support for the effects
of online customer reviews (volume and valence)
and product type (search vs. experience products) on
new product sales and to some extent the effect of
the stage of PLC (Table 4). The results suggest that
the two measures of online consumer WOM, volume
and volume, have a significant positive impact on
new product sales and support the findings of
previous studies (Dellarocas, 2003; Godes and
Mayzlin, 2004). We also find that the effect of
valence of consumer reviews on new product sales is
greater than that of volume of consumer reviews.
Moreover, negative WOM influences new product
sales more than positive WOM, confirming the
strong effect of the negativity bias in that online
consumers pay more attention to negative WOM
than to positive WOM, even though there are
generally more positive reviews than negative ones
(Kanouse and Hanson, 1972). Despite the efforts to
minimize any potential collinearity problem, the sign
of online negative WOM turns out to be positive.
The same finding was also reported in a previous
study (Liu, 2006). There may exist several
explanations for this counter-intuitive finding. The
inoculation theory suggests that once the bad news
about a product is released to the public, its negative
effect is no longer detrimental and may not alter
people's attitudes significantly (McGuire, 1961). The
winners-take-all phenomenon is another possible
reason in that popular products attract a large
number of both positive and negative reviews than
the less popular ones.
More importantly, our findings indicate that product
type moderates the relationship between online
WOM and new product sales. The volume of online
consumer WOM influences the sales of experience
products more than that of search products.
Similarly, the valence of consumer WOM influences
experience products more than search products.
Lastly, the greater influence of online WOM in
the late stage of PLC is weakly supported only for
the experience products. The lack of support for this
hypothesis could be due to several reasons.
According to Amazon.com, sales rank, unlike actual
sales data, is not cumulative, but the ranking of a
product based on weekly sales adjusted by
cumulative sales. The lack of reliable data on
THE IMPACT OF ONLINE WORD-OF-MOUSE - Sales of New Products at Amazon.Com
149

Table 4: Summary of Results.
Independent
Variables
Effect on Dependent
Variable
Volume √
Valence √
% of Negative Reviews √
% of Positive Reviews √
Product Type √
Product Lifecycle (PLC) Partial support
new product sales may lead to the poor results.
The findings reveal the significant effect of
WOM including the multiple indicators of WOM
including volume, valence and the ratio of negative
vs. positive reviews on new product sales in the
online setting. The findings of this study indicate
several interesting practical directions for
practitioners. Marketers need to observe and respond
to online WOM communication actively. They
should develop strategies to promote consumer
advocacy, to encourage consumer reviews and other
forms of WOM, and hopefully generate positive
reviews when they launch new products. Given the
speed and wide reach of online WOM, the benefit of
satisfied customers as the best advertisement can be
amplified many times. This applies to both
experience and search products, but more so for
experience products, which are subject to greater
influence from online WOM because experience
products have less tangible attributes than search
products.
Positive consumer reviews can help reduce the
uncertainty and risks associated with purchasing
new products for potential buyers. Marketers may
incorporate valuable consumer feedback, especially
the negative WOM, in the development and
marketing of new products. Meanwhile, it is not
necessary for practitioners to discourage and
manipulate the negative reviews in the forums,
because according to our finding, online negative
reviews may not directly hurt new product sales as
long as the overall effect of WOM is positive.
Finally, the effect of online WOM on new product
sales is perhaps more influential beyond the
introductory stage of a product’s life cycle for
experience products, calling for greater efforts to
monitor and respond to online WOM.
REFERENCES
Bass, F.M., 1969. A new product growth model for
consumer durables. Management Science, 15(5), 215-
227.
Brown, J., Broderick, J.A., and Lee, N. 2007. Word of
mouth communication within online communities:
conceptualizing the online social network. Journal of
Interactive Marketing, 21(3), 2-10.
Brown, J.J and Reingen, P.H. 1987. Social ties and word-
of-mouth referral behavior. Journal of Consumer
Research, 14(3), 350-362.
Chevalier, J.A. and Mayzlin, D. 2006. The effect of word
of mouth on sales: online book reviews. Journal of
Marketing Research, XLIII, 345-354
Dellarocas, C. 2003. The digitization of word of mouth:
Promise and challenges of online feedback
mechanisms. Management Science, 49(10), 1407-
1424.
Dellarocas, C., Zhang, X. and Neveen, F.A. 2007.
Exploring the value of online product reviews in
forecasting sales: The case of motion pictures. Journal
of Interactive Marketing, 21(4), 23-45.
DoubleClick. 2004. DoubleClick’s Touchpoints II: The
Changing Purchase Process. March.
Duan, W., Gu, B., and Whinston, A.B. 2008. Do online
reviews matter? - An empirical investigation of panel
data. Decision Support Systems, 45(4), 1007-1016.
Godes, D. and Mayzlin, D. 2004. Using online
conversation to study word-of-mouth communication.
Marketing Science, 23(4), 545-561.
Herr, P.M., Kardes, F.R., and Kim, J. 1991. Effects of
word-of-mouth and product-attribute information on
persuasion: An accessibility-diagnosticity perspective.
Journal of Consumer Research, 17(4), 454-462.
Kanouse, D.E. and Hanson, L.R. 1972. Negativity in
evaluations. In E. E. Jones et al. (Eds.), Attribution:
Perceiving the Causes of behavior. Morristown, NJ:
General Learning Press.
King, M.F., and Balasubramanian, S.K. 1994. The effects
of expertise, end goal, and product type on adoption of
preference formation strategy. Journal of the Academy
of Marketing Science, 22(2), 146-159.
Liu, Y. 2006. Word of Mouth for movies: Its dynamics
and impact on box office revenue. Journal of
Marketing, 70, 74-89.
McGuire, W.J. 1961. The effectiveness of supportive and
refutation defenses in immunizing defenses.
Sociometry, 24, 184-197.
Reingen, P., Foster, B., Brown, J.J., and Seidman, S. 1984.
Brand congruence in interpersonal relations: A social
network analysis. Journal of Consumer Research, 11,
1-26.
Rogers, E.M. 2003. The Diffusions of Innovations, 5th ed.,
New York: The Free Press.
Van den Bulte, C. and Lilien, G. 2001. Medical Innovation
revisited: Social contagion versus marketing effort.
The American Journal of Sociology, 106(5), 1409-
1436.
Weathers, D., Sharma, S., and Wood, L.S. 2007. Effects of
online communication practices on consumer perceptions
of performance uncertainty for search and experience
goods. Journal of Retailing, 83(4), 393-401.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
150
