
PRIVACY-AWARE DATA PROVIDING WEB SERVICES
COMPOSITION
Amin Cherbal
LIG Laboratory, Grenoble, France
Djamal Benslimane
LIRIS Laboratory, Lyon, France
Keywords:
Privacy, Data integration, Web services, Composition techniques, Data anonymity.
Abstract:
Web services are increasingly used to promote data sharing in collaborative environments such as eBusiness,
eHealth, eEnterprise, etc. They facilitate data integration and interoperability across autonomous independent
information systems in the collaboration environments. Many mediation solutions were proposed for data
integration using Web services. Unfortunately privacy aspects were not addressed in these solutions. In this
paper, we proposed a framework for privacy-preserving data integration based on Web services. Our proposal
is a centralized access control mechanism allowing for the specification and enforcement of privacy rules in
Web services composition based on domain ontologies.
1 INTRODUCTION
Web services are highly recognized in collaborative
environments for their ability to provide flexible inte-
gration and high interoperability across autonomous
independent information systems. Recently many re-
search works have proposed the use of Web services
as the means to large scale data sharing in collab-
orative information systems (Srivastava et al., 2006;
Carey, 2006). Our work is based on the mediator sys-
tem proposed in (Barhamgi et al., 2008). In this sys-
tem legacy databases are wrapped by services allow-
ing partners to collaborate. This type of Web services
are called Data Providing Web Services (DPWS),
each one is modeled as an RDF view over a medi-
ated ontology. Users expresses their queries on the
mediated ontology using SPARQL language. Queries
are resolved by composing Web services.
Web services can provide data that can be private
for two types of entities: the organizations that of-
fer these services (e.g., hospitals) and the data objects
whose data is stored by these organizations (e.g., pa-
tients). These entities may have various privacy poli-
cies and preferences regarding the disclosure of their
confidential data. Such aspects of data privacy have
not been taken into account in previous systems of
data sharing based on Web services composition.
1.1 Motivation
Assume we have a set of DPWS, for example, in a
healthcare facility, contact patients informations are
accessible through an administrative Web service and
medical patients informations are accessible through
an health Web service. Now suppose that this health-
care facility wants to apply privacy policies to ex-
presse that contact patients informations (e.g, address,
phone number, etc.) are only accessible for some ad-
ministrative staff whereas medical informations (e.g,
disease, medical test, etc.) are only accessible for
some medical staff. But in case of medical emer-
gency, qualified personal may access to all informa-
tions of the patient. This situation shows the com-
plexity of expressing and applying such policies.
The challenge that we address in this paper relates
to devising such mediator, taking into account the pri-
vacy aspects.
1.2 Problem
Our goal is to preserve data privacy in the query
answering process based on Web services composi-
tion. The semantic query expressed with SPARQL is
rewritten in terms of available Web services to enable
the composition of DPWS.
167
Cherbal A. and Benslimane D. (2009).
PRIVACY-AWARE DATA PROVIDING WEB SERVICES COMPOSITION.
In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies, pages 167-170
DOI: 10.5220/0002240301670170
Copyright
c
SciTePress

In this paper we consider privacy centralized at the
mediator system (i.e., Web services share data with-
out any privacy protection). The problem is to al-
low a context-based access only to authorized users
(e.g., scientist for infectious diseases researches). The
control access mechanism should be able to specify:
First, privacy policies as applied on the schema of
the data (e.g., policies to disclose patients address in
the hospital). Second, the privacy preferences applied
for each data objects (e.g., patients preferences to dis-
close theirs diseases for scientific researches).
1.3 Contribution
In this paper we propose a new privacy-preserving
method for data integration based on Web services
composition. We devised a centralized access con-
trol mechanism allowing for the specification and the
enforcement of privacy access rules in Web services
composition based on ontologies domain:
• It allows the high level privacy policies and pref-
erences specification. Based on the mediation on-
tology and the access rules propagation process.
This reduces the efforts required for specification.
• The access rules are extended with conditions ex-
pressed on the mediated ontology. This gives
more richness to it.
• We have proposed a new method to apply the
access rules for Web services composition, this
method is based on query rewriting techniques.
Our contribution extends the mediator system pro-
posed in (Barhamgi et al., 2008) as shown in Figure 1.
Figure 1: Mediator system for DPWS composition.
In the rest of the paper we describe in the next sec-
tion our access control mechanism, followed by the
section 3 where we give a short overview of related
works and finally we concludes the paper and give
some directions in section 4.
2 ACCESS CONTROL FOR DPWS
COMPOSITION
In this section we present our control access mecha-
nism. There are two distinct steps, see Figure 2. First,
privacy policies are specified in the form of access
rules on the mediation ontology. In the second step
these policies are enforced into services composition
process.
Figure 2: Privacy preserving mechanism.
2.1 Ontology based Privacy Policies
Specification and Propagation
Privacy policies specification is the first step in defin-
ing a access control mechanism. Also we consider
that policies can be specified and imported from ser-
vice providers. Defining such policies are the results
of analyzing the security and privacy requirements,
carried out by the security administrator. The ad-
ministrator can specify the High Level Access Rules
(HLAR) on an RDFS ontology. In our approach,
the HLAR is a set of 4-tuple comprising the Pur-
pose, the Subject, the Object and the set of Authorized
Property-Conditions couples:
[ P, S, O, Ai<Pi,Ci> ]
For example, the rule R1 express the fact that
the subject “Specialist” has only access to properties
“Name”, “Disease” and to “Test” under the condition
of location (e.g., the same floor in the hospital):
Rule R1.
[ P : Emergency,
S : Ont:Specialist,
O : Ont:Patient,
Ai : { <Ont:HasName, - >
<Ont:HasDisease, - >
<Ont:HasTest,
Ont:Patient.Location =
Ont:Specialist.Location> } ]
The data objects expresses her privacy preferences
with the same format augmented by the identifying
attribute:
ICSOFT 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
168
[ Id, P, S, O, Ai<Pi,Ci> ]
After HLAR have been expressed, we process it
to propagate all Access Rules (AR). We use a top-
down algorithm based on the subjects hierarchy of the
mediated ontology.
Figure 3: AR propagation through hierarchical part of the
mediated ontology.
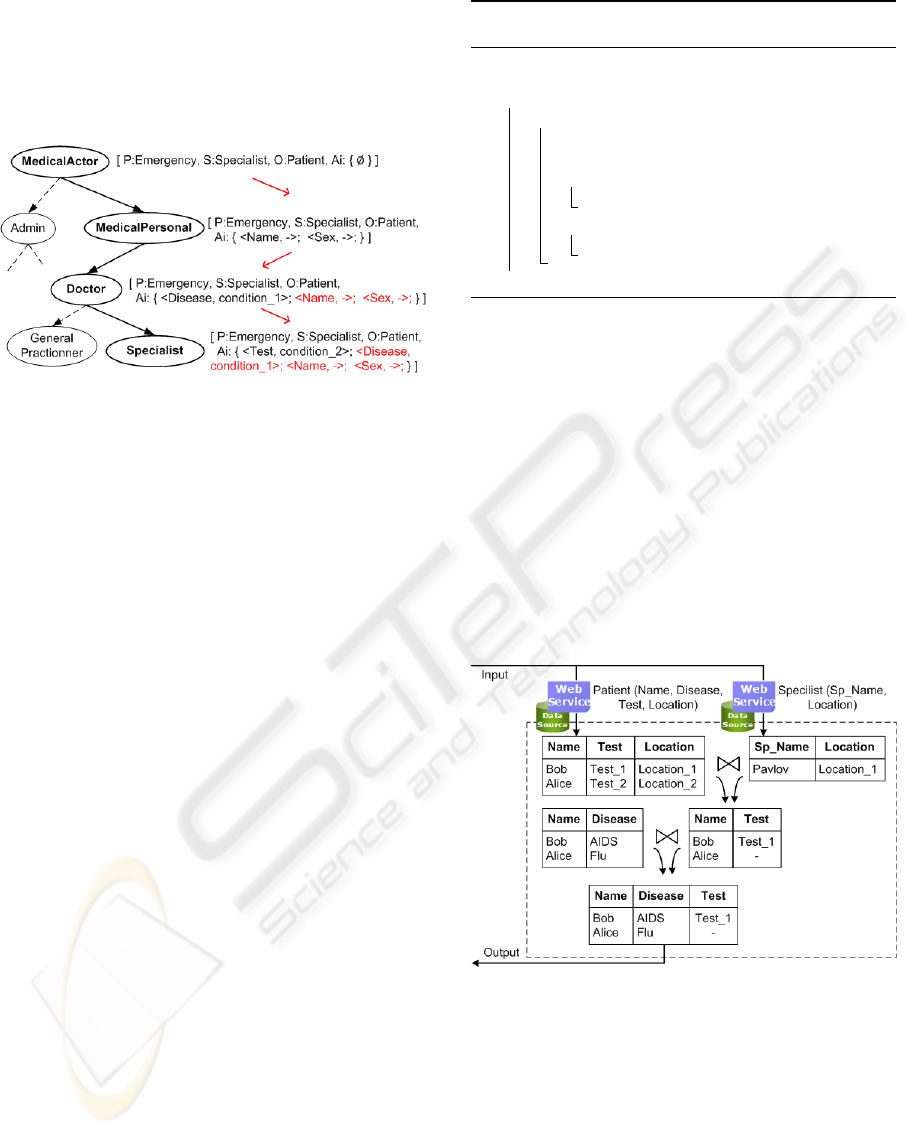
An example part of these AR propagation is
shown in Figure 3. Where AR are inherited through
the subjects hierarchy from the higher level subjects
(e.g. “MedicalActor”) to the lower levels subjects
(e.g. “Specialist”, etc).
2.2 Enforcing Policies into DPWS
Composition
In this section we explain how AR are enforced into
the DPWS composition, we explain this with an ex-
ample. Suppose that the user express the query Q:
SELECT ?Name ?Disease ?Test ?Address
WHERE { ?P rdf:type Ont:Patient
?P Ont:HasName ?Name
?P Ont:HasDisease ?Disease
?P Ont:HasTest ?Test
?P Ont:HasAddress ?Address }
Assume that we have the following context infor-
mations associating the request Q with the rule R1
seen in the previous subsection:
{ Purpose:Emergency, Subject:Specialist,
SubjectName:Pavlov }
In our mechanism, privacy is enforced by the
query rewriting techniques based on AR. Algorithm 1
describe this process, lines (4–5) allows to remove
all unauthorized properties into the query to denied
it, and lines (6–7) allow to switch-on all authorized
properties with his conditions into the query.
In our example, the query Q must be rewritten
as the following query Q
0
to denied access to the
property “Address” and switch-on condition with the
property “Test”.
Algorithm 1: Query rewriting for enforcing
AR.
Data: query Q, access rules base ARB, purpose p and subject s
Result: rewritten query Q
begin1
foreach concept o
j
in Q do2
Extract the set of property-conditions couples3
A
i
= {< pr
i
,c
i
>} from ARB(p,s,o
j
,A
i
);
forall {pr
k
} ∈ Q and {pr
k
} /∈ A
i
do4
remove {pr
k
} from Q5
forall {pr
k
} ∈ Q and {pr
k
} ∈ A
i
do6
replace {pr
k
} into Q by OPT IONAL{pr
k
∪ c
k
}7
end8
SELECT ?Name ?Disease ?Test
WHERE{ ?P rdf:type Ont:Patient
?P Ont:HasName ?Name
?P Ont:HasDisease ?Disease
OPTIONAL {
?P Ont:HasTest ?Test
?D rdf:type Ont:Specialist
?D Ont:HasName "Pavlov"
?D Ont:HasLocation ?Location
?P Ont:HasLocation ?Location } }
The rewritten query Q
0
will be answered by the
composition of available Web services, see Figure 4.
The “Test” result of “Alice” are not disclosed accord-
ing to the unresolved condition of location.
Figure 4: DPWS composition for Q
0
query answering.
Before disclosing the results of Q
0
we verify the
preferences of each data object appearing in the re-
sults. In the data filtering step (see Figure 2) we ap-
ply Q
0
on the local results and eventually by invok-
ing other DPWS if the data are missing. For exam-
ple, suppose that patient ”Bob” wish to disclose their
”Diseases” only to her physician contractor, in this
case a second DPWS composition is executed. The
results revealed in the end of this stage respects at the
same time the privacy policies and preferences.
PRIVACY-AWARE DATA PROVIDING WEB SERVICES COMPOSITION
169

3 RELATED WORK
In many scenarios individuals supply their personal
informations to data collectors under privacy con-
straints (e.g., patients to the hospitals). However, it’s
important that the collaborations and the data shar-
ing does not affect their privacy. The control access
approaches for preserving privacy are used to enable
data sharing only with the authorized thirds. Con-
ventional access control models are very studied in
databases, as DAC, MAC and RBAC. Privacy-aware
RBAC (Bertino et al., 2006) use conditions evaluation
on hierarchy of roles and objects. However, the con-
ditions in this models are concern only environment
variables. In our system the conditions are expressed
on the data domain with SPARQL.
Hippocratic databases (Agrawal et al., 2002) are
distinguished by the context management and the
management of privacy preferences at the cells gran-
ularity. This approach limits itself to a centralized
DBMS and it is not well adapted for data sharing,
even less for the composition of the Web services.
There have been many research efforts (Hamadi et al.,
2007; Kagal et al., 2004; Cheng and Hung, 2005)
addressing privacy at the services discovery time.
In (Tumer et al., 2003) the proposed mechanisms
allow inferences and negotiations deal between the
users preferences and the services policies. All
these works proposes approaches to design privacy-
preserving Web services. Our approach is designed
for automatic Web services composition, allowing it
to find alternatives and authorized data sources.
Notorious efforts for standardization of languages
for privacy policies specification were made (e.g.,
P3P, XACML). It is possible to express with XACML
conditions to evaluate access authorizations. In our
approach we specify a semantic conditions over the
mediated ontology to evaluate access authorizations
through the DPWS composition. We provide also an
mediation ontology based approach to specify a high
level access rules, that reduce efforts of privacy anal-
ysis. To our knowledge no work related to the privacy
in the data integration based on the composition of
Web services. In addition, the benefits of the seman-
tic Web have been largely exploited in our solution.
4 SUMMARY AND DIRECTIONS
In this paper we proposed a privacy-preserving frame-
work for data integration based on Web services com-
position. This work extends the mediator system pro-
posed by (Barhamgi et al., 2008) with the central-
ized access control mechanism. Allowing the high
level privacy policies and preferences specifications.
These specifications are based on the mediation ontol-
ogy and the inference process, reducing the efforts of
analyzing the privacy requirements. The access rules
are increased by conditions expressed on the medi-
ated ontology giving it more semantic richness. We
have also proposed a new method to enforce the ac-
cess rules through the Web services composition pro-
cess, based on queries rewriting techniques.
Several horizons open in our privacy approach.
First, we are studying the possibility to import stan-
dards policies specifications as XACML and we be-
lieve improve the rules inference algorithm. We have
also intend to optimize the privacy-aware Web ser-
vices composition algorithm. Finally, for lack of
space we don’t present an other privacy approach for
anonymous data integration based on Web services
composition, that can be easily combined with our ac-
cess control mechanism. These approach allows we to
find alternatives to unauthorized requests by process-
ing approximative queries.
REFERENCES
Agrawal, R., Kiernan, J., Srikant, R., and Xu, Y. (2002).
Hippocratic databases. In 28th Int’l Conf. on Very
Large Databases (VLDB), Hong Kong.
Barhamgi, M., Benslimane, D., and Ouksel, A. M. (2008).
PWSMS: A Peer-to-Peer Web service Management
System for Data Sharing in Collaborative Environ-
ments. International Journal of Computer Systems
Science and Engineering (IJCSSE), 23(2).
Bertino, E., Squicciarini, A. C., Paloscia, I., and Martino, L.
(2006). Ws-ac: A fine grained access control system
for web services. volume 9, pages 143–171, Hingham,
MA, USA. Kluwer Academic Publishers.
Carey, M. J. (2006). Data delivery in a service-oriented
world: the bea aqualogic data services platform. pages
695–705.
Cheng, V. S. Y. and Hung, P. C. K. (2005). Towards an in-
tegrated privacy framework for hipaa-compliant web
services. In 7th IEEE International Conference on E-
Commerce Technology (CEC 2005), 19-22 July 2005,
M
¨
unchen, Germany, pages 480–483.
Hamadi, R., Paik, H.-Y., and Benatallah, B. (2007). Con-
ceptual modeling of privacy-aware web service proto-
cols. In CAiSE, pages 233–248.
Kagal, L., Paolucci, M., Srinivasan, N., Denker, G., Finin,
T. W., and Sycara, K. P. (2004). Authorization and
privacy for semantic web services. IEEE Intelligent
Systems, 19(4):50–56.
Srivastava, U., Munagala, K., Widom, J., and Motwani, R.
(2006). Query optimization over web services. In
VLDB, pages 355–366.
Tumer, A., Dogac, A., and Toroslu, I. H. (2003). A semantic
based privacy framework for web services.
ICSOFT 2009 - 4th International Conference on Software and Data Technologies
170
