
APPLICATION OF REACTIVE AGENTS CONCEPTS
IN AUTOMATIC BINDINGS OF LONWORKS NETWORKS
DEVICES
Miguel dos Santos Alves Filho, Rafael de Aquino Cunha and Carlos Eduardo Cugnasca
Escola Politécnica, University of São Paulo, Av. Prof. Luciano Gualberto, travessa 3 nº 158, São Paulo, SP, Brazil
Keywords: LonWorks
®
, Multi-agents, Artificial Intelligence, Distributed systems, PBX, Telephony, Control networks.
Abstract: This paper aims to propose and test a new method to implement dynamic bindings in LonWorks
®
technology, allowing a new Distributed System of Private Telephone Switching (DSPTS), also developed
with LonWorks
®
technology, to make their telephone links. In order to do this, a method for developing
embedded systems and the reactive agent view was applied for each different device in this new system,
offering a unique, practical and innovative solution for both, LonWorks
®
and PBX systems. This view
allowed the implementation of intelligent and autonomous devices, specially in their internal process,
providing satisfactory and more efficient results based on the DSPTS requirements. This work is the kick-
off and the basis for developing new functions for telephone systems and control networks.
1 INTRODUCTION
In recent years, the paradigm of control systems
design has been changed, moving from the
traditional centralized architecture and proprietary
technology to distributed and open architectures
(Hur, Kim, Park, 2005)(Pu, Moor, 1998).
This change in paradigm takes the concept of
network control, and brings some benefits to
automation systems, such as reducing and
simplifying cabling, increasing reliability and
providing more options of manufacturers and
integrators for the user to chose from (Echelon
Corporation, 2007) (Hur, Kim, Park, 2005).
Aiming to exploit these advantages, a research
project is presented that proposes to develop a
Private Automatic Branch Exchange (PABX) (now
also called Distributed System of Private Telephone
Switching - DSPTS), with distributed architecture
and implemented with the control networking
technology LonWorks
®
. In this architecture, all
telephone extensions and devices for interfacing
with the telephone line are implemented as devices
(also called nodes) of control network that
communicate with each other, with the audio signals
(voice) digitized and transferred via messages.
The standard method for using such a technology
and the available tools to work with it provide only a
static way for the realization of logical connections
between devices (called bindings). It means that
these connections are defined during the setup
project and then will remain unchanged (Echelon
Corporation, 1999).
Considering that a PABX system must open and
close communication channels every time, it means
that the logical connections between nodes are not
pre-defined, but defined according to the need to
establish a telephone connection. Thus the use of
this control networks technology could not be
exerted in its original form.
The purpose is to propose and analyze a solution
based on the concepts of multi-agent systems to
develop devices of this distributed PABX, using the
LonWorks
®
technology, with self-management in a
previously configured environment, enabling the
creation of dynamic telephone links for the DSPTS.
The DSPTS characteristics of a distributed
application stimulated the use of the multi-agent
system concepts in its implementation (Durfee;
Rosenchein, 1994).
1.1 LonWorks
®
Technology
LonWorks
®
emerged in the 1990s, developed by
Echelon. This is a technology for automation
networks, involving not only a communication
258
dos Santos Alves Filho M., de Aquino Cunha R. and Eduardo Cugnasca C. (2009).
APPLICATION OF REACTIVE AGENTS CONCEPTS IN AUTOMATIC BINDINGS OF LONWORKS NETWORKS DEVICES.
In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics - Intelligent Control Systems and Optimization,
pages 258-264
DOI: 10.5220/0002215402580264
Copyright
c
SciTePress

protocol, but also all the necessary infrastructure for
the system development such as management tools,
product development tools and network
configuration tools (Echelon Corporation, 1999).
Its protocol was developed based on the OSI
reference model, from the link layer to the session
layer. It is an open and standardized protocol, ANSI /
EIA 709.1, also known as LonTalk (Echelon
Corporation, 2002).
An emphasis point of this protocol is its
messages structure, which allows direct messaging
between devices, broadcast messages and multicast
messages. Furthermore, it provides system
management messages, allowing a greater control of
devices and even loads and develops programs by
the network itself (Echelon Corporation, 2002).
In the implementation of control networks
various media types can be used, as well as twisted
pair, power network, optic fiber and wireless
communication, which makes the technology very
flexible (Echelon Corporation, 1999) (Chermont,
2007).
The LonWorks
®
control network nodes may be
treated as objects that communicate through
interfaces, also called functional profiles, which
have network variables of the device in question.
Through these variables, information may be shared
with other devices (Xie, Pu, Moore, 1998).
The communication between the nodes is made
through links between their network variables, a
process called binding. From these, logical
connections are used that allow messages to be sent
whenever there is a change in the network variables
values (Echelon Corporation, 1999).
Besides the LonWorks
®
technology design,
Echelon has developed a chip called NeuronChip
that is a full implementation of the LonTalk and
provides the basis for any manufacturer to develop
its products.
The NeuronChip consists of three processors
working in parallel, two of them for the treatment of
the communication protocol and the last one for the
application program execution (Motorola, 1997).
The use of NeuronChip allows developers to
treat the network variables as program variables,
aside from the whole network communication,
developing the programs associated with the
application (Motorola, 1997). A specific
programming language was developed for that
technology, called NeuronC, which follows the
ANSI C and is completely based on events (Echelon
Corporation, 1995a).
1.2 Reactive Agents
Agents are autonomous entities that work together to
achieve the same goal, being able to interact and to
organize efficiently (Liviu, Sean, 2004).
They can also be perceived as real or virtual
automatons that have knowledge of the environment
in which they are inserted, and are able to perceive
changes in that environment. They have knowledge
about other agents, being able to communicate, to
learn, to infer, to form groups or even to reject.
Finally, they are able to decide, through its own
observations, goals, knowledge and interactions
(Wooldridge, Jennings, 2002).
The most common way to classify these agents
divides them into two groups, considering the
deliberation capacity, the environment perception
and communication complexity: one is called
cognitive agent and the other, reactive agent.
The cognitive agents are characterized by having
very complex functions and by having models that
require high processing capacity (Wooldridge,
Jennings, 2002).
There are different internal architectures that can
be used for the development of such agents, being
one of the most used architecture known as “Beliefs,
Desires, Intentions” (BDI) (Rao, 1996) (Rao;
Georgeff, 1991). Its use is considered in systems that
require the ability to exchange complex information,
to own and build complete models of the world
where they belong, their own and other agents, thus
acting spontaneously, creating an organization that
serves a purpose common to all of them (Steels,
1990).
A good example of the use of cognitive agents is
presented by Bigham (2003), which consists of an
antennas chain for mobile phones, each one with a
manageable coverage area, so that intersections
between them can be done and undone.
Within the group of reactive agents, there are
those who are able to understand (though in a fairly
limited way) and to react by acting on the
environment in which they are inserted, through a
pre-defined logic and always with a final goal that
was set in project phase.
A striking feature of this model type is its simple
communication way, which often occurs indirectly,
through the environment itself (Wooldridge;
Jennings, 2002). One advantage of these agents is
the ease of implementation, which may be based on
devices with less processing capacity and great
limitation of energy.
As examples of its use, the study of the behavior
of insects and their development processes may be
APPLICATION OF REACTIVE AGENTS CONCEPTS IN AUTOMATIC BINDINGS OF LONWORKS NETWORKS
DEVICES
259
mentioned, as shown in Liviu and Sean (2004), or
control network devices with low processing
capacity. Finally, this class of agent is used in
systems in which intelligence is expected to arise
from the society overall behavior and not from each
individual (Steels, 1990) (Castelfranchi, 1998)
(Boissier; Demazeau, 1994).
It is worth mentioning that the software agents
are used in systems known as multi-agents systems
or distributed problem resolutions, which have as
one of their characteristics the lack of centralized
control, which fall within one of the DSPTS
requirements as well their simplicity, allowing their
implementation in the NeuronChips (Durfee;
Rosenchein, 1994).
1.3 The DSPTS
One of the most important systems for any
enterprise is the voice communication system.
Currently, these systems tend to be implemented
with equipment called PABX, which are nothing
more than core private telephony, which enables
internal communication between all employees who
have access to branches, and communication
between them and the outside world (external links).
One important feature of this equipment is its
centralized architecture, in which all telephone
extensions and external lines must be connected to a
central device, as illustrated in Figure 1. Among the
main limitations of this architecture there is the limit
of the expansion in the extensions number and
external lines, and the need for a large amount of
cabling, which makes it not very flexible to install
and to change the branches positions.
Figure 1: Typical PBX architecture.
The research presented in this article proposes a
new architecture for the implementation of such
systems, using the technology for control networks
LonWorks
®
, allowing to remove the mentioned
disadvantages of typical PABXs, as well the
reduction and simplification of cabling, flexibility
for changes, incremental growth (and associated
investments), and greater system reliability (gaps in
some nodes do not prevent the functioning of the
rest of the system).
Moreover, this project aims to add greater
intelligence to these systems, solving problems such
as call direction, to decide which carrier should be
used according to the call type, extensions calls
prioritization to access the outside line, etc.
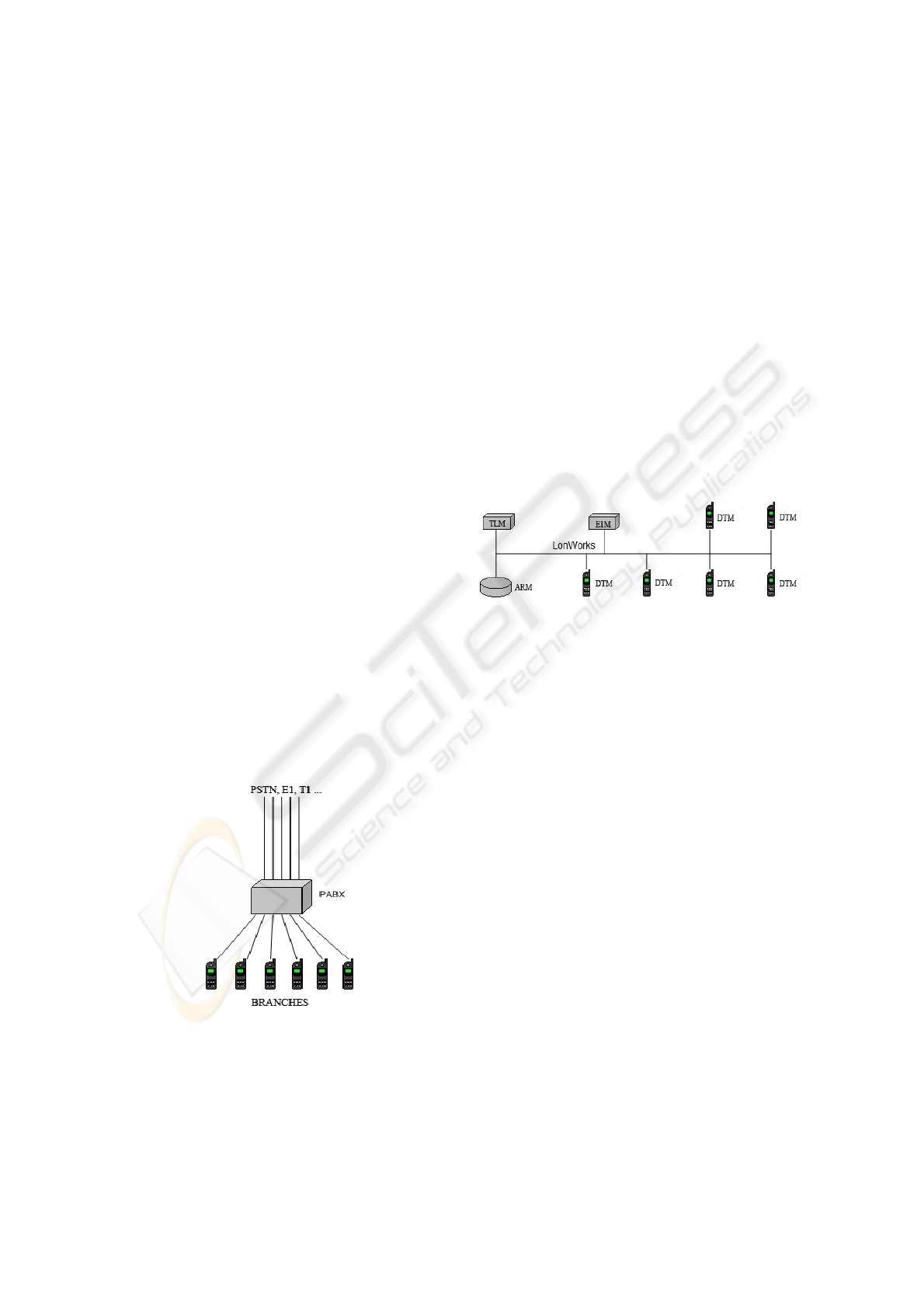
Figure 2 illustrates the architecture of the
proposed system, in which the following DSPTS
components are present:
• TLM – Trunk Line Module;
• E1M – E1 Module;
• ARM – Audible Response Module;
• DTM – Digital Telephony Module.
Figure 2: DSPTS distributed architecture.
Other features that motivated the choice of the
LonWorks
®
technology was the possibility of the
object oriented programming and the low jitter in
message exchange, due to the robust features of the
communication protocol.
For the voice message exchange, the project was
specified for the use of voice compression
algorithms, aimed at telephony. In this case, the
G.729 ADPCM algorithm was used, which provides
a good quality for telephony voice communication
and uses a low bandwidth (16 kbps per
communication channel).
Just as occurs in conventional PBX, it is
necessary for the DSPTS to close communication
channels, with the difference that in the first case the
link is physical and in the second it is logical.
In the LonWorks
®
technology, this logical link is
performed by means of bindings between the
variables of two devices that, as reviewed above, are
built with the tools in the market, during the system
configuration. This makes these links static,
preventing the intended application.
Thus, the possibility to perform bindings
dynamically is fundamental for the DSPTS because
that way two devices could exchange messages
during a phone call, after which they would be free
ICINCO 2009 - 6th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
260

to communicate with other devices and participate in
other connections.
2 MATERIALS AND METHODS
The nodes developed have low processing capacity
and low memory amount, and because it is a
research project, in which new requirements can
always be discovered during the evaluation of
prototypes, an incremental development
methodology has been adopted, but devised for
smaller equipment.
Sequence diagrams were also used, quite
common in program development and data flow
diagrams, more used in projects with
microcontrollers.
Figure 3 shows a representation of the equipment
used in the system development, as well as the
physical interconnection between them. In this
assembly, an outside line Public Switched Telephone
Network (PSTN) was used, connected to the TLM to
make external calls.
Figure 3: Experimental assembly.
NodeBuilder and LonMaker softwares were used
for the program development. Both are provided by
Echelon. LonTalk Protocol Analyzer (LPA)
software, developed by Loytec, was also used
(Loytec, 2008).
The TLM and DTM devices were developed
with NeuronChip microcontroller, and meet the
following project requirements:
• low overhead communication: to reduce the
data traffic amount on the network, leaving
a greater free bandwidth for the voice
messages traffic.
• to use of the smallest number of entries in
the tables used for device configuration: the
device aims to keep compatible to be
applied to other control network features.
• to use a telephony compatible time to the
bindings configuration (or closing the
phone link): avoid discomfort to the user,
and maintain compatibility with already
installed PABX systems.
• to dispense human operation and maintain
the device full independence: ensures that
the system does not require constant
maintenance and keeps their integrity for
long periods.
As a way to evaluate the solution proposed, the
LonWorks
®
network analyzer was used to measure
the total time consumed by the dynamic binding
process proposed, comparing with the standard
binding process, and checking whether the result
meets the time requirements of the project, that is
one second (to meet the standards of Brazilian
telephony).
Several tests were also conducted, involving
external calls request and calls receiving, forcing the
process to be performed many times.
3 PROPOSED MODEL
As a way of meeting the specifications mentioned in
the previous item, an extra software layer was added
to each device, including the functionality of the
device, and representing the reactive agent, as
illustrated in Figure 4:
Figure 4: Reactive agent layer.
APPLICATION OF REACTIVE AGENTS CONCEPTS IN AUTOMATIC BINDINGS OF LONWORKS NETWORKS
DEVICES
261

To facilitate the solution development, the
problem was divided into three stages: the first one
includes the handshake and the decision parameters
to be used in the binding configuration, the second is
to achieve the proper bindings, and the third stage
involves the process for undoing the bindings,
leaving the devices available for new connections.
3.1 Stage 1
To perform this stage, the device must be in an
initial waiting state, in which the agent is active and
attentive to any requests for connections from other
agents.
When the device receives a call or request for
assistance, the agents will exchange direct messages
between themselves, adjusting the parameters
needed to achieve the bindings.
This stage is completed when both have all the
settings necessary for the binding to be achieved.
3.2 Stage 2
With the parameters adjusted, they should begin the
configuration process. At this point, it is worth
mentioning that each agent is responsible for
conducting its own configuration process, not
interfering with the process of another agent.
If there is any failure in the execution of this
stage, the device sends a message of failure to the
other agent, indicating that the process should be
canceled.
After the setup process, they perform a check to
ensure it was successful and that the communication
can be initiated.
With a positive response of the final assessment,
the exchange messages of telephony are initiated,
including the whole call progress process and voice
message exchange. At this time, the agent gets away
from control, passing it to the basic operating
software of the device.
3.3 Stage 3
When the call is finished, the agent takes back the
control and performs all the configuration of the
device, so that the bindings are undone and the
device is ready to perform a new call.
At this stage, the communication between agents
is not necessary, because it involves only the
configuration of the internal tables of each device.
4 RESULTS ANALYSIS
The stage 1 obtained average time was
approximately 23 ms. This time is due to the need of
several message exchanges between the devices for
the parameters to get adjusted.
Furthermore, depending on the case, it is
necessary for the settings table to get swept several
times, until the agents enter into a consensus about
which values can be used.
The traditional method of conducting bindings,
made from the LonMaker tool is naturally much
faster, since it does not require the exchange of
messages between devices and the configuration tool
already knows the free values that can be used.
Various failures simulations were also
performed, such as loss of communication during
the process, and all tests showed that the solution is
effective in failure recovering and left the devices
ready for another attempt.
In stage 2, the average time needed to perform
the required configurations was approximately 602
ms.
This time was measured from the receipt of the
message containing the configuration values
adjusted between the devices and the first call
progress message.
This time is justified by the fact that the device
must make all the configuration parameters in these
tables that are stored in the EEPROM memory area,
a memory type that demands a longer time for
completing records.
When performing the same procedure with the
LonMaker, the average time obtained was 1,983 ms.
This long time is due to the fact that besides having
to write data into EEPROM memory, all the
configuration and verification is conducted through
the control network, with device management
messages.
Finally, the results analysis for stage 3 did not
take into consideration the completion time, but if
the devices were in a waiting state, as specified
before.
After this step, one can verify that the bindings
were completely undone and the devices were free
to receive new connections. Figure 5 shows the
devices tables at the end of stage 2.
The tables below, containing binding information
between the device TLM (MLT) and DTM (MTD),
show that the telephone link between them was
made.
ICINCO 2009 - 6th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
262

Figure 5: Table setup with bindings between devices.
Figure 6 shows the same table at the end of stage 3.
Figure 6: Configuration tables at the end of stage 3.
As seen, all the configuration entries have been
deleted and, therefore, the devices are free for new
connections.
5 CONCLUSIONS
The total mean obtained in completing the telephone
link process, from the beginning of the stage 1 to the
end of the stage 2, was approximately 625 ms, which
is considered a good result for telephone systems.
This result means that after the user enters a phone
number or make a request for external line, he will
hear the calling signal or external line tone signal
after about 625 ms, time barely noticeable by the
user.
At the end of stage 3, the devices had been
effective in returning to the original state and ready
to receive new calls.
From the point of view of multi-agents systems,
a reactive agent was applied with reservations to the
communication means used.
A characteristic of reactive agents is to have a
primitive method of communication, often using
only the very environment in which they are inserted
(Wooldridge, Jennings, 2002). In this solution, the
agents exchanged messages by a complex network
protocol.
However, these agents did not have any model
type: of the environment model, of other agents, and
of their own model. They were not able to make
inferences, to perform learning or to seek
knowledge.
They only reacted to external stimuli as a
previously implemented logic that could not be
changed at runtime, which are features of a reactive
agent (Wooldridge; Jennings, 2002).
Through the application agents’ concepts, the
presented solution meets the requirement of
maintaining the devices autonomy, since they do not
depend on external commands to configure
themselves.
Also, no human intervention was required during
the process execution, no form of communication
used during the exchange of voice messages is
LonWorks
®
standard and no overhead was added to
the protocol. Only the minimum necessary
parameters were used for the bindings configuration.
Thus, the conclusion is that all project
requirements were met.
As an improvement to consider, there is the
NeuronChip memory implementation. As
LonWorks
®
technology considers that bindings are
permanent, their settings are stored in an EEPROM
area, which may support approximately 1,000,000
recordings (Motorola, 1997). For example, assuming
that under heavy use 50 calls are made per day from
a certain branch, which corresponds to 100
recording procedures in the EEPROM memory, the
durability of the equipment would be approximately
27 years.
6 FUTURE WORK
In the context of the DSPTS project, one can
imagine the possibility of applying cognitive agents
APPLICATION OF REACTIVE AGENTS CONCEPTS IN AUTOMATIC BINDINGS OF LONWORKS NETWORKS
DEVICES
263

to solve greater complexity problems and that may
require a system with greater integrity and decision
capability.
As example of such problems, there is the
decision of which attendant branch will take an
incoming call for an installation where there are
many attendants’ branches. This could be solved
through the use of auctions with pre-established
metrics, method widely used in cognitive agents
societies (Benisch et al., 2004).
For a broader case that involves the entire
LonWorks
®
technology, the implementation and
evaluation of new hardware for the network nodes
can be proposed, enabling the storage of bindings
information in RAM. This would remove the
restrictions associated with the EEPROM memory,
allowing faster bindings and a longer system life
time.
A natural DSPTS continuity suggestion is related
to the design of building automation systems based
on LonWorks
®
technology that integrate the PABX
functions.
ACKNOWLEDGEMENTS
The authors wish to thank the Fundação de Amparo
à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo (FAPESP),
project number 05/56045-6, and the company
Conceito Tecnologia, for the support granted to this
research.
REFERENCES
Benisch, M., Greenwald, A., Grypari, i., Lederman, R.,
Naroditskiy, v., Tschantz, M., Botticelli. A Supply
Chain Management Agent. Proc. 3
rd
. Int. Conf. On
Autonomous Agents and Multi Agent Systems
(AAMAS´04), ACM Press (New York), p. 1174-1181,
2004.
Bigham, J., Du, L. Cooperative Negotiation in a Multi-
Agent System for Real-Time Load Balancing of a
Mobile Cellular Network. In: Proceedings of the
Second International Joint Conference on Autonomous
Agents and Multiagent Systems, 2., 2003, Melbourne
(Australia). International Conference on Autonomous
Agents. Nova York: ACM, 2003. p.568-575.
Boissier, O., Demazeau, Y. Asic: An Architecture for
Social and Individual Control and its Application to
Computer Vision. Modeling Autonomous Agents in a
Multi-Agent World, v. 1069, 1994.
Castelfranchi, C. Modeling Social Action for AI Agents.
Artificial Intelligence, Elsevier Science Publishers
Ltd, v. 103, n. 1, p. 157-182, 1998.
Conceito Tecnologia. The company's website containing
information on the LonWorks
®
technology and some
examples of application. Available at:
<http://www.conceitotecnologia.com.br>. Access at:
12 feb. de 2008.
Durfee, E. H., Rosenchein, J. S. Distributed Problem
Solving and Multi-Agent Systems. Proceedings of the
International Workshop on Distributed Artificial
Intelligence, 1994.
Echelon Corporation. The company's website containing
information on the LonWorks
®
technology. Available
at: <http://www.echelon.com>. Access at: 17 de jun.
de 2007.
Estados Unidos. Echelon Corporation. Neuron C
programmer’s guide. Palo Alto, 1995, 1 v.
Estados Unidos. Echelon Corporation. Introduction to the
LonWorks
®
System, Palo Alto, 1999. 1 v. (078-0183-
01A).
Estados Unidos. Echelon Corporation. LonMark Layer 1-6
Interoperability Guidelines, Palo Alto, 2002. 1 v.
Estados Unidos. Echelon Corporation. LonMaker User’s
Guide, Palo Alto, 2003. 3.1 v. (078-0168-02E). (a)
Estados Unidos. Echelon Corporation. NodeBuilder
User’s Guide. Palo Alto, Echelon, 2003. 1 v. (b)
Estados Unidos. Motorola. LonWorks
®
Technology
Device Data, rev. 4, 1997.
Liviu, P., Sean, L. A Pheromone-Based Utility Model for
Collaborative Foraging. Proc. 3
rd
. Int. Conf. On
Autonomous Agents and Multi Agent Systems
(AAMAS), p. 36-43, 2004.
Lonmark International. Site of standardized organ for
LonWorks technology and products certification.
Available at: <http://www.lonmark.org/>. Access at:
19 jan. 2008.
Loytec. The company's website. Available at:
<http://www.loytec.com/english/products/lcore.htm>.
Access at: 19 jan. 2009.
Rao, A. S. AgentSpeak(L): BDI Agents speak out in a
logical computable language. Australian Artificial
Intelligence Institute, 1996.
Rao, A. S., Georgeff, M. P. Modeling Rational Agents
within a BDI-Architecture. Proceedings of the 2nd
International Conference on Principles of Knowledge
Representation and Reasoning (KR'91), USA, p. 473-
484, 1991.
Shoham, Y. Agent-Oriented Programming. Journal of
Artificial Intelligence, n. 60, p. 51-92, 1991.
Steels, L. Cooperation between distributed agents through
self-organization. Intelligent Robots and Systems '90.
'Towards a New Frontier of Applications',
Proceedings. IROS '90. IEEE International Workshop,
Japan, p. 8-14, 1990.
Wooldridge, M., Jennings, N. Introduction to Multi-Agent
Systems. USA: JASSS, 2002.
Xie, C., Pu, J.-S., Moore, P. R. A case study on the
development of intelligent actuator components for
distributed control systems using LONWORK neuron
chips. Mechatronics v. 8, n. 2, p. 103-119, 1998.
ICINCO 2009 - 6th International Conference on Informatics in Control, Automation and Robotics
264
