
AN ENERGY-AWARE AND COVERAGE-PRESERVING
HIERARCHICAL ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR WIRELESS
SENSOR NETWORKS
Tzu-Shiang Lin
1
, Cheng-Long Chuang
1
, Chia-Pang Chen
1
, Chwan-Lu Tseng
2
En-Cheng Yang
3,
Chi-Shan Yu
2
and Joe-Air Jiang
1
1
Department of Bio-Industrial Mechatronics Engineering, National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan
2
Department of Electrical Engineering, National Taipei University of Technology, Taipei 106, Taiwan
3
Department of Entomology, National Taiwan University, Taipei 106, Taiwan
Keywords: Routing Algorithm, Sensing Coverage Problem, Wireless Sensor Networks (WSNs).
Abstract: Coverage-preserving and lifetime-prolonging are essential issues for wireless sensor networks (WSNs).
Providing full sensing coverage in a security-sensitive area is necessary for practical applications such as
security surveillances or military investigations. In order to prolong the duration of full sensing coverage,
we propose an Energy-aware and Coverage-presenting Hierarchical Routing (ECHR) protocol for randomly
deployed WSNs. The ECHR protocol accommodates energy-balancing and coverage-preserving while
selecting one cluster head for each round. The power consumption of radio transmission and residual energy
over the network are taken into account when determining an optimal route for a packet. The simulation
results show that ECHR prolongs the duration with full sensing coverage, which provides up to 85% extra
lifetime comparing with other protocols.
1 INTRODUCTION
Wireless sensor networks (WSNs) consist of a large
number of wireless sensor nodes. For the secure and
military applications (Stojmenović, 2005),
maintaining sensing coverage is extremely important,
because any coverage hole in a wireless sensor
network is not tolerable. Most of the previous
proposed routing protocols were designed to prolong
the lifetime of the network (Lindsey et al., 2002; Al-
Karaki et al., 2004). However, the sensor network
could become useless when the network fails to
maintain full coverage.
Usually, routing protocols were proposed to
prolong the lifetime of the network or enhance the
Quality of Service (QoS) (Mollanoori and Charkari,
2008). In order to decrease the energy consumption
of radio transmission, a Low-Energy Adaptive
Clustering Hierarchy (LEACH) routing protocol was
proposed by Heinzelman et al. (2002). Cluster heads
of the LEACH protocol provide data fusion in each
hop to reduce energy consumption, and then
transmit the sensing data to the base station (denotes
as BS). Therefore, energy consumption of sensor
node can be greatly reduced by preventing it from
transmitting the sensing data directly to the BS. In
addition, Tasi (2007) proposed a coverage-
preserving routing protocol, which was modified
from LEACH protocol and entitled it as LEACH-
Coverage-U protocol. The LEACH-Coverage-U
protocol calculates the overlap sensing areas of all
sensor nodes, and then uses this feature to select
cluster head. The simulation result shows that the
LEACH-Coverage-U protocol can prolong the
operational time when the sensing coverage is
greater than 50%. However, it produces large
amount of coverage holes during network operation.
Because of the random deployment, some
locations of nodes might be very close to each other
that causes overlapped sensing area. If these
overlapping nodes run out of energy earlier, the full
sensing coverage of the network can be maintained.
Hence, in this study, we present this study proposes
an Energy-aware and Coverage-preserving Hier-
archical Routing (referred as ECHR) protocol to
increase the duration of maintaining the full sensing
coverage in a WSN. The proposed ECHR protocol
53
Lin T., Chuang C., Chen C., Tseng C., Yang E., Yu C. and Jiang J. (2009).
AN ENERGY-AWARE AND COVERAGE-PRESERVING HIERARCHICAL ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR WIRELESS SENSOR NETWORKS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems, pages 53-56
DOI: 10.5220/0002181700530056
Copyright
c
SciTePress

always chooses one of the overlapping nodes to be
the cluster head in each round. In addition, we
applied the energy-aware hierarchical routing
mechanism to find out an optimal route for the data
measured by each node. Comparing with the
previous protocols, the ECHR protocol can
effectively prolong the duration of maintaining the
full sensing coverage in a WSN.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows:
Section 2 illustrates the radio transmission model
and coverage model of sensor nodes. The ECHR
protocol is presented in Section 3. Simulation results
are demonstrated in Section 4. Finally, concluding
remarks are given in Section 5.
2 PRELIMINARIES
In this work, assume that there are n sensor nodes
(denoted as S
1
, S
2
, …, S
n
) randomly deployed in a L
× L sensing field and the sensing field has m points
of interest (abbreviated as POI). The definition of
POI (denoted as P
1
, P
2
, …, P
m
) and the related point
coverage problem can be referred to the reference
(Cardei and Wu, 2005). Some assumptions for the
network model are also made: 1) All sensor nodes
and BS are all stationary after deployment. 2) The
BS is located far away from the sensing area. 3)
Each node has power control ability which can be
adjusted according to the transmission distance.
2.1 Radio Transmission Model of
Sensor Node
The first order radio model, which is the same as
that used in LEACH-Coverage-U protocol, was
adopted in this study (Tasi, 2007). There two
parameters, E
elec
and ε
amp
, involved in the energy
consumption model. E
elec
, the energy dissipations
per bit by the transmitter or receiver circuits, is set to
50 nJ/bit. ε
amp
, the energy dissipations per bit by the
transmitter amplifier, is set to
0.1 nJ/bit/m
α
. The
energy consumption for transmitting/receiving k-bit
data message under a given distance d, modelled in
Tasi (2007), is formulated by:
(, ) ( )
()
Tx elec amp
Rx elec
Ekd kE d
Ek kE
α
ε
=+
=
.
(1)
where E
Tx
is the energy consumption for transmitting
data, E
Rx
denotes the energy dissipation by receiving
data, and α is the pass loss exponent. The pass loss
exponent α is set to 2 for the transmission from each
node, and α is set to 2.5 for the transmission from a
cluster head to BS.
In addition, when an intermediate node receives
n k-bit message data, the node consumes energy of k
× E
DA
units to compress the data into a packet with μ
× (n × k) bits, where μ is the compression coefficient,
and E
DA
, the energy consumption per bit by data
aggregation, is set to 5 nJ/bit.
2.2 Coverage Model of Sensor Node
Each sensor node has sensing range r
s
and location
{x
i
, y
i
}, i
∈
[1, n]. The location of each POI is {x
j
, y
j
},
j
∈
[1, m]. Then, we denote a coverage set of a
sensor node S
i
by CS
i
. The set of POIs that are
covered by multiple CS
i
can be determined by the
following equation:
12
11
(...
... )
ii
ii n
OCS CS CS
CS CS CS
−+
=∩ ∪∪
∪∪∪∪
,
(2)
where O
i
is the set of POIs that are covered by
multiple sensor nodes. In addition, we define the
coverage ratio C of the network as
12 1
...
nn
CS CS CS CS
C
m
−
∪∪∪ ∪
=
.
(3)
If a node S
1
runs out of energy, CS
1
in equation (3)
will be an empty set.
3 THE PROPOSED ECHR
ROUTING PROTOCOL
In order to prolong the lifetime of the network with
full sensing coverage, a cluster head selection
mechanism based on energy-balancing and
coverage-preserving was developed and used in the
ECHR protocol. We also apply the energy-aware
hierarchy routing mechanism to determine an
optimal route for packets generated by each node.
The detail functions about these mechanisms will be
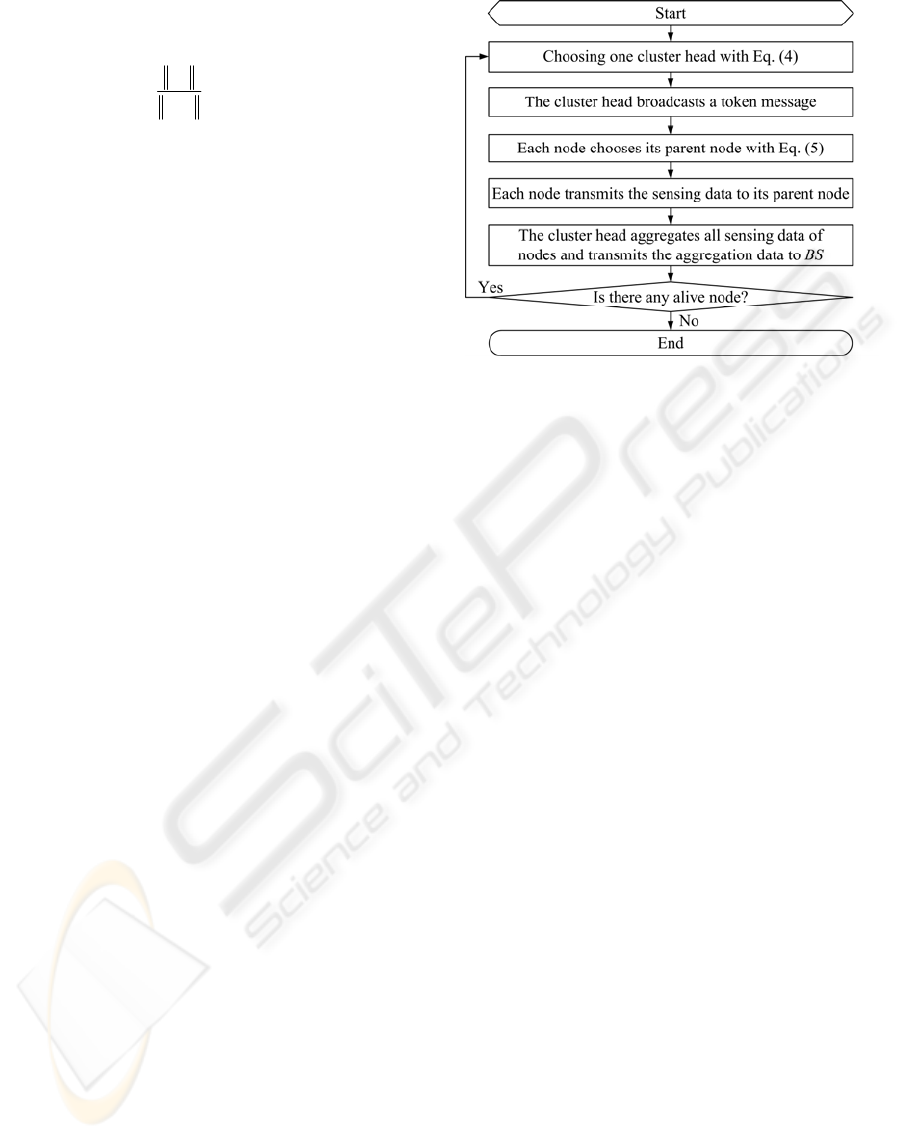
described in subsection 3.1 and 3.2. The flowchart of
the proposed ECHR protocol is shown in Figure 1.
3.1 Cluster Head Selection Mechanism
According to the radio model described in the
subsection 2.1, the transmission between a cluster
head and the BS could consume a great deal of
energy. In the ECHR protocol, there is only one
cluster head in each round. Therefore, the cluster
head selection mechanism is essential. The head-
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
54
weight H
i
for selecting node S
i
as a cluster head is
defined as
()
c
i
ii
i
O
H
RE
CS
⎞
⎛
=×
⎟
⎜
⎜⎟
⎝
⎠
,
(4)
where the RE
i
is defined as residual energy, and c is
weight adjustment exponent.
After calculating head-weight of each node, the
node with the maximum head-weight will be chosen
to be a cluster head in one round. Then, the cluster
head broadcasts a beacon message to other sensor
nodes in the network. According to the message
contained in the beacon message, each node can not
only acquire the information of the cluster head, but
also obtain the information of the neighboring nodes.
The beacon message contains information that
consists of ID, residual energy, and hop count. The
information is updated when the sensor nodes
receive messages from other nodes.
3.2 Energy-aware Hierarchy Routing
Mechanism
In order to reduce the power consumption of data
transmission, we adjust communication range of
each node. Thus, all sensing data of sensor nodes
will be transmitted by multi-hop mechanism. Each
node uses the hop count of received information in a
neighbor table. Thus, each sensor node knows which
nodes are closer to the cluster head, and these nodes
could be its parent node. However, a node S
i
might
have multiple parent nodes available for choosing.
Therefore, we calculate the parent node factor Ф
k
for
the parent node S
k
by:
(1 / ) ( )
kkk
dREΦ= ×
,
(5)
where the d
k
is the distance between the node S
i
and
the parent node S
k
. According to equation (5), each
node calculates the parent node factor according to
its parent nodes and values saved in the neighbor
table. After calculating the parent node factor, each
node starts to transmit sensing data to its parent node.
Figure 1: Flowchart of the proposed ECHR protocol.
4 SIMULATION RESULTS
In this section, the performance of the ECHR
protocol is compared with those of LEACH and
LEACH-Coverage-U via numerical simulation. The
simulation environment is a network with 100 nodes
randomly distributed in an area of 50 × 50 m
2
. This
monitoring area consists of 2500 POIs, and the BS is
located at (25, –50). The initial energy of all nodes is
assumed to be 1 joule, and the sensing range r
s
is set
to be 7.5 m. Furthermore, the compression
coefficient μ is set to 0.05, and the data packet size k
is set to 2000 bits. We set the weight adjustment
exponent c to 8.5 in equation (4) with experience
obtained in priori.
Figure 2 shows the number of alive sensor nodes
versus the simulation rounds. LEACH protocol and
LEACH-Coverage-U protocol lose the first node at
about the 700th round. On the other hand, the
proposed ECHR protocol is able to maintain all
sensor nodes surviving till the 1620th round. After
the first node of the ECHR protocol runs out of
energy, the number of the alive nodes falls rapidly. It
is because the proposed ECHR protocol is able to
equalize the energy consumption over the entire
network. Figure 3 shows the coverage ratio versus
the simulation rounds. The proposed ECHR protocol
maintains 100% coverage ratio until the 1680th
round, but the LEACH protocol and LEACH-
Coverage-U protocol lose full coverage ratio at the
900th and the 1000th round, respectively. In other
words, the proposed ECHR protocol provides about
85% extra duration with 100% sensing coverage
ratio comparing with LEACH and LEACH-
Coverage-U protocols.
AN ENERGY-AWARE AND COVERAGE-PRESERVING HIERARCHICAL ROUTING PROTOCOL FOR WIRELESS
SENSOR NETWORKS
55
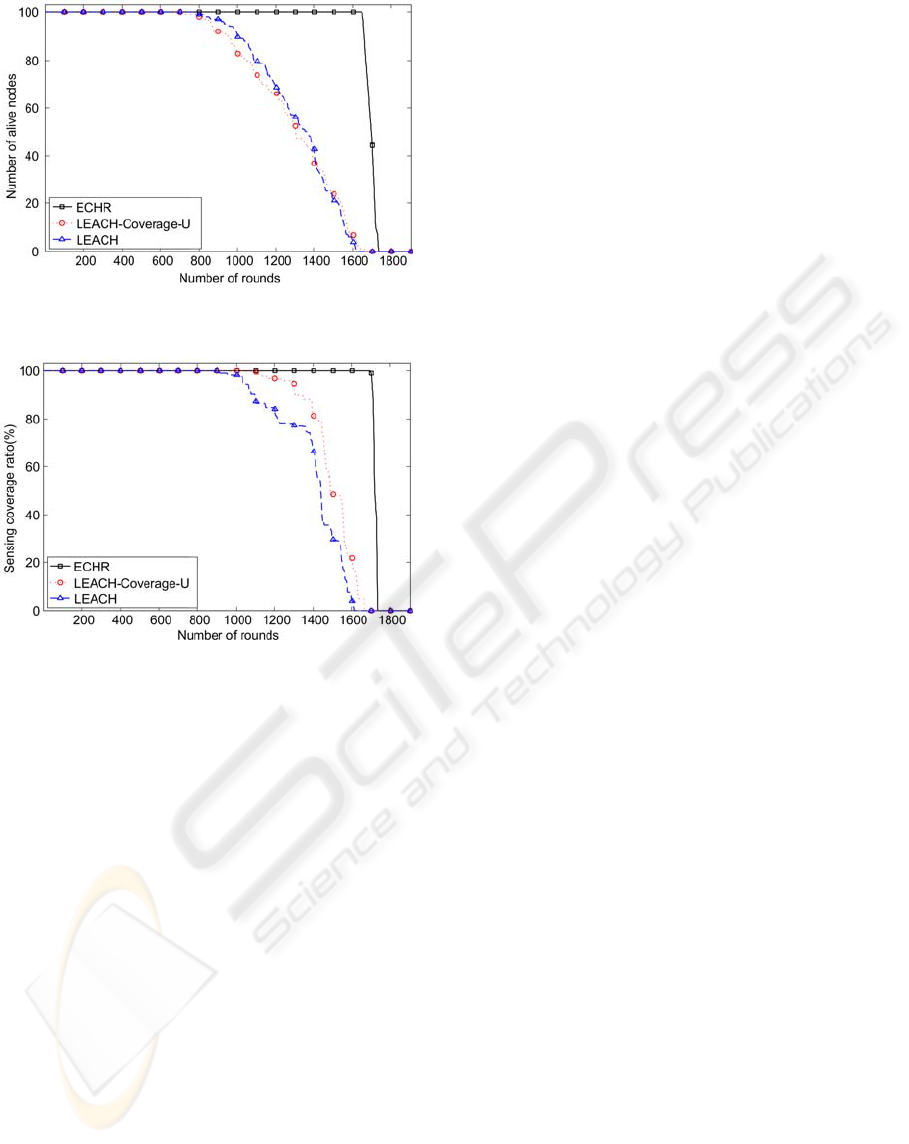
Figure 2: Comparison of the alive nodes of the proposed
ECHR protocol with those of other protocols.
Figure 3: Comparison of the coverage ratio of the
proposed ECHR protocol with those of other protocols.
Examining Figures 2 and 3, it clearly indicates
that the coverage ratio of the network adopting the
ECHR protocol is still maintained at 100% before
the first node runs out of energy at the 1620th round.
At the 1680th round, there are in total of 46 nodes
that run out of their energy, and the coverage ratio of
the entire network starts to fall out of 100%. This
result shows that the ECHR protocol is able to
prolong the duration of 100% network coverage by
choosing overlapping nodes to relay sensing data in
the most rounds of the simulation.
5 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we propose an energy-aware and
coverage-presenting hierarchy routing protocol for
wireless sensor networks. The goal of this study is to
prolong the duration for maintaining full sensing
coverage. The main idea is to combine energy-
balancing and coverage-presenting mechanisms into
routing protocol. Simulation results show that the
proposed ECHR protocol is able to prolong the
duration of the network with 100% coverage ratio,
which provides up to 85% extra lifetime comparing
with other protocols. We will try to evaluate the
performance of the ECHR protocol with respect to
transmission delay, and add some factors into our
ECHR protocol based on other information in our
future work.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors are grateful for the financial support
from the President of National Taiwan University
under contract no. 97R0533-2. This work was also
supported in part by the National Science Council,
Taiwan, R.O.C., under for financially contracts no.:
NSC 95-2218-E-002-073, NSC 96-2218-E-002-015,
and NSC 97-2218-E-002-006. Finally, the authors
would also like to thank the Council of Agriculture
of the Executive Yuan, Taiwan, for their financial
supporting under contract no.: 97AS-9.1.1-FD-
Z1(3).
REFERENCES
Al-Karaki, J.N., Kamal, A.E., 2004. “Routing techniques
in wireless sensor networks: a survey,” IEEE Wireless
Communications, vol.11, no.6, pp. 6-28.
Cardei, M., Wu, J., 2005. “Coverage in Wireless Sensor
Networks,” In Handbook of Sensor Networks, Ilyas,
M., Mahgoub, I., CRC Press: New York, vol. 1,
Chapter 19, pp. 1-12.
Heinzelman, W.B., Chandraksaan, A.P., Balakrishnan, H.,
2002. “An Application-Specific Protocol Architecture
for Wireless Sensor Networks,” IEEE Transactions on
Wireless Communications, vol. 1, no. 4, pp. 660-670.
Lindsey, S., Raghavendra, C., Sivalingam, K.M., 2002.
“Data Gathering Algorithms in Sensor Networks
Using Energy Metrics,” IEEE Transactions on
Parallel and Distributed System, vol. 13, no. 9, pp.
924-935.
Mollanoori, M., Charkari, N.M., 2008. “LAD: A Routing
Algorithm to Prolong the Lifetime of Wireless Sensor
Networks,” In Institute of Electrical and Electronics
Engineers, 2008 IEEE International Conference on
Networking, Sensing and Control. Sanya, China April
6-8 2008. USA: New York, pp. 983-987.
Stojmenović, I. 2005. Handbook of Sensor Networks:
Algorithms and Architectures, Wiley-Interscience.
United States, 1
st
edition.
Tsai, Y.R., 2007. “Coverage-Preserving Routing Protocols
for Randomly Distributed Wireless Sensor Networks,”
IEEE Transactions on Wireless Communications, vol.
6, no. 4, pp. 1240-1245.
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
56
