
A SELF-CONFIGURING MIDDLEWARE FOR MANAGING
CONTEXT AWARENESS
Ionut Anghel, Tudor Cioara, Ioan Salomie, Mihaela Dinsoreanu and Anca Rarau
Computer Science Department, Technical University of Cluj-Napoca, 15 Daicoviciu Street, Cluj-Napoca, Romania
Keywords: Pervasive Systems, Self-Configuring, Middleware, Context Awareness, Autonomic Computing.
Abstract: This paper introduces a self-configuring middleware that manages the context information acquisition and
representation processes targeting the development of context aware applications. The context information
is represented using three sets: context resources, actors and policies. The context model management
infrastructure is constructed using BDI (Believe Desire Intentions) agents that generate and administrate the
context model artefacts at run time. The self – configuring property is enforced by monitoring the real world
context in order to detect context variations or conditions for which the context artefacts must be updated.
The advantage of our approach is the transparency of the context management processes for the pervasive
application developers, allowing them to focus on the application desired functionality. The middleware was
tested and validated within the premises of our Distributed Systems Research Laboratory.
1 INTRODUCTION AND
RELATED WORK
An important challenge in developing context aware
applications is the dynamic nature of their execution
environment which makes the process of context
information acquisition and representation extremely
difficult to manage. During the context information
acquisition process, the sources of context
information (e.g. sensors) can fail or new context
information sources may be identified. The context
acquisition and representation processes need to be
reliable and fault tolerant. For example, a pervasive
application cannot wait indefinitely for an answer
from a temporary unavailable context resource. On
the other hand, many times the payoff for not taking
into consideration the new available context
resources can be very high. To provide an efficient
context information management, it is necessary to
introduce some degree of autonomy for the context
acquisition and representation processes.
Another important challenge in the context aware
application development is to assign the context
management responsibility. Current approaches put
the pervasive system developers in charge with the
context management process which makes
developing a pervasive system extremely
complicate. Our vision is that a third party context
management infrastructure must deal with processes
like context information acquisition and
representation.
This paper introduces a pervasive self-
configuring middleware that uses a context
management infrastructure to gather context
information from sensors and generate a run-time
context representation. As a consequence, the
context management processes are transparent for
the context aware application developers, allowing
them to concentrate on designing and implementing
the application desired functionality. Also, the
middleware supports dynamic configuration of the
context elements used by the pervasive application.
In order to achieve our goal we have identified
three major problems: (i) context representation, (ii)
context management and (iii) automatic discovery
and setup the new context resources. In the
following we discuss the state of research for each
problem.
For context representation, generic models for
accurately describing the real context in a
programmatic way are proposed. In (Rarau, 2006),
the concept of multi-faceted entity is defined and
used to model the set of context properties. A facet
represents the effective values of context properties
to which the context sensitive application has access.
The main drawback of this approach is the lack of
semantic information encapsulated in the facet
concept. As a result, inferring new context related
131
Anghel I., Cioara T., Salomie I., Dinsoreanu M. and Rarau A. (2009).
A SELF-CONFIGURING MIDDLEWARE FOR MANAGING CONTEXT AWARENESS.
In Proceedings of the International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems, pages 131-138
DOI: 10.5220/0002233701310138
Copyright
c
SciTePress
knowledge is difficult. An original approach to the
context modelling problem is the use of parametric
state machines for representing a context aware
system (Chen, 2006). The context is modelled using
context functions that modify the context aware
system’s state. The complexity of a real system’s
associated parametric state machine, in terms of the
number of states and transitions, is the main
disadvantage of this approach. The use of ontologies
is a new context modelling direction. The context
properties are represented as ontological concepts
during design time and instantiated with run-time
sensor captured values (Feruzan Ay, 2007), (Lee,
2007). The main disadvantage of this approach is the
high degree of inflexibility determined by the human
intervention in the context representation phase.
For the context management the researches
concentrate on developing techniques for keeping
the context representation consistent with the real
context. In (Bellavista, 2006), models for capturing
and updating the context information based on the
information type are proposed. Fournier defines
reusable components for updating the context
specific data (Fournier, 2006). These components
provide stable communication channels for
capturing and controlling context specific data. In
(Spanoudakis, 2007), the authors propose the
development of context guided behavioural models,
which allow context aware applications to detect
only those context data variations that lead to the
modification of their behaviour.
For the automatic discovery and setup of new
context resources self-configuring management
systems that can automatically discover and react to
the new identified context resources are proposed
(Bahati, 2006). A context adaptive platform based
on the closed loop control principle for managing
the context representation is proposed in (Cremene,
2007). The novelty of this proposal consists in
defining and using the concept of application-
context description to represent context related
system knowledge. The description is frequently
updated and used for automatic reconfiguring and
taking adapting decisions.
The main contribution of our approach is the
definition of a self-configuring middleware targeting
the development of context aware applications. The
fundamental element of this middleware is the
context model which represents the context
information using three sets: context resources,
actors and policies. The context model management
infrastructure is implemented by using BDI agents
(Rao, 1995) that generate and administrate the
context model artefacts at run time. The middleware
self-configuring feature is implemented by
monitoring and evaluating the environment changes
in order to keep the context artefacts updated. The
proposed middleware is tested and validated using
our laboratory, Distributed Systems Research
Laboratory (DSRL), as a smart space infrastructure.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows: in
Section 2, the middleware architecture is presented;
Section 3 presents the self-configuring enhanced
middleware; Section 4 shows how the middleware is
used to manage the context representation of an
intelligent laboratory environment while Section 5
concludes the paper and shows the future work.
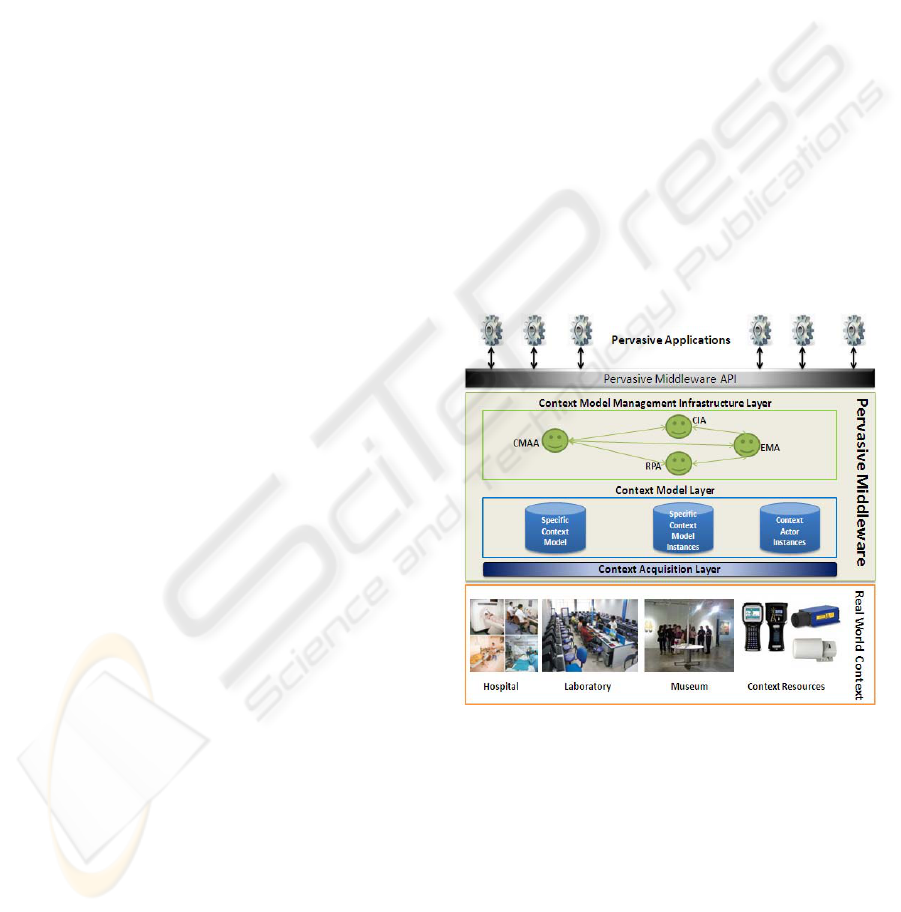
2 A PERVASIVE MIDDLEWARE
The pervasive middleware architecture defines three
main layers (Figure 1): the acquisition layer that
captures the context information from real world
contexts, the context model layer which represents
the context information in a machine interpretable
way and the context model management
infrastructure layer.
Figure 1: The Pervasive Middleware Conceptual
Architecture.
In the following we detail each of the three
middleware architectural layers.
2.1 The Context Acquisition Layer
The context information acquisition layer design
takes into consideration the following aspects: (i) the
sensor information retrieval mechanism and (ii) the
visibility of the sensor information to middleware
upper layers. From the middleware perspective we
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
132
have defined both push and pull types of sensor
information retrieval mechanisms. The push
mechanism uses event listeners gather the context
information from sensors while the pull mechanism
uses a query based approach which allows the
context information to be provided on demand. To
make sensor information visible, in an independent
manner, to the upper layers, we used the web
services technology. Each sensor has an attached
web service through which it’s values are exposed.
The context information retrieval process is shown
in Figure 2.
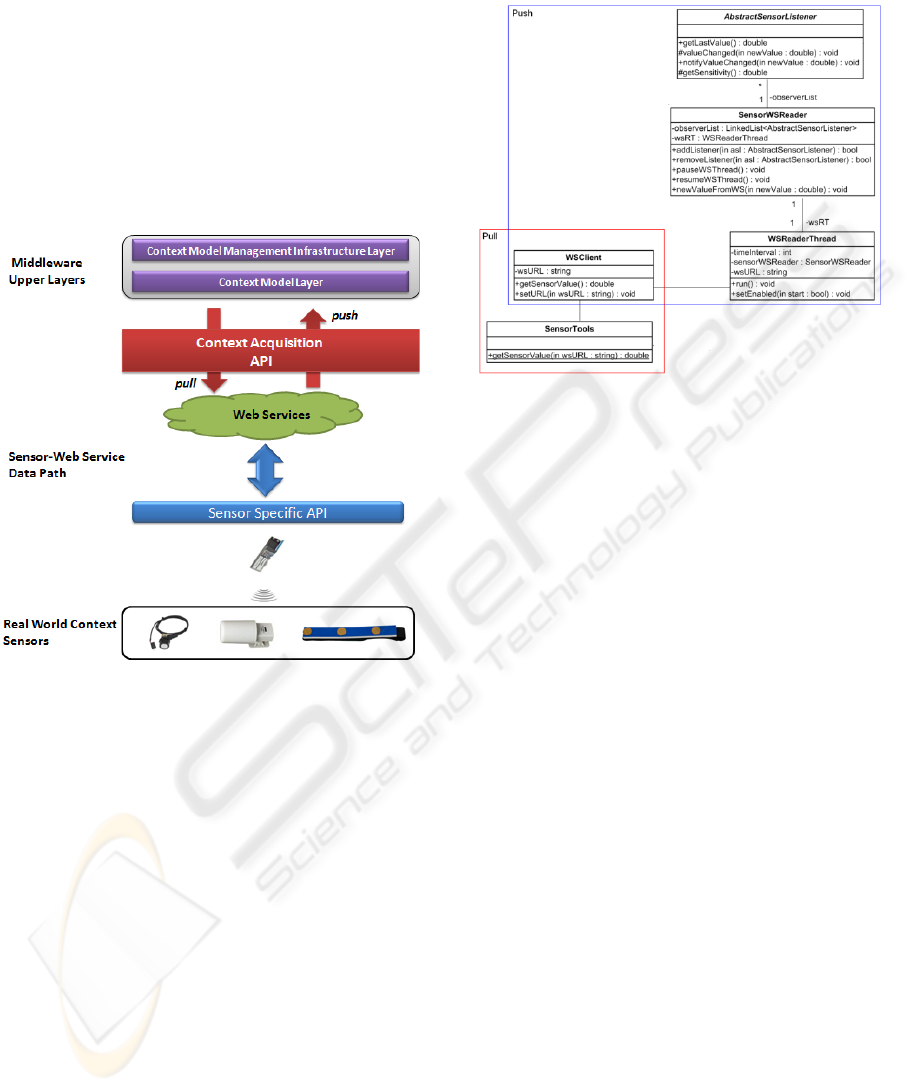
Figure 2: The context information retrieval flow.
The structure of the Context Acquisition API is
presented in Figure 3. The communication between
a sensor attached web service and the Context
Acquisition API is managed by the WSClient class.
It provides methods that: (i) build a SOAP request,
(ii) send the request to the web service and (iii) wait
for the sensor value response.
The pull information retrieval mechanism is
implemented in the SensorTools class by defining a
method that queries a specific web service to obtain
the sensor value. For the push mechanism, the
Observer design pattern is used. A SensorWSReader
instance must be created first by specifying the URL
of the web service and the time interval at which the
sensor data will be updated. The SensorWSReader
instance also contains a list of listeners that are
notified when a sensor value has changed.The
listeners are created from the middleware upper
layers by extending the AbstractSensorListener
abstract class. To verify the sensor value, separate
threads that continuously send requests to the web
service are created using the WSReaderThread.
Figure 3: The Context Acquisition API class diagram.
2.2 The Context Model Layer
To represent a real world context in an
programmatic manner (readable for the pervasive
application build on top of the middleware) the RAP
context model (Author paper reference) is used. In
this model the context is defined as a triple: C = <R,
A, P> where R is the set of context resources that
generates and / or processes context information, A
is the set of actors which interact with context
resources in order to satisfy their needs and P is the
set of real world context related policies. The set of
context resources R is split in two disjunctive
subsets: (i) the set of context resources attached to
the real world context environment R
E
and (ii) the
set of context resources attached to the actors R
A
.
In order to provide an accurate representation of
the real world context, the following context
representation artefacts are defined (see Figure 4):
specific context model, specific context model
instance and context – actor instance.
The specific context model C
S
= <R
S
, A
S
, P
S
> is
obtained by mapping the context model onto
different real contexts and populating the sets with
real context specific elements.
A specific context model instance C
SI
= <R
SI
,
A
SI
, P
SI
> contains the set of context resources with
which the middleware interacts, together with their
values in a specific moment of time t. The specific
context model represents the context situation to
which a pervasive application build onto the
middleware must adapt.
A SELF-CONFIGURING MIDDLEWARE FOR MANAGING CONTEXT AWARENESS
133

The context – actor instance CI
a
t
= <R
a
t
, a, P
t
>
contains the set of context resources with which the
actor can interact, together with their values in a
specific moment of time t. A context – actor
instance represents the projection of the specific
context model instance onto a certain actor.
Beside the above presented set representation the
RAP model offers an ontological representation of
the context model artefacts which allows for
learning and reasoning in order to obtain high-level
context information. The relationships between the
context model elements are represented in a general
purpose context ontology core.
Figure 4: The RAP context model.
The specific context model concepts are
represented as sub trees of the core ontology by
using is-a type relation. The context situation or the
context instance is represented by the core ontology
together with the specific context model concepts
and their instances in a specific moment of time.
The two ways of representing the context (set
based and ontology based) are equivalent and need
to be kept synchronized. The set based context
model is used to evaluate the conditions under which
the context management agents should execute self*
processes in order to enforce the autonomic
properties at the middleware level (self-configuring,
self-healing, self-optimizing and self-protection).
The ontology based model will be used by the
context aware applications for reasoning and
learning purposes.
2.3 The Context Model Management
Infrastructure Layer
The context model management infrastructure layer
is based on four types of intelligent, cooperative BDI
type agents (Salomie, 2008): Context Model
Administering Agents, Context Interpreting Agents,
Request Processing Agents and Execution and
Monitoring Agents.
The Context Model Administering Agent
(CMAA) is the specific context model manager. Its
main goal is the synchronization of the context
model specific artefacts with the system execution
environment. This agent is also responsible for
negotiating processes that take place when an actor
or resource is joining the context.
The Context Interpreting Agent (CIA)
semantically evaluates the information of a context
instance and tries to find the context instance
“meaning” for the pervasive application.
The Request Processing Agent (RPA)
processes the actor requests. This agent identifies
and generates the action plans that must be executed
for serving an incoming request. The RPA agent
uses the specific context model instance to identify
the proper plan to be executed by the Execution and
Monitoring Agent or for generating a new plan.
The Execution and Monitoring Agent (EMA)
processes the plans received from the RPA agent
and executes every plan action using the available
services. After mapping action plans onto services, a
plan orchestration – smart workflow which can be
executed using transactional principles is obtained.
The context management infrastructure agents
are implemented using the Java Agent Development
Framework platform (Jade). When the middleware is
deployed, CMAA is the first running agent. It
instantiates the CIA, RPA and EMA context
management agents and sends them the real world
context representation.
3 ENHANCING THE
MIDDLEWARE WITH
SELF-CONFIGURING
CAPABILITIES
The context acquisition and representation processes
implemented by the middleware need to be reliable
and fault tolerant because during run-time the
context resources can fail or new resources may be
identified. As a consequence, the context
representation constructed by de middleware needs
to accurately reflect the real world context. In order
to provide an efficient context information
management, we enhanced the middleware with
self-configuring properties, thus allowing for
dynamic configuration of the context artefacts.
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
134

The self – configuring property is enforced by
monitoring the real world context in order to detect
context variations or conditions for which the
context artefacts must be updated. We have
identified three causes that generate context
variation: (1) adding or removing context elements
(resources, actors, policies) to/from the real world
context, (2) actors’ mobility within the real world
context and (3) changes of the resources property
values (mainly due to changing the sensors’ captured
values). In the following sections we discuss each of
these context variation causes targeting to determine
(i) the context variation degree and (ii) the starting
condition of the self-configuring process.
3.1 Context Variation Generated by
Adding or Removing Context
Elements
During the context information acquisition process,
the sources of context information can fail or
randomly leave / join the context. These changes
generate a context variation are detected by the
acquisition layer and sent to the Context Model
Administration Agent which creates a new specific
context model adapted to the new real world context.
Next, we evaluate the context variation degree
generated by context resources ΔR, context policies
ΔP and context actors ΔA in relationship with a set
of associated thresholds T
R
, T
P
, and T
A
respectively.
The context resources set variation is generated
by adding or removing a context resource r (sensor
or actuator) to / from the pervasive application
execution environment. The context resource set
variation is calculated using the set difference
operation applied in two consecutive moments of
time: t and, t+1 where t+1 represent the moment
when the resource r became available. The same
reasoning can be applied when the resource r fails or
becomes unavailable:
ΔR = {R
E
t+1
ך R
E
t
} ڂ {R
E
t
ך R
E
t+1
}
(1)
In relation (1) R
E
t+1
\ R
E
t
contains the set of context
resources that become available and R
E
t
\ R
E
t+1
contains the set of context resources that become
unavailable. If Card(ΔR) ≥ T
R
a new specific
context model is generated by adding or removing
the context resources contained in ΔR.
The variation of the policy set is generated by
adding, removing or updating an execution
environment policy. The updating operation is
always achieved by removing the old context policy
followed by adding a new one. Using the same
assumptions and conclusions as for context
resources, the policy set variation is:
ΔP = {P
t+1
ך P
t
} ڂ {P
t
ך P
t+1
}
(2)
The variation of the actors set is generated by the
actors that enter or leave the pervasive application
execution context. Each context actor has an
attached context resources set during its context
interactions. In a given context, an actor is
characterized by a large number of actor-context
interaction patterns, but only two of these patterns
determine a variation of the actor context resources
set R
A
: (i) the actor enters the context and (ii) the
actor leaves the context. The actors related context
variation is:
ΔA = {A
t+1
ך A
t
} ڂ {A
t
ך A
t+1
} ڂ {R
A
t
ך R
A
t +1
} ڂ
{R
A
t+1
ך R
A
t
} (3)
Overall, the real world context variation ΔENV is
given by the union of all context elements’ variation
as shown below:
ΔENV = ΔR ڂ ΔA ڂ ΔP
Card(ΔENV) = Card(ΔR) + Card(ΔA) + Card(ΔP) (4)
The self-configuring threshold is defined as:
T
Self-Configuring
= min(T
R
, T
A
, T
P
) (5)
The CMMA agent should start the execution of the
self-configuring process and generate a new specific
context model when Card(ΔENV) ≥ T
Self-Configuring
.
3.2 Context Variation Generated by
Actors Mobility
Due to their mobility, the actors are changing their
environment location and implicitly the set of
resources with which they interact. The Context
Model Administration Agent (CMAA) identifies this
variation and generates (i) a new context – actor
instance and (ii) a new specific context model
instance.
In order to evaluate the context variation
generated by actors’ mobility we use the isotropic
context space concept, defined in (Author paper
reference). A context space is isotropic if and only if
the set of real world context resources
is invariant to
the actors’ movement. Usually, a context space is
non-isotropic, but it can be split into a set of
disjunctive isotropic context sub-space volumes in
which the isotropy degree variation is the empty set.
Such a volume is called context granule. For a given
moment of time, an actor can be physically located
in a single context granule. As a result, the space
isotropy variation ΔIZ
is non-zero only when an
A SELF-CONFIGURING MIDDLEWARE FOR MANAGING CONTEXT AWARENESS
135

actor a moves between two context granules. The
isotropy variation for a context actor is computed as:
ΔIZ
a
= {R
CG
t+1
ך R
CG
t
} ڂ {R
CG
t
ך R
CG
t+1
} (6)
The CMMA agent continuously monitors the actors’
movement in the real world context and periodically
evaluates the space isotropy variation. If for an
actor, the space isotropy variation is a non empty set,
then the self-configuring process executed by the
CMMA agent generates a new context – actor
instance. It actually represents the specific context
model instance projection onto a certain actor:
CI
a
t+1
= <R
a
t+1
, a, P
t+1
>, R
a
t+1
= R
CG
t+1
(7)
The context variation generated by all actors’
mobility in a context space is given by:
ΔCAM = ڂ
a є A
ΔIZ
a
(8)
3.3 Context Variation Generated by
Changes of Resources Property
Values
A context resource is a physical or virtual entity
which generates and / or processes context
information. The resource properties, K(r), specify
the set of relevant context information that a
resource can provide. For example, the set of context
properties for a Hot&Humidity sensor is
K(Hot&Humidity) = {Temperature, Humidity}.
In order to evaluate the context variation
generated by the changes in the resource property
values, we define a function K
val
that associates the
resource property to its value:
K
val
(R) = {(k
1
,val
1
),…, (k
n
,val
n
)}
with k
1
,…,k
n
є K
(9)
If the values captured by the Hot&Humidity sensor
in a moment of time are for temperature 5 degree
Celsius and for humidity 60%, then
K
val
(Hot&HumiditySensor) = {(Temperature, 5),
(Humidity, 60%)}.
CMAA agent calculates the context variation
generated by changes of resource properties’ values
ΔRPV as presented below.
ΔRPV = K
val
(R
t+1
) - K
val
(R
t
)=
{(k
1
,val
1
t+1
- val
1
t
),…,(k
n
,val
n
t+1
-val
n
t
)} (10)
As a result, a new specific context model
instance should be created when Card(ΔRPV) ≥ 0.
3.4 The Self-configuring Algorithm
The self-configuring algorithm is executed by
CMAA in order to keep the context model artefacts
synchronized with the real context (Figure 5). The
Context Model Administering Agent features ticker
based behaviour by periodically evaluating the
context changes. When a significant context
variation is determined, the context model artefacts
are updated using the updateOntology (owlModel,
newContextElements) method.
Algorithm CMAA_Self_Configuring
input: (1) new real world context elements: R
n
, A
n
, P
n
(2) thresholds for context elements variation:
T
R
, T
A
, T
P
output: new context artifacts C
S
n
, CI
a
n
, C
SI
n
resources: current context artifacts set representation
C
S
, CI
a
C
SI,
current context artifacts ontology as
owlModel
begin
// CMAA evaluates the context variation
ΔR = {R
E
n
ך
R
E
}
ڂ
{R
E
ך
R
E
n
}
ΔA = (A
n
ך
A
S
}
ڂ
{A
S
ך
A
n
}
ڂ
{R
A
n
ך
R
A
}
ڂ
{R
A
ך
R
A
n
}
ΔP = {P
n
ך
P
S
}
ڂ
{P
n
ך
P
S
}
∆CAM = U
a є A
ΔIZ
a
∆RPV = K
val
(R
n
) - K
val
(R)
T
Self-Conf
= min (T
R
, T
A
, T
P
)
if (Card (∆ENV) ≥ T
Self-Conf
)
begin
//CMAA tries to create a new specific context model
if (Card (∆R) ≥ T
R
)
if (R
S
∩ ∆R = Ø)
C
S
n
= C
S
+ ∆R
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) + ∆R = (R
S
ڂ
∆R, A
S
, P
S
)
else
C
S
n
= C
S
- ∆R
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) - ∆R = (R
S
\ ∆R, A
S
, P
S
)
if (Card (∆A) ≥ T
A
)
if (A
S
∩ ∆A
= 0)
C
S
n
= C
S
+ ∆A = (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) + ∆A = (R
S
, A
S
ڂ
∆A, P
S
)
else
C
S
n
= C
S
- ∆A = (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) - ∆A = (R
S
, A
S
ך
∆A, P
S
)
if (Card (∆P) ≥ T
P
)
if (P
S
∩ ∆P
= 0)
C
S
n
= C
S
+ ∆P
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) + ∆P
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
ڂ
∆P)
else
C
S
n
= C
S
- ∆P
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
) - ∆P
= (R
S
, A
S
, P
S
ך
∆P)
end
else
begin
// CMAA tries to create a new context-actor instance
T
Self-Conf
= 0
if (Card (∆CAM) > T
Self-Conf
)
foreach a € A if (∆IZ
a
≠ 0) CI
a
n
= <R
a
, a, P>
else
// CMAA tries to create a new specific context model
// instance
if (Card (∆RPV) > T
Self-Conf
) C
SI
n
= <R
a
, a, P>
end
updateOntology (owlModel, ∆R
ڂ
∆A
ڂ
∆P)
end
Figure 5: The CMAA self-configuring algorithm.
4 CASE STUDY – MANAGING A
SMART LABORATORY SPACE
For the case study we have used a real world context
represented by our Distributed System Research
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
136
Laboratory. In the laboratory the students are
marked using RFID tags and identified using a RFID
reader. The students interact with the smart
laboratory by means of wireless capable PDAs on
which different laboratory provided services are
executed (submit homework service, lesson hints
services, print services, information retrieval
services, etc.). A sensor network captures
information regarding students’ location or
orientation and also ambient information like the
temperature or humidity. In the laboratory, a set of
policies like “the ambient temperature should be 22
degrees Celsius” or “the loud upper limit is 80 dB”
should be respected.
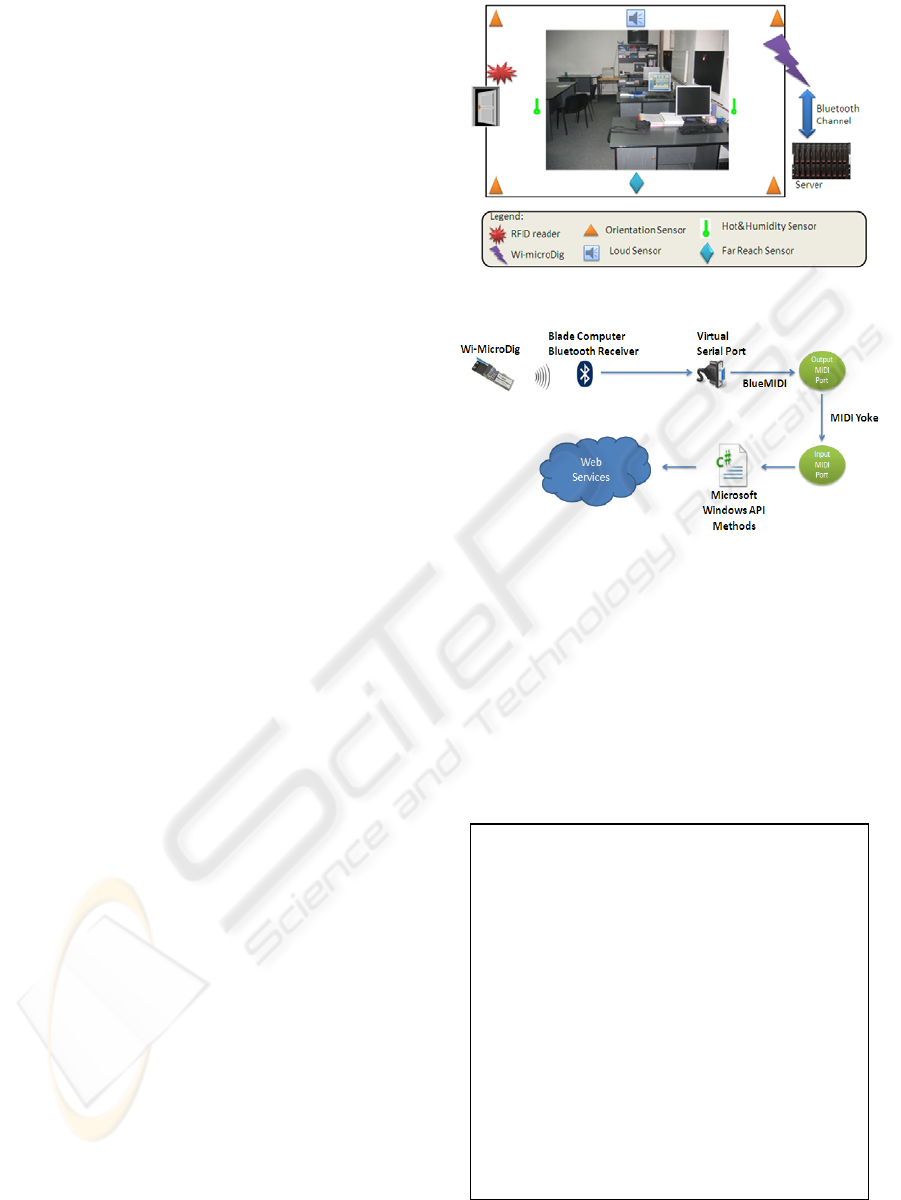
The DSRL infrastructure contains a set of
sensors through which the real context information
is collected: two Hot&Humidity sensors that capture
the air humidity and the temperature, four Orient
sensors placed in the four corners of the laboratory
that measure the orientation on a single axis, one
Loud sensor that detects sound loudness level and
one Far Reach sensor that measures distances
(Figure 6). The sensors are connected using a Wi-
microSystem wireless network produced by Infusion
Systems (IS Ltd.). The middleware is deployed on
an IBM Blade-based technology Server Center. The
IBM Blade technology was chosen because its
maintenance software offers autonomic features like
self-configuring of its hardware resources.
The context related data captured by sensors is
collected through the Wi-microSystem that has an I-
CubeX WimicroDig analogue to digital encoder as
its main part. It is a configurable hardware device
that encodes up to 8 analogue sensor signals to MIDI
messages which are real-time wirelessly transmitted,
through Bluetooth waves, to the Server Center for
analysis and/or control purposes. The Bluetooth
receiver located on the Blade computer is mapped as
a Virtual Serial Port (VSP).
In order to read/write to/from the VSP we used
two sensor manufacture applications: (i) BlueMIDI
which converts the Bluetooth waves received on the
VSP into MIDI messages and (ii) MIDI Yoke which
creates pairs of input/output MIDI ports and
associates the output MIDI port with the VSP. The
MIDI message information is extracted using the
Microsoft Windows API multimedia operations and
published through web services (see figure 7).
The Context Model Administering Agent
periodically evaluates the context information
changes at a predefined time interval (we use 1
second time intervals for this purpose). If significant
variations are detected, the context model artifacts
are created or updated using the self-configuring
algorithm presented in Section 3.4.
Figure 6: The DSRL infrastructure.
Figure 7: The context information data path form sensors
to their attached web services.
When the middleware is deployed and starts
execution (t=0) there are no context model artefacts
constructed, i.e. the R, P and A sets of the context
model are empty. After one second (t=1), when two
students John and Mary enter the lab, the Context
Model Administering Agent receives the updated
context information from the Context Acquisition
Layer and calculates the context elements variation
∆R, ∆P and ∆A as presented in Figure 8.
R
E
1
= {FarReachSensor, RFIDReader,
HotHumiditySensor1&2, LoudSensor,
OrientationSensor1&2&3&4}
R
E
0
= Ø
∆R
= (R
E
1
ך
R
E
0
)
ڂ
(R
E
0
ך
R
E
1
)
∆R = {FarReachSensor, RFIDReader, LoudSensor
HotHumiditySensor1&2, OrientationSensor1&2&3&4}
A
1
= {StudentJohn, StudentMary}
A
0
= Ø
∆A = (A
1
ך
A
0
)
ڂ
(A
0
ך
A
1
)
∆A = {StudentJohn, StudentMary}
P
1
={LoudLimit, TemperatureLimit}
P
0
= Ø
∆P = (P
1
ך
P
0
)
ڂ
(P
0
ך
P
1
)
∆P = {LoudLimit, TemperatureLimit}
Card(∆ENV) = Card(∆R) + Card(∆A) + Card(∆P) = 13
Card
(
∆ENV
)
> T
Self-Confi
g
urin
g
Figure 8: DSRL context variation at t=1.
A SELF-CONFIGURING MIDDLEWARE FOR MANAGING CONTEXT AWARENESS
137

By default the self-configuring thresholds are set
to the value 1: T
Self-Conf
= T
R
= T
A
= T
P
= 1. As a
result of evaluating the context variation at t=1, the
Context Model Administering Agent executes the
self – configuring algorithm which adds new
concepts/ populates the context model artefacts
ontology. The new added concepts originate from
the context elements set variations ∆R, ∆P and ∆A
calculated in Figure 8.
R
E
61
= {FarReachSensor, RFIDReader,
HotHumiditySensor1&2, OrientationSensor2&3}
R
E
60
= {FarReachSensor, RFIDReader, LoudSensor
HotHumiditySensor1&2,
OrientationSensor1&2&3&4}
∆R
= (R
E
61
ך
R
E
60
)
ڂ
(R
E
60
ך
R
E
61
)
∆R = {LoudSensor, OrientationSensor1&4}
A
61
= {StudentMary}
A
60
= {StudentJohn, StudentMary}
∆A = (A
61
ך
A
60
)
ڂ
(A
60
ך
A
61
)
∆A = {StudentMary}
P
61
= {LoudLimit, TemperatureLimit}
P
60
= {LoudLimit, TemperatureLimit}
∆P = (P
61
ך
P
60
)
ڂ
(P
60
ך
P
61
)
∆P = Ø
Card(∆ENV) = Card(∆R) + Card(∆A) + Card(∆P) = 4
Card
(
∆ENV
)
> T
Self-Confi
g
urin
g
Figure 9: CMAA agent evaluates the DSRL context
variation at t=61.
In order to test the middleware self-configuring
capabilities we have considered that after 60 seconds
the following context changes occurred: (i) student
John leaves the laboratory, (ii) Orientation Sensor1
and OrientationSensor4 are disabled and (iii)
LoudSensor is disabled.
The CMAA agent calculates the variation in the
new context at t = 61 (Figure 9), executes the self-
configuring algorithm and updates accordingly the
context ontology.
5 CONCLUSIONS
This paper addresses the problem of managing the
context information acquisition and representation
processes in a reliable and fault tolerant manner. We
define a self-configuring middleware that uses an
agent based context management infrastructure to
gather context information from sensors and
generate a context ontology representation at run-
time. The self-configuring property is enforced at
the middleware level by monitoring the execution
context in order to detect context variations or
conditions for which the ontology context artefacts
must be updated / populated.
For the future development we intend to provide
algorithms and generic formalisms for all four self-*
autonomic paradigms in order to enhance the
proposed middleware with context / self aware
capabilities.
REFERENCES
Anca Rarau, K. Pusztai. I.Salomie 2006. MultiFacet Item
based Context-Aware Applications. In International
Journal of Computing and Information Sciences.
Irene Y.L. Chen, Stephen J.H. Yang, 2006. Ubiquitous
Provision of Context Aware Web Services. In IEEE
International Conference on Services Computing.
Feruzan Ay, 2007. Context Modeling and Reasoning using
Ontologies. University of Technology Berlin.
Ki-Chul Lee, Jung-Hoon Kim 2007. Implementation of
Ontology Based Context-Awareness Framework for
Ubiquitous Environment. In Int. Conference on
Multimedia and Ubiquitous Engineering.
Paolo Bellavista, Antonio Corradi, Rebecca Montanari,
2006. Mobile Computing Middleware for Location
and Context-Aware Internet Data Services. In ACM
Transactions on Internet Technology, Vol. 6, No. 4.
Damien Fournier, Sonia Ben Mokhtar 2006. Towards Ad
hoc Contextual Services for Pervasive Computing. In
IEEE Middleware for Service Oriented Computing
Melbourne, Australia.
George Spanoudakis, Khaled Mahbub 2007. A Platform
for Context Aware Runtime Web Service Discovery.
In IEEE International Conference on Web Services.
Marcel Cremene, Michel Riveill, Christian Martel, 2007.
Autonomic Adaptation based on Service-Context
Adequacy Determination. In Electronic Notes in
Theoretical Computer Science, Elsevier.
Salomie I., Cioara T., Anghel I., Dinsoreanu M., 2008.
RAP - A Basic Context Awareness Model. In Proc. of
4th IEEE Int. Conf. on Intelligent Computer
Communication and Processing; ISBN: 978-1-4244-
2673-7, pp. 315-318.
DSRL, Distributed Systems Research Laboratory,
Technical University of Cluj-Napoca. dsrl.coned.
utcluj.ro
Jade, Java Agent DEvelopment Framework. http://jade.
tilab.com.
IS Ltd., Infusion Systems Ltd. http://www.
infusionsystems.com.
Raphael M. Bahati, Michael A. Bauer, 2006. Using
Policies to Drive Autonomic Management. In Proc. of
the Int. Symposium on a World of Wireless, Mobile
and Multimedia Networks.
A. S. Rao, M. P. Georgeff, 1995. BDI Agents: from
Theory to Practice. In Tech. Rep. 56, Australian
Artificial Intelligence Institute, Melbourne, Australia.
WINSYS 2009 - International Conference on Wireless Information Networks and Systems
138
