
THE IMPACT OF CUSTOMER VALUE AND INTERNET
SHOPPING MALL ON CUSTOMER LOYALTY AND
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
Hangil Sun
Division of Information Technology, Hansei University, Gunpo-city, Kyunggi-do, Korea
Keywords: e-Business, e-Commerce, e-Marketplace, Customer satisfaction, Customer loyalty.
Abstract: With the development of the internet, internet shopping is taking its place as one of digitalization’s industries
which transcends time and space beyond the scope of commercial activities as the means of goods sales and
purchase. We studied the relations of customer value, the environment of internet shopping mall, customer
satisfaction and loyalty. Customer value is customers’ subjective evaluation, which is formed after their
purchasing and consuming. Customer satisfaction can be characterized as post-purchase evaluation of product
quality given pre-purchase expectations. Customer loyalty is a potentiality or ensure of a durative relationship
between customer and enterprises. Customer satisfaction functions as an antecedent of customer loyalty, while
customer value does customer satisfaction. It prevents customer churn and consolidates retention, thereby
constituting an important cause of customer loyalty. This study shows that customer value, the environment of
internet shopping mall and customer satisfaction are each found to have a direct effect on customer loyalty. The
results provide empirical support for a relation between customer satisfaction and loyalty. The primary purpose
of this study is to increase customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in internet shopping malls. We believe
that only high quality based customer programs accompanied by well designed loyalty programs can be
effective in increasing customer retention.
1 INTRODUCTION
Numerous companies have been engaged in
commercial activities through the internet, since
internet commercialization was allowed in 1992.
Internet shopping has diverse characteristics
differentiated from general sales method in stores.
Internet shopping operators have contact with
the selected target customers. Therefore, internet
shopping pursues maximum effects with minimum
cost and provides the greatest price satisfaction to
customers through minimization of distribution
channels like producers, wholesalers and retailers,
which are the general distribution channels.
Moreover, initial stage investment cost is not
large and internet shopping business can be launched
with a small amount of capital, compared to the
existing distribution business, which needs to open a
store or secure proper site for the business operation.
Also, internet shopping business is free from spatial
and time restrictions.
And most internet shopping mall users are
middle class people in their 20s–40s with a
background of higher education, and they are
opinion constituting leaders with purchasing power
who tend to search for information. In view of this,
accessibility to the target group’s feelings and the
things which they need to purchase most is good,
advertising expenses can be low and two-way
communication is possible. In addition, there is no
limit in the volume of advertising, and measurement
of an advertising effect is feasible (Kim, 1999).
The primary purpose of this study is to increase
customer satisfaction and customer loyalty in
internet shopping mall.
279
Sun H. (2009).
THE IMPACT OF CUSTOMER VALUE AND INTERNET SHOPPING MALL ON CUSTOMER LOYALTY AND CUSTOMER SATISFACTION.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 279-286
DOI: 10.5220/0002189102790286
Copyright
c
SciTePress

2 THEORETICAL
BACKGROUND
2.1 Characteristics of Internet
Shopping
Customers’ acceptance of internet shopping is
rapidly rising. The reason is that the conditions of
mature internet shopping market including the
establishment of society based on credibility, advent
of digitalized society and improvement of
consumption life and education level are in place.
Internet shopping is taking its place as one of the
digitalization’s industries which transcends time and
space beyond the scope of commercial activities as
the means of goods sales and purchase, as
technological innovation like the internet, the PC,
telecommunications satellite, cable TV and IPTV
(Sun, 2007).
Internet shopping can be also defined as a type of
information distribution. Almost all the sectors of
human activities can be divided into tools and
information, when it comes to the concept of
information distribution. We can find such a
phenomenon of separation in consumption activity,
which is the foundation of our food, clothing and
shelter activities. In other words, customers can
select goods on the internet, rather than in a
department store or a store, the goods are delivered
to the customers after purchased on the internet and
the customers pay for the goods by credit card or
through a means of online settlement of accounts
(Lee, 1997).
Internet shopping begins between firms and
customers from the display of goods on the internet.
Customers visit the web site of internet shopping
mall from far distance through network and place
orders on computer screen, when they find goods
they want. Internet shopping is electronically
supporting such a series of commercial processes
(
Lee, 2006).
Internet shopping that establishes direct
relationships with customers through mutually
exchanging communication has the following
features: (
Lee, 2004)
First, online shopping has immediacy of
responses and effects.
Second, statistical projectability is vested in
internet shopping.
Third, data base is constructed and maintained.
Fourth, precise targeting concentration
Firth, personalization is possible in internet
shopping.
Sixth, prior-tests and various sales methods can
be carried out.
Seventh, adjustment in line with budget is
possible.
2.2 Effect of Internet Shopping
There are some positive and negative sides of the
internet shopping which can be summarized as
follows. The seven positives are listed below (Choi,
2005).
First, it offers convenience. Customers can do
the shopping at their internet including making
payment, never having to leave their house to visit
the physical markets. This helps customers save
time and expense incurred in information searching
and offers economic benefits.
Second, it will almost certainly bring about a
perfectly competitive market in the long run, where
the entry barrier is low and price competition is
severe. As a result customers can purchase products
at lower prices. In future when the online shopping
market is mature, the operating expense for the
shopping malls will be significantly lower than the
physical stores. Consequently products will be
offered at lower prices.
Thirds, customers can purchase products,
anywhere at any time, thus, literally enjoying
shopping around the clock, around the globe.
Fourth, customers can convey what they want to
the business through the two-way communications
and they can buy the products that fulfill their needs
because their complaints will be immediately taken
care of.
Fifth, a countless number of different kinds of
products are displayed on the Internet and
customers can conveniently make their choice,
using the product search function in the shopping
malls. This widens customers’ options.
Sixth, customers will be free from the problems
like product hustling or inattentiveness seen at the
traditional stores, (apart from high-class department
stores and specialty stores) and enjoy shopping with
more product information.
Seventh, search time and expense are relatively
low on the internet and customers can collect
information prior to the actual purchase. This helps
customers keep themselves from the impulsive
purchase while guiding them to a more rational
purchase.
There are also some negative sides of the online
shopping. They are as follows.
First, customers purchase products at virtual
shopping malls without actually seeing them.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
280
Accordingly they cannot see, touch, taste, hear, or
smell the products, thus not being able to enjoy
shopping to the full extent.
Second, because they do not actually see the
products before they buy them, there may be
dissatisfaction after the purchase. This will put a
certain limit to the range of products dealt on the
internet and customers will find some difficulties
when purchasing perishable goods like fish or
fashionable products like clothes.
Third, one of the characteristics of the Internet is
such that it is difficult to return the goods or get a
refund when purchased from small businesses with
low credibility or overseas.
Fourth, payment on the internet is mostly made
by credit cards and there is a risk to leakage of
individual information unless fully secured with
high technology.
3 RESEARCH MODEL AND
HYPOTHESES
3.1 Research Model
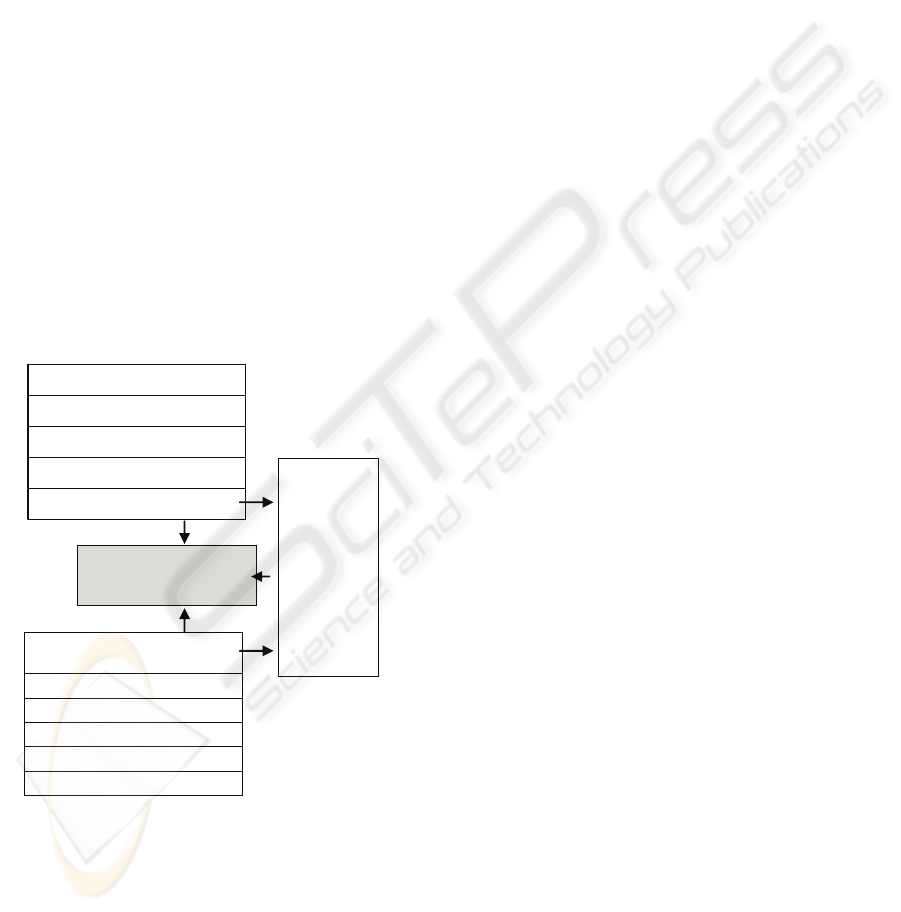
Customer value
Internet Usage Level
Frequency of shopping
Cost of purchased goods
Quantity of purchased goods
Environment of
internet shopping mall
Convenience of shopping
Shopping mall framework
Quality of products
Variety of products
Transaction Security
Customer Loyalty
Customer
Satisfaction
by using
internet
shopping
malls
Figure 1: Research Model.
Developing an understanding of customer value, the
environment of internet shopping mall, customer
satisfaction and customer loyalty has preoccupied
researches. Customer value is customers’ subjective
evaluation, which is formed after their purchasing
and consuming. Customer satisfaction can be
characterized as post-purchase evaluation of product
quality given pre-purchase expectations. Customer
loyalty is a potentiality or ensure of durative
relationship between customer and enterprises
(Babin, 1994).
Generally, customer satisfaction functions as an
antecedent of customer loyalty, while customer
value provides customer satisfaction. It prevents
customer churn and consolidates retention, thereby
constituting an important cause of customer loyalty
(Fornell, 1992). Cronin et al (2000) and Oh (1995)
developed similar models to verify the same cause
and effect relation. However, the relation between
customer satisfaction and customer loyalty is not
always a linear, although it constitutes a positive
relationship (Fornell, 1992; Soderlund, 1998). In Liu
et al. (2005) model, buyer’s perceived customer
value of a supplier has positive impact on perceived
switching costs. Based on the above theoretical
discussion, we propose the research model shown in
Figure 1.
3.2 Hypotheses
Based on a review of previous work that has looked
at customer value, environment of internet shopping
mall, customer satisfaction and customer loyalty, we
have present formulated the research model and the
following hypotheses.
Customer value can be defined as a customers’
overall assessment of the utility of a product based
on perceptions of what is received and what is given
(Zeithami, 1988). Customer value consists of
utilitarian value and hedonic value. Utilitarian value
is formed because of deliberately desiring for some
certain exceptions, which has the characteristics of
functionality, manner and cognition (Babin, 1994).
Hedonic value is a kind of their spontaneous value
evaluation during the purchasing, which has the
characteristics of individuation, non-manner,
experience, emotionality (Chaudhuri, 2001).
Customer satisfaction is based on their comments
and positive feedback after purchasing and
consuming. The viewpoint of Oliver (1999) has been
dominating the subject of the driving factor of
customer satisfaction, he proved that, customer
satisfaction is determined by the customers’
perception value of the product or service and
expectation. Loyal customers are the most important
assets for any company, which have strong
influences on company profitability via decreasing
transaction costs and price sensitivity (YAO, 2007).
Customer loyalty has two categories, the
behavior and the attitude. As a behavior, customer
loyalty has been measured as the long-term choice
THE IMPACT OF CUSTOMER VALUE AND INTERNET SHOPPING MALL ON CUSTOMER LOYALTY AND
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
281

probability for a brand, including hard-core loyalty,
repeat purchase probability. Attitudinal approaches
focused mainly on brand recommendations,
resistance to superior products, repurchase intention,
and willingness to pay a price premium. We adopt
the integrated customer loyalty that is understood as
a combination of customers’ favorable attitude and
the behaviour of repurchase. We use repurchase
intention, recommend it to other consumers and pay
price premiums items to measure this construct,
which area also similar to those reported and used
throughout the services marketing literature (Xu-
Xiaoli, 2006).
The hypotheses are as follows,
1) The impact of customer value on customer
satisfaction
H1-1 : Internet usage level has a positive effect on
customer satisfaction.
H1-2 : Frequency of internet shopping has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
H1-3 : Cost of purchased goods has a positive effect
on customer satisfaction.
H1-4 : Quantity of purchased goods has a positive
effect on customer satisfaction.
2) The impact of the environment of internet
shopping malls on customer satisfaction
H2-1 : Convenience of internet shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
H2-2 : The framework of internet shopping malls
has a positive effect on customer
satisfaction.
H2-3 : Quality of products in shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
H2-4 : Variety of products in shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
H2-5 : Transaction security has a positive effect on
customer satisfaction.
3) The impact of customer value on customer loyalty
H3-1 : Internet usage level has a positive effect on
customer loyalty.
H3-2 : Frequency of internet shopping has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
H3-3 : Cost of purchased goods has a positive effect
on customer loyalty.
H3-4 : Quantity of purchased goods has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
4) The impact of the environment of internet
shopping malls on customer loyalty
H4-1 : Convenience of internet shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer loyalty.
H4-2 : The framework of internet shopping malls
has a positive effect on customer loyalty.
H4-3 : Quality of products in shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer loyalty.
H4-4 : Variety of products in shopping malls has a
positive effect on customer loyalty.
H4-5 : Transaction security has a positive effect on
customer loyalty.
5) The impact of customer satisfaction on customer
loyalty
H5 : Customer satisfaction has a positive effect on
customer loyalty.
4 RESEARCH METHODOLOGY
4.1 Data Collection and Measurement
A structured questionnaire was modified based on a
review of the literature, in-depth pretesting with two
managers of internet shops, and three customers who
have internet shopping experience. The survey was
administered to those who had purchased from
internet shops at least once within the last three
months.
The questions were adapted to reflect
circumstances in internet shopping mall. All of the
measurement items are based on a 5-point likert type
scale.
Data collection procedure is managed by the
authors. Of the 300 customers, 260 participated in
the study, resulting in a response rate of 86.7%. The
260 respondents produced a total of 242 usable
response sets.
1) Subjects:
Total 300 people
In their 20s~50s
living in Korea
2) Method : Focus group interview with 38 survey
questions by Likert scale measurement
(based on 5-point scale)
3) Sampling Method (total 300 people):
a. Sample 200 people:
b. Booster sample 100 people:
experienced online shopping
4) Number of Survey :
Of the 300 people
260 participated in the study
The respondents produced 242 usable response
5) Statistical Method :
Analysis of Reliability and Validity,
Mean & SD, Regression Analysis
with using SPSS 16.0 version for window
The demographic characteristics of the
respondents to this survey are summarized as
follows. Gender composition is roughly half and
half, with 55.8% of men and 44.2% of women.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
282

Number of people aged in their 20s (52.8%), 30s
(32.4%), 40s(10.5%) and the others(4.3%). And the
average times to use per day of online commerce
appeared to be 1 to 3 hours. The average number e-
commerce purchases in recent one year were 11 to
15.
Operational Definition of Variables is shown in
Table1.
Table 1: Operational Definition of Variables.
Variables Operational Definition and list Literature
Internet
usage level
Degree of ability for searching products
they want
USL1 : I can search for information
through the internet.
USL2 : I can search the products I want
USL3 : I can pay for it by credit card.
USL4 : I can send my opinions to
internet shopping malls *
YAO Wei-
kun et al.
F
requenc
y
of
internet
shopping
Frequency of internet shopping
SPE1 : I am accustomed to internet
shopping malls.
SPE2 : I purchase most of my products
through internet shopping malls.
SPE3 : I get product information through
internet shopping malls.*
YAO Wei-
kun et al.
Cost of
purchased
goods
Cost of purchased goods in shopping
APG1 : I spend money on internet
shopping malls regurally.
APG2 : I think I spend on internet
shopping malls more than other
people.
APG3 : I buy the necessities of life in
internet shopping malls
Song and
Zahedi
Quantity of
purchased
goods
Quantity of purchased goods in internet
shopping malls.
NPG1 : I purchase a variety of products
in internet shopping malls.
NPG2 : I purchase many products
through internet shopping malls.
Song and
Zahedi
Convenience
of internet
shopping
mall
Degree of convenience of internet
shopping malls
CSM1 : I am satisfied with the network
speed of internet shopping malls.
CSM2 : I can easily find a product when
I want.
CSM3 : I can easily find various
information about product when
I need to.
CSM4 : There is new information about
products in shopping malls.
CSM5 : I can compare the products of
various makers.
Agarwal
and
Venkatesh
Internet
shopping
mall
framework
Framework and design of internet
shopping malls
SMF1 : I am satisfied with the frame-
work of internet shopping malls.
SMF2 : I am satisfied with the pictures of
internet shopping malls
SMF3 : There is custom-made infor-
mation like shopping baskets..
Palmer
Agarwal
and
Venkatesh
Quality of
Products in
shopping
mall
Quality of products bought through
internet shopping malls
QSM1 : I can trust internet shopping
malls.
QSM2 : I have almost never returned
goods bought in internet
shopping malls.
QSM3 : There was no difference
between the real product and the
image.
Agarwal
and
Venkatesh
Table 1: Operational Definition of Variables (Cont.).
Variety of
products in
shopping
mall
Variety of products in internet shopping
malls
VSM1 : There are many kinds of
products in internet shopping
mall.
VSM2 : There are many models of things
of various kinds.
VSM3 : There is information on the site
as soon as a new product comes out.
VSM4 : I always buy the product I want.
Song and
Zahedi
Transaction
security
Countermeasure about transaction
security through internet shopping mall
TRS1 : There is a policy of personal
information security in this
shopping mall.
TRS2 : This shopping mall observe the
policy of personal information
security
TRS3 : This shopping mall cooperates
with the special information
security agencies.
Javenspaa
and Todd
Customer
loyalty
Customer loyalty about favorite internet
shopping malls.
LSM1 : I will visit this shopping mall
when I buy products.
LSM2 : I will recommend this shopping
mall to other people.
LSM3 : I will visit this site when I need
the information of product.
LSM4 : If the same product is the equal
price, I will definitely buy it in
this shopping mall.
Zhijian
Huan
Xu-Xiaoli
et al.:
YAO Wei-
kun et al,
Customer
satisfaction
Customer satisfaction about favorite
internet shopping malls.
SSM1 : I am satisfied with this shopping
mall on the whole.
SSM2 : It may take a short time to select
and purchase a product.
SSM3 : I am satisfied with the items
bought through internet
shopping malls.
SSM4: I am satisfied with the follow-up
service of internet shopping malls
Hee-
Woong
Kim:
Ji-Seok
Yoo et al.
* : removed list for reliability
4.2 Reliability and Validity
Reliability was assessed using Cronbach’s alpha.
First, we checked Cronbach’s alpha to find all of
them were satisfactory (>0.6). We performed this
test for the 36 measurement items for the eleven
construct. Based on the Cronbach’s alpha results we
eliminated a few items that are cross-loaded – one
USL and one SPE item. After a careful examination
of the eliminated items, we determine that content
validity of the affected constructs is not seriously
hurt. Results of the reliability analysis are shown in
Table 2.
4.3 Statistical Analysis
For all statistical analyses, we used SPSS 16.0. To
investigate the causal relationships among the
constructs depicted by the Model I, we employed
multiple regression. Multiple regression analysis of
THE IMPACT OF CUSTOMER VALUE AND INTERNET SHOPPING MALL ON CUSTOMER LOYALTY AND
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
283
survey data shows in Table 3.
5 RESULT AND FINDING
The analysis of this study shows that customer
value, the environment of internet shopping mall and
customer satisfaction are each found to have a direct
effect on customer loyalty in Table 4.
In [H1-1 ~ H1-4] and [H3-1 ~ H3-4] of the
hypotheses, the importance of customer value is
emphasized. All lists of the impact customer value to
customer satisfaction and loyalty are accepted by the
research. Among factors establishing customer
value, the factors with a significant impact on
customer satisfaction appeared to be a responsive
and safe pricing structure. This suggests that, while
customers have improved buy products over the past
several years through internet shopping mall,
according to customers’ perceptions, still retain their
importance. Therefore, internet shopping malls must
concentrate their efforts on strengthening their
employees’ ability and professional skills to increase
customer contact and support.
In [H1-1 ~ H1-4] and [H3-1 ~ H3-4] of
hypothesis, this emphasizes the environment of
internet shopping malls. We notice that H2-2, H4-1
and H4-2 are rejected by research. This shows the
interests of customers are more about service or
operation than about the framework of shopping
malls in internet shopping malls.
These days, most internet shopping malls are
very well designed and luxurious. Therefore, this
result shows the interests of customers have
changed.
In the last hypothesis, we found customer
satisfaction has had a positive effect on customer
loyalty. The results provide empirical support for a
relationship between customer satisfaction and
loyalty.
Table 2: Results of the reliability analysis.
Construct N of
items
Cronbach’s
alpha
Internet usage level 3 0.615
Frequency of internet shopping 2 0.701
Cost of purchased goods 3 0.607
Quantity of purchased goods 2 0.709
Convenience of internet shopping 5 0.633
Internet shopping mall framework 3 0.676
Quality of Products in shopping 3 0.627
Variety of products in shopping 4 0.673
Transaction security 3 0.723
Customer loyalty 4 0.613
Customer satisfaction 4 0.662
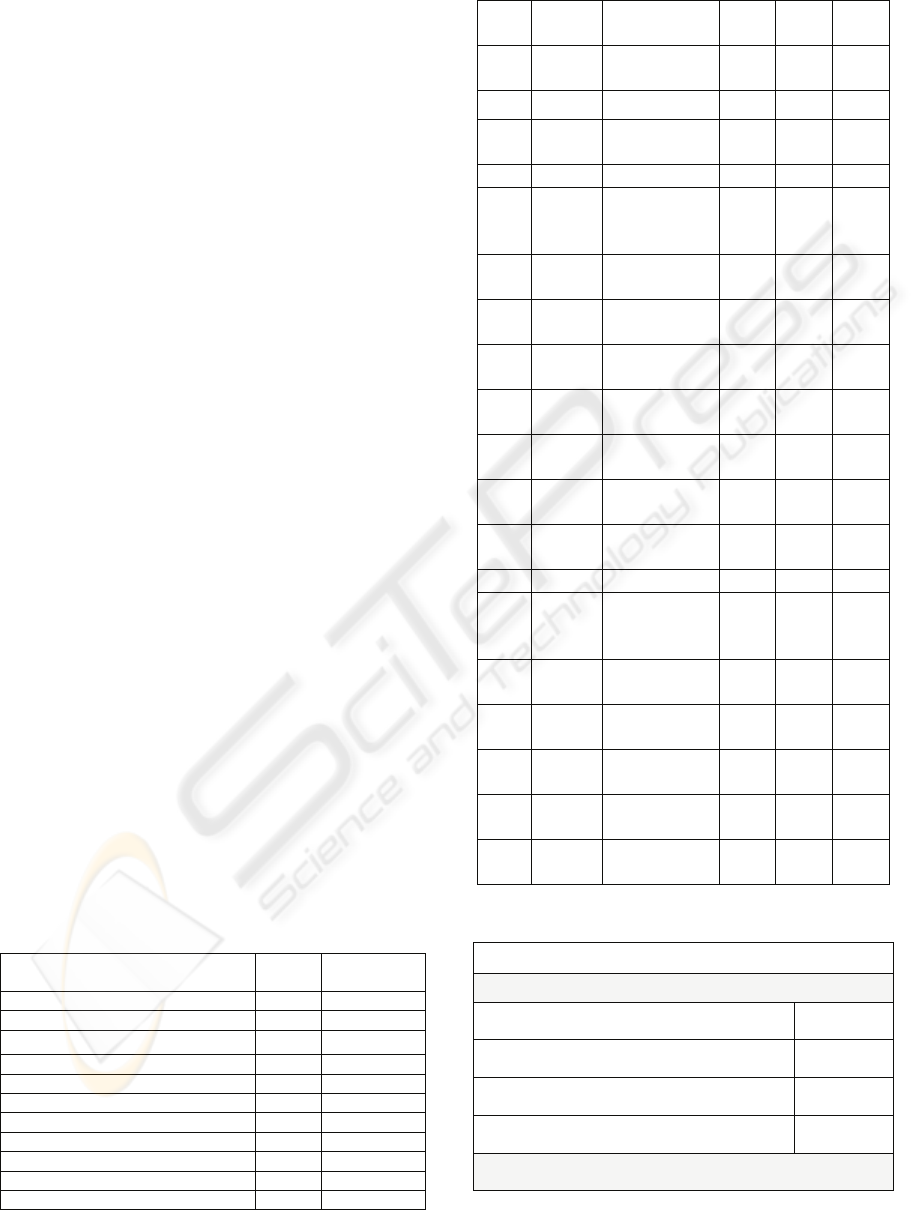
Table 3: Statistical Analysis for Hypotheses (P<0.01).
No Dep.
var
Indep.var. R²
F
value
Sig.
H1-1 SSM
USL1,USL2,
USL3
.065 5.494 .001
H1-2 SSM
SPE1,SPE2,SPE3
.075 6.475 .000
H1-3 SSM
APG1,APG2,AP
G3
.064 5.339 .001
H1-4 SSM NPG1,NPG2 .045 5.683 .004
H2-1 SSM
CSM1,CSM2.CS
M3CSM4,
CSM5
.068 3.462 .005
H2-2 SSM
SMF1,SMF2,
SMF3
.042 3.480 .017
H2-3 SSM
QSM1,QSM2,
QSM3
.091 7.964 .000
H2-4 SSM
VSM1,VSM2,
VSM3VSM4
.164 11.661 .000
H2-5 SSM
TRS1,TRS2,
TRS3, TRS4
.158 11.106 .000
H3-1 LSM
USL1,USL2,
USL3
.089 7.764 .000
H3-2 LSM
SPE1,SPE2,
SPE3
.315 36.425 .000
H3-3 LSM
APG1,APG2,AP
G3
.317 36.872 .000
H3-4 LSM NPG1,NPG2 .149 21.000 .000
H4-1 LSM
CSM1,CSM2.CS
M3CSM4,
CSM5
.049 2.407 .037
H4-2 LSM
SMF1,SMF2,
SMF3
.045 3.721 .012
H4-3 LSM
QSM1,QSM2,
QSM3
.344 41.562 .000
H4-4 LSM
VSM1,VSM2VS
M3,VSM4
.283 23.329 .000
H4-5 LSM
TRS1,TRS2,
TRS3, TRS4
.280 23.079 .000
H5 SSM
LSM1,LSM2,LS
M3,LSM4
.164 11.600 .000
Table 4: The result of Hypotheses.
Hypotheses
1) The impact of customer value on customer satisfaction
H1-1 : Internet usage level has a positive
effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H1-2 : Frequency of internet shopping has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H1-3 : Cost of purchased goods has a positive
effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H1-4 : Quantity of purchased goods has a
positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
2) The impact of the environment of internet shopping malls on
customer satisfaction
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
284
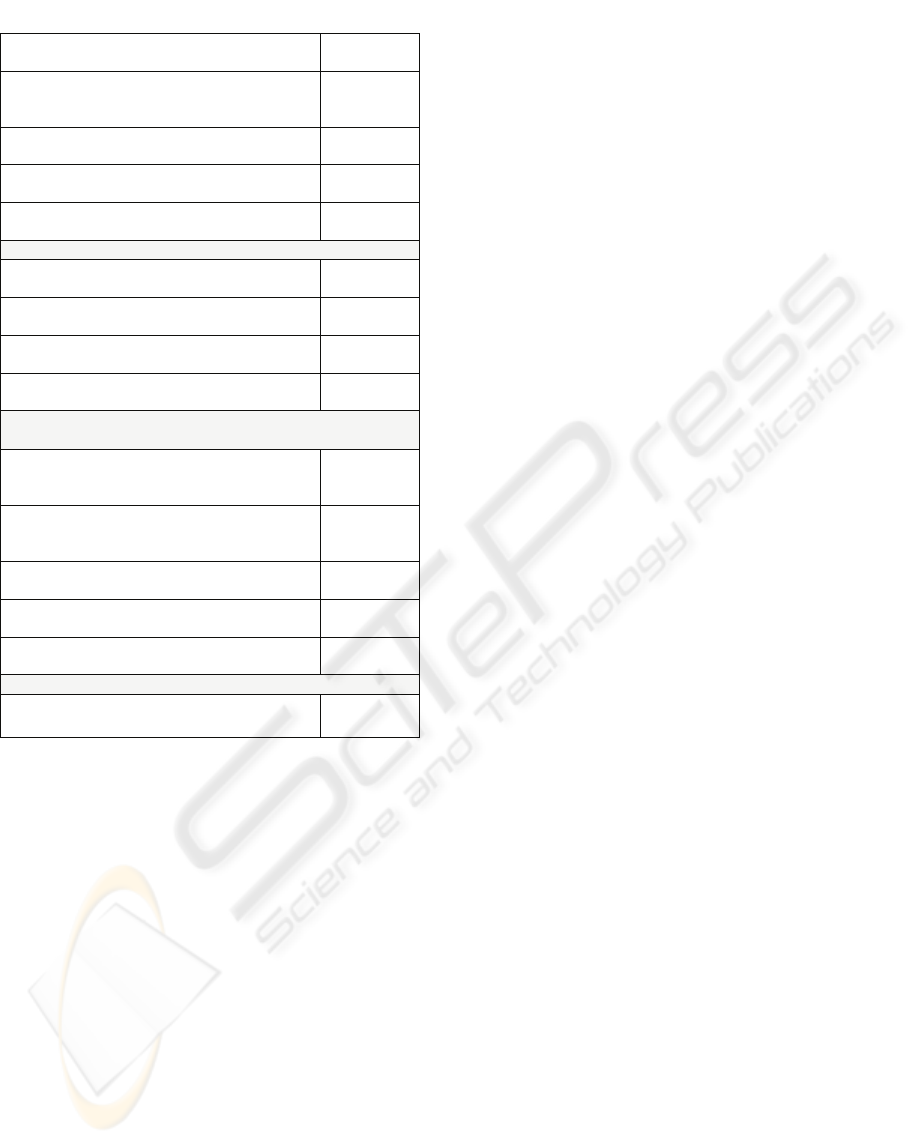
Table 4: The result of Hypotheses (Cont.).
H2-1 : Convenience of internet shopping mall
has a positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H2-2 : The framework of internet shopping
malls has a positive effect on customer
satisfaction.
Rejected
H2-3 : Quality of products in shopping malls
has a positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H2-4 : Variety of products in shopping mall
has a positive effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
H2-5 : Transaction security has a positive
effect on customer satisfaction.
Accepted
3) The impact of customer value on customer loyalty
H3-1 : Internet usage level has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
H3-2 : Frequency of internet shopping has a
positive effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
H3-3 : Cost of purchased goods has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
H3-4 : Quantity of purchased goods has a
positive effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
4) The impact of environment of internet shopping malls on
customer loyalty
H4-1 : Convenience of internet shopping
malls has a positive effect on customer
loyalty.
Rejected
H4-2 : The framework of internet shopping
malls had a positive effect on customer
loyalty.
Rejected
H4-3 : Quality of products in shopping malls
has a positive effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
H4-4 : Variety of products in shopping malls
has a positive effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
H4-5 : Transaction security has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
5) The impact of customer satisfaction on customer loyalty
H5 : Customer satisfaction has a positive
effect on customer loyalty.
Accepted
6 CONCLUSIONS AND
IMPLICATION
To increase customer satisfaction and customer
loyalty in internet shopping mall is the primary
purpose of this study.
This emphasizes the importance of customer
satisfaction through customer value and the
environment of internet shopping malls. The result
suggests that customer value is an antecedent of
customer satisfaction and that customer exerts a
strong influence on repurchase intention.
Retaining customer is only to as manage their
customers’ satisfaction levels. In the long run, more
usage increases switching costs but, at the same
time, increases the degree of feeling locked-in that
can be a major source of dissatisfaction and offset of
customer value. If not satisfied with the services of
internet shopping malls, even customers with high
switching costs are more likely to consider changing
service providers, so that they can have a better
long-term deal. This may be particularly critical for
marketing to customer because altering business
between customers is less noticeable by incumbent
vendors.
Customers must strive to develop customer loyal
programs that concretely compensate customers.
Therefore, we believe that only high quality based
customer programs accompanied by well designed
loyalty programs can be effective in increasing
customer retention.
The results of this study must be interpreted in
view of certain limitations. Results of this study are
generated from people in their 20s~30s mainly.
Furthermore, findings are based on relatively high
educated people. However, given the exploratory
nature of the present study, we emphasize the need
for more rigorous investigation into the issues
addressed here.
REFERENCES
Agarwal, R., Venkatesh, V., 2002. Assessing a Firm’s
Web Presence: A Heuristic Evaluatio n Procedure for
the Measurement of Usability. Information Systems
Research, Vol.13, No.2(2002), pp.168-186.
Babin BJ, Darden WR, Griffin M., 1994. Work and/or fun:
measuring hedonic and utilitarian shopping value. J
Consumer Reerachers. 20(3) 1994: 644-656.
Bagozzi, R. P., Yi, Y., 1988. On the Evaluation of
Structural Equation Models, Journal of the Academy
of Marketing Science, Vol.16, No.1(1988), pp.74-94.
Benbunan, R., 2001, Using protocol analysis to evaluate
the usability of a commercial web site, Information
and Management, Vol.39(2001), pp.151-163.
Castaneda, J. A., Munoz-Levia, F., Luque, T., 2007. Web
acceptance model: Moderating effects of user
experience, Information and Management,
Vol.44(2007), pp.384-396.
Chaudhuri A., Holdbrock MB., 2001. The chain of effects
from brand trust and brand affect to brand
performance: the role of brand loyalty. Journal of
marketing 65(2),:81-93.
Choi, D., 2005. The Study of the Efficiency on the Online
Shopping Mall Influent to the Satisfaction of Customer,
The Journal of MIS Research.
Cronin, JJ,. Brady, Michael K G. Hult Tomas M., 2000.
Assessing the Effects of Quality, Value, and Customer
Satisfaction on Consumer Behavioral Intentions in
Service Environments. Journal of Retailing, Volume
76(2) pp. 193–218,
Fornell, C., 1992. A national customer satisfaction
barometer: The Swedish experience. Journal of
Marketing, 56, 6–21.
Javenspaa, S. , Todd, P., 1997. Consumer Reaction to
THE IMPACT OF CUSTOMER VALUE AND INTERNET SHOPPING MALL ON CUSTOMER LOYALTY AND
CUSTOMER SATISFACTION
285

Electronic Shopping on the World Wide Web,
International Journal of Electronic Commerce, Vol. 1,
No. 2, winter, pp. 59-88.
Kim, H., 2005. Customer Retention in Electronic
Commerce. 2005 KMIS International Conference.
Kim, T., 1999. Success Strategy of Sales through
Communications.
Lee, D., Han, Y., 1997. Internet Marketing,
Lee, D.,1999. The Study of the Customer Satisfaction and
Royalty by the Characteristics of Online Shopping
Mall, The Journal of MIS Research.
Lee, J., 2006. The principles of e-Commerce.
Lee, J., Lee, J., Freick, L., 2001. The impact of switching
costs on the customer satisfaction-loyalty link: Mobile
phone service in France. Journal of Services
Marketing, 15(1), 35–48.
Lee, S., Lee, H., Kim, J., Suh, Y., May, 2004, A Study of
Customer Attitude on Internet Shopping Malls: a Com
parison with Singapore Customer, Journal of the Kore
a Society of System Integration,
Liu, Mark, Kenneth, 2005. Examining customer value
perceptions of organizational buyers when sourcing
from multiple vendors, Journal of Business Research
58 559– 568.
Oh, H., 1995. An empirical study of the relationship
between restaurant image and customer loyalty.
Unpublished Ph. D. Dissertation, Virginia Polytechnic
Institute and State University.
Oliver, R., 1999. Where consumer loyalty. Journal of
Marketing, Vol.1, No.63, Special Issue,:33-44.
Palmer, J., 2002. Website usability, design, and performa-
nce metrics, Information Systems Research, Vol.13, N
o.2, pp.151 -167.
Soderlund, M., 1998. Customer satisfaction and its
consequences on customer behavior revisited.
International Journal of Services Industries
Management, 9(2), 169–188.
Song, J., Zahedi, F., 2005. A Theoretical Approach to
Web Design in E-Commerce: A Belief Reinforcement
Model, Management Science, Vol.51, No.8, pp.1219-
1235.
Suh, K., 2008. The Moderating Effects of Internet
Shopping Involvement on the Relationship between
Usability, Trust of Internet Shopping Sites and
Customer Loyalty, Journal of the Korea Society of IT
Services, Vol. 5(3).
Sun, H., 2007. The key for success of internet shopping
mall. Book cafe.
Suh, K., 2001. A Contingent Analysis on the Relationship
Between the Characteristics of Internet Shopping Mall
and User Acceptance. The Journal of MIS Research.
Vol. 11(2), pp. 23-54.
Xu-Xiaoli, Wan-Yinghong, Huan-Zhijian, Liu-Hui, 2006.
The impact of service quality, satisfaction, value and
switching barrier on customer loyalty in Chinese
airline industry, 2006 IEEE
Yao W., Zhou M., Meng J., 2007. Value-based Customer
Loyalty Evolution, 2007 IEEE.
Yoo, J., Lee, J., Julian H., 2008. Trust in Online Shopping:
The Korean Student Experience,
Proceedings of the
41
st
Hawaii International Conference on System
Science-2008.
Zeithami, Valarie., 1981. How consumers evaluation
processes differ between goods and services. In J.H.
Donnelly & W. George (Ed.), Marketing of services
(pp. 186–190). Chicago: American Marketing
Association.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
286
