
DCADH: A GENERATING ALGORITHM OF
DELAY-CONSTRAINED MULTICAST ROUTING TREE
Yu-xi Zhu and Ling Zhou
Department of Computer Science and Technology, Foshan University, Foshan, Guangdong, China
Keywords: Multicast Routing, Average Distance Heuristic, Delay-Constrained, Least-Cost, Simulation.
Abstract: Multicast is the ability of a communication network to accept a single message from an application and
to deliver copies of the message to multiple recipients at different location. With the development of
Internet, Multicast is widely applied in all kinds of multimedia real-time application: distributed
multimedia systems, collaborative computing, video-conferencing, distance education, etc. In order to
construct a delay-constrained multicast routing tree, average distance heuristic (ADH) algorithm is
analyzed firstly, then by using which a delay-constrained algorithm called DCADH is presented.By
using ADH a least-cost multicast tree can be constructed; if the path delay can’t meet the delay upper
bound,a shortest delay path which is computed by Dijkstra’s algorithm will be merged into the existing
multicast tree to meet the delay upper bound. Simulation experiments show that DCADH has a good
performance in achieving a low-cost multicast tree.
1 INTRODUCTION
QoS-aware group communication has accelerated
the need and application of multicast, for example,
video-conference, distance education, resource
location, distributed simulation, etc. Multicast
routing algorithm is a key issue in group
communication, only by which a multicast routing
tree can be constructed correctly and efficiently. In
most conditions, it is NP-Complete and defined as a
Steiner tree problem.
From the view of managing and optimizing
network resource, it requires that the multicast tree
constructed by the multicast routing algorithm with
a least cost in order to optimize the network
resources. Taking service of quality (QoS) of the
multicast communication into consideration, the
multicast trees should meet the stringent
requirements of QoS constraints. when both the cost
and the delay need be considered to optimize, the
problem of delay-constrained least-cost (DCLC)
multicast routing is put forward. The DCLC
problem is the most common and important issues
among the QoS-constrained multicast routing
problems.
Different algorithms have been proposed to
address the multicast routing problem (Salama H. F.,
1997). Some optimized the tree cost, such as KPP,
BSMA. Some simplified the time complexity, such
as SPT, CDKS. And some others focused on how to
meet the quality of service. But it is very hard to use
any one to optimize all those parameters at the same
time.
In this paper, we concentrated on how to solve
the DCLC problem by using average distance
heuristic (ADH) algorithm.
2 RELATED WORK
Salama and other scholars have had a
comprehensive comparative study of the algorithm
which solved the DCLC problem and drew a
conclusion that there were some currently mature
DCLC algorithms such as KPP, CDKS, BSMA, and
so on. But because of the higher cost of spanning
tree or higher computational complexity, they were
some difficulty to apply to the actual network
communication.
In addition, some scholars solved the DCLC
problem using the heuristic algorithms based on
new optimization theories, including neural
networks, genetic algorithms, simulated annealing,
tabu algorithm, etc (G. Feng, C. Douligers, 2001).
Some of those bring about uncertainty in theory
analysis and convergence, some are with higher
181
Zhu Y. and Zhou L. (2009).
DCADH: A GENERATING ALGORITHM OF DELAY-CONSTRAINED MULTICAST ROUTING TREE.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications, pages 181-184
DOI: 10.5220/0002182501810184
Copyright
c
SciTePress

complexity of time, Moreover, with some specific
parameters introduced by those algorithms.
As part of our ongoing research in multicast
routing algorithm, we have developed
delay-constrained multicast routing algorithm with
mininum path heuristic (MPH) which is an
excellent algorithm to construct a DCLC multicast
tree. By using the algorithm a computing
destination node can join the multicast tree by
selecting the path which has the least cost value to
the existing multicast tree; if the path delay does not
meet the delay upper bound, a shortest path tree
based the delay will be merged into the existing
multicast to meet the delay upper bound.
Recently, we have researched the multicast
routing problem in mobile IP. In order to reduce the
transmission delay and minimize the joined latency,
we introduced an idea of bone node set. Based on
the idea a multicast routing algorithm called bone
node set-based multicast routing algorithm
(BNSBMR) was designed. It characters itself in
three aspects. Firstly, it can optimize the cost of
multicast delivery tree and reduce the bandwidth
consumption by using bone node set. Secondly, it
can reduce the latency of handover, which is helpful
for mobile node to achieve a fast handover. Thirdly,
the transmission delay for multicast packet is
lessened by sharing those bone nodes.
Moreover, we have also researched the
problem of a delay-constrained dynamic multicast
routing. Based the greedy idea a dynamic multicast
routing algorithm called delay-constrained dynamic
greedy algorithm (DCDG) was presented to
construct a dynamic multicast tree. In the resulting
tree the delay from the source to each destination
node is not destroy the delay upper bound.
At the same time, we discussed their
correctness in theory and experimented their delay
and cost performance by random network model.
3 DCADH ALGORITHM
A communication network can be modeled by an
edge weighted G=(V, E) where V is a set of host or
router nodes and E is the set of communication
links. We assume that the cost weight (u, v) is
nonnegative value for each link (u,v) E. Given a
source s and a set of destinations D,
Definition 1 (shortest path): We call the path
from u to v a shortest path if the total path weight
from v to u is the minimize one and we write the
shortest path path(u, v).
Definition 2 (multicast routing tree): A
multicast routing tree is a rooted subtree of the
graph G whose root is s, which includes all the
routing paths from s to D.
Definition 3 (delay-constrained least-cost
multicast routing tree): Given network G (V, E),
multicast source s, destination node set D, and the
delay upper △
Delay
, if a multicast tree T covers s
∪
D
and is satisfied with the following conditions:
}
,),(
)()(min{)(
∑
∈
∑
∈
=
=
DvvsPe
eCostTCostTCost
∑
∈
=
Δ≤
),(
)()),((
)),((..
vsPe
Delay
eDelayvsPDealy
vsPDelayts
(
Dv
∈
∀
,
TvsP ∈),(
),
we call the tree T as a DCLC multicast routing tree,
that is, delay-constrained steiner tree.
The problems of constructing a DCLC
multicast routing tree is NP-complete, which is
usually solved by designing a heuristic algorithm. In
this paper, we concentrated on how to solve the
DCLC problem by using average distance heuristic
(ADH) algorithm.
3.1 The Basic Idea
The basic idea of DCADH algorithm has been
two-fold. Firstly, the ADH algorithm (Yu Y. P., Qiu
P. L., 2002)
is used to calculate a low-cost multicast
routing tree T. Secondly, if T does not meet the
delay constraint △
delay
, Dijkstra shortest path tree
algorithm is used to compute the least-delay tree T,
and the shortest path based the delay will be merged
into the existing multicast to meet the delay upper
bound. So a low-cost multicast routing tree which
meets the delay upper will be constructed. When the
least-delay path was merge into the low-cost
multicast tree a new loop may appear, so we
designed a process to eliminating the loops.
The detail descriptions of the algorithm
process are as follows:
Step 1: Firstly set s as the least-delay tree;
then compute a least-delay tree spanning all the
destination members by Dijkstra shortest path tree
(SPT) algorithm. If the delay of T Delay (
.
) >△
delay
,
then exit;
Step 2: according to ADH algorithm, set all the
multicast member nodes as the initial set of T ;
Step 3: Calculate f (v) = min ( d (v, Vj) + d (v,
Vj) ), which Vi, Vj is the node set of arbitrary two
separation trees. As for v ∈ V, if f (v) is minimum ,
Ti will link Tj through v, and the paths are P (v, Vi)
and P (v,Vj);
Step 4: Modify set T and node sets, k = k-1;
Step 5: Repeat steps 3 and 4 until k = 1;
SIGMAP 2009 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
182
Step 6: Determine the delay constraint in the
multicast tree. As for
Dm
∈
∀
, if
Δ
>
⋅
)(delay
,
Path(m, s)∈T
Delay
will been merged into T;
Step 7: If a loop is formed, the process of
elimination loop will be introduced by changing the
node’s father;
Step 8: Repeat Step 6 until all the nodes meet
the delay constraints.
3.2 Performance Analysis
Theorem 1. Only when ADH tree does not meet
delay-constraint and the least-delay path is merged
into the multicast, DCADH spanning tree might
appear loops; otherwise there are no loops in
DCADH spanning tree.
Theorem 2. Only when there are at least two tree
nodes on the path at the same time, the loops might
appear; otherwise there are no loops in DCADH
spanning tree.
Theorem 3. There are no loops in the multicast tree
⇔ All the tree nodes besides the root node in the
spanning tree have only one father node.
Theorem 4. As long as there exists a multicast tree
T which meets the delay constraints, DCADH can
find the low-cost delay-constraint multicast routing
tree .
Proof: see reference (Zhou L., Sun Y. M., 2008).
Theorem 5. The time complexity of DCADH
algorithm is O (n
3
).
3.3 Simulation Experiments
Waxman firstly put forward a network model to
generate random topology in 1988 (Waxman B. M.,
1988). Waxman’s algorithm set the number of
network nodes, then decide whether there is a direct
link connected between nodes u and v according to
the following probability P
e
:
(,)
(,) exp
e
luv
Puv
L
β
α
−
=
The specific simulation parameters see Table 1.
Table1: Simulation parameters.
Parameters Description Value
N network scale 20-120
m
number of destination
nodes
20-80
α between 0-1 0.3
β between 0-1 0.3
Cost(·) cost of links between 1-5
V transmission speed 2×10
8
m/s
D
elay
Δ
upper delay 0.01-0.1s
Each experimental data test 10 random
networks, each network measures 100 times, for a
total of 1000 times, then we take the average value
as the experiment measure value. At the same time,
its performance is compared with CDKS
(Sahasrabuddhe L. H., Mukherjee B., 2000), KPP
(Kompella V. P., Pasquale J. C., and Polyzos G. C.,
2000) in the cost and delay.
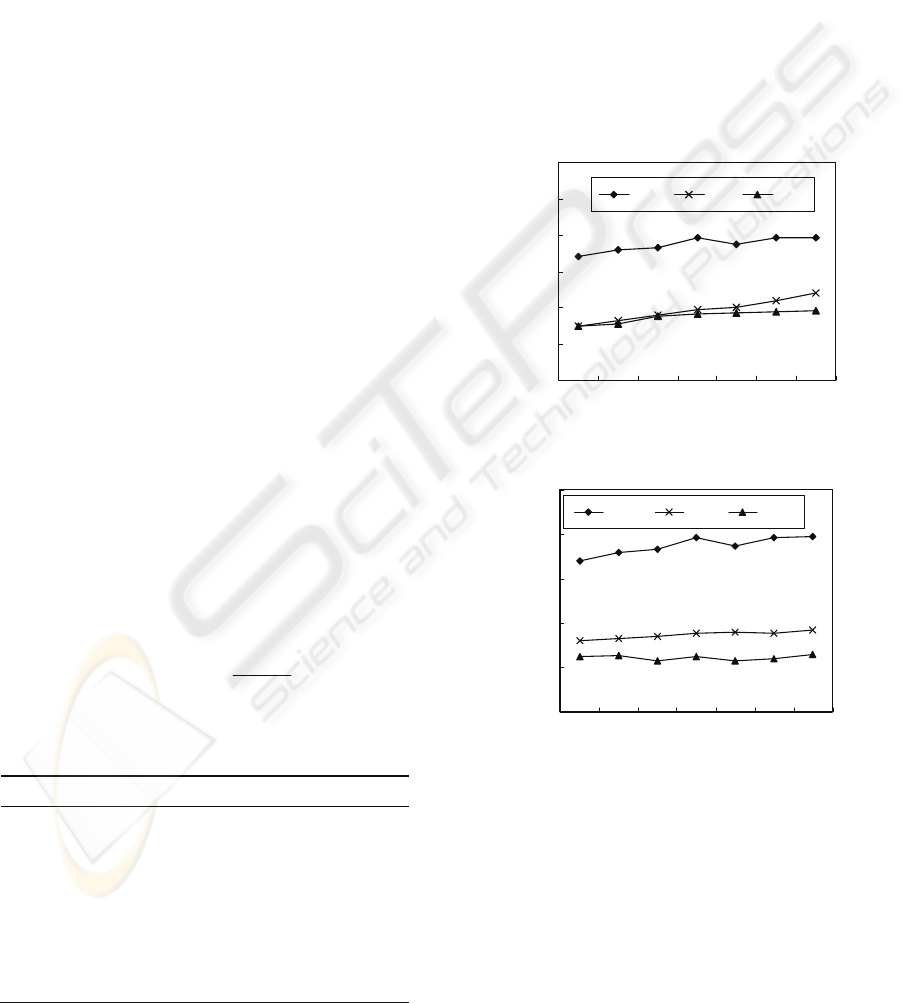
Experiment 1. Measuring the relation between the
cost of multicast routing tree and the network node
number. 20 fixed member nodes unchanged, the
number of network node size begins from 60 and
every time increases 10. The experiment results
shown in Figure 1(a) for △
delay
= 0.03s and (b) for
△
delay
= 0.06s.
0
50
100
150
200
250
300
60 70 80 90 100 110 120
Number of nodes
Cost
CDKS KPP DCADH
(a) △
delay
= 0.03s.
0
50
100
150
200
250
60 70 80 90 100 110 120
Number of nodes
Cost
CDKS KPP DCADH
(b) △
delay
= 0.06s.
Figure 1: The relation of tree cost and network scale.
Experiment 2. Measuring the relation between the
tree cost and the size of the group. 100 nodes of
fixed network scale unchanged, the number of
member nodes change from 20 to 80 and every time
increases 10. The results shown in Figure 2 (a) for
△
delay
= 0.03s and (b) for △
delay
= 0.06s.
DCADH: A GENERATING ALGORITHM OF DELAY-CONSTRAINED MULTICAST ROUTING TREE
183

0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Number of members
Cost
CDKS KPP DCADH
(a) △
delay
= 0.03s.
0
100
200
300
400
500
600
700
20 30 40 50 60 70 80
Number of members
Cost
CDKS KPP DCADH
(b) △
delay
= 0.06s.
Figure 2: The relation of tree cost and the group size.
4 CONCLUSIONS
Through the theoretical analysis and simulation to
DCADH algorithm, we can see that DCADH
algorithm can not only correctly construct a
low-cost multicast routing tree, but also meet the
delay upper. Compared with some similar DCLC
algorithms, it achieves a good performance in cost
and delay. DCADH is an excellent DCLC heuristic
algorithm.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors would like to thank the anonymous
reviewers for their good suggestions, comments, and
feedback to improve the presentation of this paper.
REFERENCES
Salama H. F., 1997. Evaluation of Multicast Routing
Algorithm for Real-Time Communication on
High-Speed Networks[J].IEEE Journal on Selected
Areas in Communication.
Feng G., Douligers C., 2001. A Neural Network Method
for Minimum Delay Routing in Packet Switched
Networks[J]. Computer Communication.
Yu Y. P., Qiu P. L., 2002. An improved algorithm for
Steiner trees. Journal of China Institute of
Communications.
Zhou L., Sun Y. M., 2008. A Delay-Constrained Steiner
Tree Algorithm Using MPH. Journal of Computer
Research and Development.
Waxman B. M., 1988. Routing of Multipoint
Connections[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in
Communications.
Sahasrabuddhe L. H., Mukherjee B., 2000. Multicast
Routing Algorithms and Protocols: A Tutorial. IEEE
Network.
Kompella V. P., Pasquale J. C., and Polyzos G. C., 2000.
Multicasting for multimedia applications [C]. Proc.
IEEE INFOCOM’9.
SIGMAP 2009 - International Conference on Signal Processing and Multimedia Applications
184
