
USING MOBILE AGENTS TO SUPPORT M-COMMERCE
Xining Li
Department of Computing and Information Science, University of Guelph, Guelph, Canada
Keywords: Mobile Device, Mobile Agents, M-commerce, Service Discovery, Database Service.
Abstract: Mobile agents are self-contained processes, dispatched by their principal, roaming the Internet to access
data and services, and carrying out their decision-making and problem-solving tasks remotely. Mobile
commerce (M-commerce), the traditional E-commerce combined with mobile devices and wireless
networks, is likely to become a major business model in the near future. Due to the flexibility and mobility,
mobile agent based M-commerce can complement the existing client/server based E-commerce model to
enable consumers to conduct business without time and space restrictions. For the purpose of applying
mobile agents to various internet applications, we have implemented an experimental mobile agent system
infrastructure that provides programming languages and virtual machines, and also integrates security,
service discovery and database access functionalities. The goal of this research is to deploy the existing
system infrastructure for M-commerce applications. We hope that the proposed research will benefit mobile
consumers who wish to access a wide choice of products and services on an anywhere and anytime basis.
1 INTRODUCTION
E-commerce is a business model of buying and
selling of goods and services via the Internet. This
model typically involves economic activities,
interactions between consumers and producers, and
commercial transactions crossing companies. There
is no doubt that the E-commerce is changing
economy and having a great influence on people’s
daily life. For consumers, E-commerce makes it
easier and more efficient to search, evaluate, and
compare products in the world market. For business
organizations, E-commerce can be used to raise
profit by increasing revenue and decreasing cost,
and explore new opportunities and expand business
into global market.
Most E-commerce applications use traditional
client/server model in which a commercial
transaction generally requires a stable
communication connection being established
between the client and the server. In recent years,
technological evolution has let to handheld
computing, such as PDA’s, mobile phones, Pocket
PC’s, etc., with combinations of wireless networks
including WiFi, Bluetooth, infrared, and GPRS or
3G telecommunication techniques. According to
IDC, almost 20 million units were shipped
worldwide in the second quarter of 2006, a 42.1%
increase, year over year. Due to technological
advances, a new E-commerce model, namely, M-
commerce has emerged and attracted a growing
number of research efforts (Shi, 2004, Bădică,
Ganzha and Paprzycki, 2005, Bai, Chou,Yen and
Lin, 2005, Kowalczyk, Braun, Frankczyk and Speck,
2003). In general, M-commerce can be identified as
the transaction conducted through the use of mobile
handheld devices over wireless or
telecommunication networks. M-commerce not only
extends Internet-based E-commerce, but also offers
a unique business opportunity with its own features,
such as ubiquity, accessibility, portability, etc.
Obviously, traditional client/server approach poses a
barrier to the development of M-commerce
applications. First, it will become expensive and
unreliable when lot of data has to be transferred
between the client and the server. Second, it will be
impossible to retain long time connectivity between
the client with a mobile device and the server. Third,
it typically requires clients to frequently check
trading opportunities and make most decisions
manually. In addition, compare with the desktop
oriented client/server or browser/web-server model,
mobile hand-operated devices have some physical
constraints, such as small screen size, poor network
connectivity, low transmission bandwidth, and
limited battery capacity. Therefore, in order to ease
the access and participation of mobile users, the
mobile agent paradigm has been increasingly
recognized as a promising framework for developing
91
Li X. (2009).
USING MOBILE AGENTS TO SUPPORT M-COMMERCE.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on e-Business, pages 91-96
DOI: 10.5220/0002189500910096
Copyright
c
SciTePress
M-commerce applications. Mobile agents are self-
contained entities capable of autonomously roaming
the Internet and launching user assigned tasks. This
paradigm brings forward the creative idea of moving
user defined computations towards network
resources, and provides a whole new architecture for
designing M-commerce applications. Deploying
mobile agents in M-commerce can reduce
unnecessary network traffic, tolerate poor network
connectivity, provide more advanced services,
support automation of decision-making, reduce
participation costs and improve trading efficiencies.
In this paper we propose an M-commerce
framework based on the Intelligent Mobile Agent
Gliding On-line (IMAGO) system (Li, 2006). The
IMAGO system is an infrastructure for developing
mobile agent based applications, such as M-
commerce or distributed data mining. In other
words, it provides an algorithmically complete
programming language and execution environment.
Based on the IMAGO system infrastructure, the goal
of this research is to use mobile agents to support M-
commerce applications. We hope that the proposed
research will benefit mobile consumers who wish to
access a wide choice of products and services on an
anywhere and anytime basis. The remainder of the
paper is organized as follows. Section 2 gives an
overview of the IMAGO M-commerce framework,
and describes the role of mobile agents on trade
transactions. In Section 3, we introduce three
important system facilities, namely, service
discovery, database management and agent
communication, and discuss their usage and
functionality. Section 4 presents the IMAGO
security mechanism. In Section 5, we present the
design of Mobile Portal that bridges a mobile user
and an M-commerce application, and show a simple
experimental example. Finally, we give the
concluding remarks as well as future work.
2 OVERVIEW OF THE IMAGO
M-COMMERCE FRAMEWORK
There is a great range of M-commerce applications
(Ngai and Gunasekaran, 2007). Typical applications
include mobile advertising, mobile inventory
management, product locating and searching, mobile
shopping, mobile entertainment services, location-
aware services, mobile financial applications, and so
on. Accordingly, there are many possible business
scenarios for developing M-commerce applications.
At this stage, our proposal focuses on the consumer-
driven M-commerce, i.e., an E-commerce model in
which the consumer initiates a trade transaction.
More precisely, our framework represents a
distributed environment that allows consumers to
dispatch mobile agents from their handheld devices
to visit E-stores for searching, comparing,
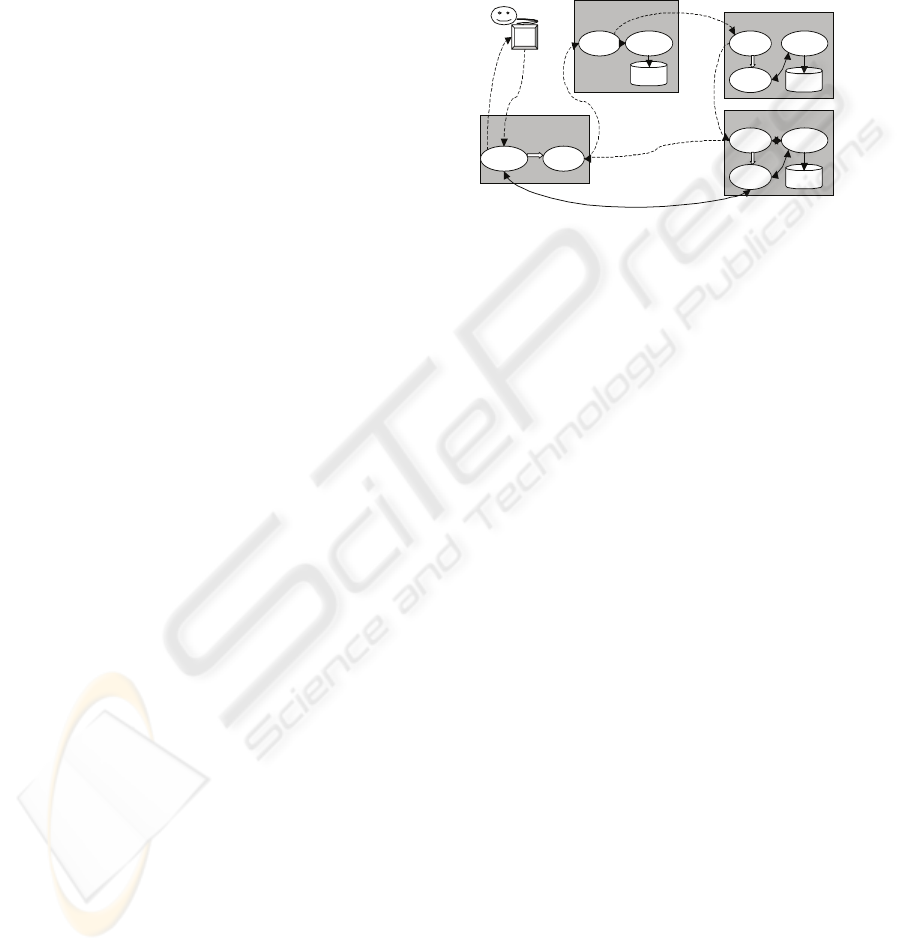
evaluation, buying and payment of goods. Figure 1
gives an example of agents occurring in the IMAGO
M-commerce system and indicates their basic
behaviours.
call back
IMAGO service
discovery server
Home IMAGO server
Figure 1 An Example of Deploying Mobile Agents in M-commerce
Remote IMAGO server A
MA1
vendor
agent
MA2
Remote IMAGO server B
MA1
vendor
agent
MA3
home
agent
MA1
MA1
DBM S
DBM S
migrate
migrate
migrate
clone
clone
communic at e ACL
DBM S
create
user
consumer
PDA
dispatch
locating
agent
Figure 1: An example of Deploying Mobile Agents in M-
commerce.
Generally speaking, the IMAGO M-commerce
framework distinguishes three major types of agents:
• Device agent: It is bound with user and
installed on the handheld device. Its major
responsibility is to enable a mobile user to
locate its home server, communicate with
the home agent to invoke an M-commerce
application. We call the device agent as
IMAGO Mobile Portal.
• Stationary agent: A stationary agent always
resides at its host. For different purposes,
we identify three kinds of stationary agents:
home agent, locating agent and vendor
agent. Home agent provides a bridge
between the mobile user and the M-
commerce application. It is responsible to
communicate with the Mobile Portal,
accept requests from user, and dispatch
corresponding mobile agents to start a trade
transaction. Locating agent provides
discovery services and resides at the
IMAGO discovery server. A vendor agent
acts as the representative of the seller to
keep track of all transactions and inquires.
• Mobile agent: A mobile agent represents
the user roaming the Internet to carry out
the task assigned by its home agent. It will
visit vendors that may carry product desired
by the customer, look for a special service,
and conduct the transaction according to a
specific trading policy.
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
92

3 SERVICE DISCOVERY,
DATABASE SERVICE AND
AGENT COMMUNICATION
A commonly used M-commerce approach is to let
consumers to search for products from physically
distributed vendor sites. However, this approach
may be impractical to a large scale of E-markets
distributed over the Internet. Deploying mobile
agent paradigm in M-commerce offers a possible
solution because the customer may dispatch agents
to search for possible vendor locations. This in turn
leads us to the service discovery problem, that is,
how to find vendor sites available to an M-
commerce application. Following this trend, it
becomes increasingly important to give agents the
ability of finding and making use of services that are
available in a network (Bettstetter and Renner,
2000). A variety of Service Discovery Protocols
(SDPs) are currently under development by some
companies and research groups. The most well
known schemes are Sun's Java based Jini
TM
(Hashman and Knudsen, 2001), Salutation
(Salutation Consortium, 1998), Microsoft's UPP
(Universal Plug and Play Forum, 2006), IETF's
Service Location Protocol (SLP) (Guttman, Perkins,
and Veizades, 1999) and OASIS UDDI (OASIS
UDDI Spec TC, 2005). Some of these SDPs are
extended and applied by several mobile agent
systems to solve the service discovery problem. For
example, GTA/Agent (Rubinstein and Carlos, 1998)
addresses the service location issue by extending
SLP, a simple, lightweight protocol for automatic
maintenance and advertisement of intranet services.
In the IMAGO system, we have implemented a
new service discovery mechanism which is called
Discovery Service via Search Engine Model
(DSSEM) (Song, Li and Ni, 2006). DSSEM is based
on a search engine, a global Web search tool with
centralized index and fuzzy retrieval. Using this
model, E-commerce service providers manually
register their services to a service discovery server.
A mobile agent locates a specific service by
migrating to the service discovery server and
subsequently submitting requests with the required
description. Before a service can be discovered, it
should make itself public. This process is called
service advertisement. A service advertisement
should consist of the service identifier, plus a simple
string describing what the service is, or a set of
strings for specifications and attributes. The most
significant feature of DSSEM is that we enrich the
service description by using web page’s URL to
replace the traditional string-set service description
in mobile agent systems. On the other hand, a
mobile agent can move to a service discovery server,
communicate with the locating agent to obtain an
itinerary that includes a list of ranked host addresses
of the service providers. Based on the given
itinerary, the mobile agent may travel from host to
host to carry out an M-commerce transaction.
In order to let vendor agents communicate with
database systems, the IMAGO system provides a set
of database access primitives, which enables agents
to establish connection with data sources and make
requests for desired information. The system offers
two ways of database accessing, i.e., the set retrieval
and the tuple retrieval. The former returns the entire
matching data set to the requesting agent, whereas
the latter allows the requesting agent to consume the
matching data on the tuple by tuple basis. The
database management module not only provides
flexible interface for accessing data, but also
manipulates database connections efficiently. At the
current stage, the database model in the IMAGO
system is MySQL, the most popular open source
DBMS system in the world.
In an M-commerce application, agents are not
working alone. They need to communicate with each
other to cooperate and generate a global data
aggregation for further analysis. For example,
mobile agents of an M-commerce application might
exchange messages to compare prices of goods they
gathered before making a shopping decision. Most
existing mobile agent systems adopt some kind of
communication models/protocols from traditional
distributed systems. However, the IMAGO system
adopts a different strategy to cope with this issue.
The idea is to deploy intelligent mobile messengers
for inter-agent communication (Li and Autran,
2005). Messengers are thin agents dedicated to
deliver messages. The IMAGO system provides a
set of built-in messengers as a part of its
programming interface. A mobile agent at any
remote sites and at any time may dispatch
messengers to deliver data to designated receivers.
For example, suppose that a mobile agent has
completed its M-commerce work at a remote vendor
server, it can either migrate back to its home server,
or dispatch a messenger to deliver result to the home
agent.
Communication among agents takes place by
means of an Agent Communication Language
(ACL). In order to facilitate open standards of
ACL’s, the IMAGO agent-based communication
model is in compliance with the FIPA ACL message
structure specification (FIPA ACL, 2005). In
addition to the various types of system built-in
messengers for sending agents, the IMAGO system
provides a set of predicates for receiving agents.
USING MOBILE AGENTS TO SUPPORT M-COMMERCE
93
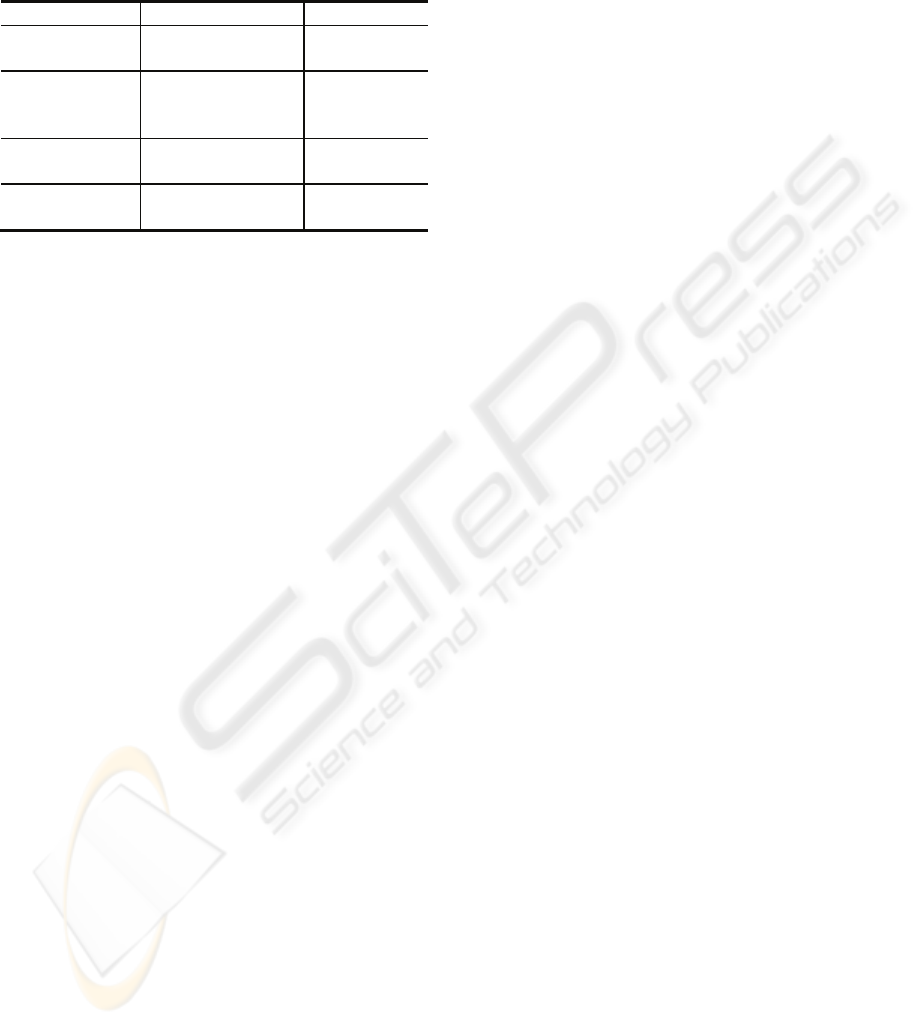
Typical IMAGO built-in predicates for service
discovery, database access, communication and
agent management are summarized in Table 1.
Table 1: Built-in Predicates.
Category Examples Server type
Service Discovery web_search IMAGO
Discovery server
Database Service db_connection,
db_search_set,
db_search_tuple, etc.
IMAGO
Database server
Communication dispatch, accept, wait_
accept, etc.
IMAGO server
Agent management create, clone, dispose,
move, etc.
IMAGO server
4 SECURE AGENT MIGRATION
CHANNEL
In a large-scale open network, we have to assume
that a mobile agent system is subject to the
fundamental security threats of disclosure,
modification, denial of service, misuse, abuse,
repudiation, and so on. The security challenge here
is much more severe than the one in traditional
client/server model. In addition, security mechanism
should be able fit the purpose of various M-
commerce applications with different security
requirements. Therefore, we are encouraged to
develop the security mechanism based on the most
well known techniques. We may adopt WAP WTLS
(WAP Forum, 2001) or TLS (Allen and Pierks,
1999) to provide message integrity, authentication
and non-repudiation between mobile devices and the
home server. On the other hands, we provide a
simple security mechanism within the execution
environment to protect mobile agents as well as
agent servers. In the current design of the IMAGO
system, the integrated security mechanism consists
of three kernel components: secure migration
protocol, agent verifier and security monitor.
As the primary identifying characteristic of
IMAGO system is the sole protocol to support both
agent mobility and inter-agent communication, we
provide a secure and authenticated connection
between two end points of a migration channel to
protect the privacy and integrity of a moving agent.
The technique incorporated with the IMAGO
migration protocol is the excellent OpenSSL. It is a
full-featured toolkit implementing socket and
transport layer security protocols as well as a set of
general-purpose cryptography algorithms. Based on
OpenSSL, we construct a secure server-to-server
agent migration protocol with ability of
authentication by using the RSA and DSA
algorithms, which are based on a pair of
complementary numerical keys.
When an agent intends to move to another
host, it will be transferred to the Agent Out module.
However, before the agent migration takes place, the
sending server requires some initial configuration if
the receiving server is first met. For each new
destined server, the initial configuration is
performed only once and then cached in a special
internal table. The main purpose of the initialization
is to exchange public keys of both parties and
negotiate the data encryption option. OpenSSL
offers multiple symmetric cryptography algorithms.
For the sake of flexibility and availability, several
cryptography options, such as, from the most secure
to the least secure, 3DES, BlowFish, IDEA, DES
and RC4, will be negotiated with respect to their
preference order, until an option is agreed by both
sending and receiving servers.
The secure migration channel guarantees the
confidentiality, integrity, and password-less
authentication of an agent moving from host to host.
However, the use of mobile agents raises another
two important security concerns, i.e., agents need
protection from malicious hosts and hosts need to be
protected against malicious agents. Unfortunately,
the problem posed by malicious hosts to agents
seems impossible to be fully solved, because there is
no easy way to enforce a host, especially a malicious
host, to obey security requirements. Once an agent
has arrived at a host, it submits itself completely to
the host and cannot stop the host from malicious
attacking. Even though some solutions have been
proposed, many of them are used for attack
detection, rather than prevent agents against
misbehaving servers. At current stage, we assume
that IMAGO M-commerce servers behave truthfully
and honestly.
On the other hand, the IMAGO system takes a
great measure to protect hosts against malicious
agents. First of all, the IMAGO virtual machine is
constructed as a sandbox, a commonly used
technique to control agent execution at the byte-code
instruction level. Secondly, there are two types of
security policies for detecting malicious agents. One
is agent verification and the other is runtime
monitoring. Agent verification is mainly used to
check an incoming mobile agent that has just arrived
from a foreign host. Unfortunately, the verification
process cannot find all potential dangers to the host
server. It is possible that some agents are
deliberately coded to damage remote servers and
some are poorly coded to cause unexpected, harmful
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
94

side effects. Even though the verifier can protect
hosts against illegal instructions, it is not power
enough to prevent denial of service attacks. In order
to prevent such potential risks, a run-time check is
required to monitor the agent’s execution. We adopt
limitation techniques to control the persistent
survivability of mobile agents, that is, to directly
control mobile agents from their dynamic
behaviours during different stages of their lifecycle.
5 AN EXAMPLE OF IMAGO
MOBILE PORTAL
The IMAGO mobile Portal is a program installed on
the handheld device. In fact, the Portal is a
simplified IMAGO IDE, a Java-GUI based program
tailored for mobile devices. Figure 2 gives the
current prototype of the Portal interface. From
which, a mobile customer may communicate with
the home server and invoke a desired M-commerce
application. As an example, suppose a customer
wants to monitor the TSX stock market, he may
invoke the Sniffer application from his Portal. The
application program is given below:
:- home_agent(stock_monitor).
stock_monitor(_) :- wait_accept(Mobile_portal, start),
create(“sniffer.ima”, sniffer,
[[s(“NT”, 26.00), s(“RY”, 43.00)], [s(“SW”,
53.00)]]),
monitor.
monitor :-wait_accept(W, Msg),
notify(W, Msg),
monitor.
notify(_, closed) :- call_back(Mobile_portal, “market
closed”),
disconnect.
notify(W, Msg) :- call_back(Mobile_portal, from(W,
Msg)).
:-end_home_agent(stock_monitor).
:- mobile_agent(sniffer).
sniffer([Buy, Sale]) :- move(imago_discovery_server),
web_search(locate(“TSX”, stock, imago_server), 1,
Server),
move(Server),
split(Buy, Sale).
split([], Sale) :- !, sniff(Sale, sale).
split(Buy, []) :- !, sniff(Buy, buy).
split(Buy, Sale) :- clone(twin, R), R == clone
→
sniff(Sale, sale); sniff(Buy, buy).
sniff(L, Act):- query(L, Act),
sleep(2000),
sniff(L, Act).
Figure 2: The IMA GO Mobile Portal.
query([], _):- !.
query([s(Stock, Limit)|L], Act):- db_search(select(Stock),
_, Value), // database service
check(Stock, Limit, Value, Act),
query(L, Act).
check(_, _, closed, _) :- !, // if market closed
dispatch($oneway_messenger, home, closed),
dispose.
check(Stock, Limit, Value, buy) :- Limit > Value, !,
dispatch($oneway_messenger, home, knock(buy,
Stock, Value)).
check(Stock, Limit, Value, sale) :- Limit < Value, !,
dispatch($oneway_messenger, home, knock(sale,
Stock, Value)).
check(_, _, _, _). // otherwise, take no action
:- end_mobile_agent(sniffer).
The code of stock_monitor defines the home
agent resided at the home stationary server. Upon
receiving the request from the Portal, the
stock_monitor creates a mobile agent called sniffer
alone with initial arguments. When the sniffer starts
execution, it migrates to the imago discovery server
and searches for the URL of TSX IMAGO server
and then moves to that server. Having arrived to the
TSX server, the sniffer continues execution by
calling split/2 which will examine the given
argument list to determine whether a clone is
necessary. If the argument involves both Buy and
Sale stocks, the sniffer clones itself such that the
original sniffs Buy list whereas the clone sniffs the
Sale list. Now, the sniffer will make queries to the
stock vendor agent periodically until the stock
market is closed. For each stock listed in its
argument, the sniffer checks if the new price is less
than the user's limit. If so, an $oneway_messenger is
dispatched to knock the home agent up, otherwise,
the next stock will be investigated. The clone, if
there is one, will do the similar work, except it
checks for the condition on sale. Clearly, it is
possible that no knock-up messengers would be
dispatched ever if the stock prices could not meet the
USING MOBILE AGENTS TO SUPPORT M-COMMERCE
95

conditions for sale or buy.
6 CONCLUSIONS
In this paper, we discussed the scheme of deploying
mobile agents in M-commerce applications. The
advantage of adopting mobile agents for M-
commerce is to scale up to large, dynamic world
market places distributed over the Internet and to
ease the access and participation of mobile users.
We presented the design of IMAGO M-commerce
framework, discussed the service discovery module
and database management module, and introduced
the work-in-progress IMAGO Mobile Portal and an
excremental example. The API of the IMAGO
system is a set built-in predicates capable to couple a
logic programming language with functionalities of
locating services and accessing remote databases.
Equipped with those system tools, mobile agents
may search for suitable market places, roam the
Internet to collect useful information, compare and
evaluate goods and prices, conduct purchasing
transactions, and communicate with each other to
generate a global view of data through the
aggregation of distributed computations.
Research on the agent based M-commerce
involves further extensions of the IMAGO system.
First, the current design of Mobile Portal should be
further refined to provide an ease-to-use interface
and fully implemented and tested. Secondly, since
E-commerce databases may contain multi-
dimensional data, retrieving such kind of
information from flat web pages is a pending
problem. We are looking to use XML meta-data to
solve the database dimensional problem. In addition,
we are making investigations on adding more
programming languages to the IMAGO system, as
well as introducing more flexible and efficient
communication tools, such as mobile socket, to
facilitate M-commerce applications.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
I would like to express my appreciation to the
Natural Science and Engineering Council of Canada
for supporting this research.
REFERENCES
Shi, N., Ed, 2004. Mobile Commerce Applications,
Hershey PA: Idea Group Publishing
Bădică, C., Ganzha, M., Paprzycki, M., 2005. Mobile
Agents in a Multi-Agent E-Commerce System, In Proc.
Of SYNASC, Timisoara: IEEE Computer Society
Press, pp. 207-214
Bai, L., Chou, D.C., Yen, D.C., Lin, B., 2005. Mobile
Commerce: Its Market Analysis, International Journal
of Mobile Communication, 3(1), 66-81
Kowalczyk, R., Braun, P., Frankczyk, B., Speck, A., 2003.
Deploying Mobile and Intelligent Agents in
Interconnected E-marketplaces, Journal of Integrated
Design and Process Science, 7( 3), 109-123
Li, X., 2006. On the Implementation of IMAGO System,
International Journal of Computer Science and
Network Security, 6( 2a), 107-118
Ngai, E.W.T., Gunasekaran, A., 2007. A Review for
Mobile Commerce Research and Applications,
Decision Support Systems, 43, 3-15
Bettstetter, C., Renner, C., 2000. A Comparison of Service
Discovery Protocols and Implementation of the
Service Location Protocol, In Proc. of EUNICE 2000,
sixth EUNICE Open European Summer School,
Enschede, The Netherlands, pp. 13-15
Hashman, S., Knudsen, S., 2001. The Application of
Jini
TM
Technology to Enhance the Delivery of Mobile
Services,
http://www.sun.com/software/jini/whitepapers/PsiNap
ticMIDs.pdf
Salutation Consortium, 1998. Salutation Architecture
Overview, White Paper,
http:// www.salutation.org/whitepaper/originalwp.pdf
Universal Plug and Play Forum, 2006. UPnP
TM
Device
Architecture, http://www.upnp.org/specs/arch/UPnP-
DeviceArchitecture-v1.0.pdf
Guttman, E., Perkins, C., Veizades, J., 1999. Service
Location Protocol, Version 2, White Paper, IETF,
RFC 2608
OASIS UDDI Spec TC, 2005. Universal Description,
Discovery and Integration v3.0.2 (UDDI),
http://www.oasis-open.org/committees/uddi-
spec/doc/spec/v3/uddi-v3.0.2-20041019.htm
Rubinstein, M., Carlos, O., 1998. Service Location for
Mobile Agent System, In IEEE/SBT International
Telecommunications Symposium (ITS'98), SP Brazil,
pp. 623-626.
Song, L., Li, X, Ni, J., 2006. A Database Service
Discovery Model for Mobile Agents, International
Journal of Intelligent Information Technologies, 2(2),
16-29
Li, X., Autran, G., 2005. Inter-agent Communication in
IMAGO Prolog, Lecture Notes in Artificial
Intelligence,
3346, 163-180
FIPA ACL, 2005. Agent Communication Language
Specifications, FIPA,
WAP Forum, 2001. WAP WTLS: Wireless Application
Protocol Wireless Transport Layer Security
Specification,
http://www1.wapforum.org/tech/terms.asp?doc=OMA
-WAP-260_101-WIM-SIN-20020107-a.pdf
Allen, C., Pierks, T., 1999. The TLS Protocol Version 1.0,
RFC2246, http://www.ietf.org/rfc/rfc2246.txt
ICE-B 2009 - International Conference on E-business
96
