
Information Driven Modeling:
The Integration of Enterprise Ontology and Enterprise
Architecture for the Mature BI
Jorge Cordeiro Duarte and Mamede Lima-Marques
Centre for Research on Architecture of Information
University of Brasilia – UnB, Brazil
Abstract. There is a huge interest in the area of engineering ontologies for a
very wide range of applications. In modern enterprises and their business
process management and decision making, modeling and Business Intelligence
(BI) play a significant role. Information Technology (IT) contribution to
business strategies and decisions has been questioned. The problem is not with
IT, but with business complexity in modern times. The challenge of enterprise
intelligence is a mission for the whole enterprise, and depends on intensive
collaboration among organizational units. Enterprise BI requires new
approaches, methods and tools focused on integration. BI must be part of
Enterprise Architecture (EA). This paper offers a new insight on Business
Intelligence. It proposes an extension of Archimate methodology in order to
integrate EA and BI efforts with enterprise ontology to provide mature
enterprise decisions.
1 Introduction
Business Intelligence (BI) is neither a product, nor technology nor methodology [24].
BI is a powerful management approach that can deliver knowledge, efficiency, better
decisions, and profit to organizations.
BI initiatives can improve business performance in many ways, including better
targeted products, improved customer relationship management, and greater
operational efficiency. It can also result in reengineering of business processes.
When BI first came on the scene, it promised a lot but often failed to deliver.
Despite the potential, success is not necessarily guaranteed. In fact, surveys revealed
that more than 60 percent of companies with BI initiatives had only limited success in
meeting user expectations. Studies also indicated managerial or business customer
resistance to data warehousing for several reasons including the fear of losing control,
lack of technical skills, costs, and uncertainty about their utility.
As the deployment of a BI system requires a multimillion-dollar investment and
other resource mobilization, a well conducted project must take place. IT contribution
to business strategies and decisions has been questioned but the problem is not IT,
The problem is business complexity in modern times. Business Intelligence is one of
Cordeiro Duarte J. and Lima-Marques M. (2009).
Information Driven Modeling: The Integration of Enterprise Ontology and Enterprise Architecture for the Mature BI.
In Proceedings of the 1st International Workshop on Ontology for e-Technologies OET 2009, pages 52-65
DOI: 10.5220/0002229300520065
Copyright
c
SciTePress

the most complex initiatives a company can have. It deals with many enterprise
domains, each one with its own complexity.
First of all, BI projects are very complex. The challenge is how to control this
complexity. BI initiative must have approaches, methods and tools that deal
objectively with complexity. The challenge for enterprise is linking information to the
organization strategic goals, culture, and strengths while tracking the technological
and administrative complexity.
In spite of the increasing importance of BI, there is little interest in academic
research about this subject. This lack of research limits our understanding of how BI
projects can succeed. There are many open question related with BI: How we can take
control of complexity in BI initiatives? How projects can be successfully conduced?
We can distinguish two major challenges in a BI project, each one with its own
complexity: a business and a technical challenge. This paper makes an exploratory
study to enhance general understanding of BI Projects, but the main focus is to
explore business variables related to BI success, specifically at the enterprise
modeling stage. The paper proposes that good enterprise models can reduce the
complexity of business side of BI projects. It explores the influence of information
and ontology in enterprise modeling and proposes a new approach of modeling the
enterprise based on information modeling. This proposal extends Archimate language,
a new approach on Enterprise Architecture (EA). The contribution of this paper is a
proposal that reduces drastically the business side of BI projects by presenting a
methodology that supports the modeling and understanding of business.
This paper is organized as follows: session 2 discusses the BI benefits and
challenges. Session 3 looks at complexity in business and technology. Session 4
explores information modeling and ontologies: its evolution, contribution and
challenges. Session 5 studies the evolution and challenges of enterprise architecture.
Session 6 resumes the relation of BI with enterprise wide modeling. Session 7 makes
a proposal of extending the Archimate language in order to support information and
ontology approaches. Session 8 shows an application of this approach being
conducted in a insurance company, Finally, session 9 presents a conclusion and
propose future works.
2 Business Intelligence Concepts and Challenges
BI is neither a product nor a system. It is an architecture and a collection of integrated
operational as well as decision-support applications and databases that provide the
business community easy access to business data [24].
There is much to say about BI concepts, finality, methods and technology. For
those interested in business and technical side of BI we recommend Larissa Moss´
[13] and Steve Williams´ [24] books. We highlight some considerations made by the
authors:
BI presents many benefits. It can increase sales, reduce costs and increase
profits.
BI requires preconditions for success. There are Business preconditions, like
strategic alignment, process engineering and change management, and
53

technical preconditions like BI technical development and BI project
management.
BI requires a methodology with many steps, like business analyses, data base
design and implementation and ETL design and implementation.
Producing reliable information is the ultimate goal of BI. The ocean of data
created with the advances of science and technologies call for integration of
data coming from heterogeneous sources that are diverse in their purposes.
BI is a collaborative project and needs the participation of application lead
developer, business representative, data Administrator, data quality analyst,
database administrator, ETL lead developer, meta data administrator, project
manager and subject matter expert.
BI presents a great rate of failure and users dissatisfaction.
In order to reach success, BI projects must have some essential abilities: (1)
ability to align and govern strategic alignment, business-IT partnership and
BI portfolio management; (2) ability to leverage cultures like information
and analytics use, continuous process improvement and decision process
engineering and (3) ability to deliver technologies like DW and BI software.
Concluding, Enterprises are complex, technology is complex and BI is a complex
project. IT projects comprises business and technological sides. Rate of failures are
high. Business and IT must collaborate to BI success.
3 BI and Enterprise Maturity
BI is an initiative of great proportions. Taking its characteristics, perhaps BI can be
considered the enterprise initiative that depends most on the integration between
business and IT. BI project has few chance of success when we do not have enterprise
and IT maturity and when the relation between both is not also mature.
Enterprise maturity is a subject much discussed is literature with a well
established proposal standard like CMMI [4]. Maturity is related with the capacity of
coordinating continuously improving results. Maturity is provided by repeatable,
well-defined and managed programs.
IT maturity also presents standards, like COBIT [5] and ITIL [11]. COBIT is
related with IT governance and consists on leadership, organizational structures and
processes that ensure that the enterprise’s IT sustains and extends the organization’s
strategies and objectives. ITIL is a library of good practices for IT services.
Chen [1] proposes a framework for undestanding Business-IT Alignment. He
identifies the alignment approaches: alignment via architecture, alignment via
governance, and alignment via communications. These three approaches are
integrated in the BITAM-SOA Framework depicted in Figure 1.
54
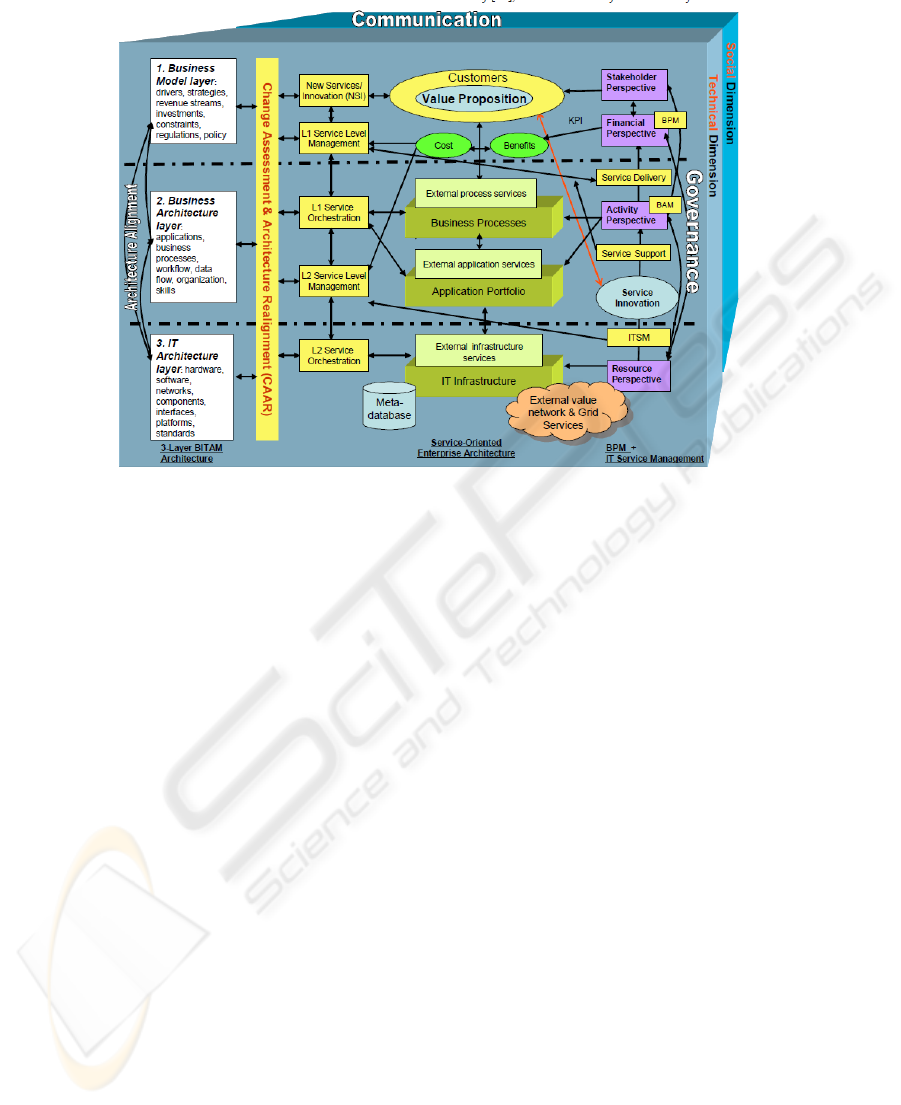
Fig. 1. BITAM-SOA Service Engineering Schematic [2].
Cumps, Viaene and Dedene [7] identified the following approaches IT must have in
order to contribute to Business-IT Alignment:
Change management
Strategic IT planning
Risk management
Enterprise architecture management
Performance management
Program/portfolio management
Service-level management
Project management
Concluding, enterprise maturity, IT maturity, and Business-IT alignment are
preconditions of success in BI projects because it is almost impossible to succeed
without IT governance and good practices and well defined and managed enterprise
wide programs.
4 BI, Information Modeling and Ontologies
BI is related with enterprise intelligence and so it is related with data, information,
knowledge and ontologies in enterprises. Enterprise Information modeling and
ontologies are attracting attention of researches [20].
55

Data modeling is one of the most mature methodologies in information systems (IS).
It has well established standards and tools [2]. It is well accepted for the community.
Data Administrator is a profession well recognized. Enterprises has not acquired the
same standard in business information yet.
Despite many researches made by famous researchers like Davenport [8],
Choo[4] and Everdeen [11], information modeling and management in business side
have not been well understood yet and little practice has been presented to the subject.
Recent contributions to information and knowledge modeling have been done by
enterprise ontology research.
Ontology is defined as a specification of a conceptualization [10]. Ontologies
provide a number of useful features for intelligent systems, as well as for knowledge
representation in general and for the knowledge engineering process [9].
Ontologies can vary in expressivity and formalism, like figure 2 shows, and have
some specific languages, like OWL and specific tools like Protege [9].
Fig. 2. Expressivity and formalization on ontologies [9].
There are many potential applications of ontologies like collaboration, interoperation,
education and modeling. Many researchers found that ontologies can help
organizations in reducing complexity, modeling strategies [15] (figure 3) and other
enterprise elements, like information systems technology [20] (figure 4).
Fig. 3. Enterprise ontologie for enterprise performance [15].
56

Fig.4. Ontologies and information systems [20].
Concluding, ontologies can be of great value for BI projects helping understanding
the business by defining its main elements and showing the relation among then.
5 BI and Enterprise Architecture
BI is related with business and technology. So it demands models from business and
from technology and models showing the relation between both. EA is the discipline
that studies these kind of enterprise wide modeling.
We can find many researches about Enterprise Architecture (EA). For those
interested on the foundations, methods, languages and tools of EA we recommend
Lankhorst´ [17], Ross´ [21] and Weske´ [23] books. Follows a resume of EA from
these authors:
EA defines a firm’s needs for standardized tasks, job roles, systems,
infrastructure, and data in core business processes.
EA is a coherent whole of principles, methods, and models that are used in
the design of an enterprise’s organizational structure, business processes,
information systems, and infrastructure.
EA identifies the main components of an organization and how they work
together to achieve defined business objectives.
EA models components include personnel, business processes, technology,
financial information and other resources.
Business and IT communities need to share a common understanding of the
principles underlying enterprise modeling.
While administration professionals tend to consider information technology
as a subordinate aspect for experts to handle, by contrast computer scientists
often consider business goals and organizational regulations as terms that do
not deserve much attention.
EA include high-level business aspects like business goals, strategies, and
value chains and also technical models, taking into account the different
stakeholders involved as figure 5 shows.
EA can use a variety of process languages, including Workflow nets, Event-
driven Process Chains, Yet Another Workflow Language, and the Business
Process Modeling Notation.
57
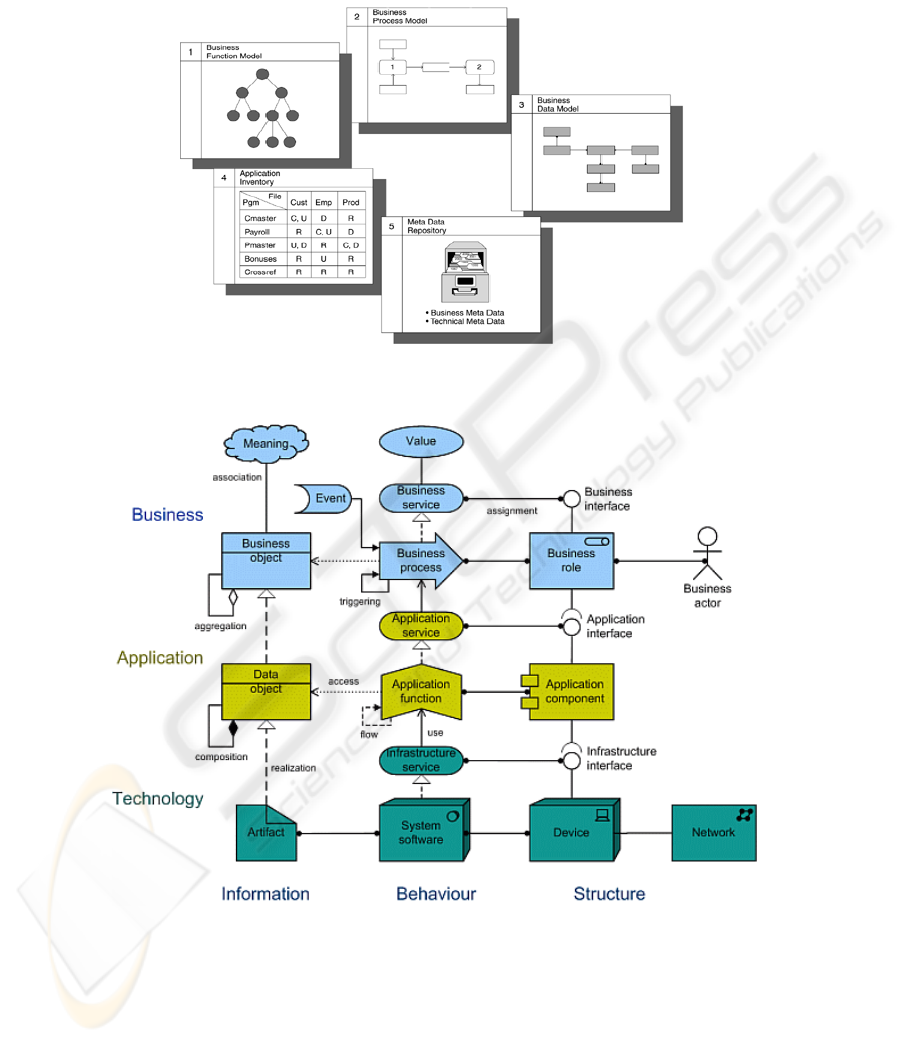
EA can have a specific language like Archimate (Figure 6).
The lack of a pattern difficult the maturity of the process.
Fig. 5. EA models [18].
Fig. 6. Archimate Language [17].
EA provides enterprise wide models of business, information, systems and
technology. It is an essential part of business side of BI. So, we can conclude that
having an EA program, we have enterprise knowledge and BI is likely to succeed.
58

6 A Mature BI Business Side
The main purpose of BI is to provide support to enterprise decisions. BI presents
business and technological sides. In previous sections we analyzed many business
sides like enterprise maturity, IT maturity and enterprise wide modeling efforts like
EA and knowledge modeling.
We found some related works at literature linking EA with BEA [22] [23] but
they are not information driven and do not use Ontologies. Considering the state of
the art of BI, data modeling, information modeling, knowledge modeling, enterprise
modeling, ontologies and EA we find they have much in common and must
collaborate. We can summarize our analyses in the following remarks:
Business side of BI must have strong sources of Knowledge about enterprise
objects.
Information and knowledge models approaches are evolving in enterprise
side and can provide sources of knowledge about enterprise objects.
Enterprise wide modeling is evolving, with the maturity of EA methodology
and tools that can help business people understand the enterprise objects.
Enterprise mature approaches can provide the environment BI needs to
succeed in its business side.
IT mature approaches can provide the technical environment BI needs to
succeed.
Business-IT alignment mature approaches can provide the global
environment BI needs to succeed.
Enterprise wide models are evolving and we need studies analyzing the impact of it in
organizations. All the remarks above are related with BI projects, based on theory and
must be proved with case studies. We suppose organizations do not have sufficient
practice for a large survey so we must validate this theory in a case study. We have
intention to make this study but first we need an integrated approach to BI which is
given in the next section.
7 Information Driven Modeling: EA for BI with Information
Modeling and Ontologies
Enterprise Modeling needs a language to integrate enterprise objects. We have many
modeling languages for specific purposes. When talking about modeling enterprise
objects we can find ontologies languages like OWL. EA approach tries to consolidate
different models in enterprise frameworks. A specifically language for EA called
Archimate has recently appeared.
We have found Archimate a good methodology for EA that can be also a good
contribution to BI. But we propose to extend Archimate for information and business
strategies modeling.
Figure one shows our proposal of Archimate extension. It presents the following
elements that Archimate does not consider:
59
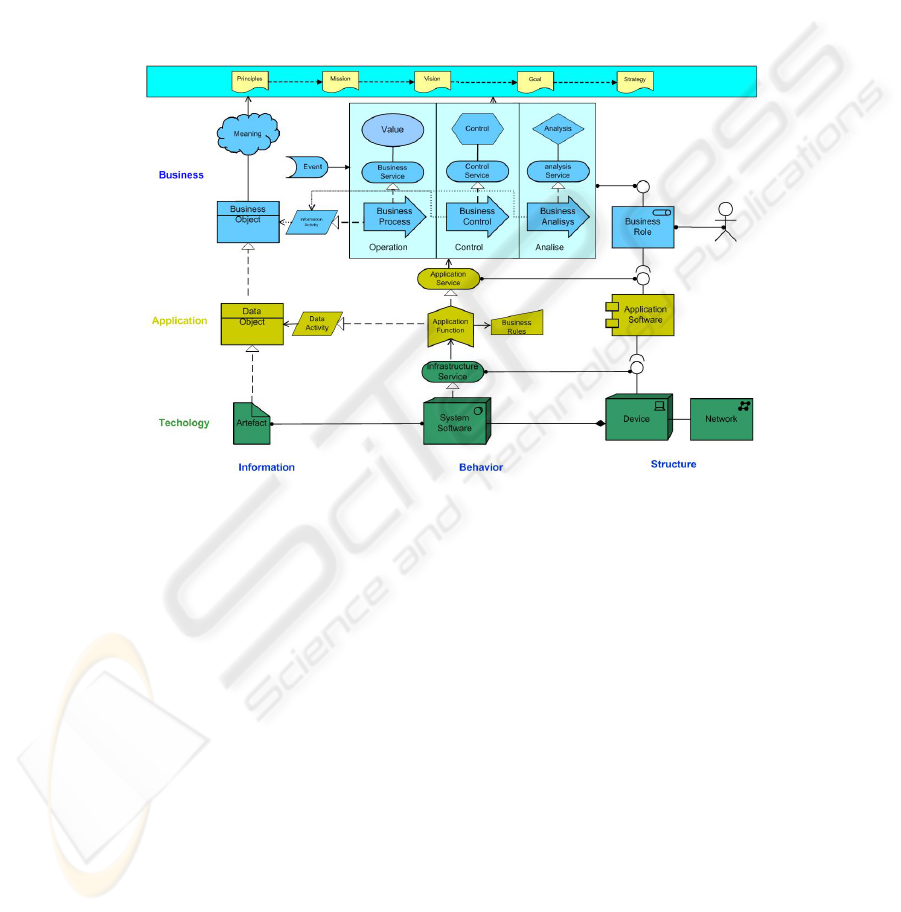
Information activity;
Control;
Decision;
Mission, goals and strategies
This proposal is based on information. What drives analyses is information activity.
We identify an information object and then its activities. It brings MER to business,
identifying information entities, information activities and establishing information
relations with all business objects.
The benefit of this approach is that is easier for people to understand. Figure 7
shows the proposal of Archimate extension.
Fig. 7. Archimate extended.
8 A Case Study
We are applying the approach described in a big insurance company in Brazil that has
a BI project in one of its units. This Unit comprises more ten million clients, twenty
million contracts and two millions transactions monthly. The BI project is very
complex in business and technical side.
In business side the complexity was reduced by adoption or the Archimate
methodology extended with the information approach. This method helps to identify
information and its relations ant also the relations of each information activity to
strategies, controls and operations.
With the use of Archimate (by a Vision stencil) people can easily understand also
the relation of information with data in the application and in the datawarehouse.
With protégé people can see the information defined and its relations.
60

Figure 8 shows a information object, its activities and each relation with operations,
controls and decisions. Figure 9 shows protege and information relations. Figure 10
shows information relations with data.
Fig. 8. Information and business relations.
Fig. 9. Information and its relations.
61
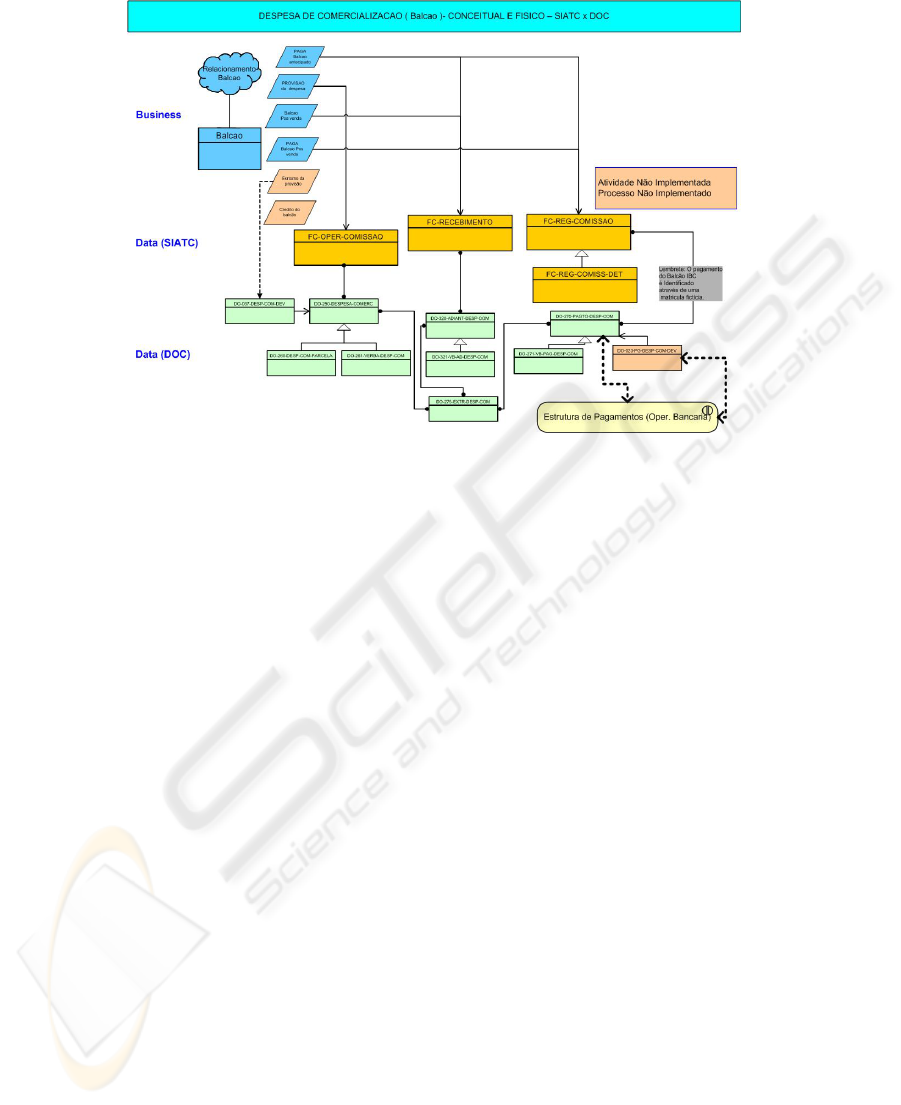
Fig. 10. Information and its relation with data.
The project is not concluded but results can be seen in adopting this approach. Objects
relations became clear. Documentation is better. Modeling activities are faster.
Overall time of activities is lower.
9 Conclusions
In this paper we analyzed BI projects, their business side and their relation with
enterprise wide modeling efforts like EA and enterprise ontologies. We explored the
benefits of the integration of BI with enterprise wide modeling efforts. We also
explored the relation of BI with enterprise maturity and IT maturity take the
information first.
Based in this theoretical analyses we conclude that enterprise wide modeling
reduce BI complexity. We also conclude that enterprise maturity and IT maturity
approaches helps BI projects to succeed.
We have proposed to model the enterprise using Archimate language in order to
provide BI with an integrated view of the organization based on information activity.
This approach was tested in a real application and proved its efficiency.
This study contributes to researchers and practitioners with a broader vision of
BI. It proposes an approach based on the integration of BI with enterprise modeling to
reduce the complexity. Certainly EA and ontologies with Archimate extended and
Protege help to reduce BI complexity and contribute to its success. BI is a field
research with many open questions. Our proposal is to continue research in tools. EA
62

tools must be better integrated better. Ontologies tools need to be integrated with ea
tools.
References
1. Cao, Longbing; Luo, Chao;Luo, Dan; Liu, Li. Ontology Services-Based Information
Integration in Mining Telecom Business Intelligence. PRICAI 2004: Trends in Artificial
Intelligence. Volume 3157, PP 85—94 (2004).
2. Chen, Hong-Mei .Towards service engineering: Service orientation and business-IT
alignment. Proceedings of the Annual Hawaii International Conference on System
Sciences. (2008).
3. Chen, Peter Pin-shan. The Entity-Relationship Model - Toward a Unified View of Data.
ACM Transactions on Database Systems. 1, 9--36 (1976).
4. Choo, Chun W. Information management for the intelligent organization: the art of
scanning the environment. ASIS monograph series (1998).
5. CMMI Product Team (2002), Capability Maturity Model Integration (CMMI), Version 1.1,
Staged Representation, CMU/SEI-2002-TR-029, ESC-TR-2002– 029, Software
Engineering Institute, Carnegie Mellon University, Pittsburgh,Pennsylvania.
6. COBIT (2000), Control Objectives for Information and related Technology (COBIT), 3rd
Edition. IT Governance Institute, Rolling Meadows, Illinois.
http://www.isaca.org/cobit.htm.
7. Cumps, B.; Viaene, S.; Dedene, G.; Managing for Better Business-IT Alignment IT
Professional Volume 8, Issue 5, Sept.-Oct. 2006 Page(s):17 – 24.
8. Davenport H., Ecologia da Informação. São Paulo: Editora Futura, 1998.
9. Dragan Gasevic,·Dragan Djuric,Vladan Devedzic. Model Driven Architecture and
Ontology Development. Springer (2006).
10. Evernden, R.The Information FrameWork. IBM System Journal. Vol. 35 , 37--68 (1996).
11. Evernden, Roger; Evernden, Elaine. Information First: Integrating Knowledge and
Information Architecture for Business Advantage. Butterworth-Heinemann, London
(2003).
12. FEAPMO. Federal Enterprise Architecture. (2004) http://www.feapmo.gov.
13. Gruber, T.R. A translation approach to portable ontology specifications. Knowledge
Acquisition. 5 (2),199—220 (2004).
14. ITIL. "ITIL® Service Management Practices: V3 Qualifications Scheme" http://www.itil-
officialsite.com/nmsruntime/saveasdialog.asp?lID=572&sID=86. Retrieved on 2009-02-24.
15. Jussupova-Mariethoz , Helena; Probst, Andre-Rene .Business concepts ontology for an
enterprise performance and competences monitoring. Computers in Industry. 58 , 118--129
(2007).
16. List, Beate and Korherr, Birgit. An evaluation of conceptual business process modelling
languages. Proceedings of the 2006 ACM symposium on Applied computing. 1532—1539
(2006).
17. Marc Lankhorst et al. Enterprise architecture at work - Modelling, communication and
analysis. Springer, Heilderberg (2005).
18.
Moss, Larissa T; Atre Shaku .Business Intelligence Roadmap: The Complete Project
Lifecycle for Decision-Support Applications. Addison Wesley (2003).
19. OMG. Unified Modeling Language (UML), Version 2.0. 2003,
http://www.omg.org/docs/formal/07-11-04.pdf. last access 02-03-2009.
20. Rebstock, Michael; Fengel, Janina; Paulheim, Heiko. Ontologies-Based Business
Integration. Springer (2008).
21. Ross, Jeanne W.;Weill, Peter; Robertson David. Enterprise Architecture As Strategy:
Creating a Foundation for Business. Harvard Business School Press, New York (2006).
63

22. Stefanov, Veronika; List Beate; and Schiefer; Josef. Bridging the Gap between Data
Warehouses and Business Processes - A Business Intelligence Perspective for Event-Driven
Process Chains. Proceedings EDOC ’05, IEEE Computer Society. 3—14 (2005).
23. Weske, Mathias. Business Process Management: Concepts, Languages, Architectures.
Springer , Heilderberg (2007).
24. Williams Steve, The Profit Impact of Business Intelligence. Morgan Kaufmann, London
(2006).
64
